Who Should Be Vaccinated For Hepatitis B
All newborns should be vaccinated. Also, people who are under 18 who were not vaccinated at birth should also get the vaccine. Other groups who should be sure to be vaccinated are those in certain high-risk categories, such as:
- People who have more than one sexual partner.
- Men who have sex with men.
- Adults with diabetes.
- Sexual partners of infected people and people who share households with infected individuals.
- People who are exposed to blood and other bodily fluids, including healthcare and public safety professionals, and people who work in jails and other places taking care of people who cant take care of themselves.
How Many People Have Hepatitis B
In the United States, an estimated 880,000 to 1.89 million people are chronically infected with HBV. New cases of HBV infection in the United States had been decreasing until 2012. Since that time, reported cases of acute hepatitis B have been fluctuating around 3,000 cases per year. In 2020, 2,157 cases of acute hepatitis B were reported however, because of low case detection and reporting, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that there were 14,000 acute hepatitis B infections. The rate of acute cases of HBV decreased by 32% after 2019 which may be related to the disruptions of the COVID-19 pandemic. For the most recent surveillance data visit CDC Viral Hepatitis Surveillance.
Globally, HBV is the most common blood-borne infection with an estimated 296 million people infected according to the World Health Organization .
Treatment Options For Antiviral Resistant Pathogens
If a virus is not fully wiped out during a regimen of antivirals, treatment creates a bottleneck in the viral population that selects for resistance, and there is a chance that a resistant strain may repopulate the host. Viral treatment mechanisms must therefore account for the selection of resistant viruses.
The most commonly used method for treating resistant viruses is combination therapy, which uses multiple antivirals in one treatment regimen. This is thought to decrease the likelihood that one mutation could cause antiviral resistance, as the antivirals in the cocktail target different stages of the viral life cycle. This is frequently used in retroviruses like HIV, but a number of studies have demonstrated its effectiveness against influenza A, as well. Viruses can also be screened for resistance to drugs before treatment is started. This minimizes exposure to unnecessary antivirals and ensures that an effective medication is being used. This may improve patient outcomes and could help detect new resistance mutations during routine scanning for known mutants. However, this has not been consistently implemented in treatment facilities at this time.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Titer Labcorp Cost
Hepatitis B Causes And Risk Factors
Itâs caused by the hepatitis B virus, and it can spread from person to person in certain ways. You can spread the hepatitis B virus even if you donât feel sick.
The most common ways to get hepatitis B include:
- Sex. You can get it if you have unprotected sex with someone who has it and your partnerâs blood, saliva, , or vaginal secretions enter your body.
- Sharing needles. The virus spreads easily via needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood.
- Accidental needle sticks.Health care workers and anyone else who comes in contact with human blood can get it this way.
- Mother to child.Pregnant women with hepatitis B can pass it to their babies during childbirth. But thereâs a vaccine to prevent newborns from becoming infected.
Hepatitis B doesnât spread through kissing, food or water, shared utensils, coughing or sneezing, or through touch.
Who Is Likely To Be A Hepatitis B Carrier
People living with chronic hepatitis B can be carriers. Often, carriers do not have symptoms. This means that they may unknowingly transmit the virus to others.
However, within the U.S., there is a low rate of hepatitis B infections, which means that there is a small number of carriers. To prevent transmission, people can receive the hepatitis B vaccine.
A person living with chronic hepatitis B who is an asymptomatic carrier can still spread the virus to others.
The ways to transmit the infection include:
- having genital contact with others
- sharing needles
You May Like: Antiviral Medications For Hepatitis B
What Treatments Are Available For Chronic Hepatitis B If Medications Dont Work
If you have advanced hepatitis B, you might also become a candidate for a liver transplant. This path does not always result in a cure because the virus continues in your bloodstream after a transplant. To prevent being infected again after your transplant, you may be prescribed hepatitis B immunoglobulin with an antiviral agent.
