Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Some people who are infected with the hepatitis B virus have mild, flu-like symptoms and some do not become sick at all. Children who are infected are less likely to have an illness or get sick after getting hepatitis B than adults.
In more severe cases, hepatitis B can cause:
- Loss of appetite.
- Pain in the joints.
Normally, these health problems disappear in a few weeks, but even when the person feels much better, they may still be infectious.
Most adults who become infected with the hepatitis B virus recover completely and do not become infected again. A few people become very ill in the time just after infection and need to go to hospital some may even die.
What Our Customers Say
- Thank you so much. I had alot of issues with getting results sooner and ARC point lab of Tampa got them in 48 hrs and the staff is very friendly and understanding. They were all very informative as well. Thanks ladies.
Taneisha Watson
Google ReviewNeeded a Covi-19/Sars test no more than 72 hours before departure to travel to France. Staff was very helpful, procedure painless and results in 15mn. Merci!
Aleth Voarick
Google ReviewThe test was comfortable , fast and the results came sooner than expected The staff and management very friendly and attentiveIf you having to take this test for traveling purposes this is the right place .
Antonio Kaik
Google Review
- The Food Sensitivity Test was easy to order, fast with results and the report was easy and simple to read. I would recommend this test to all of my family and friends. This was a very seamless and easy testing process.
Anthony Oliver
Facebook ReviewGreat experience at the Columbus, Ohio location! The staff was exceptionally friendly and so gentle and patient with my daughter who hates needles. I highly recommend them!
Emily Speltz West
Facebook ReviewARCpoint Labs around the country are known for their outstanding service with high integrity! The place to go if you are looking for workplace or judicial drug and alcohol testing, DNA testing and clinical testing services.
Gauri Bhalakia
High Titers Of Hepatitis B Surface Antibodies Indicating Low Risk Of Hepatitis B Virus
Sung-Nan Pei, Ming-Chung Wang, Ming-Chung Ma, Ching-Yuan Kuo, Chien-Hung Chen, Po-Nan Wang High Titers of Hepatitis B Surface Antibodies Indicating Low Risk of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatitis in Lymphoma Patients Treated with Rituximab-Based Chemotherapy. Blood 2015 126 : 3869. doi:
Also Check: Hepatitis B Virus Dna Quantitative
You May Like: Is Hepatitis C Contagious Sexually
Question 2 What Is The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
The hepatitis B surface antibody is the antibody that is produced in response to hepatitis B surface antigen , a protein present on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. Anti-HBs appears after convalescence from acute infection and lasts for many years. It can also be produced in response to hepatitis B vaccination.
Other hepatitis B antibodies are not produced in response to vaccination. This is because these antigens are not in the vaccine.
Data Analysis And Statistics
All analyses were done using nonparametric statistical software with penalized maximum likelihood to remove first-order bias. A p-value < 0.05 for two-sided tests was considered statistically significant. Continuous variables were expressed as means plus/minus standard deviation or mean , categorical variables as numbers . Conditional logistic regression analysis was used to estimate risk ratios and 95% confidence intervals for loss of anti-HBs putative associated factors included age, sex, type of rheumatic disease, conventional DMARDs, biologic DMARDs , comorbidity, and baseline anti-HBs titer.
Read Also: Unspecified Viral Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma
Question 7 Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Antibody Always Acquired After A Completed Vaccination Protocol
No. After 3 intramuscular doses of vaccine, > 90% of healthy adults and > 95% of those < 19 years of age develop immunity .1 However, there is an age-specific decline in development of immunity. After age 40 years, about 90% of people become immune, but by age 60 years, only 75% of people become immune.1 Larger vaccine doses or an increased number of doses are required to induce immunity in many hemodialysis patients and in other immunocompromised people.1
References
This FAQ is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. A clinicians test selection and interpretation, diagnosis, and patient management decisions should be based on his/her education, clinical expertise, and assessment of the patient.Document FAQS.105 Revision: 0
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
Also Check: Whatâs The Difference Between Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
You May Like: Hepatitis C Antibodies In Blood
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Qualitative
Test Code: 499
Methodology: Immunoassay
Clinical Significance: The detection of anti-HBs is indicative of a prior immunologic exposure to the antigen or vaccine. To determine immune status as 10 mIU/mL as per CDC guidelines, please order Hepatitis B Surface Antibody, Quantitative.
