What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
How Serious Is It
- People can be sick for a few weeks to a few months
- Most recover with no lasting liver damage
- Although very rare, death can occur
- 15%25% of chronically infected people develop chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer
- More than 50% of people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop a chronic infection
- 5%-25% of people with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis over 1020 years
How Are Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Spread From Person To Person
Like HIV, the hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses spread:
- From mother to child: Pregnant women can pass these infections to their infants. HIV-HCV coinfection increases the risk of passing on hepatitis C to the baby.
- Sexually: Both viruses can also be transmitted sexually, but HBV is much more likely than HCV to be transmitted sexually. Sexual transmission of HCV is most likely to happen among gay and bisexual men who are living with HIV.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Prevent Hepatitis B Infections In Newborns
If you are pregnant and have hepatitis B, talk with your doctor about lowering the risk that the infection will spread to your baby. Your doctor will check your virus levels during pregnancy. If virus levels are high, your doctor may recommend treatment during pregnancy to lower virus levels and reduce the chance that hepatitis B will spread to your baby. Your doctor may refer you to a liver specialist to find out if you need hepatitis B treatment and to check for liver damage.
When it is time to give birth, tell the doctor and staff who deliver your baby that you have hepatitis B. A health care professional should give your baby the hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG right after birth. The vaccine and HBIG will greatly reduce the chance of your baby getting the infection.
Whats The Prognosis For Hepatitis B
Your doctor will know youâve recovered when you no longer have symptoms and blood tests show:
- Your liver is working normally.
- You have hepatitis B surface antibody.
But some people don’t get rid of the infection. If you have it for more than 6 months, youâre whatâs called a carrier, even if you donât have symptoms. This means you can give the disease to someone else through:
- Unprotected sex
- Contact with your blood or an open sore
- Sharing needles or syringes
Doctors donât know why, but the disease does go away in a small number of carriers. For others, it becomes whatâs known as chronic. That means you have an ongoing liver infection. It can lead to cirrhosis, or hardening of the organ. It scars over and stops working. Some people also get liver cancer.
If youâre a carrier or are infected with hepatitis B, donât donate blood, plasma, body organs, tissue, or sperm. Tell anyone you could infect — whether itâs a sex partner, your doctor, or your dentist — that you have it.
Show Sources
CDC: âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for Health Professionals,â âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Mayo Clinic: âHepatitis B.â
UpToDate: âHepatitis B virus: Screening and diagnosis.â
CDC.
HealthyPeople.gov: âHepatitis B in Pregnant Women: Screening.â
Annals of Internal Medicine: âScreening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.â
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
As hepatitis B infection is highly transmissible via accidental needlesticks, healthcare providers involved in taking care of a patient with HBV should exercise caution and practice proper preventative measures such as vaccination. Patient education should also include counseling about HBV transmission. The interprofessional team’s role is crucial in ensuring the best patient outcomes.
The vaccination rate is low in many developing countries, and the majority of patients are undiagnosed. Educational programs and improved awareness among the general public and healthcare providers are necessary to improve the identification of the patients, reduce transmission of the disease, and reduce the complications of hepatitis B infection.
Treatment Of Acute Liver Failure Due To Hepatitis B
No placebo-controlled trial has been published in the setting of established acute liver failure, but several cases series have suggested lower mortality in patients with fulminant hepatitis B compared to case series of patients who did not receive antiviral therapy. Most of these studies recruited patients before they had progressed to more advanced hepatic encephalopathy . In a study recruiting patients with more advanced liver failure, no benefit of nucleoside on survival was observed , but those authors still concluded that nucleoside analogues would be indicated in such patients to reduce viral load prior to potential liver transplantation. It is likely that early intervention is crucial. N-acetyl cysteine, which is highly effective in preventing death from liver failure from paracetamol/acetaminophen overdosing, has limited efficacy once hepatic encephalopathy is present. While early antiviral intervention is likely to be more effective when given early, we suggest that it should also be given at later time points, as it at least diminishes the risk of HBV reinfection should liver transplantation be required. In case of transplantation, it is unclear whether antiviral therapy can be stopped soon after or if long-term antiviral treatment is required. If transplantation can be avoided, antiviral treatment should be continued at least until HBsAg clearance.
Read Also: How Do You Test For Hepatitis C
You May Like: What Kind Of Virus Is Hepatitis C
How Common Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is fairly common in Africa and the western Pacific region. Throughout the world, there are about 292 million people who are infected with chronic hepatitis B. In the U.S., the figure exceeds 2 million people.
