Specimen Collection And Processing
Ten milliliters of venous blood were taken from each study participant at each site and was dispensed into an ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid tube and transported on dry ice to Armauer Hansen research institute , where the plasma was separated via centrifugation at 3500 rpm/ 5min, transferred into cryotubes, and stored at – 20 °C until used for HIV, HBV, and HCV serology.
Hiv/aids And Skin Conditions
Skin conditions are common in people with HIV/AIDS. Many, including Kaposi sarcoma, thrush, and herpes, are caused by germs that take advantage of a weakened immune system. Thats why they are called opportunistic infections. Others, like photodermatitis, may be linked to inflammation caused by an overactive immune system as it revives during antiretroviral drug therapy or due to the drugs themselves.
Here are some of the more common skin conditions related to HIV/AIDS.
What Is The Connection Between Hiv And Hcv
Because both HIV and HCV can spread in blood, a major risk factor for both HIV and HCV infection is injection drug use. Sharing needles or other drug injection equipment increases the risk of contact with HIV- or HCV-infected blood.
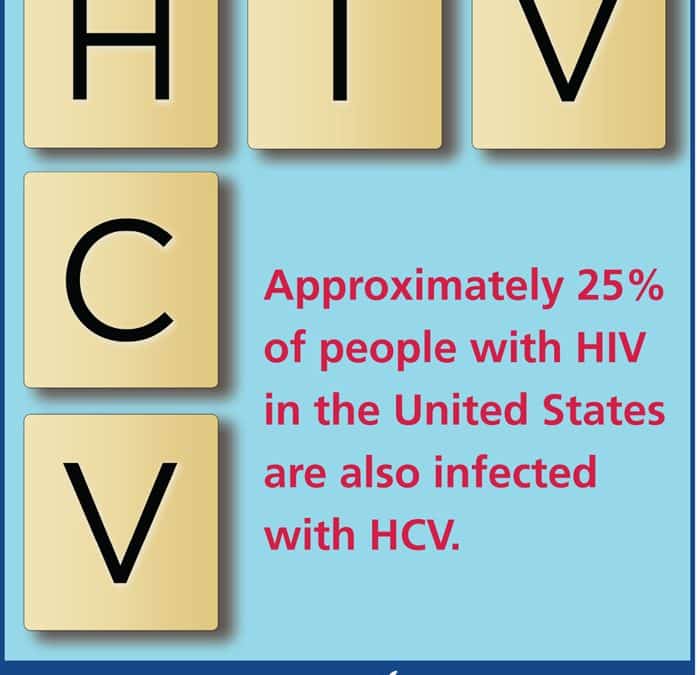
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , approximately 21% of people with HIV in the United States also have HCV. Infection with both HIV and HCV is called HIV/HCV coinfection.
In people with HIV/HCV coinfection, HIV may cause chronic HCV to advance faster. Whether HCV causes HIV to advance faster is unclear.
You May Like: What Hepatitis Is Caused By Alcohol
Special Considerations For Antiretroviral Therapy In Patients With Hepatitis C Virus/hiv Coinfection
Special considerations for ART in patients coinfected with hepatitis C virus and HIV include the following:
Patients receiving or considering therapy with ribavirin should avoid didanosine, stavudine, and zidovudine.
Use caution with antiretroviral agents with the greatest risk of DILI .
Assess cirrhotic patients for signs of liver decompensation according to the Child-Turcotte-Pugh classification system hepatically metabolized antiretroviral drugs may require dose modification or avoidance in patients with Child-Pugh class B and C disease.
Treatment of both HCV and HIV can be complicated by drug interactions, drug toxicities, and pill burden. Many of the newer directly acting anti-HCV drugs have significant interactions with antiretroviral agents however, ledipasvir with sofosbuvir and daclatasvir plus sofosbuvir have been demonstrated as efficacious.
Regimen selection for HCV infection can vary based on genotype, history of prior HCV treatment, stage of underlying liver fibrosis, and, in rare cases, the presence of baseline NS5A inhibitor resistanceâassociated substitutions.
Diagnosing Hepatitis C In People Living With Hiv
Everyone with HIV should be tested to see if they also have hepatitis C. A blood test for antibodies to hepatitis C is used to see whether you have been exposed to the virus. You might be given a PCR test to confirm infection.