Alternative Name: Anti-HBS Anti-HBS Qual Anti-HBSAG Australian Antibody HB Surface Ab
Supply: T01 â Red/Gray SST 8.5mL
Preferred Specimen: Serum
Transport Container: Serum Separator Tube
Transport Temperature: Room Temperature
Specimen Stability: Room Temperature: 5 days
Rejection Criteria: Gross Hemolysis, Gross Lipemia
For additional supply or collection device information, please contact DLOâs Customer Service at 891-2917, option 2.
The information contained here on the Diagnostic Laboratory of Oklahoma website is not to be construed as medical recommendations or professional advice. Neither DLO nor its affiliates, agents or any other party involved in the preparation or publication of the works presented is responsible for any errors or omissions in information from the use of such information. Readers are encouraged to confirm the information contained herein with other reliable sources and to direct any questions concerning personal health care to licensed physicians or other appropriate health care professionals.
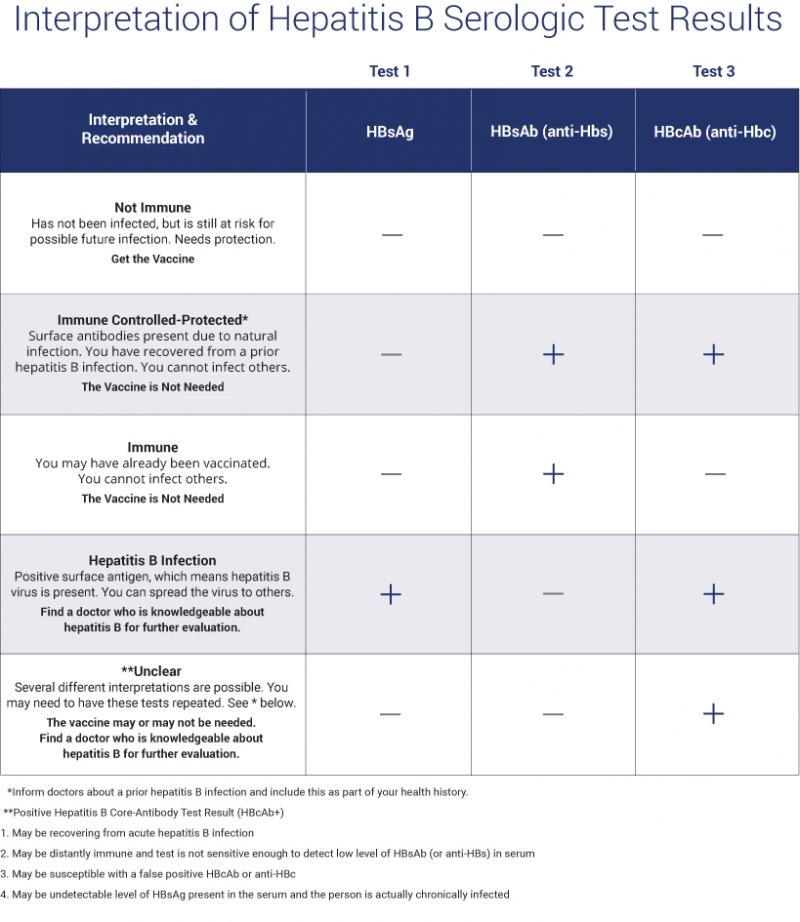
What Do Hepatitis B Test Results Mean
Hepatitis B test results help determine if HBV infection is negative or positive, and if positive, whether the infection is acute or chronic, or if recovery is complete. A combination of results are considered to identify and classify HBV infection status.
The following are some interpretations of hepatitis B test results:
Table: Hepatitis B test results and interpretations
| Test |
|---|
You May Like: Ok Google What Is Hepatitis C
Additional Specimen Collection Information
Collect blood in a lithium heparin, green-top, EDTA purple-topor red-top tube. PST and SST are acceptable. Serum orplasma should be separated from contact with the cells within 2hours of collection. Specimens not centrifuged within 4 hours ofcollection may be rejected. Refrigerate the specimen if unable toassay within 8 hours of collection. Samples with > 1+ lipemiamust be cleared prior to analysis.
Sequence Following An Initial Negative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
As you obtain documentation, please submit documentation of each step to CastleBranch
- Initial Hepatitis B titer negative for immunity
- Receive Hepatitis B challenge dose/booster
- Repeat Hepatitis B titer 4-6 weeks after challenge/booster vaccine
Don’t Miss: Just Food For Dogs Hepatic Support
Discussing Screening Results With Clients
The medical personnel who ordered or arranged the screening test, not counselors, usually explain the results. Hepatitis screening should be part of the intake physical examination in an opioid treatment program, and medical personnel may report the results. However, the client may want to discuss the results with the counselor or ask the counselor questions.
