Interpretation Of Diagnostic Tests
Hepatitis B surface antigen is the first marker of HBV detectable in serum in acute infection. By the time clinical and biochemical hepatitis is present after an incubation period of up to 140 days, other serologic markers of HBV infection appearâincluding antibody to HBV core antigen . Hepatitis B core antigen, a marker of viral replication found in infected hepatocytes, does not circulate in serum. However, its corresponding antibody does. Documented HBsAg positivity in serum for 6 or more months suggests chronic HBV with a low likelihood of subsequent spontaneous resolution. Chronic HBV is diagnosed by the absence of IgM anti-HBc antibody. IgM anti-HBc antibody is a marker of acute or recent acute hepatitis B and is detectable for 6 months after infection, whereas IgG anti-HBc is lifelong. If acute HBV resolves, neutralizing antibody against HBsAg develops. If HBV infection becomes chronic, other HBV markersâincluding HBV viremia and hepatitis e antigen âshould be sought. Both of these markers imply viral replication and thus greater infectivity, although any patient who is HBsAg positive is potentially infectious.
Rima Fawaz, Maureen M. Jonas, in, 2011
Why Do I Need This Test
You may need this test if your healthcare provider believes you have a liver infection caused by HBV. You may need this test if you have symptoms of hepatitis B. Symptoms often start slowly. Many people have no symptoms or only feel like they have a mild case of the flu. You may not have symptoms until the infection becomes severe or chronic.
The most common symptom is extreme tiredness. Other symptoms may include:
-
Swelling and confusion. This is in extreme cases.
You may also have this test if you have a history that puts you at risk for being in contact with the virus. Risk factors for hepatitis B infection include:
-
Having sex with someone infected with the virus
-
Living in close contact with someone who has the virus
-
Being a man who has sex with men
-
Being a child born to a mother who has the virus
-
Sharing needles for IV drug use
-
Working in a healthcare center where you are exposed to blood
-
Getting a blood transfusion or organ transplant. This is less common with active screening.
You may also have this test several times if you’ve already been diagnosed with hepatitis B to see whether your infection is getting better.
Assessment Of Hbsag And Anti
During the study, two techniques were employed. The Electrochemiluminescence technique was used as the primary method for detecting HBsAg and Anti-HBcAb, and the enzyme immunoassay technique was used as a backup if the ECL technique is not available.
Blood samples were aseptically collected by trained lab technicians using a disposable syringe. The blood sample was allowed to clot in a sterile tube before centrifugation. A total of 11,121 serum samples were separated and analyzed for HBsAg and Anti-HBcAb by the ECL technique using the Immunoassay Cobas e 411 analyzers . The remaining 3178 serum samples were analyzed for HBsAg and total anti-HBcAb by the enzyme immunoassay technique according to manufacturer instructions.
The HBsAg is the first line of screening for HBV infections in blood donors prior to donation. Samples that have initially reactive results are tested repeatedly in duplicate. If one or both tests are positive, the blood donor is deferred indefinitely for donation. Confirmatory testing using HBV NAT is not routinely done but is available in the Blood Center and special private laboratories at the blood donors expense.
Don’t Miss: How To Tell If You Have Hepatitis C
Specification Of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
The LINEAR Hepatitis B Antigen Cassette Test detects HBSAG concentration greater than 2 ng/ml in human serum by the development of a colored line in the test region of the test device.
The LINEAR Hepatitis B Antigen Cassette Test uses an antibody that is highly specific for Hepatitis B Antigen in serum. A result of 99.5 % concordance to the ELISA test was determined by a clinical study of 1208 samples.
Possible Association Of E Antigen With Hepatitis B Virus And The Surface Antigen
Hepatitis B e antigen is frequently found together with significant amounts of hepatitis B virus particles in surface antigen-positive sera . As the complete virus particle contains a unique DNA polymerase activity, it has been suggested that e antigen may represent this enzyme . Neurath and Strick investigated this possibility by examining the behaviour of the antigen on columns containing pyran-Sepharose or immobilized DNA. Partially purified e antigen prepared by ion chromatography failed to bind to immobilized calf thymus DNA or to pyran-Sepharose using conditions suitable for the retention of nucleic acid polymerases. These observations indicated that e antigen is not a polymerase enzyme. Although it has been suggested that anti-e depresses DNA polymerase activity in certain sera , the antibody activity is not clearly distinguished from core antibody. In addition there was no correlation between the levels of DNA polymerase activity and the presence or absence of e antigen in the sera tested. It is therefore unlikely that e antigen is related to the hepatitis B associated DNA polymerase.
