Prevention Of Hepatitis D
- Exclusion of people with hepatitis D from childcare, preschool, school and work is not necessary.
- Hepatitis B vaccination will prevent infection with hepatitis D. Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for infants and those at a higher risk of acquiring hepatitis B infection and/or at higher risk of severe infection. Vaccination for hepatitis B, when given to newborn infants, is effective in preventing hepatitis D .
- Any open sores, cuts or abrasions should be covered with waterproof dressings
- Practice safer sex use condoms consistently and correctly.
- Injecting drug users should never share injecting equipment.
- If required to handle blood or body fluids, the use of standard precautions will reduce the risk of spreading hepatitis D virus.
- Infected health care workers must comply with the requirements of their professional boards.
How Hcv Is Spread
The hepatitis C virus is transmitted primarily through blood to blood contact, meaning that a person can become infected with the virus should the blood of a person who carries the virus be introduced into another person’s bloodstream.
Therefore, as with hepatitis B, blood transfusions , tattooing and body piercing, occupational exposure, medical procedures, and intravenous drug use can all lead to possible exposure to the virus. Unlike hepatitis B, however, sexual contact and childbirth have both been shown to be an inefficient route of exposure to HCV.
The hepatitis G virus is thought to be transmitted in a similar way to HCV.
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis D
-
Chronic hepatitis B Hepatitis B, Chronic Chronic hepatitis B is inflammation of the liver that is caused by the hepatitis B virus and that has lasted more than 6 months. Most people with chronic hepatitis B have no symptoms, but some… read more suddenly becomes much worse in people who are chronically infected with hepatitis B.
-
Chronic hepatitis B progresses more rapidly than it typically does.
If hepatitis D is suspected, a blood test to detect antibodies produced by the person’s immune system in response to the hepatitis virus D is done to confirm the diagnosis.
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis From Saliva
How Is Hepatitis A Spread
Hepatitis A
The hepatitis A virus is usually spread by putting something in your mouth that is contaminated with the virus. The virus is found in the stool of people with hepatitis A and is spread when someone’s stool accidentally contaminates food or water. This can happen when an infected person does not adequately wash their hands after using the bathroom then touches other things such as food. When other people eat that food, they can get infected with hepatitis A. Usually the transmission is between people in very close personal contact.
Foods themselves can be contaminated with hepatitis A virus, such as raw oysters harvested from sewage-contaminated water. When people eat food contaminated with hepatitis A virus, they can get infected with the virus.
Hepatitis A is usually spread through:
- household contact with an infected person
- sexual contact with an infected person
- eating or drinking contaminated food or water
- sharing eating utensils that are contaminated
- touching contaminated surfaces and then placing your hands near or in the mouth
How Can I Catch Hbv
Hepatitis B virus is transmitted between people by contact with the blood or other body fluids of an infected person. In Africa the virus is mainly transmitted early in life, from mother-to-child or between children. HBV is spread through a break in the skin , or through sexual intercourse. HBV is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV. Unlike HIV, HBV can survive outside the body for at least 7 days. During that time, the virus can still cause infection if it enters the body of a person who is not infected.
Unless vaccinated at the time of birth, these babies can become chronic carriers, which means they are infected with the virus for life. Of children who become infected with the virus between one and five years of age, 30-50 percent become carriers.
In many developed countries , patterns of transmission are different than those mentioned above. Today, the majority of infections in these countries are transmitted during young adulthood by sexual activity and injecting drug use. HBV is a major infectious occupational hazard of health workers.
HBV is not spread by contaminated food or water, and cannot be spread casually in the workplace.
The virus incubation period is 90 days on average, but can vary from about 30 to 180 days. HBV may be detected 30 to 60 days after infection and persist for widely variable periods of time.
You May Like: How Is Hepatitis A Caused
Also Check: Treatment Of Hepatitis B In Dialysis Patients
What Causes Hepatitis D
The hepatitis D virus causes hepatitis D. The hepatitis D virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood or other body fluids. Contact can occur by
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
The hepatitis D virus rarely spreads from mother to child during birth.
You cant get hepatitis D from
- being coughed on or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking water or eating food
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
Sexual Transmission And Viral Hepatitis
Certain adults who are sexually active should be vaccinated against hepatitis B.
CDC and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommend hepatitis B vaccination for
- sexually active people with more than one sex partner during the previous 6 months
- people seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually transmitted disease
- sex partners of people with hepatitis B and
- men who have sex with men .