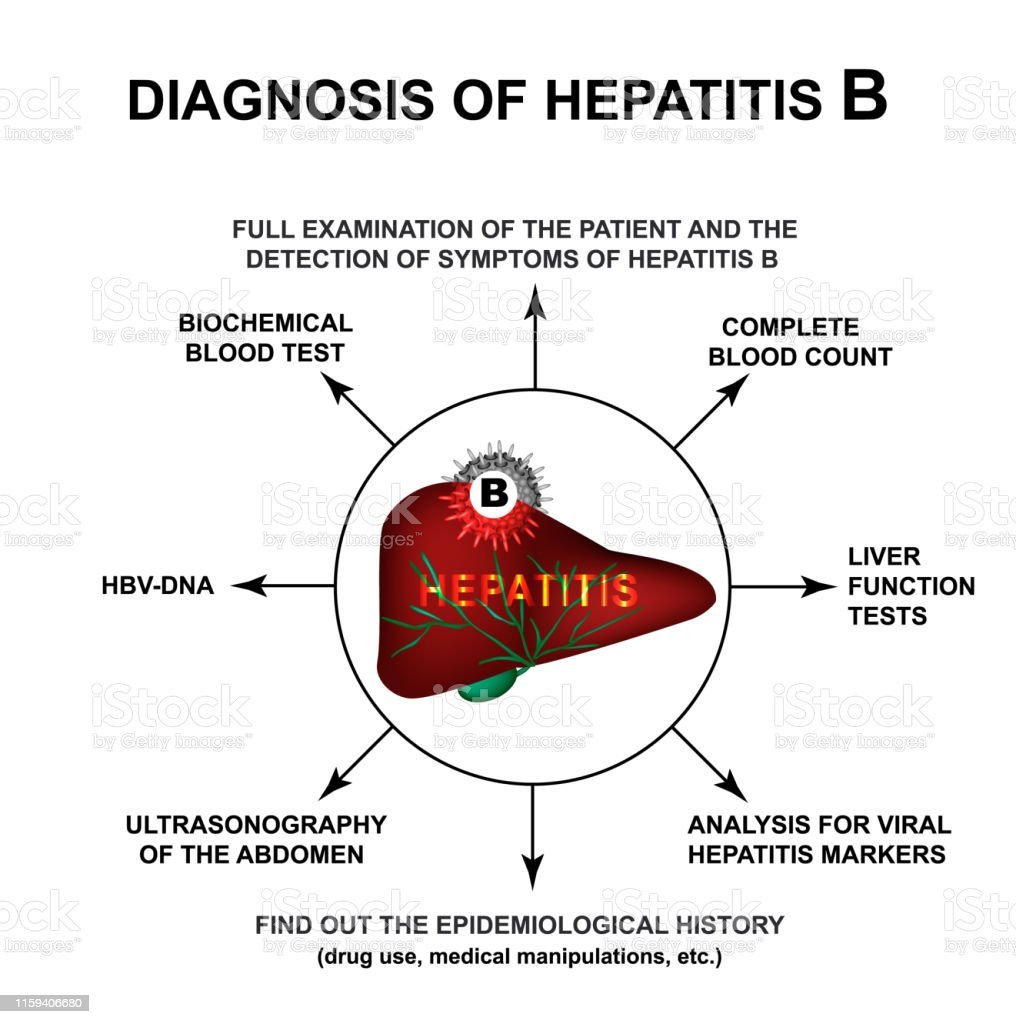
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
There are three main ways to diagnose HBV infection. They include:
- Blood tests: Tests of the blood serum shows how your bodys immune system is responding to the virus. A blood test can also tell you if you are immune to HBV.
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to show the size and shape of your liver and how well the blood flows through it.
- Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis.
The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit. Often, people whove become infected first learn they have hepatitis B when they go to donate blood. Blood donations are routinely scanned for the infection.
The virus can be detected within 30 to 60 days of infection. About 70% of adults with hepatitis B develop symptoms, which tend to appear an average of 90 days after initial exposure to the virus.
You May Like: How Do You Catch Hepatitis C
Prevent Hepatitis B Infections In Newborns
If you are pregnant and have hepatitis B, talk with your doctor about lowering the risk that the infection will spread to your baby. Your doctor will check your virus levels during pregnancy. If virus levels are high, your doctor may recommend treatment during pregnancy to lower virus levels and reduce the chance that hepatitis B will spread to your baby. Your doctor may refer you to a liver specialist to find out if you need hepatitis B treatment and to check for liver damage.
When it is time to give birth, tell the doctor and staff who deliver your baby that you have hepatitis B. A health care professional should give your baby the hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG right after birth. The vaccine and HBIG will greatly reduce the chance of your baby getting the infection.
Hepatitis B Virus Antigens And Antibodies
The Structure of Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus is a small DNA virus with unusual features similar to retroviruses, which is a prototype virus of the Hepadnaviridae family. HBV causes acute and chronic hepatitis in humans. The hepatitis B virus consists of an outer lipid envelope and an icosahedral nucleocapsid core composed of protein. The virus is one of the smallest enveloped animal viruses with a virion diameter of 42 nm, and also named Dane particles. Dane particles contains both envelope and core.