The number of infections had been falling in the U.S., but fewer vaccinations among adults combined with the onset of the opioid crisis and injected drug usage has resulted in the numbers rising again. Infected women can pass the infection on to their babies. Children who are infected before age 5 are more likely to have chronic infection than those infected later in life.
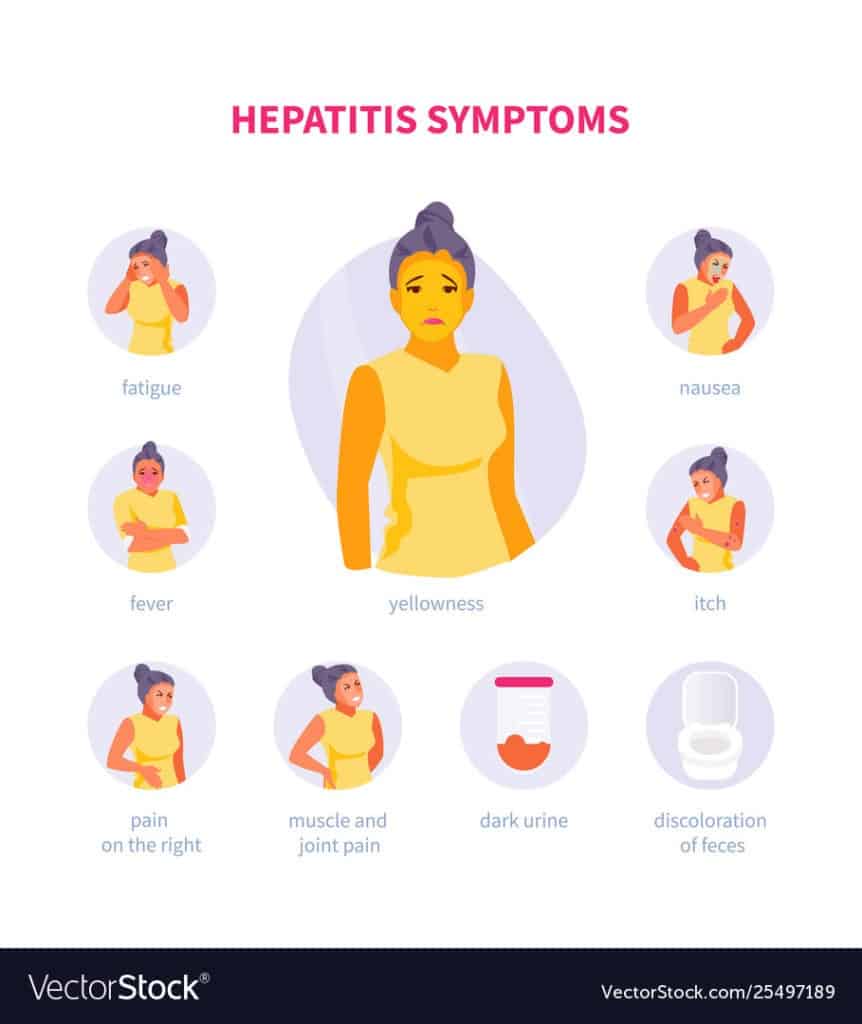
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Some people with hepatitis do not have symptoms and do not know they are infected. If you do have symptoms, they may include:
- Jaundice, yellowing of your skin and eyes
If you have an acute infection, your symptoms can start anywhere between 2 weeks to 6 months after you got infected. If you have a chronic infection, you may not have symptoms until many years later.
Read Also: Can Hepatitis B And C Be Cured
What Other Problems Can Hepatitis B Cause
In rare cases, acute hepatitis B can cause liver failure.
Chronic hepatitis B can develop into a serious disease that causes long-term health problems such as cirrhosis , liver cancer, and liver failure.
If you have ever had hepatitis B, the virus may become active again, or reactivated, later in life. This could start to damage the liver and cause symptoms.
Treatment For Suspected Exposure
Anyone who has had potential exposure to HBV can undergo a postexposure prophylaxis protocol.
This consists of HBV vaccination and hepatitis B immunoglobin . Healthcare workers give the prophylaxis after the exposure and before an acute infection develops.
This protocol will not cure an infection that has already developed. However, it decreases the rate of acute infection.
