How The Test Works
The HCV antibody test requires a small blood sample. This sample is usually taken by a lab technician who draws a vial of blood from a vein in your arm. The actual blood draw usually takes less than a minute.
Your blood sample is then analyzed to see if antibodies for hepatitis C are present in your blood. Antibodies are Y-shaped proteins that your body creates to fight off pathogens.
Antibodies are specific to the virus or infection they are created to target, so if youve ever had hepatitis C, your body will have produced antibodies to fight it. If youve never had a hep C infection, those antibodies wont be present in your blood.
Results from the test can take anywhere from a few days to a week or two. Rapid tests for hepatitis C are also available if you need the results in an hour or less.
If your HCV antibody test comes back as reactive, it means that one of two things is true:
- you have an active case of hepatitis COR
- you have had hepatitis C at some point in the past
If you have hepatitis C, your body will have the ability to produce hepatitis C antibodies for the rest of your life. This is why a reactive result doesnt always mean that you have an active infection.
If your HCV antibody test comes back as nonreactive, it means two things are true:
- you dont currently have hepatitis C AND
- youve never had an active hepatitis C infection
What Does This Hep C Virus Ab 0 1 Mean
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Hepatitis C Testing And Diagnosis
Doctors will start by checking your blood for:
Anti-HCV antibodies: This blood test is the first — and sometimes only — one you may get. Also called the ELISA screen, it checks for antibodies that your body releases to fight the virus. These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection. Your test will be either negative or positive for antibodies. It usually takes a few days to a week to get results, though a rapid test is available in some places.
What the results mean
Negative . This is when your blood shows no signs of HCV antibodies. Most of the time, thatâs because you never came in contact with the virus and you do not have hep C.
Sometimes, your negative result can be false, meaning you have HCV. That may happen if you:
- Took the test too soon after your exposure. This test checks for only HCV antibodies, which can take several months to appear.
- Have HIV, a donated organ, or other conditions that weaken your immune system, which can suppress your antibodies
- Get hemodialysis for kidney problems
If youâve been exposed in the last 6 months, youâll need to be retested.
Positive . This means youâve been infected with HCV. But false positives are surprisingly common. More than 1 in 5 people who test positive donât actually have hepatitis C. Possible reasons include:
What the results mean
Read Also: Why Is My Doctor Testing Me For Hepatitis C
Hcv Core Antigen Testing
The hepatitis C core antigen is a viral protein. Since the core antigen is part of hepatitis C virus, it can usually be found in the bloodstream two weeks after infection.
Since HCV core antigen testing is simpler and less expensive than viral-load testing, some experts suggest using it in resource-limited settings. Core antigen testing can be usedoften with HCV antibody testingto detect acute HCV or to confirm chronic HCV infection. HCV core antigen testing can also be used to measure treatment outcome. Although it does not detect low levels of HCV , usually the hepatitis C viral load is much higher in people who relapse after HCV treatment.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Catch Hepatitis C
How Hepatitis C Is Diagnosed
To determine a hepatitis C diagnosis, your doctor will:
- Get your medical history .
- Perform a physical exam, especially checking for changes in skin color, swelling in your lower extremities, and tenderness in your abdomen.
- Order certain diagnostic blood tests.
The first diagnostic tool in the screening process is a blood test that screens for HCV antibodies proteins the body produces in response to the virus. An enzyme immunoassay is used to perform this test.
A negative result for the antibody test means that youve never had HCV in your blood, while a positive result means you were exposed to the virus at some point in your life. Up to a quarter of people spontaneously clear the virus from their blood within six months of contracting it.
Because EIA sometimes produces false-positive results, a test called recombinant immunoblot assay may be used to confirm that you have the HCV antibody. This test is not necessary for most patients, and it is more commonly performed by blood banks to check for the virus in donated blood.
A negative EIA result may just mean that your body has not yet produced the HCV antibody , and you may need to be tested again in a few months.
If you have a positive antibody test, your doctor will then use another blood sample to conduct a qualitative polymerase chain reaction test or a process called transcription-mediated amplification , which looks for the presence or absence of RNA of HCV in your blood.
You May Like: How Much Is Hepatitis C Treatment
How Does Hepatitis C Testing Work In Canada
Typically, two tests are required to diagnose a hepatitis C infection: a screening test and a confirmatory test.The first test looks for hepatitis C virus antibodies and determines if a person has ever had hepatitis C. If the screening test result is positive for hepatitis C antibodies, a second test is required to determine whether the person has a current hepatitis C infection. The confirmatory test detects the presence of virus in the blood. In Canada, it is typically an RNA test.
Hepatitis C tests in Canada are conducted on a blood sample. The blood sample can be collected through a standard blood draw by venipuncture, which is the most common way hepatitis C tests are done in Canada, or through blood from a finger prick.