Stephanos J. Hadziyannis, … Emilia Hadziyannis, in, 2013
Also Check: Can Hepatic Steatosis Be Reversed
Please Explain What Does Hepatitis B Antibody Surface Ql Reactive Mean
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â itâs anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â itâs anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Read Also: How Does Hepatitis Affect The Body
How The Test Is Done
- An elastic band is wrapped around the arm to diminish the blood flow and to make needle insertion easier
- The site of insertion is cleaned with an alcohol swab
- Needle is inserted into the vein
- A tube is attached with the needle to collect the blood
- Once blood sample is taken, the elastic band is removed
- Cotton ball or gauze pad is placed on the site of insertion pressure is applied followed by bandage.
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis C Transmitted Cdc
How Much Does A Hepatitis B Titer Test Cost
The cost of a hepatitis B test varies based on where you get the test. Prices range from roughly $24 to $110.
Your insurance may cover some or all of the cost. Under the Affordable Care Act, all new health plans must cover preventative services including hepatitis B vaccination and testing without a deductible or copay.
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to HBV, your body mounts an immune defense to specifically target and neutralize the invader. Unlike innate immunity which mounts a generalized defense against all invaders, this type of immunity is disease-specific.
This immune response occurs whether you are exposed to HBV through blood or sexual contact, or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The virus has proteins on its surface, called antigens, that serve as unique identification tags. When HBV enters the body, the immune system “encodes” antibodies specific to these antigens so that it can recognize and attack the virus should it appear again.
There are two types of antibodies produced in response to the virus:
- Immunoglobulin M is the antibody that mounts the initial attack but eventually fades away.
- Immunoglobulin G is the antibody that provides long-lasting immune protection against HBV. The immunity can last for many years, but it gradually wanes over time.
Also Check: Whats The Difference Between Hepatitis Ab And C
Natural History Of Hbv Infection
Exposure to HBV has a variable outcome that is largely determined by the age and immune status of an infected individual. In healthy adolescents and adults, the most common population exposed to HBV in northern Europe and most of North America, exposure to HBV typically leads to acute hepatitis, followed by loss of detectable HBsAg and loss of circulating HBV DNA . Chronic infection, identified by persistence of HBsAg, may follow infections in infants, persons with immunosupression, and a small number of otherwise healthy individuals. Such chronic infection may be associated with active viral replication , or with nonreplicating infection, in which HBsAg continues to be produced but HBV DNA is undetectable in the circulation. Replicating forms of infection can convert to nonreplicating forms, either spontaneously or after treatment with either interferon or nucleotide analogs. Rarely , HBsAg will also disappear from the circulation, followed by appearance of antibody to HBsAg . This antibody is thought to be protective, and is the antibody produced with successful responses to the HBV vaccine.
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
Hepatitis B can be transmitted from a birthing parent to a newborn infant. This is because the newborn is exposed to blood and bodily fluids during delivery.
In fact, 90% of mothers with an acute hepatitis B infection and 10% to 20% of mothers with chronic hepatitis B will transmit the virus to their newborn, estimates the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
For this reason, birthing parents are routinely screened for hepatitis B during each pregnancy.
Additionally, the hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin are both administered to infants with an HBV-positive birthing parent within of birth to prevent infection.
According to the
- people with hepatitis C infection
- men who have sex with men
- people with multiple sexual partners
- people who are seeking treatment for a sexually transmitted infections
- people with current or recent injection drug use
- family members or sexual partners of those with hepatitis B
- people with chronic liver disease
- people traveling to areas with high rates of hepatitis B
- people on maintenance dialysis
- people who are incarcerated
The hepatitis B vaccine is usually administered in three shots, given 1 month and 6 months after the first dose. Another recently approved vaccine is completed in two doses spaced 1 month apart.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Discussing Screening Results With Clients
The medical personnel who ordered or arranged the screening test, not counselors, usually explain the results. Hepatitis screening should be part of the intake physical examination in an opioid treatment program, and medical personnel may report the results. However, the client may want to discuss the results with the counselor or ask the counselor questions.
