What Are The Risk Factors For Hepatitis B And C
Hepatitis B: Although most commonly acquired early in life, adults can also contract it. Hepatitis B is largely transmitted through bodily fluids. It can be passed at birth from a hepatitis B-infected mother or through exposure in early childhood to body fluids, blood or contaminated medical instruments. Hepatitis B can also be transmitted through intranasal and injection drug use as well as infected tools used during tattooing and body piercing.
Hepatitis C: The key risk factors are also intranasal and injection drug use, tattoos and body piercings, high-risk sexual contact, blood transfusions before 1992 and organ transplantation.
Another key risk factor for hepatitis C is being born from 1945 to 1965, during the baby-boom years. Eighty percent of all people who currently have hepatitis C in the United States were born in that timeframe.
Although the reasons that baby boomers are more likely to have hepatitis C than others arent entirely understood, its believed that most were infected in the 1970s and 1980s, when rates of hepatitis C were at their peak.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend that all U.S. adults born from 1945 to 1965 undergo a one-time screening test for hepatitis C. Connecticut is one of several states that has written this recommendation into law. In Connecticut ,the law requires that primary care clinicians screen all adults born within those years.
What Causes Hepatitis A
The hepatitis A virus causes this type of hepatitis and spreads through contact with an infected persons stool. Contact can occur by
- eating food made by an infected person who did not wash his or her hands after using the bathroom
- drinking untreated water or eating food washed in untreated water
- placing a finger or an object in your mouth that came into contact with an infected persons stool
- having close personal contact with an infected person, such as through sex or caring for someone who is ill
You cannot get hepatitis A from
- being coughed on or sneezed on by an infected person
- sitting next to an infected person
- hugging an infected person
You May Like: Side Effects Of Hepatitis C Medication
How Can I Avoid Getting Hepatitis B
There is a safe and effective vaccine that can protect you from getting hepatitis B. The vaccine is usually given in three doses over a six month period. The vaccine will give you long-lasting protection. A combined vaccine for hepatitis A and hepatitis B is also available.
Other ways to protect yourself or your loved ones include:
- Adopt safe sex practices.
- Avoid sharing personal hygiene items
- If you have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus , an injection of hepatitis B immune globulin may help protect you.
- If you are pregnant, make sure you are screened for hepatitis B. If the test result shows that you have the virus, make sure your baby receives the free hepatitis B vaccine. If you have hepatitis B, breastfeeding is safe if the baby has received both protective antibody called immune globulin, and the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine within the first 12 hours of life. Talk to your doctor about having your newborn immunized .
- If you decide to have a tattoo, piercing, manicure or pedicure, ensure that the facility uses single-use needles and inks and/or follows proper sterilization procedures.
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of Acute Hepatitis
How Is Hepatitis A Treated
HAV usually goes away on its own within six months.
Doctors often recommend bed rest, drinking lots of fluids, eating a healthy diet and avoiding alcohol. Medicines are not used to treat HAV. Talk to your doctor before taking prescription or over-the-counter drugs, vitamins or herbal supplements.
Itchy skin caused by HAV can be treated with non-prescription anti-itch medicine.
It is important to see your doctor regularly to make sure your body has fully recovered from the virus. Also, talk to your doctor about getting vaccinated for hepatitis B.
Abnormalities In Heme Metabolism And Excretion
One way to understand jaundice pathophysiology is to organize it into disorders that cause increased bilirubin production or decreased bilirubin excretion .
Prehepatic pathophysiology
Prehepatic jaundice results from a pathological increase in bilirubin production: an increased rate of erythrocyte hemolysis causes increased bilirubin production, leading to increased deposition of bilirubin in mucosal tissues and the appearance of a yellow hue.
Hepatic pathophysiology
Hepatic jaundice is due to significant disruption of liver function, leading to hepatic cell death and necrosis and impaired bilirubin transport across . Bilirubin transport across hepatocytes may be impaired at any point between hepatocellular uptake of unconjugated bilirubin and hepatocellular transport of conjugated bilirubin into the gallbladder. In addition, subsequent cellular due to inflammation causes mechanical obstruction of the intrahepatic biliary tract. Most commonly, interferences in all three major steps of bilirubin metabolism â uptake, conjugation, and excretion â usually occur in hepatocellular jaundice. Thus, an abnormal rise in both unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin will be present. Because excretion is usually impaired to the greatest extent, conjugated hyperbilirubinemia predominates.
