Hepatitis B Vaccine On The Nhs
A hepatitis B-containing vaccine is provided for all babies born in the UK on or after 1 August 2017. This is given as part of the 6-in-1 vaccine.
Hospitals, GP surgeries and sexual health or GUM clinics usually provide the hepatitis B vaccination free of charge for anyone at risk of infection.
GPs are not obliged to provide the hepatitis B vaccine on the NHS if youâre not thought to be at risk.
GPs may charge for the hepatitis B vaccine if you want it as a travel vaccine, or they may refer you to a travel clinic for a private vaccination. The current cost of the vaccine is around £50 a dose.
Recommended Reading: How Can I Catch Hepatitis
What Is Hepatitis B Virus
Hepatitis B virus attacks the liver. Hepatitis B virus infections are known as the “silent epidemic” because many infected people don’t experience symptoms until decades later when they develop hepatitis , cirrhosis , or cancer of the liver . Every year in the United States about 22,000 new hepatitis B infections occur and about 2,000 people die from their infections.
Study Design And Subjects
In 2001, healthy adolescents aged between 11 and 15 years were enrolled into a single-blind, randomised, multi-country study conducted in Belgium, Australia and Ukraine. The subjects received either two doses of Engerix-B Adult formulation following a 0, 6 months schedule or three doses of Engerix-B Paediatric formulation following a 0, 1, 6 months schedule . Group HBV_2D additionally received an injection of physiological saline as placebo at second vaccination time point to maintain the blinding. The vaccines were administered as deep intramuscular injections in the deltoid region of the arm .
The study was conducted respecting the Good Clinical Practice guidelines and Declaration of Helsinki. Two of the four centres were eliminated from the evaluation of anamnestic response to the challenge dose the investigator from the study centre was not confident that their team would be able to recruit a sufficient number of subjects and therefore did not participate in this phase of the study while the subjects at another study centre were excluded from the primary analysis due to GCP non-compliance.
You May Like: Chronic Vs Acute Hepatitis C
Persons With Chronic Diseases
Refer to Immunization of Persons with Chronic Diseases in Part 3 for additional general information about vaccination of people with chronic diseases.
Chronic renal disease and patients on dialysis
People with chronic renal disease may respond sub-optimally to HB vaccine and experience more rapid decline of anti-HBs titres, and are therefore recommended immunization with a higher vaccine dose. Individuals undergoing chronic dialysis are also at increased risk for HB infection. In people with chronic renal disease anti-HBs titre should be evaluated annually and booster doses using a higher vaccine dose should be given as necessary.
Neurologic disorders
People with conditions such as autism spectrum disorders or demyelinating disorders should receive all routinely recommended immunizations, including HB-containing vaccine.
Chronic liver disease
HB immunization is recommended for non-immune persons with chronic liver disease, including those infected with hepatitis C, because they are at risk of more severe disease if infection occurs. Vaccination should be completed early in the course of the disease, as the immune response to vaccine is suboptimal in advanced liver disease. Post-immunization serologic testing may be used to confirm vaccine response.
Non-malignant hematologic disorders
Persons with bleeding disorders and other people receiving repeated infusions of blood or blood products are considered to be at higher risk of contracting HB and should be offered HB vaccine.