In people living with HIV, the diagnosis of hepatitis C can be more difficult, as the infection may not show up on their antibody tests.
If you think you may be at risk of hepatitis C infection, you should have regular tests to see if you have been infected with the virus.
Also Check: What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B Virus
You May Like: Hepatic Artery Infusion Liver Cancer
Is Hepatitis Testing Recommended For People With Hiv
Yes. Everyone with HIV should be tested for HBV and HCV when they are first diagnosed with HIV and begin treatment. People with HIV who have ongoing risk factors for getting hepatitis B or hepatitis C should be tested annually.
In addition, HCV screening recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention call for:
- One-time screening for all adults 18 years and older
- Screening of all pregnant women during every pregnancy
- Testing for all persons with risk factors, with testing continued periodic testing those with ongoing risk.
How Is The Health Of Your Liver Monitored
Everyone living with HIV should have regular tests to monitor the health of their liver as part of the routine check-ups carried out by their HIV clinic. These tests are especially important if you have hepatitis C.
These include liver function tests that monitor levels of liver enzymes. Ultrasounds and scans are also important monitoring tools which may be used if more information is needed.
Sometimes its necessary to have a liver biopsy. This involves the removal of a small amount of the liver, under a local anaesthetic, for further tests on the health of your liver.
Also Check: First Line Treatment For Hepatitis C
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B
Acute hepatitis B does not typically require treatment
Acute infection typically resolves on its own within six months. If symptoms are severe, a healthcare provider can consider treatment to relieve the symptoms or interrupt viral replication, but there is no specific treatment for acute hepatitis B infection.
Treatment for chronic hepatitis B
Not everyone with chronic hepatitis B needs treatment. Treatment is required when the immune system is unable to control the virus or there is ongoing liver damage. The goal of current hepatitis B therapies is to control the replication of the virus to prevent and even reverse liver injury. These treatments do not offer a complete cure or completely eliminate the risk of liver cancer.
In a very small number of people, treatment can result in clearing the hepatitis B virus , which is considered a functional cure for hepatitis B.
Currently, two types of hepatitis B treatments are available: interferon-based treatments that are taken weekly by injection, and antiviral pills ide analogues) that are taken daily. A healthcare provider will recommend the treatment that is best for a person on the basis of several factors such as their medical history, clinical evaluations and access to medications.
Detection Of Hbsag And Hbcab
Different 3rd generation enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits from Bio-Rad Company were used to screen plasma samples for evidence of HBV infection: HBsAg and Anti-HBc .23 Patients with positive HBsAg and HBcAb tests were considered for HBV co-infection. All the assays were performed as per the manufacturers instruction.
Also Check: What Are The Signs Of Hepatitis B
More About Hepatitis And Hiv Infections
HEPATITIS
- Symptoms of hepatitis B and hepatitis C may be mild, and not start until 2 weeks to 6 months after contact with the virus. Sometimes, there are no symptoms.
- Hepatitis B often gets better on its own and sometimes does not need to be treated. Some people develop a long-term infection that leads to liver damage.
- Most people who become infected with hepatitis C develop a long-term infection. After many years, they often have liver damage.
After someone is infected with HIV, the virus stays in the body. It slowly harms or destroys the immune system. Your bodys immune system fights disease and helps you heal. When it is weakened by HIV, you are more likely to get sick from other infections, including ones that would not normally make you sick.
Treatment can help people with all of these infections.
Hepatitis B can be prevented by a vaccine. There is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C or HIV.
You May Like: How Does Hiv Become Aids
Children Under 18 Months Of Age
For children under 18 months of age, standard adult blood tests for HIV antibodies or antigens are not helpful, because the blood of an infant born to an HIV-infected mother almost always contains HIV antibodies passed through the placenta even if the infant is not infected. So, to definitively diagnose HIV infection in children under 18 months of age, special blood tests called nucleic acid amplification tests are done. These tests detect genetic material using polymerase chain reaction Polymerase chain reaction Genetic diagnostic technologies are scientific methods that are used to understand and evaluate an organisms genes. Genes are segments of deoxyribonucleic read more tests. The diagnosis of HIV infection is confirmed if the NATs detect genetic material from HIV in the childs blood.