The outer envelope contains embedded proteins which are involved in viral binding of susceptible cells. There are three types of proteins: small hepatitis surface proteins, middle hepatitis surface proteins and large hepatitis surface proteins, they are totally composed of hepatitis B surface proteins. The nucleocapsid encloses the viral DNA and a DNA polymerase that has reverse transcriptase activity.
There are three types of Hepatitis B Virus particles in infectious serum by electron microscopy, Dane particles, filamentous particles and spherical particles. Except for Dane particles , there also exist pleomorphic forms, as filamentous particles and spherical particles .
Hepatitis B Virus Antigens
Hepatitis B surface antigen HBsAg
Hepatitis B core antigen-HBcAg
Hepatitis B e antigen-HBeAg
The X gene codes for HBxAg. The product of the X gene is hepatitis B x antigen . It may be involved in carcinogenesis.
Hepatitis B Virus Antibodies
Referrence
Also Check: How Hepatitis B And C Are Transmitted
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk In Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B
Chronic hepatitis B is now recognized as one of the most important cause for the development of HCC, accounting for over 50% of the HCC cases worldwide. However, it was not until the mid-1970s that scientists recognized the causative role of chronic hepatitis B in HCC development. This was following the discovery of the hepatitis-associated antigen, now known as the HBsAg, which has been reported to persist in patients with chronic hepatitis B with or without cirrhosis, leading to HCC development in a significant proportion of patients.41 Various mechanisms have been proposed in the pathogenesis of HCC in patients with chronic HBV infection. Integration of the HBV DNA into the hepatocyte genome and the epigenetic regulation of the minichromosome cccDNA result in chromosomal instability and activation of cancer-related genes along with inactivation of cancer-suppressive genes through interference with various cellular transcription and signal transduction processes.42 In addition, chronic hepatitis B results in release of cytokines and growth factors as part of the adaptive immune response, leading to hepatocyte necrosis and fibroblast proliferation, resulting in liver fibrosis/cirrhosis.43
As such, patients with chronic hepatitis B, especially those at high risk, should be continuously screened for HCC, regardless of the virologic remission .27
James E. Balow, … Howard A. AustinIII, in, 2008
What Other Problems Can Hepatitis B Cause
In rare cases, acute hepatitis B can cause liver failure.
Chronic hepatitis B can develop into a serious disease that causes long-term health problems such as cirrhosis , liver cancer, and liver failure.
If you have ever had hepatitis B, the virus may become active again, or reactivated, later in life. This could start to damage the liver and cause symptoms.
Read Also: How To Know If You Have Hepatitis
What Is Chronic Hepatitis B
Doctors refer to hepatitis B infections as either acute or chronic:
- An acute HBV infection is a short-term illness that clears within 6 months of when a person is exposed to the virus.
- A person who still has HBV after 6 months is said to have a chronic hepatitis B infection. This is a long-term illness, meaning the virus stays in the body and causes lifelong illness. An estimated 850,000 to more than 2 million people in the U.S. have chronic HBV.
The younger someone is when infected, the greater the chances for chronic hepatitis B.
Detection Of Antiviral Resistance
National and international surveillance is performed by the CDC to determine effectiveness of the current FDA-approved antiviral flu drugs. Public health officials use this information to make current recommendations about the use of flu antiviral medications. further recommends in-depth epidemiological investigations to control potential transmission of the resistant virus and prevent future progression. As novel treatments and detection techniques to antiviral resistance are enhanced so can the establishment of strategies to combat the inevitable emergence of antiviral resistance.
Dont Miss: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Hepatic
You May Like: When Should You Get Hepatitis A Vaccine
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if you have an active infection. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can transmit the virus to others. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B.
This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the state of a hepatitis B infection.
What If I Am Pregnant
Its recommended that all pregnant women have a blood test for hepatitis B in early pregnancy.
If you have hepatitis B and are pregnant, treatments can reduce the risk of transmission of hepatitis B to the baby.
If you have hepatitis B, it is important to protect others from infection.
Important ways to prevent the spread of hepatitis B include:
- vaccination of all your close contacts
- practise safe sex until your sexual contacts are fully vaccinated and immune
- do not donate blood, organs or body tissue
- do not allow your blood to contact another person
- inform healthcare workers
- if your work involves potential for your blood or other body fluid to spread to other people, discuss your situation with your doctor
The hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective in protecting against hepatitis B infection, providing protection in 95 in 100 vaccinated people.
In Australia, hepatitis B vaccination is part of the standard immunisation schedule for all newborn babies and infants. Its also recommended for adults who are at high risk of exposure, people who are immunosuppressed or have other liver disease. People in these risk groups should be vaccinated against hepatitis B. Talk to your doctor about your level of risk and whether hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for you.