Testing Can Be Performed In A Variety Of Locations
Point-of-care tests have the potential to increase the number of people tested because they can be administered and interpreted in non-traditional settings outside of medical and laboratory facilities.810 For example, point-of-care tests have been delivered in a variety of settings where people are already accessing services such as pharmacies,11 harm reduction services including needle and syringe programs and supervised consumption sites,1215 substance use disorder treatment programs,16 prisons,17,18 services that support people experiencing homelessness19 and mobile services.20 Self-contained single-use point-of-care tests such as the OraQuick HCV Rapid Antibody Test can be administered and interpreted during outreach.21
Through delivery in non-traditional settings, point-of-care tests have the potential to engage more individuals, especially those who not do have equitable access to healthcare such as people who use drugs9 and people in remote settings.1,22
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Is Caused By
Pregnancy And Hepatitis C
Should pregnant women be tested for HCV antibodies?
Yes. All pregnant women should be screened for anti-HCV during each pregnancy, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is < 0.1% . Pregnant women with known risk factors should be tested during each pregnancy, regardless of setting prevalence. Any pregnant women testing positive for anti-HCV should receive a PCR test for HCV RNA to determine current infection status.
Can a mother with hepatitis C infect her infant during birth?
The overall risk of an infected mother transmitting HCV to her infant is approximately 4%8% per pregnancy . Transmission occurs during pregnancy or childbirth, and no prophylaxis is available to protect the newborn from infection. The risk is significantly higher if the mother has a high HCV viral load, or is coinfected with HIV with which the rate of transmission ranges from 8%15% . Most infants infected with HCV at birth have no symptoms.
Should a woman with hepatitis C be advised against breastfeeding?
When should children born to HCV-infected mothers be tested to see if they were infected at birth?
Hepatitis C Testing Strategy
The goal of hepatitis C screening is to identify persons who are currently infected with HCV. Hepatitis C testing should be initiated with a U.S. Food and Drug Administration -approved anti-HCV test. Persons who test anti-HCV positive are either currently infected or had past infection that has resolved naturally or with treatment. Immunocompetent persons without hepatitis C risks who test anti-HCV negative are not infected and require no further testing. Persons testing anti-HCV positive should have follow-up testing with an FDA-approved nucleic acid test for detection of HCV RNA. NAT for HCV RNA detection determines viremia and current HCV infection. Persons who test anti-HCV positive but HCV RNA negative do not have current HCV infection. CDC encourages use of reflex HCV RNA testing, in which specimens testing anti-HCV positive undergo HCV RNA testing immediately and automatically in the laboratory, using the same sample from which the anti-HCV test was conducted. Hepatitis C testing should be provided on-site when feasible.
You May Like: What Type Of Hepatitis Can Be Cured
Test Results Are Available At The Same Appointment Which Can Reduce Loss To Follow
When clients are able to have a blood sample collected and learn their test result within the same encounter, it can be possible to obtain a swift diagnosis, and the emotional burden associated with having to wait for the results can be alleviated.17 This can also simplify the testing process and reduce the number of clinic visits or interactions with service providers related to hepatitis C care that a client will have to have.1,9,10,17,22,23
Diagnosis And Hepatitis C Elimination
In one report, the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine explored the feasibility of hepatitis C elimination and concluded that hepatitis C could be eliminated as a public health problem in the United States, but that substantial obstacles exist . In another report, specific actions were recommended to achieve elimination considering information, interventions, service delivery, financing, and research . These reports were the culmination of decades of progress in the development of HCV infection diagnostic and therapeutic tools.
Also Check: What Is Chronic Viral Hepatitis C
Don’t Miss: Best Diet For Hepatic Steatosis
Adverse Effects Of Treatment
Adherence to treatment remains a major factor influencing the rates of sustained virologic response.33,42 Discontinuation of therapy because of adverse events is common and has been reported in up to one third of patients. Approximately 50 to 60 percent of patients may exhibit self-limited influenza-like symptoms with interferon-based therapy.2 Effective management of treatment-related adverse events is essential to improve adherence to treatment therefore, patients should be monitored closely for hematologic, renal, and thyroid abnormalities. Approximately 30 percent of patients undergoing treatment for HCV infection experience depression, emotional lability, or anger, but treatment is rarely associated with suicidal ideation or hallucinations.43 Treatment for HCV infection is contraindicated in persons with uncontrolled major depression.32 A recent randomized trial found that the overall adverse effects of pegylated interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin and pegylated interferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin were similar.40 Adverse effects of pegylated interferon and ribavirin for the treatment of HCV infection are listed in Table 8.32
Adverse Effects of Pegylated Interferon and Ribavirin for the Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Information from reference 32.