Testing using NATs should be done at frequent intervals, typically in the first 2 weeks of life, at about 1 month of age, and between 4 months and 6 months of age. Such frequent testing identifies most HIV-infected infants by 6 months of age. Some infants who have a very high risk of developing HIV may be tested more frequently.
All infants should be tested if they are born to mothers who
-
Have HIV infection
Recommended Reading: Is Bactrim Good For Tooth Infection
You May Like: Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Hiv Treatment And Prevention
Simple, effective treatments for HIV are widely available in Australia. In addition to protecting the health and wellbeing of people living with HIV, these treatments significantly reduce the risk of HIV transmission. Almost all people on HIV treatments have very low levels of virus in their body. This is called having an undetectable viral load. There is no risk of HIV transmission from a person with an undetectable viral load. This is sometimes referred to as undetectable equals untransmissible, or U=U.
For people who do not have HIV, but may be at higher risk of it, affordable medication is available that is more than 99 per cent effective at preventing HIV. Known as PrEP , this medication is available through the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme from your regular GP.
Treating Hepatitis C Together With Hiv

If youre HIV positive and have hepatitis C infection, then you must receive care from a doctor skilled in the treatment of both HIV and hepatitis.
Due to the new direct-acting antiviral drugs, people living with HIV and hepatitis C co-infection can be treated with most of the same hepatitis C drug regimens as HIV-negative people. Research has shown that cure rates are the same.
Unlike treatment for HIV, hepatitis C treatment is not for life. New drugs to treat hepatitis C only need to be taken for up to 3 months.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis B And C Curable
Hiv And Aids Treatment
More than 25 antiretroviral therapy drugs are approved to treat the virus. Your doctor will prescribe a mix of these medications.
The drugs will help stop HIV from making copies of itself. That will keep you healthy and lower your risk of spreading it.
Thereâs no cure for HIV or AIDS. ARTâs goal is to lower your viral load and keep your immune system healthy. The idea is to lower the viral load to âundetectableâ and keep it that way, by taking your medicine every day as prescribed.
How Can You Prevent Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B: Vaccination is the best way to prevent all the ways that hepatitis B is transmitted. People with HIV who do not have active HBV infection should be vaccinated against it. The hepatitis B vaccine is now recommended for all infants, children and adults ages 19-59, as well as adults ages 60+ at high risk for infection. There is a 3-dose series of hepatitis B vaccine given over 6 months, and a 2-dose series given over 1 month. Additionally, there is a 2-dose combination vaccine that protects against both hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C: No vaccine exists for HCV and no effective pre- or post-exposure prophylaxis is available. Injection drug use is one of the risk factors for hepatitis C. For people who inject drugs, the best way to prevent hepatitis C infection is to always use new, sterile needles or syringes, and never reuse or share needles or syringes, water, or other drug preparation equipment. Community-based prevention programs, such as medication-assisted treatment and syringe services programs provide support and services aimed at preventing and reducing the transmission of HCV. Although the risk of sexual transmission of HCV is considered to be low, avoiding unprotected sexual exposure by using condoms has been shown to reduce the chance of sexually transmitted infections.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitative
Who Is At Risk For Mac
People who have a weakened immune system, due to HIV, cancer, long-term use of corticosteroid drugs, or an organ or bone marrow transplant, are at risk of developing MAC.
People with HIV most at risk of developing MAC are those who:
- have a CD4 count below 50 cells/mm3
- have a viral load over 100,000 copies/ml
- have previously had MAC or another opportunistic infection
Can Hcv Infection Be Prevented
The best protection against HCV is to never inject drugs. If you do inject drugs, always use new, sterile needles, and do not reuse or share needles, syringes, or other injection drug equipment.
People, including people with HIV, can also take the following steps to reduce their risk of HCV infection:
- Do not share toothbrushes, razors, or other personal items that may come in contact with another personâs blood.
- If you get a tattoo or body piercing, make sure the instruments used are sterile.
- Use condoms during sex. The risk of HCV infection through sexual contact is low, but the risk increases in people with HIV. Condoms also reduce the risk of HIV transmission and infection with other sexually transmitted diseases, such as gonorrhea and syphilis.
Don’t Miss: How Does Hepatitis A Affect The Body
Control And Prevention Of Hepatitis A
In areas of high prevalence, most children are infected early in life and suchinfections are generally asymptomatic. Infections acquired later in life are ofincreasing clinical severity. Less than 10% of cases of acute hepatitis A inchildren up to the age of six are icteric, but this increases to4050% in the 614 age group and to 7080% inadults.
