Treatment Options For Antiviral Resistant Pathogens
If a virus is not fully wiped out during a regimen of antivirals, treatment creates a bottleneck in the viral population that selects for resistance, and there is a chance that a resistant strain may repopulate the host. Viral treatment mechanisms must therefore account for the selection of resistant viruses.
The most commonly used method for treating resistant viruses is combination therapy, which uses multiple antivirals in one treatment regimen. This is thought to decrease the likelihood that one mutation could cause antiviral resistance, as the antivirals in the cocktail target different stages of the viral life cycle. This is frequently used in retroviruses like HIV, but a number of studies have demonstrated its effectiveness against influenza A, as well. Viruses can also be screened for resistance to drugs before treatment is started. This minimizes exposure to unnecessary antivirals and ensures that an effective medication is being used. This may improve patient outcomes and could help detect new resistance mutations during routine scanning for known mutants. However, this has not been consistently implemented in treatment facilities at this time.
Also Check: Whatâs The Signs Of Hepatitis C
Treatment For Chronic Hbv
In the majority of adults HBV infection is self-limiting and does not require any treatment similar to many other viral infections. In chronic HBV infection the virus persistently replicates in hepatocytes leading to immune mediated hepatocyte damage. Therapies have been instituted to inhibit viral replication to prevent or at least to delay the progression of hepatitis to cirrhosis and HCC. A number of prophylactic and treatment measures using HBV vaccines, immunomodulators such as interferon alpha and pegylated IFN- and antiviral agents called nucleotide/nucleoside analogues have been developed for the treatment of chronic HBV infection .
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
There are three main ways to diagnose HBV infection. They include:
- Blood tests: Tests of the blood serum shows how your bodys immune system is responding to the virus. A blood test can also tell you if you are immune to HBV.
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to show the size and shape of your liver and how well the blood flows through it.
- Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis.
The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit. Often, people whove become infected first learn they have hepatitis B when they go to donate blood. Blood donations are routinely scanned for the infection.
The virus can be detected within 30 to 60 days of infection. About 70% of adults with hepatitis B develop symptoms, which tend to appear an average of 90 days after initial exposure to the virus.
Also Check: 2nd Dose Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
How Serious Is It
- People can be sick for a few weeks to a few months
- Most recover with no lasting liver damage
- Although very rare, death can occur
- 15%25% of chronically infected people develop chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer
- More than 50% of people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop a chronic infection
- 5%-25% of people with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis over 1020 years
What Laboratory Tests Are Available For Hepatitis B