Adverse Effects of Pegylated Interferon and Ribavirin for the Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Information from reference 32.
What Are Cdcs Hepatitis C Screening Recommendations
All patients 18 years and older should be screened for hepatitis C at least once in their lifetime, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is < 0.1%.
Patients with recognized exposures should be tested for hepatitis C regardless of age or setting prevalence, and regular periodic testing should continue as long as risk persists.
Two tests need to be done to discover if you have hepatitis C:
- Antibody test: Which establishes whether you have ever been exposed to the hepatitis C virus.
- PCR test: Which establishes whether the virus is still active and needs treating.
The two tests can often be done from one sample of blood which means you may only need to provide the sample once. Both tests can then be done on your sample at the laboratory. However, some services will perform one test and then call you back for a further blood sample to perform the second test.
Antibody test
A hepatitis C antibody test is the first test undertaken. This is to determine whether you have ever been exposed to the hepatitis C virus. It works by testing for the presence of antibodies to the virus generated by your immune system. If you receive a negative hepatitis C antibody test but have been experiencing symptoms or have been recently exposed to hepatitis C, then you are likely to be advised to have a second test.
PCR test
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis C Be Cured Without Treatment
Uspstf Hcv Screening Recommendations
In March 2020, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force issued updated recommendations regarding screening for HCV. The USPSTF now recommends routine screening for all adults in the United States 18-79 years of age, including pregnant women . The 2020 USPSTF recommendation for HCV screening was categorized as a grade B recommendation, which means that the USPSTF concludes with moderate certainty that screening for HCV in adults 18-79 years of age has substantial net benefit and that health care providers should offer this service . The USPSTF notes that most adults will require HCV screening only once, but those with ongoing risk of acquiring HCV will need periodic screening. For persons younger than 18 or older than 79 years of age, screening for HCV can be considered if the individual is considered at high risk for having acquired HCV. The 2020 USPSTF recommendations for HCV screening is clearly a major change from the prior 2013 USPSTF recommendations to screen adults born during 1945-1965 and those with known risk.
What Is Being Tested
Hepatitis C is a virus that causes an infection of the liver that is marked by liver inflammation and damage. Hepatitis C tests are a group of tests that are performed to diagnose hepatitis C infection and to guide and monitor treatment of the infection.
Hepatitis C tests include:
Hepatitis C is one of five viruses identified so far, including A, B, D, and E, that are known to cause hepatitis.
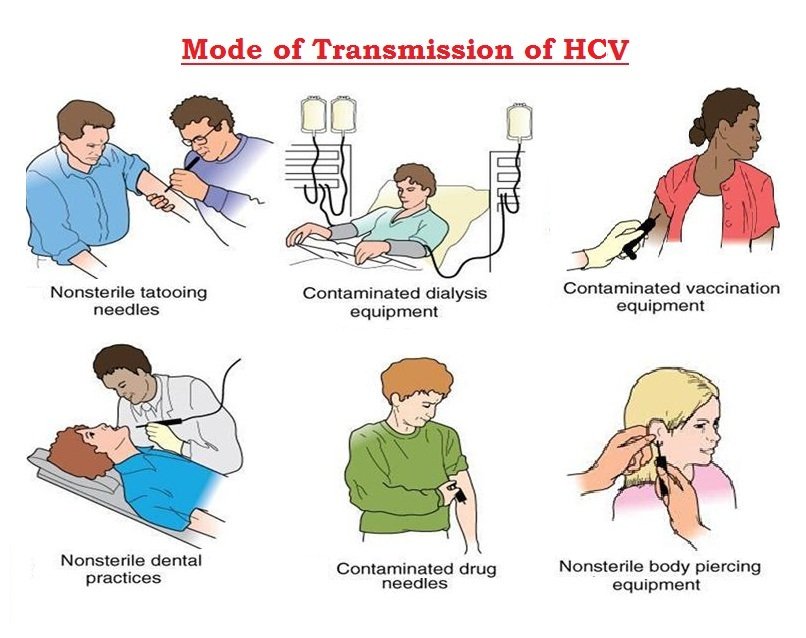
HCV is spread when contaminated blood enters the body, primarily though sharing needles and syringes during IV drug use. HCV is spread less commonly by sharing personal items contaminated with blood , through sex with an infected person, needlestick injuries to healthcare workers, unregulated tattooing, and from mother to baby during pregnancy and childbirth. Before tests for HCV became available in the 1990s, HCV was often transmitted by blood transfusions. Currently, there is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C.
Read Also: What Organ Does Hepatitis C Affect
You May Like: Hepatitis A What Is It
Other Things To Know:
- After a successful course of treatment for hepatitis C, the hepatitis C antibody remains detectable, but the hepatitis C RNA will be undetectable.
