Accelerated Us Children And Adult Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
In some instances, it may be necessary to vaccinate within a short period of time to ensure protection before travel. There are accelerated schedules to provide the highest level of protection over a short period of time. Individuals who need an accelerated schedule must have a booster dose at 1 year to ensure long-term protection. Note that the 2-dose Heplisav-B vaccine will also ensure maximum protection over a 1-month period without the need for a booster dose at 1 year.
4-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
Engerix-B is a 3-dose vaccine that can be given on an accelerated, four-dose schedule, with 3 shots administered within 2 months, and a booster dose at 1 year to provide maximum long-term protection.
4-Dose Combination Hepatitis A and B Vaccine Series
Twinrix is a 4-dose vaccine that can be given on an accelerated schedule to provide protection against hepatitis A and B. Three doses are administered within 1 month, followed by a booster shot at 1 year. This is a common choice of vaccine for those travelling on short-notice outside the U.S. It is important to complete the booster dose at 1 year, to ensure long-term protection.
2-Dose Vaccine Series
Additional Resource Links:
Hepatitis B Vaccine On The Nhs
A hepatitis B-containing vaccine is provided for all babies born in the UK on or after 1 August 2017. This is given as part of the 6-in-1 vaccine.
Hospitals, GP surgeries and sexual health or GUM clinics usually provide the hepatitis B vaccination free of charge for anyone at risk of infection.
GPs are not obliged to provide the hepatitis B vaccine on the NHS if you’re not thought to be at risk.
GPs may charge for the hepatitis B vaccine if you want it as a travel vaccine, or they may refer you to a travel clinic for a private vaccination. The current cost of the vaccine is around £50 a dose.
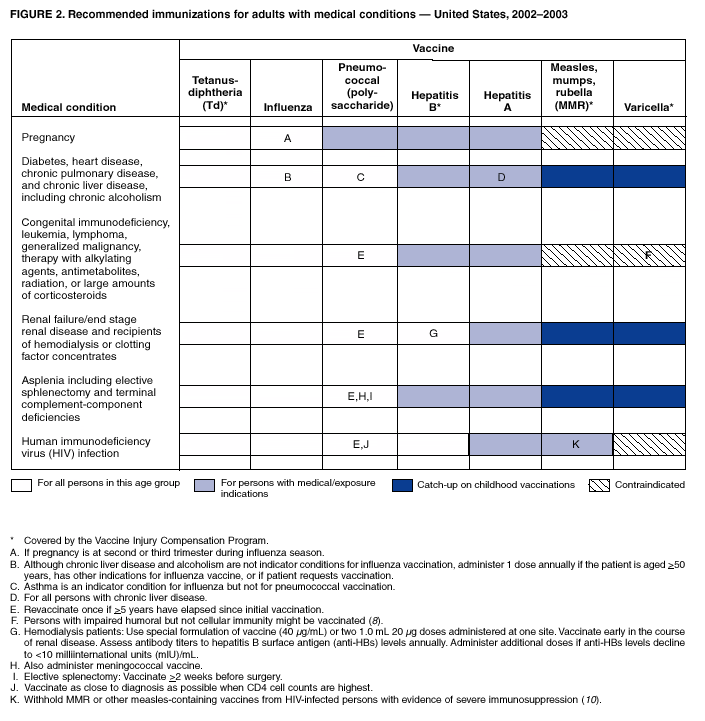
Indications For Hepatitis A Vaccine
HepA vaccine also is indicated when any of the following is present:
-
A desire for protection from hepatitis A in people not previously vaccinated
-
Travel to or work in endemic areas
-
Occupational exposure
-
Sex between men
-
Use of illicit drugs , such as methamphetamine
-
HIV infection in all people 1 year of age
-
A chronic liver disorder
-
Anticipated close personal contact with an adopted child during the first 60 days after the child’s arrival in the US from an endemic area
-
Healthy adults 40 years who have recently been exposed to hepatitis A virus and adults > 40 if hepatitis A immunoglobulin cannot be obtained
-
Pregnant women who are identified to be at risk of HAV infection during pregnancy or who are at risk of having a severe outcome resulting from HAV infection
During hepatitis A outbreaks, people 1 year of age who are at risk of HAV infection should be vaccinated.
The combination HepA and HepB vaccine can be used in people 18 years who have indications for either hepatitis A or hepatitis B vaccine and who have not been previously vaccinated with one of the vaccine components.
Also Check: Most Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Who Should Receive The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Vaccination is the most reliable way to prevent getting hepatitis B or developing serious related medical complications.
The CDCs Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends that people in all age groups get the hepatitis B vaccine, including:
- All infants within 24 hours after birth
- Children and teens who have not previously been vaccinated against hepatitis B
- Adults ages 19 to 59
- Adults ages 60 and older with at least one risk factor for hepatitis B
Adults over 60 who are not at risk of developing hepatitis B can also receive the HepB vaccine if they choose.
Guidance On Reporting Adverse Events Following Immunization
Vaccine providers are asked to report, through local public health officials, any serious or unexpected adverse event temporally related to vaccination. An unexpected AEFI is an event that is not listed in available product information but may be due to the immunization, or a change in the frequency of a known AEFI.
Refer to Reporting Adverse Events Following Immunization in Canada and Adverse events following immunization in Part 2 for additional information about AEFI reporting.
Recommended Reading: Cvs Hepatitis A Vaccine Cost
Emergency Hepatitis B Vaccination
If you have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and have not been vaccinated before, you should get immediate medical advice, as you may benefit from having the hepatitis B vaccine.
In some situations, you may also need to have an injection of antibodies, called specific hepatitis B immunoglobulin , along with the hepatitis B vaccine.
HBIG should ideally be given within 48 hours, but you can still have it up to a week after exposure.
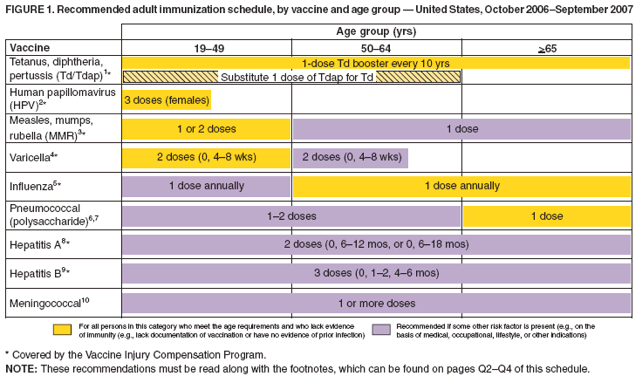
Routine Administration Schedule For Hepatitis B Vaccine In Adults
- The dosing schedule is 0, 1 to 2 months, and 4 to 6 months.
- There is some flexibility in the schedule, but be sure to keep in mind the minimum intervals between doses:
- At least four weeks between doses #1 and #2
- At least eight weeks between doses #2 and #3
- At least 16 weeks between doses #1 and #3
- If your patient falls behind on the hepatitis B vaccination schedule , continue vaccinating from where your patient left off. The series does NOT need to be restarted.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Hepatitis From Saliva
For Children And Adolescents
The dosage for both MMR and MMRV is 0.5 mL. All three vaccines are administered by the subcutaneous route.
The minimum age for both MMR vaccines and MMRV is 12 months of age. The typical age for the second dose of either vaccine is at 4 to 6 years of age. The maximum age for administration of MMRV is 12 years. It should not be administered to anyone 13 years of age or older. Both MMR vaccines may be administered to anyone 12 months of age or older.
The minimum interval between MMR doses is 4 weeks . The minimum interval between MMRV doses is 3 months.
The preferred injection site in small children is the anterolateral aspect of the thigh. The posterior triceps aspect of the upper arm is the preferred site for older children and adolescents.
Testing For Hepatitis B Immunity
Generally a serology result of 10 IU/L is considered immunity to hepatitis B. Vaccinated individuals who have laboratory confirmation of anti-HBs 10 IU/L are considered to have lifetime immunity to hepatitis B even if antibody levels wane to undetectable levels in subsequent serology. This is because an anamnestic immune response will be protective against future hepatitis B exposure.
Refer to the current Immunisation Handbook for information on post-vaccination serology testing and management of non-responders. Non-responders require case-by-case consideration.
You May Like: Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Why Is The Hepb Vaccine Recommended
People who dont know they’re infected can spread the hepatitis B virus. So it cant be avoided just by being careful. That’s why health experts recommend that all babies get the vaccine right from birth.
The HepB injection usually creates long-term immunity. Most infants who get the HepB series are protected from hepatitis B infection beyond childhood, into their adult years.
Eliminating the risk of infection also decreases risk for cirrhosis of the liver, chronic liver disease, and liver cancer.