Don’t Miss: If You Have Hepatitis B Can It Go Away
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis B
People are more likely to get hepatitis B if they are born to a mother who has hepatitis B. The virus can spread from mother to child during birth. For this reason, people are more likely to have hepatitis B if they
- were born in a part of the world where 2 percent or more of the population has hepatitis B infection
- were born in the United States, didnt receive the hepatitis B vaccine as an infant, and have parents who were born in an area where 8 percent or more of the population had hepatitis B infection
People are also more likely to have hepatitis B if they
- are infected with HIV, because hepatitis B and HIV spread in similar ways
- have lived with or had sex with someone who has hepatitis B
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have sex with men
- are injection drug users
- work in a profession, such as health care, in which they have contact with blood, needles, or body fluids at work
- live or work in a care facility for people with developmental disabilities
- have been on kidney dialysis
- live or work in a prison
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before the mid-1980s
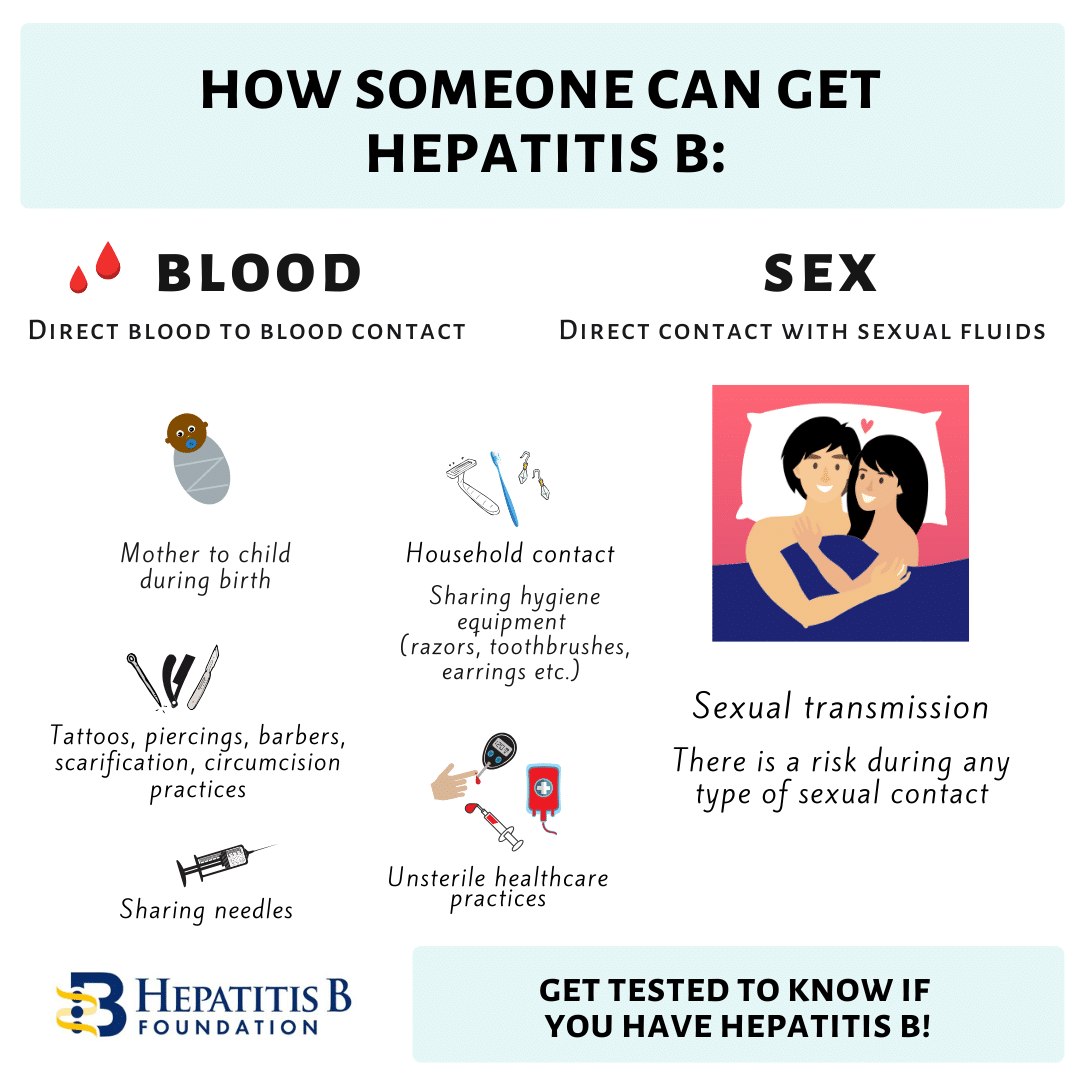
In the United States, hepatitis B spreads among adults mainly through contact with infected blood through the skin, such as during injection drug use, and through sexual contact.12
Deterrence And Patient Education
Patient education remains one of the most important components in preventative measures regarding HBV infection.