- If you plan to donate blood, you will be tested for the hepatitis C antibody and will be turned away even if you do not have an active infection.
- Any patient with a positive test result for the hepatitis C antibody should have additional tests to determine whether or not the virus is still active.
When Should I Get Hepatitis C Testing
When used for early detection in patients without symptoms of hepatitis C, screening is recommended at least once for all adults aged 18 years or older, except in locations with very low prevalence of HCV. Screening is also recommended during pregnancy and for patients of any age with risk factors for HCV infection. In patients with risk factors, periodic screening is recommended for as long as risk factors persist.
Risk factors for HCV include:
- Current or past injectable drug use
- Having a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- Receiving kidney dialysis
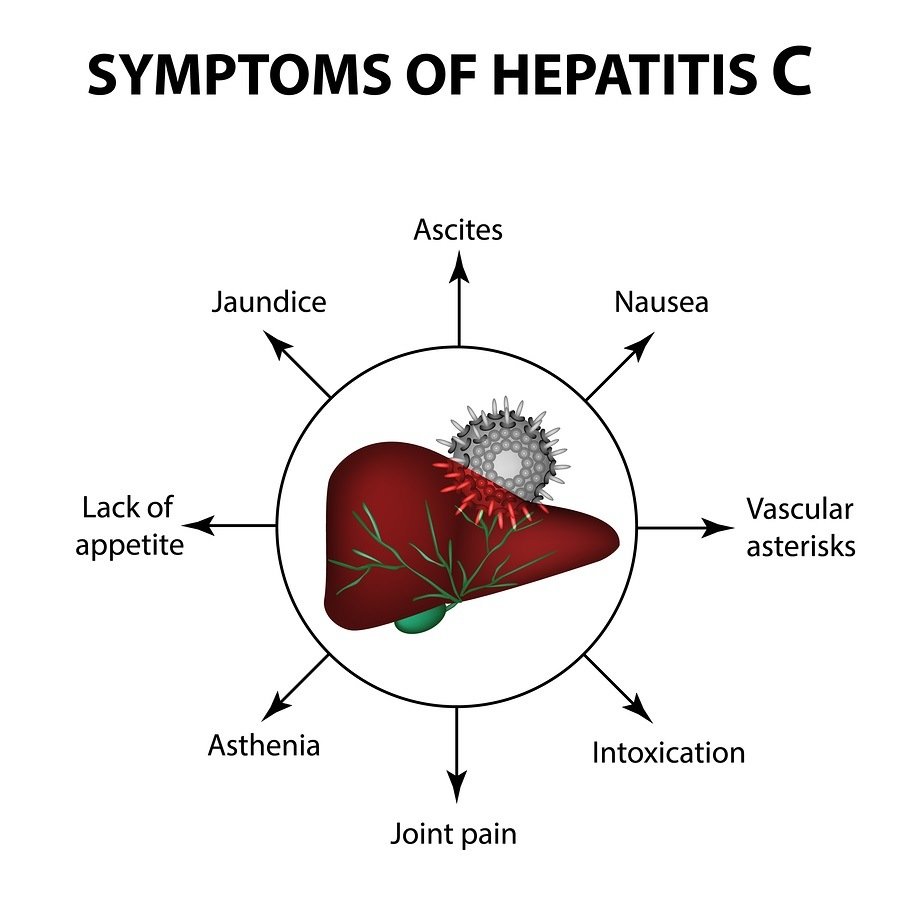
- Pain in the abdomen or joints
- Nausea, vomiting, or loss of appetite
- Jaundice or yellowish skin and eyes
Hepatitis C testing may also be performed when liver tests are abnormal or when diagnosing the cause of existing liver damage.
Also Check: What Is Hepatic Metastatic Disease
Read Also: The Signs Of Hepatitis C
Limitations Of Using Only Risk
A prior study that analyzed effectiveness of risk-based HCV screening found that 45 to 85% of adults with chronic HCV infection in the United States were unaware of their HCV infection status. Problems with using risk-based screening were highlighted in the Chronic Hepatitis Cohort Study survey of 4,689 persons living with HCV infection who were asked about their choice of location and reason for their HCV testing. The study analyzed data from 2006-2010 that revealed that 60% of persons living with HCV had their initial testing ordered at a physician’s office and 45% underwent testing because of clinical indications related to liver disease fewer than 25% of the persons with HCV infection had identifiable risk factors for acquiring HCV that would have prompted testing using the 1998 CDC Risk-Based HCV Screening Recommendations. Notably, 78% of those diagnosed with HCV were born during the time period of 1945 to 1965.