What To Do If You Miss A Scheduled Dose
The recommended schedule for the HBV vaccine follows a three-dose pattern, with all doses complete within 6 months. The good news is that if you miss a dose, you dont need to start the series of shots all over.
If you missed getting the second dose 1 month after the first, make an appointment as soon as possible. If you miss the third dose, you should also try to get it as quickly as possible. Keep in mind that the second and third doses
You May Like: What Happens When You Have Hepatitis C
Concurrent Administration Of Vaccines
HB-containing vaccines may be administered concomitantly with other vaccines or with HBIg. Different injection sites and separate needles and syringes must be used for concurrent parenteral injections.
Refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1 for additional information about concurrent administration of vaccines.
Preparations Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B vaccine is produced using recombinant DNA technology. A plasmid containing the gene for hepatitis B surface antigen is inserted into common bakers yeast, which then produces HBsAg. The HBsAg is harvested and purified. This vaccine cannot cause hepatitis B virus infection because no potentially infectious viral DNA or complete viral particles are produced during this process.
Single-antigen and a combination formulation that combines hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines are available. Two single-antigen vaccines, Engerix-B® and Recombivax HB®, are conjugated with aluminum. A newer formulation, HepB-CpG , uses the immune-stimulating adjuvant, cytidine-phosphate-guanosine oligodeoxynucleotide .
Recommended Reading: How Is Hepatitis B Transferred
Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
Most people only experience mild, short-term side effects from the hepatitis B vaccine. Common side effects include:
- Pain, redness, or swelling at the site of injection
Severe allergic reactions to the hepatitis B vaccine are very rare. If you have symptoms of an allergic reaction shortly after getting the HepB vaccinesuch as difficulty breathing, facial swelling, or hivesseek medical help immediately.
The hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective for most people. However, there are certain people who should not get the HepB vaccine, including:
- People who are moderately or severely ill at the time of vaccination
- People who have had a severe allergic reaction to yeast
- People who have had a severe allergic reaction to a hepatitis B vaccine in the past
What Is Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B is a serious disease caused by a virus. Hepatitis causes inflammation of the liver, vomiting, and jaundice . Hepatitis can lead to liver cancer, cirrhosis, or death.
The hepatitis B adult vaccine is used to help prevent this disease in adults. The dialysis form of this vaccine is for adults receiving dialysis.
This vaccine helps your body develop immunity to hepatitis B, but it will not treat an active infection you already have.
Vaccination with hepatitis B adult vaccine is recommended for all adults who are at risk of getting hepatitis B. Risk factors include: living with someone infected with hepatitis B virus having sexual contact with infected people having hepatitis C, chronicliver disease, kidney disease, diabetes, HIV or AIDS being on dialysis using intravenous drugs living or working in a facility for developmentally disabled people working in healthcare or public safety and being exposed to blood or body fluids living or working in a correctional facility being a victim of sexual abuse or assault and traveling to areas where hepatitis B is common.
Like any vaccine, the hepatitis B vaccine may not provide protection from disease in every person.
Read Also: Hepatitis C In Babies Symptoms
General Information About Vaccination Outside The Us
In developing countries, the pentavalent vaccine, a combination 5-in-one vaccine that protects against five diseases, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, Hib and hepatitis B, may be given to babies more than 6 weeks of age, and can be given up to 1 year of age. The first dose is given at 6 weeks, and the second and third doses are given at 10 and 14 weeks of age. The pentavalent vaccine may be made available free of charge with the support of GAVI, the vaccine alliance. Check the GAVI country hub to see the resources and immunizations that may be available:
For babies born to mothers with hepatitis B, waiting for the first dose of the pentavalent vaccine is too late and will NOT protect the baby from vertical or horizontal transmission of hepatitis B. Babies born to a mother with hepatitis B have a greater than 90% chance of developing chronic hepatitis B if they are not properly treated at birth.
WHO recommends the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth for ALL babies. Plan ahead and inquire about the availability and cost of the monovalent , birth dose of the vaccine, as it is not a GAVI provided immunization. This is particularly important to women who are positive for hepatitis B.
If you are unsure of your hepatitis B status, please be sure your doctor tests you for hepatitis B!
*WHO does not recommend a birth dose of HBIG, which may not be available in all countries. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Page updated September 2022.