CDC recommends one-time hepatitis C testing of all adults and regular testing for people with risk factors.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Contact Hepatitis A
Hepatitis D Questions And Answers For The Public
What is hepatitis D?Hepatitis D is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis D virus. Only people infected with the hepatitis B virus can get hepatitis D. They can become infected with both viruses at the same time or get hepatitis D after first being infected with hepatitis B virus . Hepatitis D can cause severe symptoms and serious illness that can lead to life-long liver damage and even death.
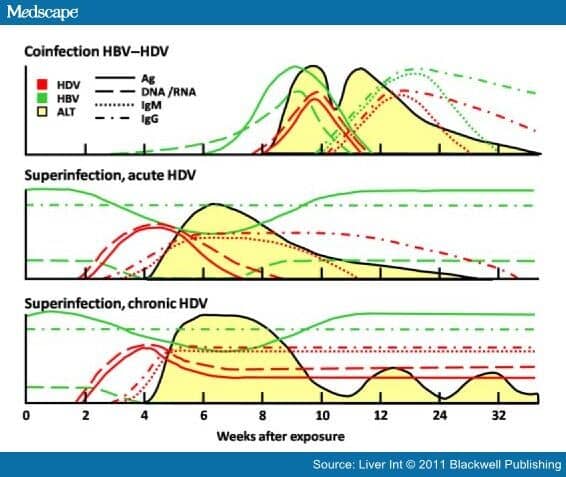
What is hepatitis B/hepatitis D coinfection?People who get infected with both hepatitis B and hepatitis D at the same time are considered to be coinfected. Coinfection with hepatitis B and hepatitis D can cause serious, short-term health problems and even liver failure, but it usually does not lead to life-long illness.
What is hepatitis D superinfection?Superinfection happens when people get hepatitis D after having been first infected with the hepatitis B virus. This type of infection is more likely to result in long-term illness, including rapid development of liver fibrosis, liver failure, and even death.
How common is hepatitis D in the United States?Hepatitis D is considered to be uncommon in the United States. However, the number of people with hepatitis D is unknown, because this infection is not tracked by public health departments or by CDC.
How is hepatitis D spread?You can only get hepatitis D after coming into contact with the blood or body fluids of someone who is infected with the hepatitis D virus. This can happen through
What Are The Modes Of Transmission Of Viral Hepatitis
Asked by: Nuno Costa de Torres | Last update: 23. März 2022
Score: 4.8/5
What are the forms of transmission??
- Contact with contaminated blood, by sharing needles, syringes and other objects for drug use
- Reuse or failure to sterilize medical or dental equipment
- Sterilization failure of manicure equipment
Read Also: Hepatitis B Surf Ab Quant
Don’t Miss: False Positive For Hepatitis C
Viral Structure And Life Cycle
Hepatitis D virus viral life cycle and sites of drug target. 1. Hepatitis D virus virion attaches to the hepatocyte via interaction between hepatitis B surface antigen proteins and the sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide , a multiple transmembrane transporter. 2. HDV ribonucleoprotein is translocated to nucleus mediated by the hepatitis D antigen . 3. HDV genome replication occurs via a rolling-circle mechanism. 4. HDV antigenome is transported out of the nucleus to the endoplasmic reticulum . 5. HDV antigenome is translated in the ER into small HDAg and large HDAg . 6. L-HDAg undergoes prenylation prior to assembly. 7. S-HDAg is transported back to the nucleus where it supports HDV replication. 8. New HDAg molecules are associated with new transcripts of genomic RNA to form new RNPs that are exported to the cytoplasm. 9. New HDV RNP associates with hepatitis B virus envelop proteins and assembled into HDV virions. 10. Completed HDV virions are released from the hepatocyte via the trans-Golgi network.
Finally, once the RNP interacts with the envelop protein of HBV and the HDV is assembled, the HDV virion is now ready for release. The HDV virion is released via the trans-Golgi network, where it can go on to infect other hepatocytes. However, the exact mechanism of HDV-virion release remains unknown .
What Are The Complications Of Chronic Hepatitis D
Chronic hepatitis D may lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer. People who have chronic hepatitis B and D are more likely to develop these complications than people who have chronic hepatitis B alone.20 Early diagnosis and treatment of chronic hepatitis B and D can lower your chances of developing serious health problems.
