How Many People Have Hepatitis B
In the United States, an estimated 880,000 to 1.89 million people are chronically infected with HBV. New cases of HBV infection in the United States had been decreasing until 2012. Since that time, reported cases of acute hepatitis B have been fluctuating around 3,000 cases per year. In 2020, 2,157 cases of acute hepatitis B were reported however, because of low case detection and reporting, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that there were 14,000 acute hepatitis B infections. The rate of acute cases of HBV decreased by 32% after 2019 which may be related to the disruptions of the COVID-19 pandemic. For the most recent surveillance data visit CDC Viral Hepatitis Surveillance.
Globally, HBV is the most common blood-borne infection with an estimated 296 million people infected according to the World Health Organization .
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B
Prevention is recommended by receiving a vaccine for HBV.
Receiving an injection of the hepatitis B immune globulin within 12 hours of coming in contact with the virus may help prevent the development of the disease.
At present, there is no specific treatment for patients with acute hepatitis B. Acute infection is usually short and will often resolve on its own. Your health care provider may recommend rest, and adequate nutrition and fluids to help your body fight the infection. Hospitalization may be required for patients who suffer from severe vomiting and who are unable to maintain adequate nutritional levels. It may also be required to prevent the development of complications.
While chronic infection cannot be cured, there are two standard treatments in Canada that may control the virus and prevent further damage to the liver.
- Antiviral medications can fight the virus and slow damage to the liver.
- Interferon which may be given for short periods and if effective, results in suppression of the virus.
How Do People Get The Hbv Virus
Hepatitis B virus is found in the blood of people with HBV infection. It enters the body through blood-to-blood contact.
Reliable blood tests for HBV were developed many years ago. Since blood donors and blood products are tested for HBV, this is no longer the typical means of infection.
In many parts of the world, hepatitis B virus infects more than 8% of the population. HBV-infected women pass the infection to their babies during the birth process. People can also get hepatitis B by sharing needles for injection drug use, through sexual contact with an infected person, by an accidental needlestick with a contaminated needle, or from improperly sterilized medical, acupuncture, piercing, or tattooing equipment.
Recommended Reading: Where Does Hepatitis A Come From
Who Is At Risk Of Having Hepatitis B
- Anyone who has come in direct contact with hepatitis B virus-infected bodily fluids is at risk.
- Were born to an hepatitis B virus-infected mother
- Work or live in a place where you can be exposed to infected blood, such as a healthcare institution or correctional facility
- Have ever lived with a person infected with chronic hepatitis B virus
- Have ever had unprotected sex with an infected person
- Have ever had multiple sexual partners
- Have ever had a sexually transmitted disease
- Are a man who has sex with men
- Have your blood filtered by a machine because your kidneys arent working
- Have ever traveled to or are born in countries where hepatitis B virus is common, including places in Africa, Central and Southeast Asia, and Eastern Europe
Treatment For Acute Hepatitis B
If youre diagnosed with hepatitis B, your GP will usually refer you to a specialist, such as a hepatologist .
Many people dont have any troublesome symptoms, but if you do feel unwell, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter painkillers, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen, for abdominal pain
- maintain a cool, well-ventilated environment, wear loose clothing, and avoid hot baths or showers if itching is a problem
- take medication such as metoclopramide to stop you feeling sick and chlorphenamine to reduce itching your doctor can give you a prescription for these if necessary
Most people recover completely in a couple of months, but youll be advised to have regular blood tests to check that youre free of the virus and havent developed chronic hepatitis B.
Donât Miss: Hepatitis B What Causes It
Also Check: What Causes Hepatitis B And C
What Are Clinical Trials For Hepatitis B
Clinical trialsand other types of clinical studiesare part of medical research and involve people like you. When you volunteer to take part in a clinical study, you help doctors and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future.
Researchers are studying many aspects of hepatitis B, such as
- progression of hepatitis B and long-term outcomes
- new treatments for hepatitis B
- prevention of reactivated or worsening hepatitis B in people receiving cancer treatment
Causes Of Liver Cancer
“Primary liver cancer is most prevalent in a background of chronic liver disease or cirrhosis of liver. Chronic liver disease secondary to chronic hepatitis due to hepatitis B and hepatitis C virus infection are the most common cause. Other causes like alcoholic liver disease secondary to chronic alcohol abuse also very prevalent nowadays,” says Dr Dipankar Sankar Mitra, Associate Director Minimal Access Gastrointestinal and Bariatric Surgery, Marengo QRG Hospital, Faridabad.
Dr Mitra also reveals other causes of liver cancer.
