Looking To Other Models Of Care
Mental health has lagged other high-prevalence HCV populations in terms of decentralization of screening programs,8,69 although some data exist regarding intensified support within traditional outpatient models.70 In other high-risk settings, such as the prison and opioid-substitution contexts, decentralized models of HCV care service delivery augmented by community nurse engagement, case management, and enhanced motivational support have demonstrated efficacy in engaging and improving HCV treatment access when compared to traditional health care models.17 People with SMI are often integrated within community mental health services, and a remodeling of the current care paradigm bolstered by enhanced clinician education could translate to effective BBV screening and treatment.35,7072 These pathways could be supported through point-of-care HCV antigen assays, integration of nurse practitioners, improved clinician education, streamlined screening strategies, and horizontal integration of specialists, through either visiting sites or telehealth platforms.70,73 Notwithstanding potential barriers in the SMI setting, decentralization of traditional models of care could yield markedly improved access to highly tolerable curative therapies.58,59,74
How Soon Will It Work
All four doctors say that how fast someone can expect to notice a difference depends on both the person and the medication. Generally, antidepressants may take four to eight weeks in order to work. However, with some other medications and even some specific antidepressants you may notice a difference much earlier, Dr. Chen says.
If you have been taking your medication for eight weeks and dont notice a difference, Dr. Gold says to bring it up to your healthcare provider. They may decide to change the dosage or prescribe a different medication.
Hcv Seroprevalence Relative To Control Populations
To contextualize the attributable risk of SMI to HCV, we specifically examined studies that included a non-SMI comparator cohort. Control groups were derived either from non-SMI individuals within large cohort studies or, when reported, from general population data, such as healthy blood donors. A total of 7 studies were included .12,24,30,32,41,49,53 The studies varied in their respective data collection and comparator populations, though 4 of the studies used large data sets to compare ICD-coded HCV between people with SMI and matched controls. Across each of the studies, HCV seroprevalence was 3.0- to 11.3-fold higher in people with SMI relative to control cases. The range was tighter, 6.8- to 8.7-fold, after excluding lower and upper limit data.12,24,30,32
Read Also: How Many Doses For Hepatitis B Vaccine
The Hidden Mental Health Effects Of Hepatitis C
According to research, mental health has an impact on hepatitis C. According to a study, people with hepatitis C have more psychiatric disorders than people without the disease. Anxiety and depression can also be increased as a result of Hepatitis C virus infection. To stay clear of mood swings caused by Hepatitis C virus, it is critical to remember that you can also experience them, so it is important to consult your doctor if you experience any changes in mood.