Posthepatic pathophysiology
| Present | Present |
Laboratory findings depend on the cause of jaundice:
Don’t Miss: Can Your Body Heal Itself From Hepatitis C
How Is The Liver Damaged
Your liver responds to any injury by becoming inflamed. Any inflammation of the liver is known as hepatitis, whatever its cause. Inflammation that is sudden is known as acute hepatitis whereas inflammation that lasts longer than six months is known as chronic hepatitis.
The hepatitis B virus attacks the liver cells causing them to swell and over time this leads to the development of scar tissue. This is called fibrosis. Inflammation is a natural part of the body’s response to repairing damaged tissue. A temporary fibrous ‘scaffold’ forms, like a scab forming over a grazed knee, whilst the liver regenerates itself. If your liver experiences repeated injury then new liver cells cannot regenerate fast enough and the fibrous tissue remains as a scar. This is called fibrosis and takes different length of time to develop in different people.
The development of fibrosis causes the liver to become harder in texture. This hardening is also known as cirrhosis. There is an increased risk of liver cancer in those who have gone on to develop cirrhosis.
When the liver become hard it becomes difficult for it to function properly. The liver, unlike any other organ in the body, can repair itself and so compensate for a lot of damage. However, once it become so damaged that it can no longer carry out its functions, the liver is then said to be
Is There A Link Between The Increased Cases Of Hepatitis And Covid
There is no link between these new cases of hepatitis and COVID-19. Many of the children were tested for COVID-19 and were negative. COVID-19 can cause a hepatitis, but it is usually not as severe as these new cases. To date, COVID-19 has not led to liver transplant in a patient who did not already have liver disease.
If your child is showing signs of hepatitis, be sure to contact your childs primary care provider, or make an appointment with our Children’s Center for Liver Disease at Hasbro Children’s Hospital.
About the Author:
Also Check: How Does A Person Get Hepatitis C
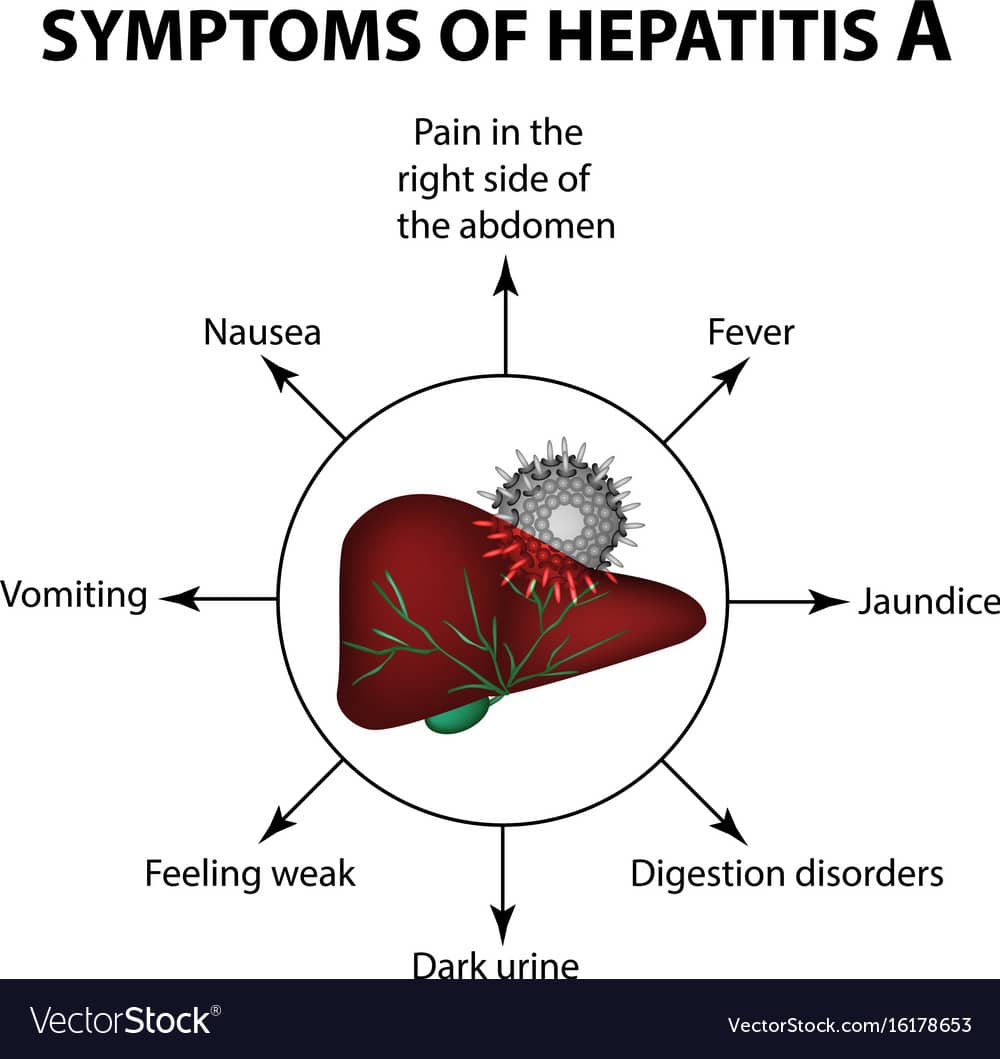
How Does Hepatitis Affect The Body
Typically, symptoms for all types of hepatitis occur once the infection begins causing damage to the liver. In acute cases, symptoms develop quickly and in chronic instances, signs may take up to 6 months to begin showing concern.
General signs and symptoms for acute and chronic hepatitis
All hepatitis types will have the following signs and symptoms in common:
- Flu-like symptoms
Other signs and symptoms for hepatitis B and D
- Abdominal discomfort
