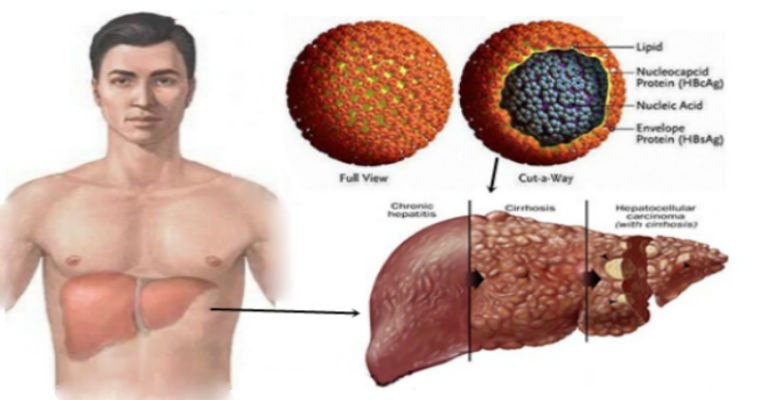
What Laboratory Tests Are Available For Hepatitis B
Tests are available to detect the types of antigens used to identify the hepatitis B virus. The tests determine if the virus is present in the body tissue or blood. The amount of each type of antigen present indicates how advanced the disease is and how infective the individual has become.
Other tests are available to detect the bodys reaction to the viral infection or the bodys reaction to vaccination against the virus. These tests work by measuring the number of antibodies present in the blood.
How Common Is Hepatitis B
The number of people who get this disease is down, the CDC says. Rates have dropped from an average of 200,000 per year in the 1980s to around 20,000 in 2016. People between the ages of 20 and 49 are most likely to get it.
About 90% of infants and 25-50% of children between the ages of 1-5 will become chronically infected. In adults, approximately 95% will recover completely and will not go on to have a chronic infection.
As many as 1.2 million people in the U.S. are carriers of the virus.
Incomplete Or Failed Response To Treatment
Some people with autoimmune hepatitis have an incomplete response to treatment, meaning that treatment helps but does not lead to remission. If you have an incomplete response to treatment, you may need to take different medicines to help prevent liver damage.
Some people may fail to respond to treatment, meaning that the inflammation and liver damage of autoimmune hepatitis keep getting worse. Your doctor may recommend additional blood tests and higher doses of medicines. If liver damage leads to complications, you may need treatment for complications.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Contract Hepatitis C
Immunisation For Hepatitis B
Immunisation is the best protection against hepatitis B infection. A course of vaccination is recommended for all babies and people in high-risk groups.
Immunisation can be with a vaccine against hepatitis B alone or with a combination vaccine. To be immunised, contact your doctor or local council.
Protection against hepatitis B is available free of charge under the National Immunisation Program Schedule. In Victoria, immunisation against hepatitis B is free for:
- Babies at birth immunisation against hepatitis B alone as soon as possible after birth.
- Babies at 2, 4 and 6 months combination immunisation in the form of a diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, hepatitis B, polio and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine .
- Premature babies at 12 months premature babies born under 32 weeks gestation or under 2,000g birth weight receive a single booster dose.
- Children up to and including 9 years of age.
- People aged less than 20 years having a catch-up immunisation.
- Refugees and humanitarian entrants aged 20 years and above.
In Victoria, free hepatitis B vaccine is provided for people who are at increased risk of infection, including:
Immunisation is also recommended, but not necessarily free, for people who are at increased risk of infection, including:
What Are Clinical Trials For Hepatitis B
Clinical trialsand other types of clinical studiesare part of medical research and involve people like you. When you volunteer to take part in a clinical study, you help doctors and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future.
Researchers are studying many aspects of hepatitis B, such as
- progression of hepatitis B and long-term outcomes
- new treatments for hepatitis B
- prevention of reactivated or worsening hepatitis B in people receiving cancer treatment
Recommended Reading: Autoimmune Hepatitis Primary Biliary Cholangitis
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatic Steatosis Be Reversed
Causes Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is spread through contact with blood that contains the hepatitis B virus. If infected blood or body fluids enter another persons bloodstream, that person may become infected.
The time from exposure to the hepatitis B virus to the appearance of the illness is 45 to 180 days.
Risky activities that can cause infection include:
- Sharing unsterile or unclean equipment for injecting drugs.
- Piercing the skin with equipment that is not properly cleaned, disinfected and sterilised.
- Sharing razor blades or toothbrushes.
- Coming into contact with infected blood through open cuts or the mucous membranes of another person.
- Having unprotected sex , especially if there is blood present.
Mothers who have hepatitis B can pass the virus to their babies or children at the time of birth or after birth. If the newborn baby is quickly immunised with 2 vaccines, they can be protected from getting hepatitis B.
All blood and blood products produced for medical purposes in Australia are carefully screened for hepatitis B and other blood-borne viruses. The risk of getting infected with hepatitis B from a blood transfusion is extremely low .
Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis B
Doctors may recommend antiviral medication for people with chronic hepatitis B, which occurs when the virus stays in your body for more than six months.
Antiviral medication prevents the virus from replicating, or creating copies of itself, and may prevent progressive liver damage. Currently available medications can treat hepatitis B with a low risk of serious side effects.
NYU Langone hepatologists and infectious disease specialists prescribe medication when they have determined that without treatment, the hepatitis B virus is very likely to damage the liver over time. People with chronic hepatitis B may need to take antiviral medication for the rest of their lives to prevent liver damage.
There are many different types of antiviral medications available, and your doctor recommends the right type for you based on your symptoms, your overall health, and the results of diagnostic tests. A doctor may take a wait-and-see approach with a person who has a healthy liver and whose blood tests indicate a low viral load, the number of copies of the hepatitis B virus in your bloodstream.
Someone with HIV infection or AIDS may have a weakened immune system and is therefore more likely to develop liver damage. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention strongly recommends that people with HIV infection who are diagnosed with hepatitis B immediately begin treatment with antiviral medication.
Also Check: How Can A Person Get Hepatitis C
How Do People Get The Hbv Virus
Hepatitis B virus is found in the blood of people with HBV infection. It enters the body through blood-to-blood contact.
Reliable blood tests for HBV were developed many years ago. Since blood donors and blood products are tested for HBV, this is no longer the typical means of infection.
In many parts of the world, hepatitis B virus infects more than 8% of the population. HBV-infected women pass the infection to their babies during the birth process. People can also get hepatitis B by sharing needles for injection drug use, through sexual contact with an infected person, by an accidental needlestick with a contaminated needle, or from improperly sterilized medical, acupuncture, piercing, or tattooing equipment.
Current Immunotherapies For Chronic Hbv Infection
Key points of immune regulation that can be targeted for therapy have been identified in studies done in animal models and HBV-infected patients. Injection of ligands targeting Toll-like receptors or RIG-I leads to suppression of viral replication in HBV mouse models., This observation has led to the development of drugs targeting TLR-7, TLR-8, and RIG-I for use in chronically HBV-infected patients. Numerous experiments have revealed that blocking inhibitory receptors can enhance expansion and function of HBV-specific T cells, both in vitro and in vivo., This has motivated the use of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in phase 1 studies in chronically HBV-infected patients. Furthermore, interleukin-12 appears critical to restoring T-cell expansion and function in chronic infection. This has led to interleukin-12, or adjuvants inducing it, being incorporated into the new generation of therapeutic vaccines for chronic HBV.
Also Check: How Can Hepatitis C Be Transmitted Sexually
Can Hepatitis B Be Controlled By Eating Right And Exercising
It is important that people with liver disease follow a healthy, nutritious diet as outlined by Health Canada in Eating Well with Canadas Food Guide.
Alcohol can also damage the liver so it is best that people with hepatitis B do not drink. Following a healthy lifestyle may also prevent fatty liver disease, another liver disease highly prevalent in Canada.
However, hepatitis B cannot be controlled by healthy eating and exercise alone. Hepatitis B can only be controlled by currently available treatment as prescribed by your doctor. Your doctor will need to do regular blood tests to know how much of the active virus is in your blood . The viral load test is used to monitor and manage hepatitis B patients. Viral load can tell your doctor if you need treatment for hepatitis B and how well you are responding to treatment.
How Do Doctors Treat Autoimmune Hepatitis
Doctors treat autoimmune hepatitis with medicines that suppress, or decrease the activity of, your immune system, reducing your immune systems attack on your liver. The medicines doctors most often prescribe are corticosteroidsprednisone or prednisolonewith or without another medicine called azathioprine.
Doctors typically start with a relatively high dose of corticosteroids and then gradually lower the dose. Your doctor will try to find the lowest dose that works for you. Your doctor will use blood tests to find out how you are responding to the treatment. A decrease in levels of the liver enzymes alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase shows a response to treatment. ALT and AST falling to normal levels shows a full response. In some cases, a doctor may repeat a liver biopsy to confirm the response to treatment and find out whether the damage has resolved.
Treatment can relieve symptoms and prevent or reverse liver damage in many people with autoimmune hepatitis. Early treatment of autoimmune hepatitis can lower the chances of developing cirrhosis and other complications. A minority of people who have no symptoms or only a mild form of the disease may or may not need medicines.
Read Also: Most Common Way To Get Hepatitis C
Complications Of Hepatitis B
A small proportion of people who become infected with the hepatitis B virus develop a long-term hepatitis B infection. They may have the virus in their bloodstream for most of their life without realising they are infected.
People with chronic hepatitis B infection may not notice any health problems until they develop liver problems such as liver disease or liver cancer later in life. Treatment for hepatitis B is essential because it is not possible to be a healthy carrier of the hepatitis B virus. Chronic hepatitis B infection occurs more commonly in some communities, including:
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities.
- In people from parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, such as:
- North-East Asia
- Sub-Saharan Africa.
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis B

Doctors typically dont treat hepatitis B unless it becomes chronic. Doctors may treat chronic hepatitis B with antiviral medicines that attack the virus.
Not everyone with chronic hepatitis B needs treatment. If blood tests show that hepatitis B could be damaging a persons liver, a doctor may prescribe antiviral medicines to lower the chances of liver damage and complications.
Medicines that you take by mouth include
A medicine that doctors can give as a shot is peginterferon alfa-2a .
The length of treatment varies. Hepatitis B medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Tell your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, you also should talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Also Check: Foods To Eat When You Have Hepatitis
Pay Attention To Your Emotions
Living with hepatitis can be depressing, and its common for people with HBV to feel worried or anxious. However, you can prevent your emotions from spiraling downwards by connecting with others who understand. Studies have shown that the right support can have a tremendous positive impact on the patients ability to cope. Hepatitis support groups are widely available search for one online or ask your doctor about any local groups.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Hepatitis A After Vaccination
A Global Scientific Strategy To Cure Hepatitis B
Don’t Miss: When Should You Get Hepatitis A Vaccine
Accessibility And Hbsag Clearance Rate
HBsAg clearance occurs spontaneously or via antiviral treatment in CHB patients. The most commonly used drugs are nucleoside analogue and pegylated interferon . NA drugs include entecavir , tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and tenofovir alafenamide fumarate . The 2018 AASLD guidelines recommend Peg-IFN, ETV, or TDF as the preferred initial therapy for adults with immune-active CHB. It also suggests that alanine transaminase levels be tested at least every 6 months for adults with immune-tolerant CHB to monitor for potential transition to immune-active or immune-inactive CHB . The 2017 EASL guideline recommends ETV, TDF and TAF as the preferred monotherapy regimens, and the extension of the duration of Peg-IFN therapy beyond week 48 may be beneficial in selected HBeAg-negative CHB patients . The potential side effects of NAs include lactic acidosis for ETV and nephropathy, osteomalacia, lactic acidosis for TDF. CHB patients should be clinically monitored. The most frequently reported side effects for Peg-IFN are flu-like syndrome, myalgia, fatigue, mood disturbances, weight loss, hair loss and local reactions at the site of injection, and these side effects may be partially managed with dose reduction . Currently, the clearance of HBsAg is based primarily on sequential or combined treatment with NA and Peg-IFN.
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
Also Check: How To Test For Hepatitis
If I Have No Symptoms How Would I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
To confirm whether or not you have hepatitis B, you will need blood tests.
If you have at least one risk factor , you should ask your health care provider to be tested for hepatitis B. Also, you should be tested for hepatitis B if:
- you were born in a region where hepatitis B is more common, including Asia, Africa, southern and eastern Europe, the Pacific Islands, the Middle East, and the Arctic
- one or both of your parents immigrated from a region where hepatitis B is more common
- you live or travel to regions where hepatitis B is more common
- you have a family history of liver disease or liver cancer
- you have been in prison
- you are pregnant
- you have ever used injection drugs, even just once
- you have unexplained abnormal liver enzymes or if
- you receive medicines that suppress the immune system.
Recommended Reading: Side Effects Of Having Hepatitis C
What Are The Complications Of Hepatitis B
The course of hepatitis B infection depends mostly on the age at which a person is infected.
People infected as infants are likely to develop long term infection and can get complications such as scarring of the liver or liver cancer. Infants have a 9 in 10 chance and children have a 3 in 10 chance of developing a chronic, lifelong infection.
People infected as teenagers or adults are likely to become unwell with symptoms , but have a smaller chance of developing a chronic infection. Others develop a silent infection, without any symptoms.
Most people infected as adults clear the virus from the body within 6 months. They develop immunity to future hepatitis B infections and do not develop long-term liver damage.
However, approximately 1 in 20 adults cannot clear the virus and develop chronic hepatitis B. They are at risk of developing complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer in the longer term.
Also Check: How Can Hepatitis C Be Contracted
Can Hepatitis B Go Away Completely
Hepatitis B is a liver disease caused by the hepatitis B virus . The hepatitis B virus was the first hepatitis virus to be identified. It is a disease that affects 300 million people in the world and is estimated to be responsible for between 250,000 and 500,000 deaths per year. The prevalence of infection with the hepatitis B virus varies greatly in different parts of the world. The highest rates of infection are found in Southeast Asia, China, and southern Africa.
Most people who acquire the hepatitis B virus recover without consequences. This form of infection, which lasts less than 6 months, is known as acute hepatitis B. On the contrary, when the infection lasts for more than 6 months, it is known as chronic hepatitis B. Approximately 5% of adults who acquire the infection develop the chronic form. The likelihood of developing chronic hepatitis B depends on the age and immune status of the patient, being higher when acquired in childhood than when acquired as an adult.
In the last time a series of new alternatives for the treatment of the disease have been developed. On the other hand, there is a highly effective and safe vaccine to prevent infection.
Recommended Reading: Is Hiv Transmitted More Easily Than Hepatitis
Treatment For Suspected Exposure
Anyone who has had potential exposure to HBV can undergo a postexposure prophylaxis protocol.
This consists of HBV vaccination and hepatitis B immunoglobin . Healthcare workers give the prophylaxis after the exposure and before an acute infection develops.
This protocol will not cure an infection that has already developed. However, it decreases the rate of acute infection.
Read Also: Is There A Pill That Cures Hepatitis C
Also Check: Herbal Cure For Hepatitis B