Of 115,551 cases of hepatitis A in the USA between 1983 and 1987, only 9% of thecases, but more than 70% of the fatalities, were in those aged over 49. It isimportant, therefore, to protect those at risk because of personal contact withinfected individuals or because of travel to a highly endemic area. Other groupsat risk of hepatitis A infection include staff and residents of institutions forthe mentally handicapped, day care centers for children, sexually active malehomosexuals, intravenous drug abusers, sewage workers, certain groups of healthcare workers such as medical students on elective studies in countries wherehepatitis A is common, military personnel, and certain low socio-economic groupsin defined community settings. Patients with chronic liver disease, especiallyif visiting an endemic area, should be immunized against hepatitis A. In somedeveloping countries, the incidence of clinical hepatitis A is increasing asimprovements in socio-economic conditions result in infection later in life, andstrategies for immunization are yet to be developed and agreed.
You May Like: How Long Does It Take To Show Signs Of Hiv
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus . The abbreviation HBV can stand for either the virus or the infection it causes.
HBV can be a short-term or a long-term illness:
- Acute HBV occurs within 6 months after a person is exposed to HBV. In some people, acute HBV can lead to chronic HBV.
- Chronic HBV is a lifelong disease. Without treatment, chronic HBV can cause liver cancer or liver damage that leads to liver failure.
HBV is a contagious infection that can spread from person to person.
You May Like: How To Cure Hepatitis B
How Can I Know If I Have Hiv
You cant tell if someone has HIV just by looking at them, and you may not have any symptoms if youre infected by HIV. The only way to know if you have HIV is to take an HIV test.
Since nearly 1 out of 7 people with HIV dont know it, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control & Prevention recommends screening people between the ages of 13 to 64 at least once as part of routine healthcare. This test is voluntary and confidential.
Looking After Your Liver When You Have Hepatitis B
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Stick to a healthy diet.
- If your skin is itchy keep cool, avoid hot showers and baths and wear loose clothes.
- Avoid alcohol and recreational drugs.
- Attend all your medical appointments and check-ups.
Ibuprofen or paracetamol can help with stomach pain in the acute phase. Check with a clinician if youre unsure whether you should take them.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Hepatitis B
How Can Infection With Hepatitis B Be Prevented
Hepatitis B can be avoided by:
- using a condom or dental dam during oral sex
- not sharing sex toys
- not sharing drug-taking and injecting equipment.
If youre living with HIV, do not have hepatitis B, and a test shows that youre not naturally immune against hepatitis B, you should be vaccinated.
People living with HIV can lose their immunity to hepatitis B if their immune system weakens, and should have their level of immunity checked regularly to see whether they need a booster dose of the vaccination.
There is a combined vaccination for hepatitis A and hepatitis B, though it might be less effective than the separate vaccinations for people with a low CD4 count or a detectable viral load. Ask your doctor which would be most suitable for you.
Immunisation Against Viral Infection Is Not Always Possible
It is possible to vaccinate against many serious viral infections such as measles, mumps, hepatitis A and hepatitis B. An aggressive worldwide vaccination campaign, headed by the World Health Organization , managed to wipe out smallpox. However, some viruses such as those that cause the common cold are capable of mutating from one person to the next. This is how an infection with essentially the same virus can keep dodging the immune system. Vaccination for these kinds of viruses is difficult, because the viruses have already changed their format by the time vaccines are developed.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Hepatitis B Or C
Microbes As The Cause Of Hepatitis
The five viruses that cause hepatitis are transmitted differently:
- Hepatitis A and E are spread through ingestion of food or water that has been contaminated by fecal material from an infected person, also known as the fecal-oral route of transmission.
- Hepatitis C is transmitted through exposure to infected blood.
- Hepatitis A can be transmitted through sexual contact, and hepatitis C can be transmitted rarely from sexual contact.
- Hepatitis D is also transmitted through contact with infected blood or other body fluids, but only people already infected with hepatitis B are at risk because hepatitis B allows hepatitis D to survive in the body.
Treatments for hepatitis B, C, and D suppress the virus in the human body to protect the liver and other organs from damage.