Read Also: Hepatitis B And C Treatment Guidelines
Prevention And Control Of Hepatitis B
- The hepatitis B vaccine is the mainstay of hepatitis B prevention.
- WHO recommends that all infants receive the hepatitis B vaccine as soon as possible after birth, preferably within 24 hours.
- Simple environmental procedures can limit the risk of infection to health care workers, laboratory personnel, and others. Examples of specific precautions include the following:
- Gloves should be used when handling all potentially infectious materials
- protective garments should be worn and removed before leaving the work area
- masks and eye protection should be worn whenever splashes or droplets from infectious material pose a risk
- only disposable needles should be used
- needles should be discarded directly into special containers without re-sheathing
- work surfaces should be decontaminated using a bleach solution and laboratory personnel should refrain from mouth pipetting, eating, drinking, and smoking in the work area.
- Metal objects and instruments can be disinfected by autoclaving or by exposure to ethylene oxide gas.
You May Like: Whatâs The Signs Of Hepatitis C
What Problems Can Hepatitis B Cause
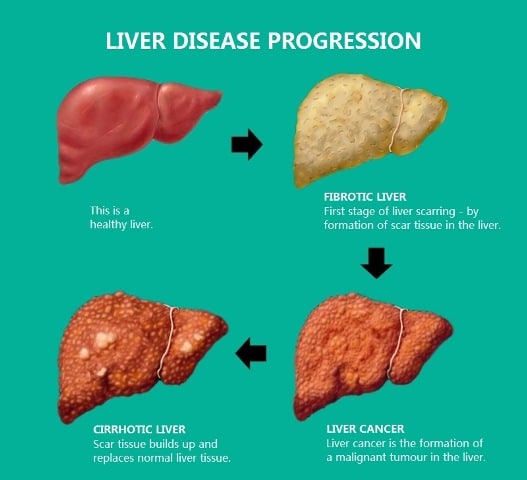
Hepatitis B is a serious infection. It can lead to cirrhosis of the liver, liver failure, or liver cancer, which can cause severe illness and even death.
If a pregnant woman has the hepatitis B virus, her baby has a very high chance of having it unless the baby gets a special immune injection and the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine at birth.
Sometimes, HBV doesn’t cause symptoms until a person has had the infection for a while. At that stage, the person already might have more serious problems, such as liver damage.
Read Also: How Would I Know If I Have Hepatitis C
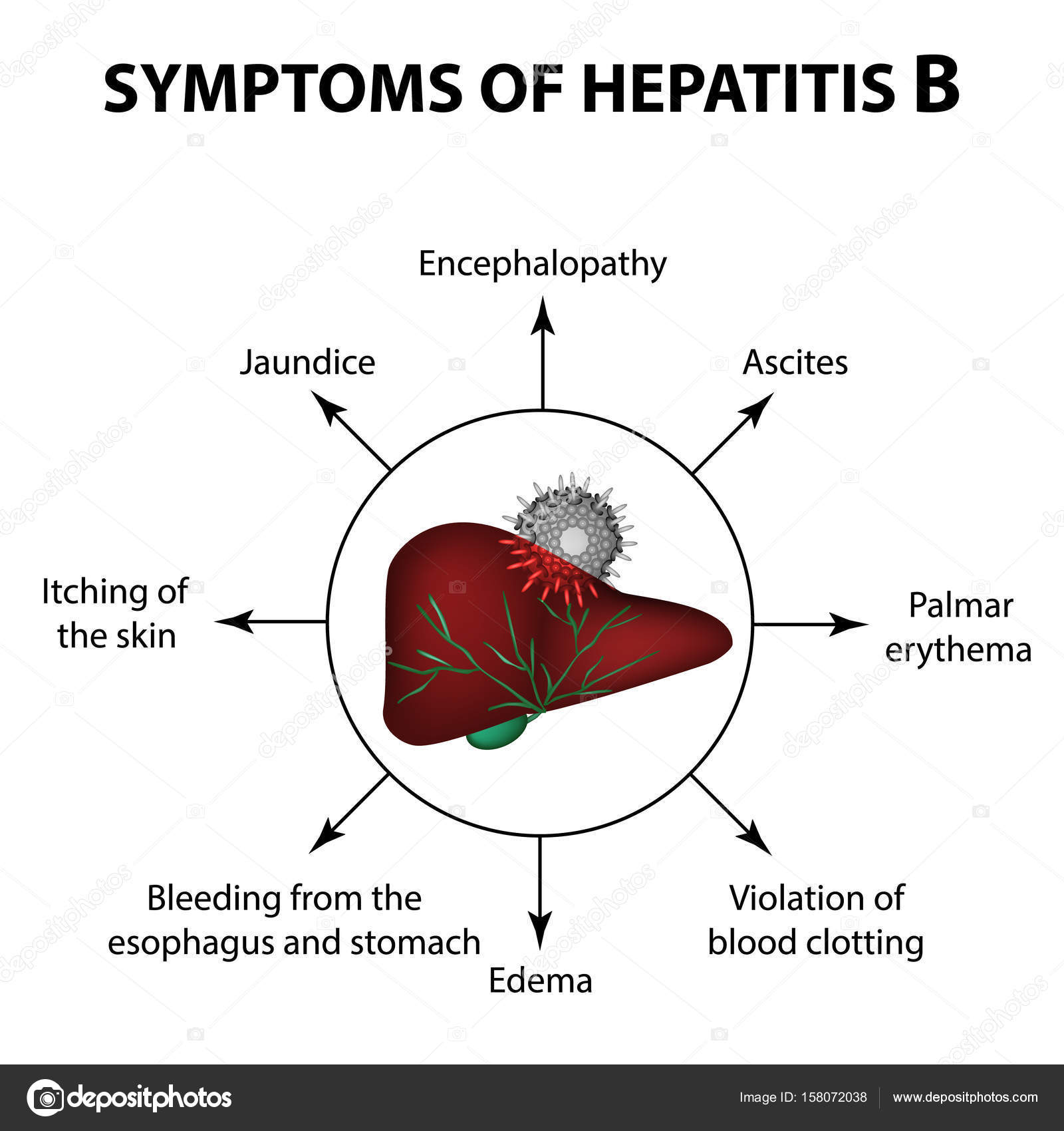
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Some people who are infected with the hepatitis B virus have mild, flu-like symptoms and some do not become sick at all. Children who are infected are less likely to have an illness or get sick after getting hepatitis B than adults.
In more severe cases, hepatitis B can cause:
- Loss of appetite.
- Pain in the joints.
Normally, these health problems disappear in a few weeks, but even when the person feels much better, they may still be infectious.
Most adults who become infected with the hepatitis B virus recover completely and do not become infected again. A few people become very ill in the time just after infection and need to go to hospital some may even die.
Hepatitis B Causes And Risk Factors
Itâs caused by the hepatitis B virus, and it can spread from person to person in certain ways. You can spread the hepatitis B virus even if you donât feel sick.
The most common ways to get hepatitis B include:
- Sex. You can get it if you have unprotected sex with someone who has it and your partnerâs blood, saliva, , or vaginal secretions enter your body.
- Sharing needles. The virus spreads easily via needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood.
- Accidental needle sticks.Health care workers and anyone else who comes in contact with human blood can get it this way.
- Mother to child.Pregnant women with hepatitis B can pass it to their babies during childbirth. But thereâs a vaccine to prevent newborns from becoming infected.
Hepatitis B doesnât spread through kissing, food or water, shared utensils, coughing or sneezing, or through touch.
Recommended Reading: Over The Counter Hepatitis Test
About The Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus is a small DNA virus that belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family. Related viruses in this family are also found in woodchucks, ground squirrels, tree squirrels, Peking ducks, and herons.
Structure of the Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus contains an outer envelope and an inner core.
- The outer envelope of the virus is composed of a surface protein called the hepatitis B surface antigen or “HBsAg”. The HBsAg can be detected by a simple blood test and a positive test result indicates a person is infected with the hepatitis B virus.
- The inner core of the virus is a protein shell referred to as the hepatitis B core antigen or “HBcAg,” which contains the hepatitis B virus DNA and enzymes used in viral replication.
Life Cycle of the Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus has a complex life cycle. The virus enters the host liver cell and is transported into the nucleus of the liver cell. Once inside the nucleus, the viral DNA is transformed into a covalently closed circular DNA , which serves as a template for viral replication . New HBV virus is packaged and leaves the liver cell, with the stable viral cccDNA remaining in the nucleus where it can integrate into the DNA of the host liver cell, as well as continue to create new hepatitis B virus. Although the life cycle is not completely understood, parts of this replicative process are error prone, which accounts for different genotypes or genetic codes of the hepatitis B virus.
How Common Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is fairly common in Africa and the western Pacific region. Throughout the world, there are about 292 million people who are infected with chronic hepatitis B. In the U.S., the figure exceeds 2 million people.
The number of infections had been falling in the U.S., but fewer vaccinations among adults combined with the onset of the opioid crisis and injected drug usage has resulted in the numbers rising again. Infected women can pass the infection on to their babies. Children who are infected before age 5 are more likely to have chronic infection than those infected later in life.