If you werent vaccinated against hepatitis B as a child, or if youre not sure whether you are vaccinated, talk to your doctor about whether you need a catch-up vaccine.
Read Also: Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Abnormalities In Heme Metabolism And Excretion
One way to understand jaundice pathophysiology is to organize it into disorders that cause increased bilirubin production or decreased bilirubin excretion .
Prehepatic pathophysiology
Prehepatic jaundice results from a pathological increase in bilirubin production: an increased rate of erythrocyte hemolysis causes increased bilirubin production, leading to increased deposition of bilirubin in mucosal tissues and the appearance of a yellow hue.
Hepatic pathophysiology
Hepatic jaundice is due to significant disruption of liver function, leading to hepatic cell death and necrosis and impaired bilirubin transport across . Bilirubin transport across hepatocytes may be impaired at any point between hepatocellular uptake of unconjugated bilirubin and hepatocellular transport of conjugated bilirubin into the gallbladder. In addition, subsequent cellular due to inflammation causes mechanical obstruction of the intrahepatic biliary tract. Most commonly, interferences in all three major steps of bilirubin metabolism â uptake, conjugation, and excretion â usually occur in hepatocellular jaundice. Thus, an abnormal rise in both unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin will be present. Because excretion is usually impaired to the greatest extent, conjugated hyperbilirubinemia predominates.
Posthepatic pathophysiology
| Present | Present |
Laboratory findings depend on the cause of jaundice:
How Are Hepatitis B And C Diagnosed
Hepatitis B is diagnosed by a series of blood tests. The test may show an ongoing infection or antibodies that indicate that the patient is protected against hepatitis B. In patients who have a positive screening test that suggests the possibility of ongoing infection, further testing is done to determine the levels of the virus in the bloodstream.
Hepatitis C is diagnosed via a blood test called a Hepatitis C Antibody Test. A positive result means that hepatitis C antibodies are present in the blood. But a positive antibody test doesnt necessarily mean a person has hepatitis C. A further blood test is needed to confirm the diagnosis. This second blood test quantifies the amount of the virus or the viral load in the liver and the bloodstream.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Prevention And Treatment
Treatments For Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B usually clears up on its own without treatment. You may be offered medicine to help with the symptoms, such as painkillers or medicines to stop you feeling sick.
Your GP will refer you to see a liver specialist who will check how well your liver is working.
If hepatitis B lasts for over 6 months it is called long-term hepatitis B.
It is usually treated with antivirals and medicine to help relieve symptoms such as itchiness, pain, and sickness. You will also need to see a liver specialist for regular check-ups.
What Is Involved In A Liver Transplant
A liver transplant is considered necessary when the liver is damaged and cannot function or in some cases of liver cancer. Your liver is very important. It is responsible for many functions related to making sure that your body stays healthy and is able to digest foods.
You may be eligible for a transplant if you have chronic hepatitis B infection or some of the diseases that may result from it, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. You will have to complete testing and be evaluated before being approved for a transplant. It is likely that you will be placed on a waiting list while an appropriate organ is found.
Donated livers come from two types of donors: living and deceased. Because the liver can regenerate, it is possible to use part of a liver for transplant. The remaining sections in both the donor and the receiver will grow into livers of adequate size.
People who get liver transplants must take anti-rejection drugs for the rest of their lives. These drugs make you more susceptible to infection. However, liver transplants have become more successful over time and continue to improve.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Hepatitis Panel
Hepatitis B During Pregnancy
If a woman with HBV becomes pregnant, they may transmit the virus to their baby. Women should inform the doctor who delivers their baby that they have HBV.
The infant should receive an HBV vaccine and HBIG with 1224 hours of birth. This significantly reduces the risk that they will develop HBV.
The HBV vaccine is safe to receive while pregnant.
People with a high risk of HBV include:
- the infants of mothers with HBV
- the sexual partners of people with HBV
- people who engage in sexual intercourse without contraception and those who have multiple sexual partners
- men who have sex with men
- people who inject illicit drugs
- those who share a household with a person who has a chronic HBV infection
- healthcare and public safety workers who are at risk of occupational exposure to blood or contaminated bodily fluids
- people receiving hemodialysis, which is a type of kidney treatment
- people taking medications that suppress the immune system, such as chemotherapy for cancer
People can prevent HBV infection by:
- wearing appropriate protective equipment when working in healthcare settings or dealing with medical emergencies
- not sharing needles
- following safe sexual practices
- cleaning any blood spills or dried blood with gloved hands using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 10 parts water
A vaccine against HBV has been available since 1982.
People who should receive this vaccine include: