How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
There are three main ways to diagnose HBV infection. They include:
- Blood tests: Tests of the blood serum shows how your bodys immune system is responding to the virus. A blood test can also tell you if you are immune to HBV.
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to show the size and shape of your liver and how well the blood flows through it.
- Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis.
The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit. Often, people whove become infected first learn they have hepatitis B when they go to donate blood. Blood donations are routinely scanned for the infection.
The virus can be detected within 30 to 60 days of infection. About 70% of adults with hepatitis B develop symptoms, which tend to appear an average of 90 days after initial exposure to the virus.
Key Facts About Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis B is a viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic liver disease, including cancer.
- The virus is transmitted through contact with the blood or other body fluids of an infected person.
- About 2 billion people worldwide have been infected with the virus and about 370 million live with chronic infection and liver damage.
- Two thirds of those infected with HBV are unaware of their infection
- An estimated 800 000 people die each year due to HBV induced liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Despite there being a vaccine, globally HBV kills one person every minute
- About 25% of adults who become chronically infected during childhood later die from liver cancer or cirrhosis caused by the chronic infection.
- The hepatitis B virus is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV.
- Hepatitis B is preventable with a safe and effective vaccine.
Detection Of Antiviral Resistance
National and international surveillance is performed by the CDC to determine effectiveness of the current FDA-approved antiviral flu drugs. Public health officials use this information to make current recommendations about the use of flu antiviral medications. further recommends in-depth epidemiological investigations to control potential transmission of the resistant virus and prevent future progression. As novel treatments and detection techniques to antiviral resistance are enhanced so can the establishment of strategies to combat the inevitable emergence of antiviral resistance.
Don’t Miss: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Hepatic
How Do People Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C virus is found in the blood of people with HCV infection. It enters the body through blood-to-blood contact.
Until reliable blood tests for HCV were developed , people usually got hepatitis C from blood products and blood transfusions. Now that blood and blood products are tested for HCV, this is no longer the typical means of infection.
Currently, people usually get hepatitis C by sharing needles for injection drug use. An HCV-infected woman can pass the infection to her baby during birth. It is also possible to get hepatitis C from an infected person through sexual contact, an accidental needlestick with a contaminated needle, or improperly sterilized medical, acupuncture, piercing, or tattooing equipment.
Read Also: Is Chronic Hepatitis C Curable
What Are Clinical Trials For Hepatitis B
Clinical trialsand other types of clinical studiesare part of medical research and involve people like you. When you volunteer to take part in a clinical study, you help doctors and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future.
Researchers are studying many aspects of hepatitis B, such as
- progression of hepatitis B and long-term outcomes
- new treatments for hepatitis B
- prevention of reactivated or worsening hepatitis B in people receiving cancer treatment
Also Check: Is A Vaccine Available For Hepatitis B
Hiv And Hbv Coinfection
About 2% of people with HIV in the United States are coinfected with HBV both infections have similar routes of transmission. People with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HBV infection. All people with HIV are recommended to be tested for HBV, and if susceptible, are further recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccination or, if chronically infected, evaluated for treatment to prevent liver disease and liver cancer. For more information about HIV and HBV coinfection, visit HIV.govâs pages about hepatitis B and HIV coinfection.
Hepatitis B World Prominence
Hepatitis B virus causes the disease Hepatitis. Hepatitis is considered to be the leading cause of liver cancer worldwide . Hepatitis B virus can be found in almost every region of the world but is most prevalent in countries where the virus is endemic. HBV is endemic in some countries located in Asia, Africa, South America, and the Caribbean.
Approximately two billion people have been infected with HBV which means almost 1 out of 3 people have been infected. Every year an estimated 1.5 million people will become newly infected and roughly 10% of those individuals will go undiagnosed. Every year, an estimated 820,000 people die from Hepatitis B infection and related HBV complications.