The Hepatitis B Vaccine And Immunosuppressants
If you are taking or about to start taking a medication that suppresses your immune response, let your healthcare provider know. Immunosuppressants may make certain vaccines less effective. Your healthcare provider may recommend that you get the hepatitis B vaccine at a particular time during your course of medication.
Read Also: How Many Hepatitis Are There
Billing Guidelines: Hepatitis B Vaccine Adjuvanted Solution For Intramuscular Injection Hcpcs Code 90739
CSRA
Effective with date of service Jan. 8, 2018, the North Carolina Medicaid and NC Health Choice programs covers hepatitis B vaccine , adjuvanted solution for intramuscular injection for use in the Physicians Drug Program when billed with HCPCS code 90739 – Hepatitis B vaccine , adult dosage, two dose schedule, for intramuscular use.
Heplisav-B is available as a solution for injection supplied as a 0.5 mL single-dose vial and is indicated for the prevention of infection caused by all known subtypes of hepatitis B virus in adults 18 years of age and older.
The recommended dose is two doses administered intramuscularly one month apart.
See full prescribing information for further detail.
Us Infant Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
Since 1991, ALL medically stable infants with a birth weight of at least 2,000 g in the U.S. are recommended to receive the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth. The additional 2 doses are given at 1 month and 6 months of age.
4-Dose Vaccine Combination Series for Infants
Combination vaccines, such as the pentavalent and hexavalent vaccines, include protection against 5 or 6 diseases, including hepatitis B. The first shot is usually given at 6 weeks of age, but in order to protect infants from hepatitis B beginning at birth, a monovalent or single dose of the hepatitis B vaccine is also recommended within 24 hours of birth. The hepatitis B vaccine series can then be completed with the pentavalent or hexavalent vaccine with the recommended schedule.
Also Check: Drugs Used To Treat Hepatitis C
Persons New To Canada
Health care providers who see persons newly arrived in Canada should review the immunization status and update immunization for these individuals, as necessary. In many countries outside of Canada, HB vaccine is in limited use.
All persons from a country that is endemic for HB should be assessed and vaccinated against HB if not immune and not infected. Individuals born in developing countries are more likely to be carriers of HB, necessitating vaccination of their sexual and household contacts based on review of their serologic test results. HB vaccine is recommended for all household contacts whose families have immigrated to Canada from areas in which there is a high prevalence of HB and who may be exposed to HB carriers through their extended families or when visiting their country of origin.
Children adopted from countries in which there is a high prevalence of HB infection should be screened for HBsAg and, if positive, household or close contacts in the adopting family should be immunized before adoption or as soon as possible thereafter. Adults going to pick-up children from these countries should be vaccinated before departure. Refer to Immunization of Persons New to Canada in Part 3 for additional information.
Persons With Inadequate Immunization Records

Evidence of long term protection against HB has only been demonstrated in individuals who have been vaccinated according to a recommended immunization schedule. Independent of their anti-HBs titres, children and adults lacking adequate documentation of immunization should be considered susceptible and started on an immunization schedule appropriate for their age and risk factors. Refer to Immunization of Persons with Inadequate Immunization Records in Part 3 for additional information.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Hepatitis B And C
Why Do You Need A Hepatitis B Shot
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that cant be transferred person-to-person unless you have contact with an infected persons bodily fluids. Annual infection rates of HBV are going down in the United States thanks to vaccines. So you might be wondering if you or your child needs a shot to protect against hepatitis B.
International Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
The hepatitis B vaccine is an injection that is generally given in the arm and as a three-dose series. The World Health Organization recommends a 0, 1, and 6-month vaccine schedule, though schedules may vary based on a countrys national immunization program. Completing the hepatitis B vaccine series, preferably beginning at birth, will ensure protection against hepatitis B, hepatitis delta and lower the lifetime risk of liver cancer. Greater than 90% of babies and up to 50% of young children who are not vaccinated and are infected with hepatitis B will have lifelong infection, which makes the birth dose essential to their protection. Please note that the vaccine brand name, manufacturer and associated schedules for adults, children and infants may be unique to different countries, though there is a list of WHO prequalified vaccines.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
The World Health Organization recommends all infants receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth and to complete the vaccine series with additional shots at 1 month and 6 months of age. Beginning the hepatitis B vaccine at birth will ensure protection against hepatitis B for life.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
4-Dose Combination Vaccine Series for Infants
Additional Resource Links:
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Hepatitis From Drinking