Education should be provided to expecting parents about the importance of vaccination and to clarify erroneous beliefs about vaccinations.Patient education should also include counseling about the avoidance of risky behaviors that predispose an individual to be infected, including promiscuous sexual activity or intravenous drug abuse. They should also be advised not to share items such as shaving razors, toothbrushes, or hair combs due to possible transmission via mucosal contact or through microtrauma to protective barriers.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitative Titer
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if you have an active infection. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can transmit the virus to others. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B.
This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the state of a hepatitis B infection.
Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis B
Currently, there is no complete cure for hepatitis B. But when managed properly, those living with the virus can expect to live a normal life. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding alcoholic beverages and tobacco products are crucial components in managing the disease.
You should also visit a doctor familiar with hepatitis B at least annuallythough twice a year might be best to monitor your liver through blood tests and medical imaging. As with most diseases, detecting it early leads to a better outcome. If youre exposed to the virus, you should get an antibody injection within 12 hours of exposure.
Read Also: Fatty Liver And Hepatitis B
What Should You Know About Hepatitis B Before You Travel
Hepatitis B is quite common in China and other Asian countries, where as many as 1 in 12 people have the virus, though many dont know it. Before traveling to those places, you should make sure youve been vaccinated against the virus.
In addition to getting the vaccine, you can take these additional precautions to reduce your risk of contracting the virus:
- Refrain from taking illegal drugs.
- Always use latex or polyurethane condoms during sex.
- Make sure new, sterile needles are used during all piercings, tattoos and acupuncture sessions.
- Avoid direct contact with blood and bodily fluids.
- Know the HBV status of all your sexual partners.
- Ask your doctor about possible vaccination before you travel to a place where hepatitis B is common.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Hepatitis B is a liver disease that can cause serious damage to your health. One reason that is dangerous is that it can easily go undetected for years while damaging your liver. Talk with your healthcare provider about being tested for hepatitis B if you have any reason to believe that you were not vaccinated or if you have engaged in risky behavior. If you do test positive, follow the directions from your healthcare provider so that you can live a longer, healthier and happier life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/09/2020.
References
Acute Vs Chronic Infection
If you have been diagnosed with hepatitis B, it is important to understand if your infection is acute or chronic.
When a person is first infected with the hepatitis B virus, it is called an acute infection . Many people are able to naturally get rid of an acute infection.
If the infection persists for more than 6 months, it is considered a chronic infection.
Acute infections have few, if any, lasting effects. People with chronic infections are at greater risk for developing serious liver diseases, including cirrhosis and liver cancer, and should take precautions to keep their liver healthy.
Why do some people naturally get rid of the virus while others develop chronic infections? The risk of developing a chronic hepatitis B infection is directly related to the age at which a person is first exposed to the hepatitis B virus. The younger a person is when they are first infected, the greater the risk of developing a chronic hepatitis B infection.
Read Also: Hepatitis C 0.1 Results
Don’t Miss: How Do You Catch Hepatitis B
Treatment Options For Antiviral Resistant Pathogens
If a virus is not fully wiped out during a regimen of antivirals, treatment creates a bottleneck in the viral population that selects for resistance, and there is a chance that a resistant strain may repopulate the host. Viral treatment mechanisms must therefore account for the selection of resistant viruses.
The most commonly used method for treating resistant viruses is combination therapy, which uses multiple antivirals in one treatment regimen. This is thought to decrease the likelihood that one mutation could cause antiviral resistance, as the antivirals in the cocktail target different stages of the viral life cycle. This is frequently used in retroviruses like HIV, but a number of studies have demonstrated its effectiveness against influenza A, as well. Viruses can also be screened for resistance to drugs before treatment is started. This minimizes exposure to unnecessary antivirals and ensures that an effective medication is being used. This may improve patient outcomes and could help detect new resistance mutations during routine scanning for known mutants. However, this has not been consistently implemented in treatment facilities at this time.