The spread of Hepatitis B virus in the western world occurs most often through sexual intercourse or needle sharing by intravenous drug users . IVDU show the highest rate of HBV infection in Europe and North America. There are also higher rates of Hepatitis B infection among men who have sex with men . Risk of being infected with HBV increases with having multiple sex partners.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis B A Virus
Cost Of Hepatitis C Medicines
The newer direct-acting antiviral medicines for hepatitis C can be costly. Most government and private health insurance prescription drug plans provide some coverage for these medicines. Talk with your doctor about your health insurance coverage for hepatitis C medicines.
Drug companies, nonprofit organizations, and some states offer programs that can help pay for hepatitis C medicines. If you need help paying for medicines, talk with your doctor. Learn more about financial help for hepatitis C medicines.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B From
Viral Hepatitis Definition And Overview
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Many illnesses and conditions can cause inflammation of the liver, for example, drugs, alcohol, chemicals, and autoimmune diseases. Many viruses, for example, the virus causing mononucleosis and the cytomegalovirus, can inflame the liver. Most viruses, however, do not attack primarily the liver the liver is just one of several organs that the viruses affect. When most doctors speak of viral hepatitis, they are using the definition that means hepatitis caused by a few specific viruses that primarily attack the liver and are responsible for about half of all human hepatitis. There are several hepatitis viruses they have been named types A, B, C, D, E, F , and G. As our knowledge of hepatitis viruses grows, it is likely that this alphabetical list will become longer. The most common hepatitis viruses are types A, B, and C. Reference to the hepatitis viruses often occurs in an abbreviated form The focus of this article is on these viruses that cause the majority of human viral hepatitis.
Hepatitis viruses replicate primarily in the liver cells. This can cause the liver to be unable to perform its functions. The following is a list of major functions of the liver:
You May Like: What Does Hepatitis C Mean
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Hepatitis D And E
Hepatitis B: How Does It Spread
You can get it through contact with the blood or body fluids of an infected person. In the U.S., its most often spread through unprotected sex. Its also possible to get hepatitis B by sharing an infected persons needles, razors, or toothbrush. And an infected mother can pass the virus to their baby during childbirth. Hepatitis B is not spread by hugging, sharing food, or coughing.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine Drug Information
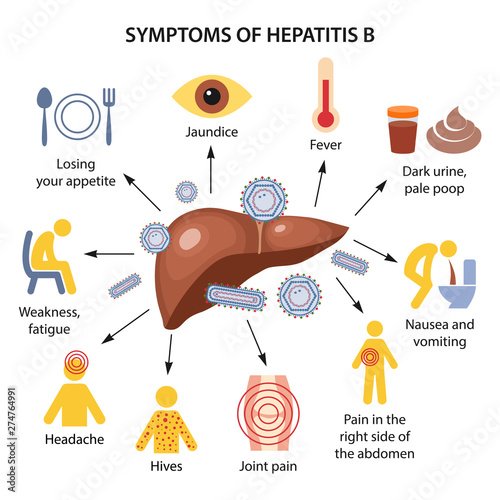
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Some people who are infected with the hepatitis B virus have mild, flu-like symptoms and some do not become sick at all. Children who are infected are less likely to have an illness or get sick after getting hepatitis B than adults.
In more severe cases, hepatitis B can cause:
- Loss of appetite.
- Pain in the joints.
Normally, these health problems disappear in a few weeks, but even when the person feels much better, they may still be infectious.
Most adults who become infected with the hepatitis B virus recover completely and do not become infected again. A few people become very ill in the time just after infection and need to go to hospital some may even die.
You May Like: What Test Is Done For Hepatitis C
What Is Chronic Hepatitis B
Doctors refer to hepatitis B infections as either acute or chronic:
- An acute HBV infection is a short-term illness that clears within 6 months of when a person is exposed to the virus.
- A person who still has HBV after 6 months is said to have a chronic hepatitis B infection. This is a long-term illness, meaning the virus stays in the body and causes lifelong illness. An estimated 850,000 to more than 2 million people in the U.S. have chronic HBV.
The younger someone is when infected, the greater the chances for chronic hepatitis B.
What Are The Complications Of Hepatitis B

The course of hepatitis B infection depends mostly on the age at which a person is infected.