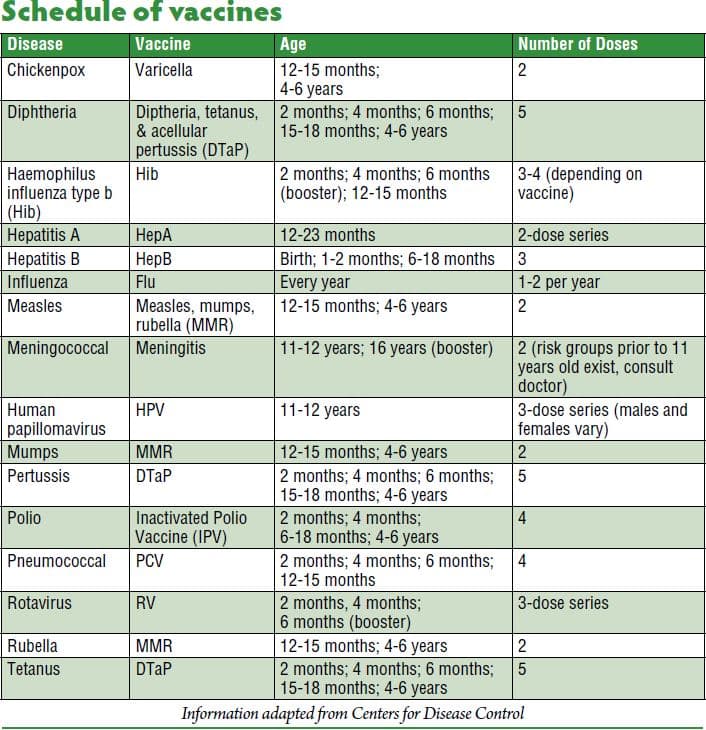
Us Infant Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
Since 1991, ALL medically stable infants with a birth weight of at least 2,000 g in the U.S. are recommended to receive the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth. The additional 2 doses are given at 1 month and 6 months of age.
4-Dose Vaccine Combination Series for Infants
Combination vaccines, such as the pentavalent and hexavalent vaccines, include protection against 5 or 6 diseases, including hepatitis B. The first shot is usually given at 6 weeks of age, but in order to protect infants from hepatitis B beginning at birth, a monovalent or single dose of the hepatitis B vaccine is also recommended within 24 hours of birth. The hepatitis B vaccine series can then be completed with the pentavalent or hexavalent vaccine with the recommended schedule.
Read Also: Hepatitis Panel Acute W/reflex To Confirmation
Hepatitis A And B: Diseases Of The Liver
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver, most often caused by a viral infection. There are three common types of hepatitis caused by viruses: hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. Vaccines have been developed that protect people from contracting hepatitis A and B. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C.
Hepatitis A and hepatitis B can be spread from person to person, although in different ways. They have similar symptoms, which include abdominal pain, fever, fatigue, joint pain, and jaundice .
Over the last 20 years, there has been a 90% decrease in cases of hepatitis A and an 80% decrease in hepatitis B cases in the U.S. Health experts believe that immunization efforts have led to this drop in rates of infection.
Hepatitis B Vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide
For health professionals
Last partial content update : May 2022
The footnotes in and the accompanying text description for the figure have been revised to align with the corresponding figure in Protocole d’immunisation du Québec, 5e édition from which it was adapted.
Last complete chapter revision :
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatic Steatosis Of The Liver
Who Should Receive The Hepatitis B Vaccine
For most people, the hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective. About 90% of people who receive three vaccine doses are protected against hepatitis B for over 30 years.
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends the hepatitis B vaccine for the following groups:
- All babies, starting just after birth
- Children and adolescents under 19 years old
- Adults ages 1959 who have not previously completed vaccination
- Adults ages 60 and over with a high risk of contracting HBV
Adults ages 60 and over who do not have any hepatitis B risk factors can receive the hepatitis B vaccine, but it is optional.
Hepatitis B spreads when the bodily fluids of an infected person enter another person’s body. Sexual contact is one way it can be spread. A person with HBV can spread it to their baby during childbirth. Other ways in which HBV may be transmitted include:
- Sharing medical equipment, whether at home or in a hospital setting, with a person who has an HBV infection
- Sharing syringes with a person who has hepatitis B, such as during injection drug use or at-home piercing or tattooing
- Sharing personal items, such as razors or toothbrushes, with someone who has hepatitis B
- Coming into contact with the sores or blood of a person who has hepatitis B
I Am A Healthcare Worker Who Did Not Develop Hepatitis B Antibodies After Immunization What Should I Do
Two versions of hepatitis B vaccine are available. One, called Heplisav-B, contains a novel adjuvant that was not present in previous versions used by adults . Some people did not respond to the older version hepatitis B vaccine. In fact, in a group of adults younger than 40 years of age who received two doses of the older version vaccine 75 of 100 were protected. Following the third dose, this number increased to 90 of 100. However, people older than 40 years of age were less likely to respond to the vaccine with increasing age. On the other hand, 90 to 100 of 100 adults 18 years of age and older respond to Heplisav-B, which was approved for use in 2018.