Anxiety might interfere with some clients ability to comprehend or retain information, which might need to be repeated.
Suggestions for conversations with clients when the test results are negative include the following:
- Explain results clearly and simply: So the HCV screening result was negative? This means that, as of 6 months ago, you did not have .
- Emphasize that a negative result to an HCV test does not indicate to and that the client should take precautions to avoid . If a relapse to drug use occurs, advise clients to avoid sharing any drug paraphernalia or equipment. Specify that this includes cookers, cotton, water, needles, syringes, pipes, and straws.
- Emphasize the importance of getting HAV and HBV vaccinations. Provide information about the availability of low- or no-cost vaccinations.
Clients whose screening test results are positive for will need additional tests and examinationsusually with doctors who specialize in diseases of the liver to get accurate diagnoses and to determine their health status and the extent of liver damage. These tests are described in .
What Does The Test Measure
Hepatitis B testing looks for antigens, antibodies, or the genetic material of the hepatitis B virus. HBV antigens are substances from the virus that cause a patientâs body to produce an immune response. Antibodies are substances made by the immune system in response to the hepatitis B virus.
Initial tests for hepatitis B measure antibodies and antigens related to HBV including:
If a patient is diagnosed with hepatitis B based on these initial tests, additional hepatitis B testing may be used to monitor the disease, guide treatment, and determine if a person can spread hepatitis B to others. These additional tests may include:
- Hepatitis B e antigen : Hepatitis B e antigen is a protein from the hepatitis B virus found in some patients who are positive for hepatitis B surface antigen. Measuring this antigen can help doctors understand infectivity, which describes a personâs ability to spread HBV to others.
You May Like: Drugs Used For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Titer Test Panelmost Popular
The Hepatitis B Titer Test Panel panel contains 3 tests with 4 biomarkers.
Hepatitis B Titer Test
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen with Reflex Confirmation
- Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Immunity, Quantitative
- Hepatitis B Core Antibody, Total
The Hepatitis B Titer Test is ordered when a person needs proof of immunity to Hepatitis B or just want to check their immune status.
The Hepatitis Titer Test includes immunity testing for Hepatitis B. Hepatitis is a viral disease which affects the liver. Vaccinations for Hepatitis B can provide protective antibodies which immunize a person from catching the virus. Additionally, a person who has been affected by Hepatitis B and recovers can develop natural immunity. Titer testing looks for the antibodies which typically indicate that a person is immune to a particular virus or infection.
Hepatitis B Immunity
Not Immune and no active or prior infection may be a good candidate for vaccine
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen = Negative
- Hepatitis B Surface Antibody = Negative
- Hepatitis B Core Antibody, Total = Negative
Immunity due to vaccination
Laboratory Findings And Diagnostic Tests
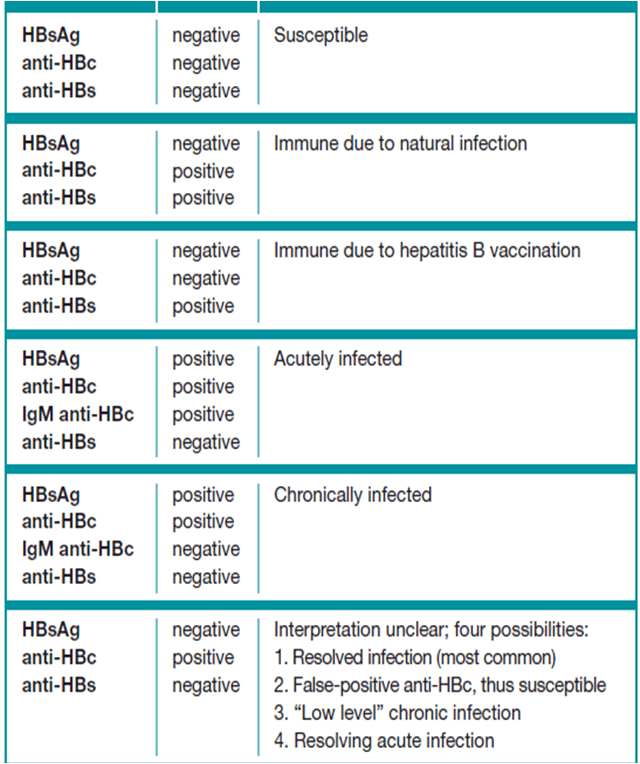
Serum HBsAg and anti-HBs are the most useful screening tests for chronic HBV infection or immunity to HBV. HBsAg is present in most chronically infected persons. Lack of anti-HBs in an unvaccinated HBsAg-negative person indicates susceptibility to HBV infection.3
Screening for HBsAg is recommended at the first prenatal visit for all pregnant women.3,109 Women in labor without HBsAg test information should have HBsAg serology on arrival. In addition, pretested women who have a history of certain risk factors should be retested at the time of admission to the hospital for delivery.3,110
Fabrizio Fabrizi MD, … Paul Martin MD, in, 2017
Don’t Miss: Standard Process Canine Hepatic Support
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. It spreads through contact with infected blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not spread through sharing utensils or kissing. It also doesnt spread through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding. Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure and can last for 212 weeks. However, you are still contagious, even
To screen for hepatitis B, your doctor will perform a series of blood tests.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine For Infants Schedule
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to HBV, your body mounts an immune defense to specifically target and neutralize the invader. Unlike innate immunity which mounts a generalized defense against all invaders, this type of immunity is disease-specific.