Abnormalities In Heme Metabolism And Excretion
One way to understand jaundice pathophysiology is to organize it into disorders that cause increased bilirubin production or decreased bilirubin excretion .
Prehepatic pathophysiology
Prehepatic jaundice results from a pathological increase in bilirubin production: an increased rate of erythrocyte hemolysis causes increased bilirubin production, leading to increased deposition of bilirubin in mucosal tissues and the appearance of a yellow hue.
Hepatic pathophysiology
Hepatic jaundice is due to significant disruption of liver function, leading to hepatic cell death and necrosis and impaired bilirubin transport across . Bilirubin transport across hepatocytes may be impaired at any point between hepatocellular uptake of unconjugated bilirubin and hepatocellular transport of conjugated bilirubin into the gallbladder. In addition, subsequent cellular due to inflammation causes mechanical obstruction of the intrahepatic biliary tract. Most commonly, interferences in all three major steps of bilirubin metabolism â uptake, conjugation, and excretion â usually occur in hepatocellular jaundice. Thus, an abnormal rise in both unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin will be present. Because excretion is usually impaired to the greatest extent, conjugated hyperbilirubinemia predominates.
Posthepatic pathophysiology
| Present | Present |
Laboratory findings depend on the cause of jaundice:
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Hepatitis A From Food
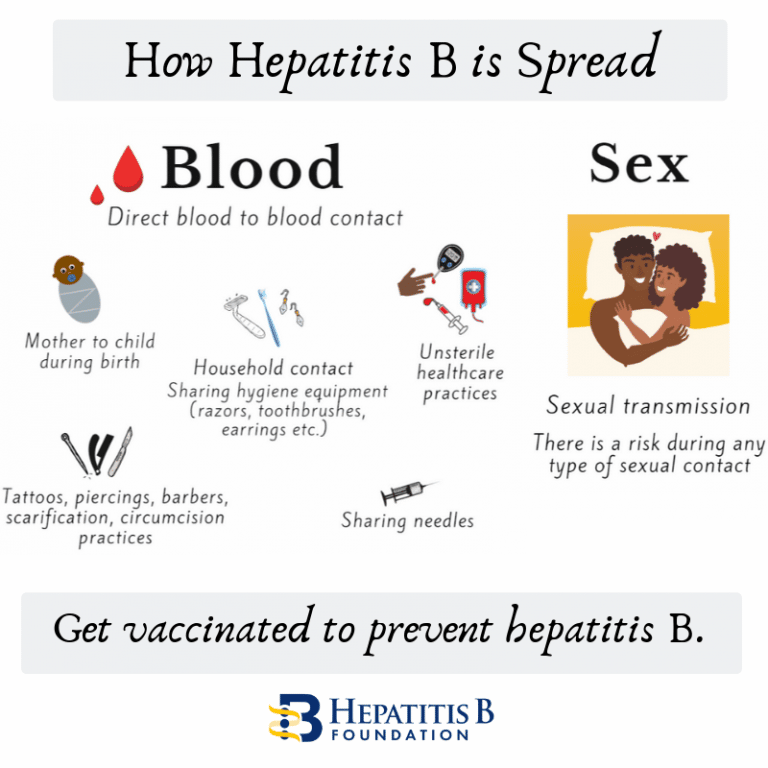
How Is Hepatitis B Spread
- Having unprotected sex.
- Sharing or using dirty needles for drug use, tattoos or piercing.
- Sharing everyday items that may contain body fluids, including razors, toothbrushes, jewelry for piercings and nail clippers.
- Being treated medically by someone who does not use sterile instruments.
- Being bitten by someone with the infection.
- Being born to a pregnant woman with the infection.
Hepatitis B is not spread by:
- Kissing on the cheek or lips.
- Coughing or sneezing.
- Hugging, shaking hands or holding hands.
- Eating food that someone with the infection has prepared.
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. Its transmitted through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not transmitted through sharing utensils or kissing. Its also not transmitted through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure. Symptoms can last for several weeks.
But even without symptoms, you can still transmit the infection to others. The virus can live outside the body and remains infectious for at least
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious condition. Its associated with many serious complications, some of which can be life threatening.
But there are many treatment options available and multiple ways you can prevent infection, including getting vaccinated.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a doctor to prevent infection and determine the best course of treatment for you.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Ab W Reflex Hcv Rna Quant Rt Pcr
You May Like: How Do You Get Hepatitis C From Alcohol