People infected as infants are likely to develop long term infection and can get complications such as scarring of the liver or liver cancer. Infants have a 9 in 10 chance and children have a 3 in 10 chance of developing a chronic, lifelong infection.
People infected as teenagers or adults are likely to become unwell with symptoms , but have a smaller chance of developing a chronic infection. Others develop a silent infection, without any symptoms.
Most people infected as adults clear the virus from the body within 6 months. They develop immunity to future hepatitis B infections and do not develop long-term liver damage.
However, approximately 1 in 20 adults cannot clear the virus and develop chronic hepatitis B. They are at risk of developing complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer in the longer term.
You May Like: How To Control Hepatitis C
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis B
Blood tests are available to determine if you are or have been infected with hepatitis B. It may take 6 months from the time of infection before a blood test can detect antibodies to hepatitis B, so follow-up testing may be required. During this 6-month period, until you know whether you are infected or not, take action to prevent potential infection of other people.
There are also tests that can assess liver damage from hepatitis B. The interpretation of these tests can be complicated and specialist advice is needed, so talk to your doctor.
All pregnant women are tested for hepatitis B. If you are found to have chronic hepatitis B, your doctor can help reduce the risk of transferring the infection to your newborn child.
Whats The Prognosis For Hepatitis B
Your doctor will know youâve recovered when you no longer have symptoms and blood tests show:
- Your liver is working normally.
- You have hepatitis B surface antibody.
But some people don’t get rid of the infection. If you have it for more than 6 months, youâre whatâs called a carrier, even if you donât have symptoms. This means you can give the disease to someone else through:
- Unprotected sex
- Contact with your blood or an open sore
- Sharing needles or syringes
Doctors donât know why, but the disease does go away in a small number of carriers. For others, it becomes whatâs known as chronic. That means you have an ongoing liver infection. It can lead to cirrhosis, or hardening of the organ. It scars over and stops working. Some people also get liver cancer.
If youâre a carrier or are infected with hepatitis B, donât donate blood, plasma, body organs, tissue, or sperm. Tell anyone you could infect — whether itâs a sex partner, your doctor, or your dentist — that you have it.
Show Sources
CDC: âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for Health Professionals,â âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Mayo Clinic: âHepatitis B.â
UpToDate: âHepatitis B virus: Screening and diagnosis.â
CDC.
HealthyPeople.gov: âHepatitis B in Pregnant Women: Screening.â
Annals of Internal Medicine: âScreening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.â
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Cost Cvs
Ethics Approval And Consent To Participate
Ethical approval with a referenced protocol number LHREC/2020/07 to conduct the study was granted by Lubaga hospital research ethical review committee following thorough review to ensure adherence to safety and protection of the rights of human subjects. All the study methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations . The aim, benefits and risks of the study were explained to the participants before requesting them to participate which they had to consent . Informed consent was obtained from each participant employed for the study.
Who Should Be Tested
Testing for hepatitis A is not routinely recommended.
CDC recommends hepatitis B testing for:
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- People with elevated ALT levels
- Infants born to HBV-infected mothers
CDC recommends hepatitis C testing for:
- All adults aged 18 years and older
- All pregnant women during each pregnancy
- About 24,900 new infections each year
- About 22,600 new infections in 2018
- Estimated 862,000 people living with hepatitis B
- About 50,300 new infections in 2018
- Estimated 2.4 million people living with hepatitis C
You May Like: What Virus Causes Hepatitis B
Also Check: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Canine Hepatic
Reduce Your Chance Of Infection
You can reduce your chance of hepatitis B infection by
- not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- wearing gloves if you have to touch another persons blood or open sores
- making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools
- not sharing personal items, such as toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- using a latex or polyurethane condom during sex
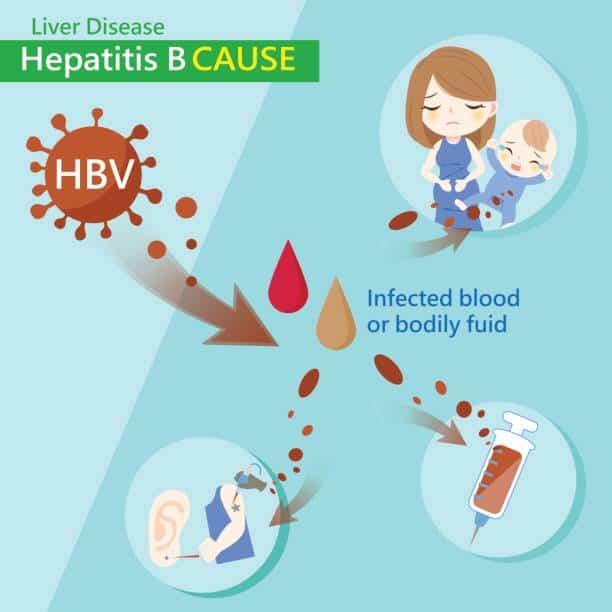
Causes Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is spread through contact with blood that contains the hepatitis B virus. If infected blood or body fluids enter another persons bloodstream, that person may become infected.