You May Like: How Do You Screen For Hepatitis C
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Hepatitis D only occurs in patients with hepatitis B. Thus, healthcare workers, including the nurse practitioner should consider serological testing for HDV in patients with hepatitis B. This can be obtained by detection of total anti-HDV antibody followed by confirmatory staining for HDAg in liver tissues and/or measurement of serum HDV RNA. As HBV replication is suppressed in chronic HDV infection, hepatitis B e-antibodies are typically present.
As HDV depends on HBV, prevention can be achieved with hepatitis B vaccination. If the host is immune to HBV, they are subsequently protected against HDV. Patients who are at risk of contracting HDV infection should be encouraged to receive the hepatitis B vaccine.
At the moment there is no specific treatment for hepatitis D but unlike hepatitis B, the former is a benign infection.
Dont Miss: I Think I Have Hepatitis
How Can Hepatitis D Be Prevented
The only known way to prevent hepatitis D is to avoid infection with hepatitis B. You can take the following preventive measures to reduce your risk for hepatitis B:
- Get vaccinated. Theres a vaccine for hepatitis B that all children should receive. Adults who are at high risk for infection, such as those who use intravenous drugs, should also be vaccinated. The vaccination is usually given in a series of three injections over a period of six months.
- Use protection. Always practice safe sex by using a condom with all of your sexual partners. You should never engage in unprotected sex unless youre certain your partner isnt infected with hepatitis or any other sexually transmitted infection.
- Avoid or stop using recreational drugs that can be injected, such as heroin or cocaine. If youre unable to stop using drugs, make sure to use a sterile needle each time you inject them. Never share needles with other people.
- Be cautious about tattoos and piercings. Go to a trustworthy shop whenever you get a piercing or tattoo. Ask how the equipment is cleaned and make sure the employees use sterile needles.
Last medically reviewed on May 17, 2018
Also Check: What Is The Most Common Cause Of Hepatitis
Research And Statistics: How Many People Have Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D was first identified as a distinct form of hepatitis in 1977. A systematic review and meta-analysis published on April 23, 2020, in the Journal of Hepatology estimated its worldwide prevalence at 12 million people. 30220-8/fulltextâ rel=ânofollowâ> 14)
Hepatitis D is rare in the United States, and most cases occur among people who migrate or travel to the United States from countries that have a higher rate of HDV.
Hepatitis D is not a nationally notifiable condition, so the actual number of people who have it is unknown.
Study results published in Clinical Infectious Diseases found that approximately 0.11 percent of the more than 21,000 subjects had antibodies, which would indicate they had hepatitis D infection. That would correspond to approximately 357,000 people in the United States with a past or ongoing HDV infection.
The researchers found that the prevalence of hepatitis D is highest in Asian Americans and people born outside the United States.
Where Is The Hepatitis B Virus Found And How Is It Transmitted
Blood is the major source of the hepatitis B virus in the workplace. It can also be found in other tissues and body fluids, but in much lower concentrations. The risk of transmission varies according to the specific source. The virus can survive outside the body for at least 7 days and still be able to cause infection.
Read Also: How Contagious Is Hepatitis C
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know You Have Hepatitis C
Sexual Transmission And Hepatitis A
Transmission of hepatitis A virus can occur from any sexual activity with an infected person and is not limited to fecal-oral contact. People who are sexually active are considered at risk for hepatitis A if they are MSM, live with or are having sex with an infected person, or inject drugs. Vaccination is the most effective means of preventing hepatitis A transmission among people at risk for infection. CDC has published recommendations for prevention of hepatitis A that identify all groups recommended for vaccination, including hepatitis A vaccination for MSM.
What Is Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D is a viral infection that causes liver inflammation and damage. Inflammation is swelling that occurs when tissues of the body become injured or infected. Inflammation can damage organs.
Viruses invade normal cells in your body. Many viruses cause infections that can spread from person to person.
The hepatitis D virus is unusual because it can only infect you when you also have a hepatitis B virus infection. In this way, hepatitis D is a double infection. You can protect yourself from hepatitis D by protecting yourself from hepatitis B by getting the hepatitis B vaccine.
Hepatitis D spreads the same way that hepatitis B spreads, through contact with an infected persons blood or other body fluids.
The hepatitis D virus can cause an acute or chronic infection, or both.