Dont Miss: Hepatitis C Viral Load Range
Blood Donations Before September 1991
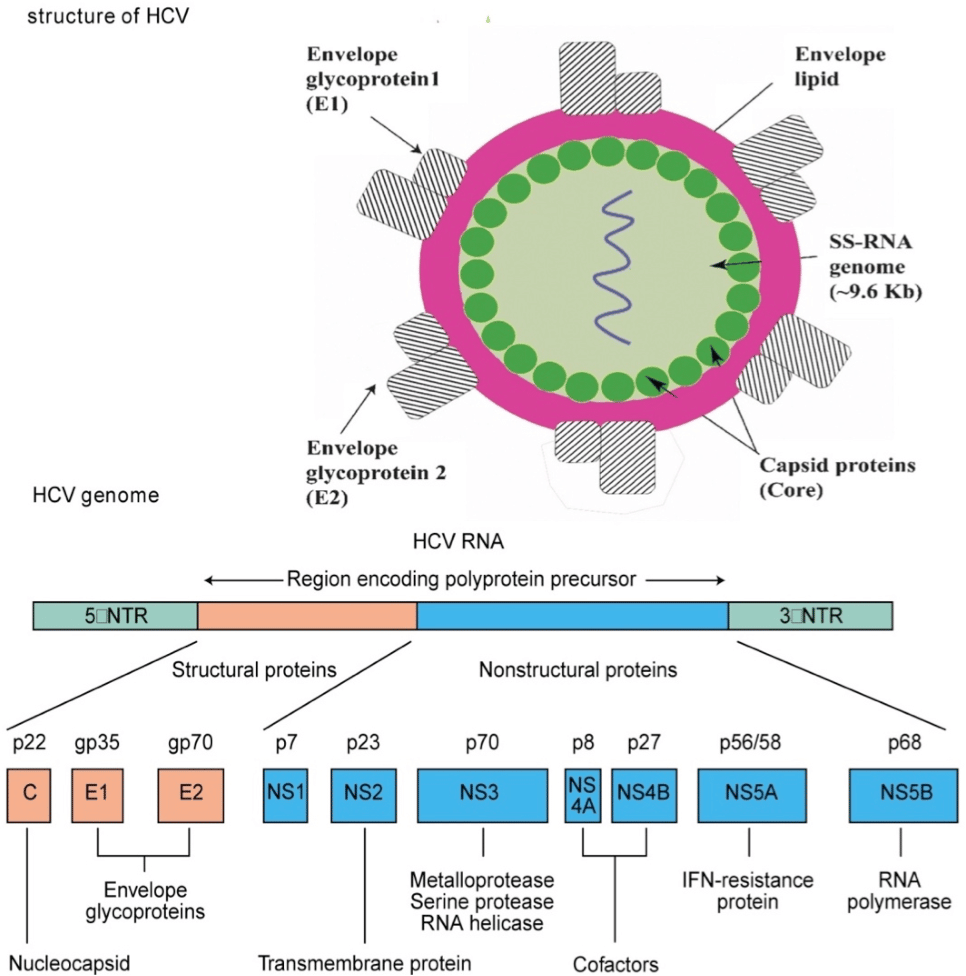
Since September 1991, all blood donated in the UK is checked for the hepatitis C virus.
Theres a small chance you may have been infected with hepatitis C if:
- you received a blood transfusion or blood products before September 1991
- you received an organ transplant before 1992
Before 1992 donated organs were not routinely screened for hepatitis C and there is a very small risk a donated organ from someone with hepatitis C could spread the infection.
There are blood tests to check for hepatitis C infection
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C And Aids The Same Thing
How Hepatitis C Treatments Can Help Improve Your Mental Health
Learning more about the high success rate of treatments for the virus may help you better cope with anxiety. Medication can now cure more than 90 percent of people with hepatitis C, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
A study published in October 2018 in the journal PLoS One found that when people with hepatitis C took direct-acting antiviral medication, they were not only cured of hepatitis C but also experienced reduced anxiety and depression and an improvement in overall quality of life.
Its important to keep in mind that the new DAAs have some side effects but are far more tolerable than the older injections of interferon, Graham notes. People living with hepatitis C shouldnt be fearful of seeking treatment.
The side effects from antiviral medications tend to be mild and include nausea, fatigue, and insomnia. Keep in mind, too, that the treatment lasts only 8 to 12 weeks, so any side effects are likely temporary, she says.
Clinical Spectrum And Natural History Of Hepatitis C
Most acute infections with the hepatitis C virus are asymptomatic, despite elevations in liver enzyme levels. Approximately 30% of the people with newly acquired hepatitis C infection develop symptoms, such as malaise, loss of appetite, and jaundice. Only rarely does acute hepatitis C cause fulminant liver failure. The acute episode resolves in approximately 15% of patients, while the rest develop chronic hepatitis .
Chronicity is defined as evidence of persistent infection for at least 6 months after exposure to the virus. In the chronic phase of hepatitis C, 20% of infected persons have clinical liver disease and complain of fatigue and malaise, 50% are asymptomatic but have increased liver enzyme levels, and 30% are asymptomatic and have normal liver enzyme levels . The progression of chronic hepatitis C is slow often the first clinical indication of chronic infection is liver failure, hepatic encephalopathy, jaundice, or ascites. In the United States, hepatitis C currently is the leading cause of chronic liver disease and the most common indication for liver transplantation .
Cirrhosis develops in approximately 20% of chronic carriers, and subsequent liver failure, portal hypertension, and hepatocellular carcinoma may develop. Once cirrhosis develops, the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma increases, occurring at a rate of approximately 1%4% per year .