Also Check: How Often Should You Be Tested For Hepatitis C
What Are The Symptoms Of Hbv
Hepatitis B virus can cause an acute illness with symptoms that last several weeks, including yellowing of the skin and eyes , dark urine, extreme fatigue, nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain. Most of the time HBV infection is ASYMPTOMATIC.
Joint pains, muscle aches, rash, and jaundice may occur in some people. People can take several months to a year to recover from the symptoms. These people may not know that they are infected, and may therefore not go and see a doctor. People with chronic hepatitis B infection may later develop serious problems like liver cancer and liver failure. These people may not know that they are infected, and may therefore not go and see a doctor. People with chronic hepatitis B infection may later develop serious problems like liver cancer and liver failure.
Eating Diet And Nutrition For Hepatitis B
If you have hepatitis B, you should eat a balanced, healthy diet. Obesity can increase the chance of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease , and NAFLD can increase liver damage in people who have hepatitis B. Talk with your doctor about healthy eating and maintaining a healthy weight.
You should also avoid alcohol because it can cause more liver damage.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine For Newborns Pros And Cons
What Treatments Are Available For Chronic Hepatitis B If Medications Dont Work
If you have advanced hepatitis B, you might also become a candidate for a liver transplant. This path does not always result in a cure because the virus continues in your bloodstream after a transplant. To prevent being infected again after your transplant, you may be prescribed hepatitis B immunoglobulin with an antiviral agent.
How Is Hepatitis B Spread
- Having unprotected sex.
- Sharing or using dirty needles for drug use, tattoos or piercing.
- Sharing everyday items that may contain body fluids, including razors, toothbrushes, jewelry for piercings and nail clippers.
- Being treated medically by someone who does not use sterile instruments.
- Being bitten by someone with the infection.
- Being born to a pregnant woman with the infection.
Hepatitis B is not spread by:
- Kissing on the cheek or lips.
- Coughing or sneezing.
- Hugging, shaking hands or holding hands.
- Eating food that someone with the infection has prepared.
Read Also: Best Treatment For Hepatitis C
What Is Delta Hepatitis
Delta hepatitis is caused by a virus that only infects people who already have hepatitis B. The delta hepatitis virus is an RNA virus, meaning that its genetic material is made up of ribonucleic acid. It is spread through exposure to contaminated blood, especially with illicit, intravenous drug use, and by sexual contact. Delta hepatitis can be acquired at the same time as acute hepatitis B. When this happens, infected people are quite sick but most are eventually able to eliminate the viruses from their bodies. People who already have chronic hepatitis B can acquire delta hepatitis as well. This often causes severe inflammation of the liver, and the viruses are less likely to be cleared.
Delta hepatitis makes chronic hepatitis B much worse. It increases the risk of complications, especially cirrhosis, which occurs in up to two-thirds of patients.
There is no vaccine against delta hepatitis. Interferon treatment may cause improvement in the hepatitis, but relapse is common after therapy is stopped. Prevention includes avoiding contaminated needles and practicing safer sex . Universal vaccination of newborns with hepatitis B vaccine effectively prevents delta hepatitis because the delta hepatitis virus only causes disease in the presence of hepatitis B virus.
Abnormalities In Heme Metabolism And Excretion
One way to understand jaundice pathophysiology is to organize it into disorders that cause increased bilirubin production or decreased bilirubin excretion .
Prehepatic pathophysiology
Prehepatic jaundice results from a pathological increase in bilirubin production: an increased rate of erythrocyte hemolysis causes increased bilirubin production, leading to increased deposition of bilirubin in mucosal tissues and the appearance of a yellow hue.
Hepatic pathophysiology
Hepatic jaundice is due to significant disruption of liver function, leading to hepatic cell death and necrosis and impaired bilirubin transport across . Bilirubin transport across hepatocytes may be impaired at any point between hepatocellular uptake of unconjugated bilirubin and hepatocellular transport of conjugated bilirubin into the gallbladder. In addition, subsequent cellular due to inflammation causes mechanical obstruction of the intrahepatic biliary tract. Most commonly, interferences in all three major steps of bilirubin metabolism â uptake, conjugation, and excretion â usually occur in hepatocellular jaundice. Thus, an abnormal rise in both unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin will be present. Because excretion is usually impaired to the greatest extent, conjugated hyperbilirubinemia predominates.
Posthepatic pathophysiology
| Present | Present |
Laboratory findings depend on the cause of jaundice:
Don’t Miss: What Is The Most Common Genotype Of Hepatitis C
What Other Problems Can Hepatitis B Cause
In rare cases, acute hepatitis B can cause liver failure.
Chronic hepatitis B can develop into a serious disease that causes long-term health problems such as cirrhosis , liver cancer, and liver failure.
If you have ever had hepatitis B, the virus may become active again, or reactivated, later in life. This could start to damage the liver and cause symptoms.
Hepatitis B Vs Hepatitis C
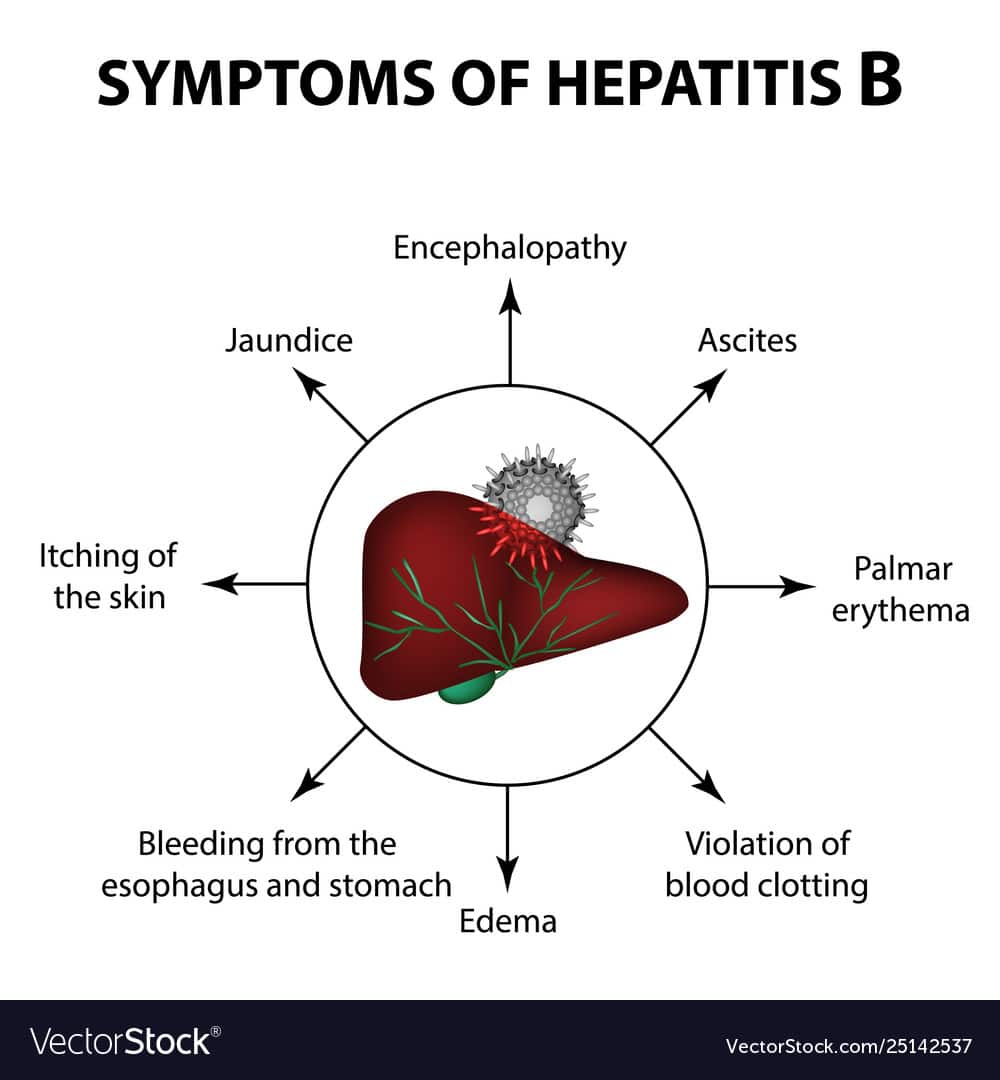
Hepatitis has many different types. HBV and the hepatitis C virus have both acute and chronic forms.
The main difference between HBV and HCV is how they spread from person to person. Although HCV is transmissible via sexual activity, this is rare. HCV usually spreads when blood that carries the virus comes into contact with blood that does not.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Immunity
What Causes Hepatitis B
- being born to a mother with hepatitis B
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools that were used on an infected person and werent properly sterilized, or cleaned in a way that destroys all viruses and other microbes
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
You cant get hepatitis B from
- being coughed on or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking unclean water or untreated water that has not been boiled
- eating food that is unclean or has not been properly cooked
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
Mothers who have hepatitis B can safely breastfeed their babies. If a baby receives hepatitis B immune globulin and starts receiving the hepatitis B vaccine to prevent hepatitis B infection shortly after birth, hepatitis B is unlikely to spread from mother to child through breastfeeding.15