About 5-10 of every 100 children and adults younger than 40 years of age do not respond to the third dose of the hepatitis B vaccine. Some of these people will be recommended to get vaccinated again. About 5 of 100 people will still not respond after getting all recommended doses of both series. Note that children younger than 18 years of age cannot get Heplisav-B.
If the people who do not respond to vaccination are determined not to have chronic hepatitis B, they will be reliant on taking precautions to reduce the chance of exposure and relying on those around them for protection. In other words, these people will be reliant on herd immunity.
Also Check: How Did I Get Hepatitis C
Indications For Hepatitis B Vaccine
HepB vaccine is a routine childhood vaccination .
HepB vaccine also is indicated for all adults aged 19 through 59 years who have not been previously vaccinated.
HepB vaccine also is indicated for adults aged 60 years and older who have not been previously vaccinated and who have any of the following:
-
A desire for protection from hepatitis B
-
A sexually active lifestyle in people who are not in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship
-
Need for evaluation or treatment of a sexually transmitted infection
-
Current or recent use of illicit injection drugs
-
Sex between men
-
Employment in which workers may be exposed to blood or other potentially infectious body fluids
-
Diabetes in people < 60 years and sometimes in those 60 years
-
End-stage renal disease
-
A chronic liver disorder
-
Household contact and/or sexual contact with people who are positive for hepatitis B surface antigen
-
Travel to endemic areas
-
Time spent in correctional facilities or in facilities that provide sexually transmitted infection treatment, HIV testing and treatment, drug abuse treatment and prevention services, services to injection-drug users or men who have sex with men, or care for patients with developmental disabilities or with end-stage renal disease
The combination HepA and HepB vaccine can be used in people 18 years who have indications for either hepatitis A or hepatitis B vaccine and who have not been previously vaccinated with one of the vaccine components.
Persons New To Canada
Health care providers who see persons newly arrived in Canada should review the immunization status and update immunization for these individuals, as necessary. In many countries outside of Canada, HB vaccine is in limited use.
All persons from a country that is endemic for HB should be assessed and vaccinated against HB if not immune and not infected. Individuals born in developing countries are more likely to be carriers of HB, necessitating vaccination of their sexual and household contacts based on review of their serologic test results. HB vaccine is recommended for all household contacts whose families have immigrated to Canada from areas in which there is a high prevalence of HB and who may be exposed to HB carriers through their extended families or when visiting their country of origin.
Children adopted from countries in which there is a high prevalence of HB infection should be screened for HBsAg and, if positive, household or close contacts in the adopting family should be immunized before adoption or as soon as possible thereafter. Adults going to pick-up children from these countries should be vaccinated before departure. Refer to Immunization of Persons New to Canada in Part 3 for additional information.
You May Like: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Saliva
What Other Drugs Interact With Hepatitis B Vaccine
If your doctor has directed you to use this medication, your doctor or pharmacist may already be aware of any possible drug interactions and may be monitoring you for them. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicine before checking with your doctor, health care provider, or pharmacist first.
- Severe Interactions of Hepatitis B Vaccine include:
This information does not contain all possible interactions or adverse effects. Therefore, before using this product, tell your doctor or pharmacist of all the products you use. Keep a list of all your medications with you, and share this information with your doctor and pharmacist. Check with your health care professional or doctor for additional medical advice, or if you have health questions, concerns, or for more information about this medicine.
Babies And Hepatitis B Vaccination

Pregnant women have a routine blood test for hepatitis B as part of their antenatal care.
Babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B need to be given a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of their birth, followed by further doses at 4, 8, 12 and 16 weeks of age, plus a final dose when they’re 1 year old.
Babies of mothers identified by the blood test as particularly infectious might also be given an injection of HBIG at birth on top of the hepatitis B vaccination to give them rapid protection against infection.
All babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B should be tested at 1 year of age to check if they have become infected with the virus.
Read Also: How Does Someone Contract Hepatitis C
What To Do If You Miss A Scheduled Dose
The recommended schedule for the HBV vaccine follows a three-dose pattern, with all doses complete within 6 months. The good news is that if you miss a dose, you dont need to start the series of shots all over.