- Tan-coloured stools
All symptom for hepatitis B must be assessed and treated by a medical professional as quickly as possible to prevent an infection developing into HDV and further health complications. If you are exposed to the virus and can seek treatment within the first 24 hours following exposure, an infection can be prevented with prompt medical attention.
A HDV infection may not always display obvious symptoms but when they do, they are very similar to those of hepatitis B. Symptoms of HDV can often make those of HBV worse, which can make diagnosis a little trickier.
Other signs and symptoms for hepatitis C
- Abdominal discomfort
Read Also: How Does A Person Contract Hepatitis C
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Some people with hepatitis do not have symptoms and do not know they are infected. If you do have symptoms, they may include:
- Jaundice, yellowing of your skin and eyes
If you have an acute infection, your symptoms can start anywhere between 2 weeks to 6 months after you got infected. If you have a chronic infection, you may not have symptoms until many years later.
Read Also: Can Hepatitis C Cause Diarrhea
What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
What Is Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is contagious. The virus lives in poop from people who have the infection. That’s why it’s so important to wash your hands before eating and after going to the bathroom. If you don’t, and then go make yourself a sandwich, hep A virus might end up on your food, and then in you! People who recover from hepatitis A have immunity to the virus and won’t get it again.
The hepatitis A vaccine has made the infection less common in the United States and other developed countries. Getting vaccinated helps a person’s body make antibodies that protect against hepatitis infection. The hepatitis A vaccine is given to all kids when they’re between 1 and 2 years old, and to people who travel to countries where the virus could get into the food and water supply.
These steps also help keep people safe from hepatitis A:
- regular hand washing, especially after going to the bathroom or diapering a baby, and before eating
- washing fruits and vegetables before eating them
- not eating raw shellfish, such as raw oysters
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule Adult
Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis B
Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis B. Many people who have hepatitis B dont have symptoms and dont know they are infected with hepatitis B. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis B, which can lower your chances of developing serious health problems.