Anxiety might interfere with some clients ability to comprehend or retain information, which might need to be repeated.
Suggestions for conversations with clients when the test results are negative include the following:
- Explain results clearly and simply: So the HCV screening result was negative? This means that, as of 6 months ago, you did not have .
- Emphasize that a negative result to an HCV test does not indicate to and that the client should take precautions to avoid . If a relapse to drug use occurs, advise clients to avoid sharing any drug paraphernalia or equipment. Specify that this includes cookers, cotton, water, needles, syringes, pipes, and straws.
- Emphasize the importance of getting HAV and HBV vaccinations. Provide information about the availability of low- or no-cost vaccinations.
Clients whose screening test results are positive for will need additional tests and examinationsusually with doctors who specialize in diseases of the liver to get accurate diagnoses and to determine their health status and the extent of liver damage. These tests are described in .
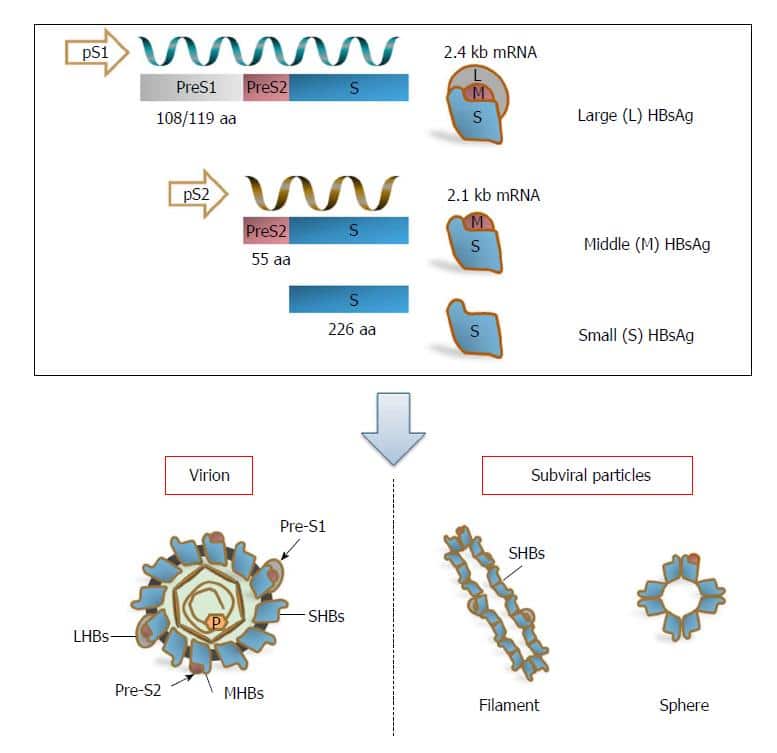
Hbsag Mutants Associated With Immune Escape
The MHR region, which is exposed to the outer surface of the virion, is situated between aa 99-169 of HBsAg. The antibodies produced after HBV vaccination and those used in diagnostic assays to detect serum HBsAg are both directed against this region and, specifically, to a cluster of B-cell epitopes, common to all subtypes of the virus, called a determinant and showing a two-loop structure of aa . Mutations may occur on both loops of the a determinant and may be responsible for a lack of protection and the occurrence of HBV infection in immunized patients or for failure to protect by the HBIG administered as a prophylactic measure or failure to detect HBsAg in diagnostic assays. Table Table22 lists the studies suggesting the association of HBsAg mutants with vaccine escape or failed HBsAg detection.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis Ca Sexually Transmitted Disease
What Are My Next Steps Once I Get My Results
It can be difficult to understand what the results of your test mean. A healthcare provider can help you interpret your results and decide whether you need to take further action:
- If your results suggest that youre already immune to hepatitis B and arent contagious, you likely wont need to do anything.