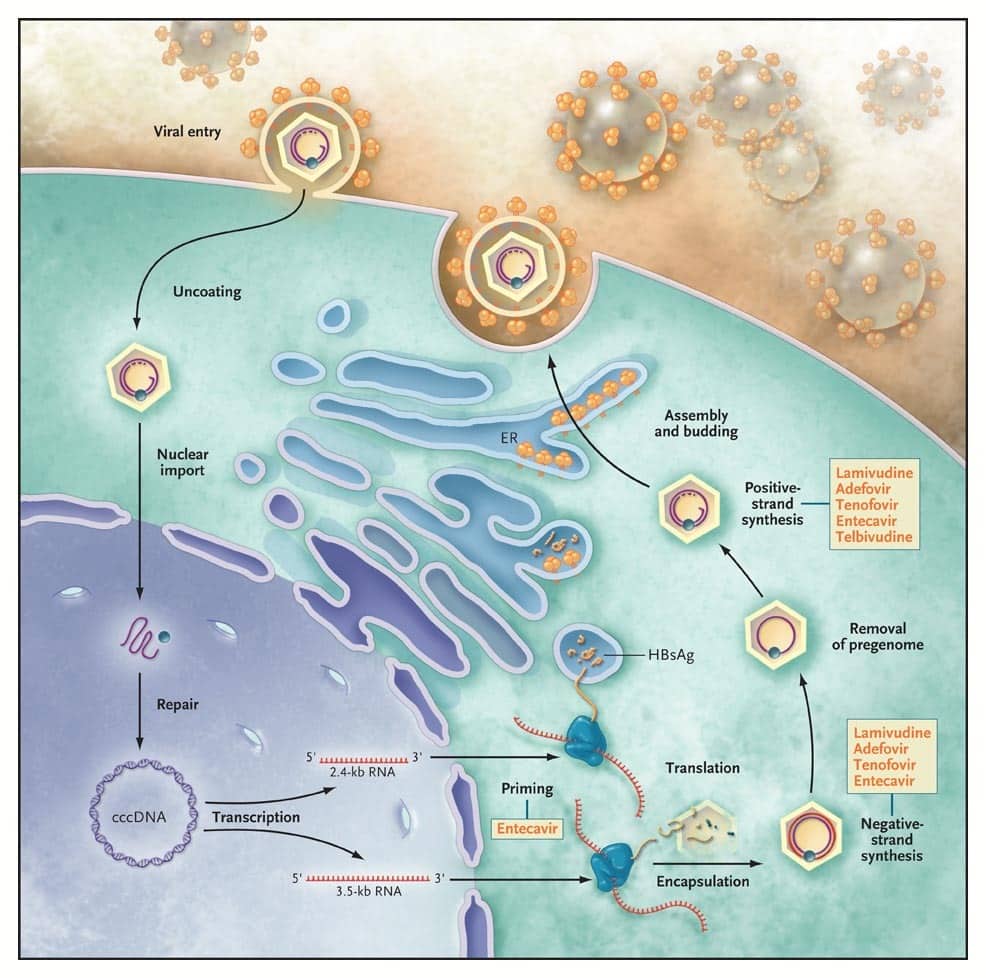
Tests are available to detect the types of antigens used to identify the hepatitis B virus. The tests determine if the virus is present in the body tissue or blood. The amount of each type of antigen present indicates how advanced the disease is and how infective the individual has become.
Other tests are available to detect the body’s reaction to the viral infection or the body’s reaction to vaccination against the virus. These tests work by measuring the number of antibodies present in the blood.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Antibody Test Non Reactive
Detection Of Antiviral Resistance
National and international surveillance is performed by the CDC to determine effectiveness of the current FDA-approved antiviral flu drugs. Public health officials use this information to make current recommendations about the use of flu antiviral medications. further recommends in-depth epidemiological investigations to control potential transmission of the resistant virus and prevent future progression. As novel treatments and detection techniques to antiviral resistance are enhanced so can the establishment of strategies to combat the inevitable emergence of antiviral resistance.
Vi Management Of Household And Sexual Contacts
A. Household and Sexual Contacts that Have a History of Three Doses of Vaccine and Immune to HBV, or Who Have Been found Previously to be Hepatitis B Positive, Need Not be Screened or Vaccinated
B. Serologic Testing Should be Done on All Household and Sexual Contacts that Have No History of Disease or Vaccination
C. Susceptible Household and Sexual Contacts Should be Immunized
D. Sexual Contacts Should Have Post-Vaccination Serology Done 1-2 Months after the Administration of the Last Dose of Vaccine
You May Like: What Is Chronic Hepatitis C
What Makes Hepatitis B A Serious Illness
Many people with hepatitis B do not know they are infected since they do not look or feel sick, yet they can still spread the virus to others. Acute infection can lead to chronic infection, which can cause cirrhosis , liver cancer, liver failure, and death. During childbirth, a mother may pass hepatitis B to her baby. Newborns infected with hepatitis B have a 90 percent chance of developing chronic hepatitis B. Between 4,000 and 5,000 people die each year in the U.S. from liver disease caused by hepatitis B.
Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis B
Currently, there is no complete cure for hepatitis B. But when managed properly, those living with the virus can expect to live a normal life. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding beverages that contain alochol and tobacco products are crucial components in managing the disease.
You should also visit a doctor familiar with hepatitis B at least annually though twice a year might be best to monitor your liver through blood tests and medical imaging. As with most diseases, detecting it early leads to a better outcome. If youre exposed to the virus, you should get an antibody injection within 12 hours of exposure.
Don’t Miss: 3rd Dose Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Complications Of Hepatitis B
Most people do not have any lasting problems after having a hepatitis B infection.
If left untreated, chronic hepatitis B can cause liver damage and increase your risk of getting liver cancer.
It is important to take any medicine you have been prescribed and go for regular check-ups to make sure your liver is working properly.
Page last reviewed: 01 July 2022 Next review due: 01 July 2025
What If I Am Pregnant
It’s recommended that all pregnant women have a blood test for hepatitis B in early pregnancy.
If you have hepatitis B and are pregnant, treatments can reduce the risk of transmission of hepatitis B to the baby.
If you have hepatitis B, it is important to protect others from infection.
Important ways to prevent the spread of hepatitis B include:
- vaccination of all your close contacts
- practise safe sex until your sexual contacts are fully vaccinated and immune
- do not donate blood, organs or body tissue
- do not allow your blood to contact another person
- inform healthcare workers
- if your work involves potential for your blood or other body fluid to spread to other people, discuss your situation with your doctor
The hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective in protecting against hepatitis B infection, providing protection in 95 in 100 vaccinated people.
In Australia, hepatitis B vaccination is part of the standard immunisation schedule for all newborn babies and infants. It’s also recommended for adults who are at high risk of exposure, people who are immunosuppressed or have other liver disease. People in these risk groups should be vaccinated against hepatitis B. Talk to your doctor about your level of risk and whether hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for you.
If you werent vaccinated against hepatitis B as a child, or if youre not sure whether you are vaccinated, talk to your doctor about whether you need a catch-up vaccine.
You May Like: When To Treat Hepatitis B
Who Should Be Vaccinated
Children
- All children aged 1223 months
- All children and adolescents 218 years of age who have not previously received hepatitis A vaccine
People at increased risk for hepatitis A
- International travelers
- Men who have sex with men
- People who use or inject drugs
- People with occupational risk for exposure
- People who anticipate close personal contact with an international adoptee
- People experiencing homelessness
People at increased risk for severe disease from hepatitis A infection
- People with chronic liver disease, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C
- People with HIV
Other people recommended for vaccination
- Pregnant women at risk for hepatitis A or risk for severe outcome from hepatitis A infection
Any person who requests vaccination
There is no vaccine available for hepatitis C.
An Ounce Of Prevention

As a liver transplant specialist, Dr. Choi notes that the most common reasons for a liver transplant in the U.S. are alcohol-related liver disease and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease also known as fatty liver.
Alcohol use and metabolic syndromeobesity plus diabetes, high cholesterol and high blood pressurehave been on the rise in our country, and we are seeing their impact in the liver world, he says, concluding that adopting a healthier lifestyle can prevent both diseases.
As well, the HBV vaccine should be offered to all infants and children, and to adults who are not immune to the virus.
Dr. Choi also points to several diseases that are not always preventable, such as autoimmune liver disease. Fortunately, he says, most of these diseases can be treated or controlled so that you wont develop cirrhosis or liver cancer. Thats why screening to diagnose liver disease early is so crucial.
While a liver transplant can save your life, not needing one in the first place is the best outcome, he adds.
Also Check: How I Cured Myself Of Hepatitis B
Also Check: Hepatitis B Treatment Antiviral Drugs
What Are The Complications Of Hepatitis B
The course of hepatitis B infection depends mostly on the age at which a person is infected.
People infected as infants are likely to develop long term infection and can get complications such as scarring of the liver or liver cancer. Infants have a 9 in 10 chance and children have a 3 in 10 chance of developing a chronic, lifelong infection.
People infected as teenagers or adults are likely to become unwell with symptoms , but have a smaller chance of developing a chronic infection. Others develop a silent infection, without any symptoms.
Most people infected as adults clear the virus from the body within 6 months. They develop immunity to future hepatitis B infections and do not develop long-term liver damage.
However, approximately 1 in 20 adults cannot clear the virus and develop chronic hepatitis B. They are at risk of developing complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer in the longer term.
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis B
People are more likely to get hepatitis B if they are born to a mother who has hepatitis B. The virus can spread from mother to child during birth. For this reason, people are more likely to have hepatitis B if they
- were born in a part of the world where 2 percent or more of the population has hepatitis B infection
- were born in the United States, didnt receive the hepatitis B vaccine as an infant, and have parents who were born in an area where 8 percent or more of the population had hepatitis B infection
People are also more likely to have hepatitis B if they
- are infected with HIV, because hepatitis B and HIV spread in similar ways
- have lived with or had sex with someone who has hepatitis B
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have sex with men
- are injection drug users
- work in a profession, such as health care, in which they have contact with blood, needles, or body fluids at work
- live or work in a care facility for people with developmental disabilities
- have been on kidney dialysis
- live or work in a prison
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before the mid-1980s
In the United States, hepatitis B spreads among adults mainly through contact with infected blood through the skin, such as during injection drug use, and through sexual contact.12
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Antibody
Who Should Be Tested
Testing for hepatitis A is not routinely recommended.
CDC recommends hepatitis B testing for:
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household and sexual contacts of people with hepatitis B
- People requiring immunosuppressive therapy
- People with end-stage renal disease
- People with hepatitis C
- People with elevated ALT levels
- Infants born to HBV-infected mothers
CDC recommends hepatitis C testing for:
- All adults aged 18 years and older
- All pregnant women during each pregnancy
- About 24,900 new infections each year
- About 22,600 new infections in 2018
- Estimated 862,000 people living with hepatitis B
- About 50,300 new infections in 2018
- Estimated 2.4 million people living with hepatitis C
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
Hepatitis B can be transmitted from a birthing parent to a newborn infant. This is because the newborn is exposed to blood and bodily fluids during delivery.
In fact, 90% of mothers with an acute hepatitis B infection and 10% to 20% of mothers with chronic hepatitis B will transmit the virus to their newborn, estimates the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
For this reason, birthing parents are routinely screened for hepatitis B during each pregnancy.
Additionally, the hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin are both administered to infants with an HBV-positive birthing parent within of birth to prevent infection.
According to the
- people with hepatitis C infection
- men who have sex with men
- people with multiple sexual partners
- people who are seeking treatment for a sexually transmitted infections
- people with current or recent injection drug use
- family members or sexual partners of those with hepatitis B
- people with chronic liver disease
- people traveling to areas with high rates of hepatitis B
- people on maintenance dialysis
- people who are incarcerated
The hepatitis B vaccine is usually administered in three shots, given 1 month and 6 months after the first dose. Another recently approved vaccine is completed in two doses spaced 1 month apart.
You May Like: Facts About Hepatitis B Vaccine
What Are The Risk Factors
Some people are at an increased risk for contracting HAV, including:
- people traveling to areas of the world where hepatitis A is common
- men who have sex with men
- people who use injectable or noninjectable drugs
- caregivers for those who have hepatitis A
- people who are experiencing homelessness
- people living with a child whos been adopted from an area where hepatitis A is common
Hepatitis B Causes And Risk Factors
Itâs caused by the hepatitis B virus, and it can spread from person to person in certain ways. You can spread the hepatitis B virus even if you donât feel sick.
The most common ways to get hepatitis B include:
- Sex. You can get it if you have unprotected sex with someone who has it and your partnerâs blood, saliva, , or vaginal secretions enter your body.
- Sharing needles. The virus spreads easily via needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood.
- Accidental needle sticks.Health care workers and anyone else who comes in contact with human blood can get it this way.
- Mother to child.Pregnant women with hepatitis B can pass it to their babies during childbirth. But thereâs a vaccine to prevent newborns from becoming infected.
Hepatitis B doesnât spread through kissing, food or water, shared utensils, coughing or sneezing, or through touch.
Also Check: Labcorp Hepatitis C Viral Load
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
As hepatitis B infection is highly transmissible via accidental needlesticks, healthcare providers involved in taking care of a patient with HBV should exercise caution and practice proper preventative measures such as vaccination. Patient education should also include counseling about HBV transmission. The interprofessional team’s role is crucial in ensuring the best patient outcomes.
The vaccination rate is low in many developing countries, and the majority of patients are undiagnosed. Educational programs and improved awareness among the general public and healthcare providers are necessary to improve the identification of the patients, reduce transmission of the disease, and reduce the complications of hepatitis B infection.
What Is Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the blood, and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis. However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
Read Also: Booster Dose Of Hepatitis B Vaccine