If you missed getting the second dose 1 month after the first, make an appointment as soon as possible. If you miss the third dose, you should also try to get it as quickly as possible. Keep in mind that the second and third doses
For Adults And Children
This vaccine schedule involves three doses within 2 months, followed by a booster dose at 1 year.
The initial accelerated doses provide immediate protection from HBV, and the booster dose helps provide long-term protection.
Below is the accelerated vaccination schedule approved for both adults and children:
| Vaccine series | |
|---|---|
| 2 months after the first dose | 1 year after the first dose |
Recommended Reading: Can You Catch Hepatitis C Sexually
Who Should Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
All infants should get their first dose of hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth and will usually complete the series at 6 months of age.
All unvaccinated children and adolescents younger than 19 years of age should also get vaccinated.
All adults 19 through 59 years of age are recommended to get vaccinated.
Adults 60 years and older with risk factors should get vaccinated. Risk factors include:
- People whose sex partners have hepatitis B
- People who live with someone with hepatitis B
- Sexually active people who are not in a long-term relationship
- People getting evaluated or treated for a sexually transmitted infection
- Men who have sex with men
- People who share needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment
- Health care and public safety workers at risk for exposure to blood or body fluids
- People with chronic liver disease, who are on dialysis, have HIV infection, or hepatitis C infection
- People with diabetes
- Developmentally disabled persons in long-term care facilities
- People in prison or jail
- Travelers to areas with high rates of hepatitis B
Who Is At Higher Risk For Hepatitis B
Although everybody can acquire hepatitis B, the following groups are more susceptible:
Also Check: What Are Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
How Common Is Hepatitis B
One U.S. study following trends in hepatitis B infection over a three-year periodfound that 4.3% of the population had a past or present HBV infection.
Estimates suggest that about 240 million people around the world have chronic hepatitis B. Up to 1.89 million people in the United States have a chronic HBV infection.
The Hepatitis B Vaccine And Immunosuppressants
If you are taking or about to start taking a medication that suppresses your immune response, let your healthcare provider know. Immunosuppressants may make certain vaccines less effective. Your healthcare provider may recommend that you get the hepatitis B vaccine at a particular time during your course of medication.
Don’t Miss: How Can Hepatitis Be Transmitted
Adjuvants In Recombinant Hbv Vaccines
Modern recombinant vaccines are very refined and contain less antigenic components . As a result, adding adjuvants is essential to induce a better immune response. Among the adjuvants, aluminum salts are widely used. These salts can form insoluble particles, cause retention and release of vaccine antigens gradually like a depot, and thereby induce innate immunity.14 The various adjuvant systems used with recombinant HBV vaccines are AS01B , AS01E , AS02A , AS02B , AS02V , AS03 , AS04 , etc.14
Dont Miss: How To Reduce Hepatitis B Viral Load Naturally
Why Should I Vaccinate My Newborn Child If I Know That I Am Not Infected With Hepatitis B Virus
Before the hepatitis B vaccine, every year in the United States about 18,000 children were infected with hepatitis B virus by the time they were 10 years old. This statistic is especially important because people are much more likely to develop liver cancer or cirrhosis if they are infected early in life, rather than later in life .
About 9,000 of the 18,000 children infected in the first 10 years of life caught the virus from their mother during birth. However, many young children didn’t catch the disease from their mother. They caught it from either another family member or someone else who came in contact with the child. Because hepatitis B can be transmitted by relatively casual contact with items contaminated with the blood of an infected person, and because many people who are infected with hepatitis B virus don’t know that they have it, it is virtually impossible to be “careful enough” to avoid this infection.
For these reasons, all young children are recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccine. The best time to receive the first dose is right after birth. This will ensure that the child will be protected as early as possible from catching hepatitis B from people who dont know that they are infected with the virus.
Listen to Dr. Offit explain why newborns get the hepatitis B vaccine by watching this short video, part of the series Talking About Vaccines with Dr. Paul Offit.
Read Also: What Is The Vaccine For Hepatitis B