- If your results suggest that youre not immune, a doctor may recommend vaccination, especially if youre somebody whos at a high risk of infection.
You may also need additional testing if more information is needed to interpret your results.
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
Recommended Reading: How Can A Person Get Hepatitis
Whats The Hepatitis B Titer Test Used For
A hepatitis B titer test measures antibodies in your blood to see if youre immune either due to vaccination or previous infection.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that targets your liver. It can be transmitted by coming into contact with the bodily fluids of an infected person. A person with the virus can also infect their child during birth.
Hepatitis B can develop into a chronic infection. Chronic infection occurs when your body cant fight off the virus within six months. Chronic hepatitis B infections most commonly develop less than six years old, especially in infants.
Hepatitis B titer tests can be used to evaluate:
- whether a high-risk person is immune to hepatitis B
- whether hepatitis B immunoglobulin is needed after a needle prick
- men who have sex with men
- people born in countries with a hepatitis B prevalence greater than 2 percent
- people born in the United States not vaccinated as children and with parents born in regions with more than 8 percent hepatitis B prevalence
You may need your titer test results as proof of hepatitis B immunity in order to get into healthcare programs at many schools for example, the nursing program at Lone Star College. In the United States, employers are not allowed to withdraw a job offer if they learn you have hepatitis B.
Hbsag/hcv Ab Rapid Test
The OnSite HBsAg/HCV Ab Rapid Test is a lateral flow chromatographic immunoassay for the qualitative detection and differentiation of hepatitis B surface antigen and anti-hepatitis C virus antibodies in human serum, plasma or whole blood.
- Use serum, plasma or whole blood
- Two results in 15 minutes
- Can be performed without the use of laboratory equipment
- Individually sealed foil pouches containing:
- One cassette device
Also Check: What Causes The Hepatitis C Virus
Don’t Miss: At What Age Do You Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
What Does Hepatitis B Envelope Antigen Mean
Hepatitis refers to liver inflammation caused by a viral infection. This is one of the most widespread and contagious diseases in the world with more than 400 million people being a carrier of the hepatitis B virus. When the hepatitis B virus is actively circulating and replicating in the blood, it produces the hepatitis B antigen protein. The presence of this antigen protein means that the person is infected with the virus and can spread the infection to other people.
There are different tests for hepatitis A and hepatitis B. A positive test is considered abnormal.
A positive test may mean:
- You currently have a hepatitis infection. This may be a new infection , or it may be an infection that you have had for a long time .
- You had a hepatitis infection in the past, but you no longer have the infection and cant spread it to others.
Hepatitis A test results:
- IgM anti-hepatitis A virus antibodies, you have had a recent infection with hepatitis A
- Total antibodies to hepatitis A, you have a previous or past infection, or immunity to hepatitis A
Hepatitis B test results:
Antibodies to hepatitis C can most often be detected 4 to 10 weeks after you get the infection. Other types of tests may be done to decide on treatment and monitor the hepatitis C infection.
Laboratory Findings And Diagnostic Tests
Serum HBsAg and anti-HBs are the most useful screening tests for chronic HBV infection or immunity to HBV. HBsAg is present in most chronically infected persons. Lack of anti-HBs in an unvaccinated HBsAg-negative person indicates susceptibility to HBV infection.3
Screening for HBsAg is recommended at the first prenatal visit for all pregnant women.3,109 Women in labor without HBsAg test information should have HBsAg serology on arrival. In addition, pretested women who have a history of certain risk factors should be retested at the time of admission to the hospital for delivery.3,110
Fabrizio Fabrizi MD, … Paul Martin MD, in, 2017
You May Like: What Do You Get Hepatitis B From
Question 2 What Is The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
The hepatitis B surface antibody is the antibody that is produced in response to hepatitis B surface antigen , a protein present on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. Anti-HBs appears after convalescence from acute infection and lasts for many years. It can also be produced in response to hepatitis B vaccination.
Other hepatitis B antibodies are not produced in response to vaccination. This is because these antigens are not in the vaccine.
Read Also: What Does Hepatitis B Do To You