This immune response occurs whether you are exposed to HBV through blood or sexual contact, or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The virus has proteins on its surface, called antigens, that serve as unique identification tags. When HBV enters the body, the immune system “encodes” antibodies specific to these antigens so that it can recognize and attack the virus should it appear again.
There are two types of antibodies produced in response to the virus:
- Immunoglobulin M is the antibody that mounts the initial attack but eventually fades away.
- Immunoglobulin G is the antibody that provides long-lasting immune protection against HBV. The immunity can last for many years, but it gradually wanes over time.
You May Like: What Kinds Of Hepatitis Are There
Key Facts And Figures
- HBV is a vaccine-preventable disease that is highly infectious far more so than either HIV or HCV. It is transmitted through perinatal, percutaneous, or sexual exposure to an infected personâs blood / body fluids household contacts are also at risk of infection.
- Acute and chronic HBV infections are frequently asymptomatic or present with nonspecific symptoms about two-thirds of chronically infected people are unaware of their status, and most will only be detected through proactive screening.
- Of those infected as adults, 5% will become chronically infected in contrast, about 90% of infants infected at birth will develop chronic infection.Endnote 1
- Without intervention, 15%40% of chronically infected people will go on to develop cirrhosis, end-stage liver disease, and/or HCC.
HBV is a notifiable disease in all provinces and territories in Canada. As such, it must be reported to the regional/local Medical Officer of Health.
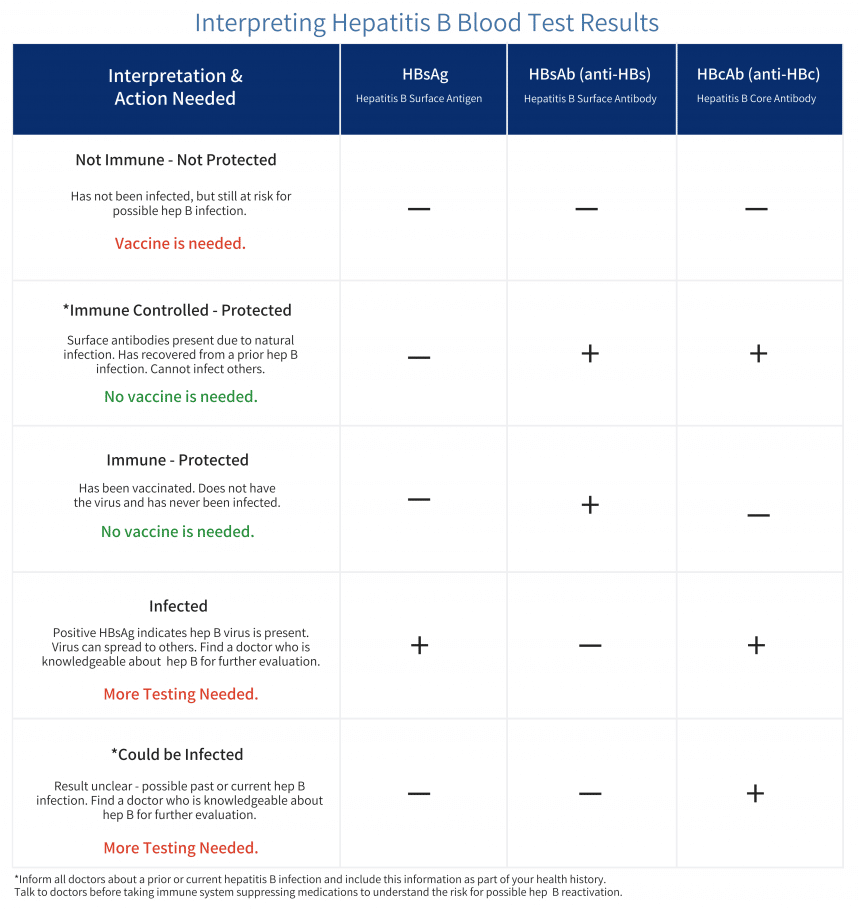
Results And Next Steps
The results of a hepatitis B titer panel can help a doctor determine a persons hepatitis B status. The results can be confusing if a person has never been through this type of testing before, but the doctor can explain the findings.
The results for the titer come back as either negative or positive on each subtest of the panel. Positive means that the virus or antibodies showed up on the test, while negative means that they did not.
The following table outlines what positive and negative results mean on different parts of the test and the possible next steps.
The information comes from the Immunization Action Coalition:
| Test |
|---|
Also Check: Where Can I Get Tested For Hepatitis B
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
Recommended Reading: How Can Hepatitis C Be Transmitted Sexually
For Patients With Chronic Hbv
Reducing the risk of liver damage
- Have liver enzymes monitored every 6-12 months.
- Reduce or eliminate alcohol.
- Stop smoking, as it increases the risk of liver cancer.
- You may drink coffee 3 or more cups per day may reduce the risk of liver cancer.Endnote 21
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A if you are not already immune â talk to your HCP or contact your local public health department.
- Stick to your medication schedule and your regular lab testing and follow-up visits.
- Tell your HCP before starting any immunosuppressive therapy.
About medications for patients with cirrhosis
- Avoid aminoglycosides , benzodiazepines, and narcotics including codeine .
- Whenever possible, avoid ASA or NSAIDs. Acetaminophen, oral contraceptive pills, and statins are safe to use.
- Do not drink alcohol.
- If you require surgery, discuss it with your specialist first.
- If you have black stools, call your specialist immediately or go to the ER.
- Tell your HCP about any complementary/alternative therapies or over the counter supplements including herbal remedies that you are taking.
- Follow your HCPâs advice on how frequently you require abdominal ultrasounds.
Living well with HBV
Read Also: How Soon Can You Test For Hepatitis C
Preparation Prior To Transport
Label the specimen container with the patients full name, date of collection and one other unique identifier such as the patients date of birth or Health Card Number. Failure to provide this information may result in rejection or testing delay.
Centrifuge if using SST. Place specimen in biohazard bag and seal. Specimens should be stored at 2-8ðC following collection.
Specimens more than the following number of days post collection will not be tested:
- > 6 days for Hepatitis B surface antigen
- > 7 days for Hepatitis B e Antigen and Hepatitis B e Antibody
- > 10 days for Hepatitis B core Antigen and Hepatitis B surface Antibody
Read Also: Hepatitis B Acute Or Chronic
Kinetics And Risk Of De Novo Hepatitis B Infection In Hbsagnegative Patients Undergoing Cytotoxic Chemotherapy
- CheeKin HuiCorrespondenceAddress requests for reprints to: CheeKin Hui, MD, University of Hong Kong, Queen Mary Hospital, Department of Medicine, 102 Pokfulam Road, Hong Kong SAR, China. fax: 2281 84030.Centre For The Study of Liver Diseases, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaResearch Centre For Infection and Immunity, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
- HaiYing ZhangAffiliationsCentre For The Study of Liver Diseases, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaResearch Centre For Infection and Immunity, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
- YuiHung YuengAffiliationsCentre For The Study of Liver Diseases, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaResearch Centre For Infection and Immunity, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
- John M. LukAffiliationsCentre For The Study of Liver Diseases, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaDepartment of Surgery, Queen Mary Hospital, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
- George K.K. LauAffiliationsCentre For The Study of Liver Diseases, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaResearch Centre For Infection and Immunity, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
Background & Aims:Methods:Results:
Abbreviations used in this paper:
Lancet.J Hepatol.
Donât Miss: Immune To Hepatitis B Means
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Ab Non Reactive