Your doctor may recommend screening for hepatitis B if you9,14
- were born in an area of the world where 2 percent or more of the population has hepatitis B infection, which includes Africa, Asia, and parts of the Middle East, Eastern Europe, and South America
- didnt receive the hepatitis B vaccine as an infant and have parents who were born in an area where 8 percent or more of the population had hepatitis B infection, which includes sub-Saharan Africa and parts of Asia
- are HIV-positive
- are a man who has sex with men
- have lived with or had sex with a person who has hepatitis B
- have an increased chance of infection due to other factors
Also Check: Is There A Home Test For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis And The Liver
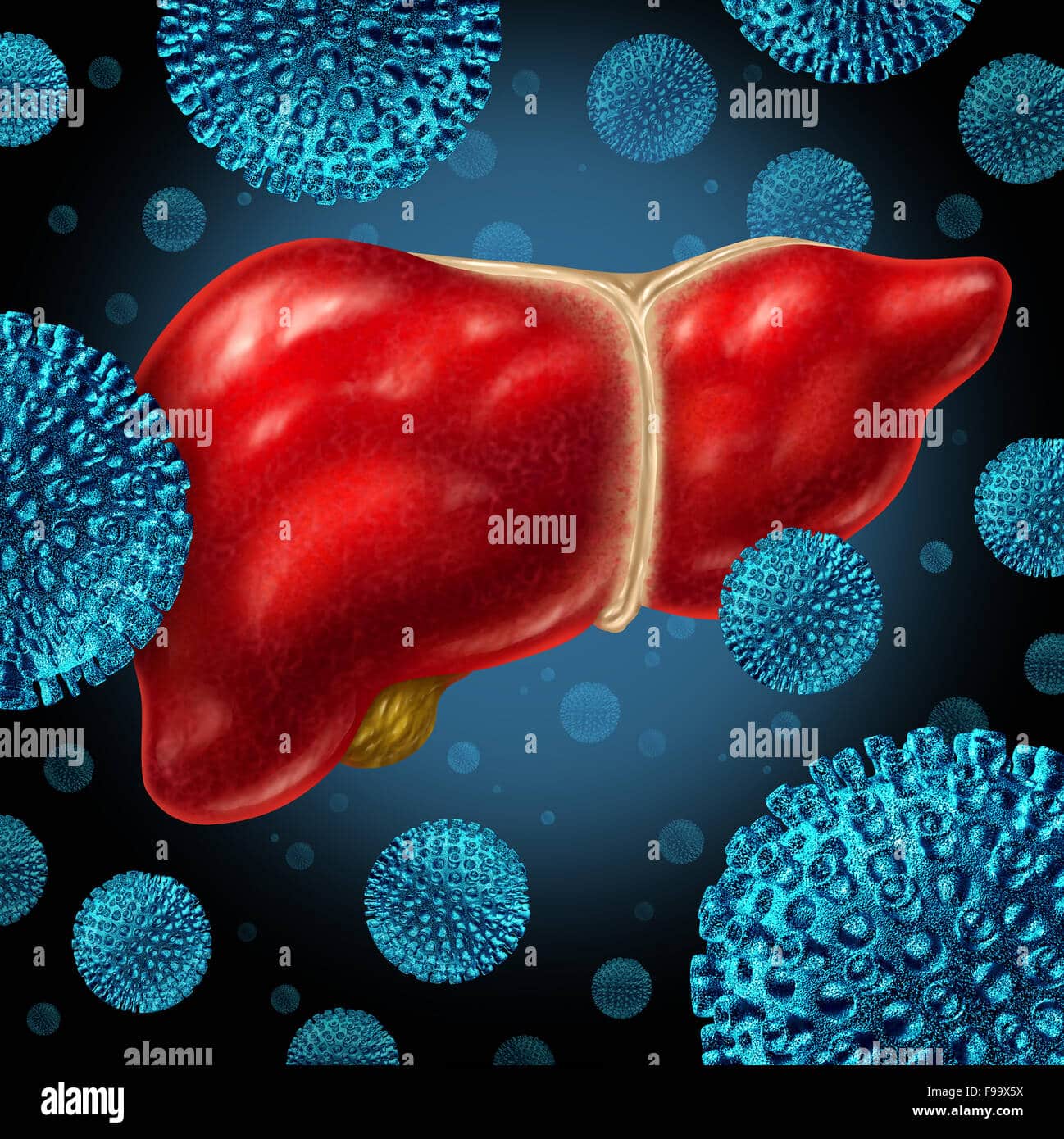
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is important for a range of functions in the body. These include regulating metabolism, making proteins, storing vitamins and iron, removing toxins and producing bile.