Don’t Miss: What Types Of Hepatitis Have Vaccines
Etiologic And Clinical Manifestation
Hepatitis D virus is a small 36 nm single-stranded negative sense RNA virus that requires the presence of hepatitis B virus for its assembly and replication. Co-infection and super-infection represent two types of HDV known infections. During co-infection, the patient acquires HDV and HBV at the same time while super-infection occurs when a patient with chronic HBV infection becomes infected with HDV. Hepatitis D virion is composed of an outer lipoprotein envelope made of the surface antigen of the HBV and an inner ribonucleoprotein structure in which the HDV genome resides. HDV produces one protein with two forms a 27 kDa large-HDAg , and a small-HDAg of 24 kDa . The N-terminals of the two forms are identical they differ by an additional 19 amino acids in the C-terminal of the large HDAg. These two proteins play diverging roles during the course of an infection. HDAg-S is produced in the early stages of an infection and enters the nucleus supporting viral replication. HDAg-L, in contrast, is produced during the later stages of an infection, acts as an inhibitor of viral replication, and is required for the assembly of viral particles. Eight different genotypes of HDV have been identified, each with different geographic distribution and distinct clinical course. Genotype I shows wide geographic distribution including Europe and the United States.
When To See A Healthcare Provider
Recognizing the signs of infection is crucial in diagnosing hepatitis D and avoiding any serious complications.
If you notice symptoms such as fever, fatigue, nausea, pain in the upper abdomen, dark-colored urine, or jaundice, its important to contact a healthcare professional as soon as possible and accessible. Theyll be able to run blood tests to determine the diagnosis.
You May Like: Why Test For Hepatitis C
Immunization Of Newborns And Follow
4 ml of blood from the femoral vein was taken immediately after birth for detection of serum HBV markers and HBV DNA. Newborns who were HBV positive were immunized with 20 µg of recombinant hepatitis B vaccine prepared by yeast gene engineering technology , and 200 IU HBIG . Newborns were immunized again at the age of 1 month and 6 months with 20 µg HBVac, while HBIG treatment was repeated once at the same dose 15 days later. HBVM and HBV DNA were measured once again at age of 1 month and 7 months.
Identification Of Hepatitis D
Onset of disease is usually abrupt, with signs and symptoms resembling those of HBV infection.
HDV infection may be severe.
HDV infection may occur as an acute co-infection with HBV infection or as a superinfection in people with chronic HBV infection.
Acute HDV co-infection is usually self-limiting, whereas HDV superinfection usually progresses to chronic hepatitis. Fulminant cases occur in superinfections rather than in co-infections.
Children can have a severe clinical course, which usually progresses to severe chronic hepatitis.
You May Like: What Is Hepatic Metastatic Disease
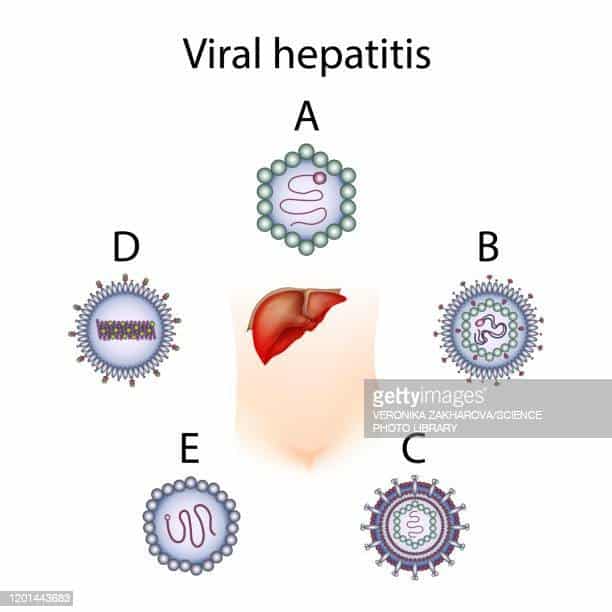
The Types Of Viral Hepatitis
There are five main types of viral hepatitis known as hepatitis A , hepatitis B , hepatitis C , hepatitis D , and hepatitis E . That said, there have been cases of acute hepatitis that could not be attributed to one of these five types of hepatitis viruses, alcohol, drugs, or autoimmune disease, which lead researchers to try to find another cause.
Though the etiology of these viruses have not yet been fully established, researchers have identified three other types of viral hepatitis , which they have named hepatitis F , hepatitis G , and transfusions transmitted virus . As relatively new diseases and viral discoveries, information about them and how they work is relatively scarce. We do know, however, that cases of TTV have only been associated with hepatitis in people who have had a blood transfusion.