The time from exposure to the hepatitis B virus to the appearance of the illness is 45 to 180 days.
Risky activities that can cause infection include:
- Sharing unsterile or unclean equipment for injecting drugs.
- Piercing the skin with equipment that is not properly cleaned, disinfected and sterilised.
- Sharing razor blades or toothbrushes.
- Coming into contact with infected blood through open cuts or the mucous membranes of another person.
- Having unprotected sex , especially if there is blood present.
Mothers who have hepatitis B can pass the virus to their babies or children at the time of birth or after birth. If the newborn baby is quickly immunised with 2 vaccines, they can be protected from getting hepatitis B.
All blood and blood products produced for medical purposes in Australia are carefully screened for hepatitis B and other blood-borne viruses. The risk of getting infected with hepatitis B from a blood transfusion is extremely low .
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis A And B And C
How Are Hepatitis B And C Diagnosed
Hepatitis B is diagnosed by a series of blood tests. The test may show an ongoing infection or antibodies that indicate that the patient is protected against hepatitis B. In patients who have a positive screening test that suggests the possibility of ongoing infection, further testing is done to determine the levels of the virus in the bloodstream.
Hepatitis C is diagnosed via a blood test called a Hepatitis C Antibody Test. A positive result means that hepatitis C antibodies are present in the blood. But a positive antibody test doesnt necessarily mean a person has hepatitis C. A further blood test is needed to confirm the diagnosis. This second blood test quantifies the amount of the virus or the viral load in the liver and the bloodstream.
How Do Doctors Treat The Complications Of Hepatitis B
If chronic hepatitis B leads to cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Doctors can treat the health problems related to cirrhosis with medicines, minor medical procedures, and surgery. If you have cirrhosis, you have an increased chance of liver cancer. Your doctor may order blood tests and an ultrasound or another type of imaging test to check for liver cancer.
If chronic hepatitis B leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does A Person Live With Hepatitis C
What If I Am Pregnant
It’s recommended that all pregnant women have a blood test for hepatitis B in early pregnancy.
If you have hepatitis B and are pregnant, treatments can reduce the risk of transmission of hepatitis B to the baby.
If you have hepatitis B, it is important to protect others from infection.
Important ways to prevent the spread of hepatitis B include:
- vaccination of all your close contacts
- practise safe sex until your sexual contacts are fully vaccinated and immune
- do not donate blood, organs or body tissue
- do not allow your blood to contact another person
- inform healthcare workers
- if your work involves potential for your blood or other body fluid to spread to other people, discuss your situation with your doctor
The hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective in protecting against hepatitis B infection, providing protection in 95 in 100 vaccinated people.
In Australia, hepatitis B vaccination is part of the standard immunisation schedule for all newborn babies and infants. It’s also recommended for adults who are at high risk of exposure, people who are immunosuppressed or have other liver disease. People in these risk groups should be vaccinated against hepatitis B. Talk to your doctor about your level of risk and whether hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for you.
If you werent vaccinated against hepatitis B as a child, or if youre not sure whether you are vaccinated, talk to your doctor about whether you need a catch-up vaccine.