If the liver doesnt work properly, it can cause serious illness or sometimes even death.
Hepatitis may be caused by infection, viruses, chemicals, alcohol and other drug use and other factors.
Chronic hepatitis means ongoing inflammation of the liver, irrespective of the underlying cause.
Also Check: Hepatitis C And Liver Cancer
You May Like: Medicine For Hepatitis C Virus
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
There are three main ways to diagnose HBV infection. They include:
- Blood tests: Tests of the blood serum shows how your bodys immune system is responding to the virus. A blood test can also tell you if you are immune to HBV.
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to show the size and shape of your liver and how well the blood flows through it.
- Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis.
The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit. Often, people whove become infected first learn they have hepatitis B when they go to donate blood. Blood donations are routinely scanned for the infection.
The virus can be detected within 30 to 60 days of infection. About 70% of adults with hepatitis B develop symptoms, which tend to appear an average of 90 days after initial exposure to the virus.
How Serious Is It
- People can be sick for a few weeks to a few months
- Most recover with no lasting liver damage
- Although very rare, death can occur
- 15%25% of chronically infected people develop chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer
- More than 50% of people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop a chronic infection
- 5%-25% of people with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis over 1020 years
Recommended Reading: Which Test For Hepatitis B
Whats The Best Way To Stop The Spread Of Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A vaccination is the best way to prevent hepatitis A. The hepatitis A vaccine is given in 2 doses, usually about 6 months apart.
Other ways to stop the spread of HAV are:
- Always washing your hands with soap and warm water immediately after using the bathroom or changing a diaper
- Always washing your hands with soap and warm water before preparing or eating food
Transmission Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is less easily transmitted than hepatitis A. Transmission commonly occurs when needles are reused without being first sterilizedas when people share needles to inject drugs or when needles are reused to apply tattoos.
Transmission through blood transfusions is possible but is now rare in the United States because blood is screened.
Transmission may occur between sex partners, both heterosexual and homosexual. Also at increased risk are people living in close quarters because contact with another persons body fluid is more likely.
Anyone with hepatitis B, even people who do not have symptoms, can transmit the virus.
Whether insect bites can transmit this virus is not clear.
Many cases of hepatitis B have no known source.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatic Function Panel
Alcohol And Your Liver
- The alcohol content of a drink, rather than the type of beverage consumed, is significant to the development of cirrhosis.
- Males whose daily consumption of alcohol exceeds 80g are at a high risk of developing cirrhosis for females this limit is 40g per day.1,2
- Binge drinking is less injurious to the liver than continued daily drinking.1
- Women are more susceptible than men are to liver damage and they subsequently develop cirrhosis at an earlier age. The influence of female sex hormones might be a possible explanation for this difference between genders.3
When Is That Pain Hep B
When people with chronic hepatitis B experience abdominal pain, we often wonder if its related to our liver and if our hepatitis B is getting worse.
According to experts, hepatitis B rarely causes abdominal pain. Here are some insights to help you understand what might be behind your abdominal pain when you live with chronic hepatitis B.
First, its not called the silent infection for nothing. When first infected, most children and nearly 70 percent of adults never experience any direct symptoms from hepatitis B. When people do have symptoms, such as aches, nausea and fever, they usually last for only a few days. Only a very small percentage have symptoms that persist long-term.
But chronic hepatitis B is different. Most of us have had this infection since childhood and over time it rarely causes us any symptoms. Usually, disease causes pain, it is natures way of telling us that a health problem is getting worse. However, with diseases such as chronic hepatitis B, diabetes or high blood pressure, we often dont feel any symptoms until the disease reaches an advanced state.
This palpable pushing against the membrane is why fatty liver disease, for example, causes abdominal pain, while early-stage hepatitis B does not. The fatty liver is enlarged from the fat thats accumulated and its accompanying inflammation, it has literally outgrown its membrane.
Dont Miss: Hepatitis B Curable Or Not
You May Like: Can Hepatitis Be Sexually Transmitted