Also Check: Hepatitis C And Hair Loss
The New Year Resolutions That Can Help Your Health
Professor Sir Stephen Powis, NHS England’s national medical director, said the NHS is “leading the world” in the drive to save lives and eliminate Hepatitis C while also tackling a “significant” health inequality.
He said: “Thanks to targeted screening and because the NHS has a proven track record of striking medicine agreements that give patients access to the latest drugs, we are on track to beat global targets and become the first country to eliminate Hepatitis C by 2030 – which will be a landmark achievement.”
St Mungo’s is one of the charities behind the Find And Treat outreach programmes which aim to ensure no one, including those historically hard to reach and treat, is left behind in the fight against Hepatitis C.
It has seen specialist teams provide same-day screenings along with help to complete a full course of treatment.
Hcv Treatment Outcomes Among Persons With Alcohol Use
Most of the studies that have addressed whether alcohol use impacts treatment outcomes were performed in the pre-DAA treatment era and results from these studies were mixed.
DAA Treatment Era
- In the DAA treatment era, a large observational study out of the Veterans Affairs healthcare system evaluated the impact of alcohol use on HCV DAA-based treatment outcomes. Of the 15,151 persons who initiated DAA therapy and had a documented AUDIT-C score, 68.5% were categorized as abstinent, 22.6% as low-level drinking, and 8.9% as unhealthy drinking. Overall SVR12 rates were high among all persons in the study, regardless of alcohol use, with no statistical difference between HCV genotype or by cirrhosis status . These findings support current recommendations to not exclude persons from HCV treatment based on their alcohol use.
Interferon and Peginterferon Treatment Era
Also Check: Will Hepatitis C Go Away
Read Also: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Kissing
Peripheral Nervous System Disorders
During HCV infection, a high prevalence of peripheral neuropathy has been reported, which involves 40% to 75% of patients.
This finding is more evident in patients with mixed cryoglobulinemia, in whom fascicular ischemia and axonal degeneration are observed as a result of vasculitis of the vasa nervorum or necrotizing arteritis of medium-sized vessels. In fact, up to 60% of patients with cryoglobulinemia present peripheral neuropathy, while a smaller percentage presents involvement of the central nervous system due to direct involvement of cerebral arterioles.
However, peripheral neuropathy has been demonstrated in subjects who do not have mixed cryoglobulinemia. In these cases, immune complexes or autoimmune mechanisms induced by virus and dependent on T lymphocytes, may play a role in inducing vascular and perivascular inflammation.
In any case, the pathogenesis is indirect and predominantly inflammatory as the virus does not invade peripheral nerves or muscle tissue.
Sensory or motor axon degeneration disrupts communication between the central and peripheral nervous systems. Motor damage can be responsible for weakness, while sensory damage can cause paresthesia, hyperalgesia, allodynia, pain and numbness. Autonomic damage can result in organ damage.
The most frequent form of peripheral neuropathy is symmetrical axonal sensory or sensorimotor polyneuropathy which is typically characterized by loss of sensation and weakness in the lower leg region.
The Link Between Anxiety Depression And Hepatitis C
Mood changes, including anxiety and irritability, can come with a diagnosis of hepatitis C. You may feel anxious about the illness and your future when you learn youre at risk for liver cancer or other complications, says Camilla Graham, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
Depression can also be common, affecting anywhere from 20 to 50 percent of people who have hepatitis C, according to a review published in August 2021 in the World Journal of Gastroenterology.
There can be an unfortunate stigma attached to a hepatitis C diagnosis, especially when people dont understand the condition. A study published in November 2020 in the Journal of Viral Hepatitis found 95 percent of study participants reported experiencing some type of stigma related to their infection.
As a result, people with hepatitis C may become isolated, which can pave the way to depression, says Dr. Graham. Many people with hepatitis C become withdrawn and depressed, because they feel judged or shunned by others.
People with hepatitis C may also struggle with substance abuse today, the virus is often contracted through needles or other equipment used to inject drugs as well as the mental health issues that can go hand in hand with it, she says.
Read Also: Is Hepatitis A Vaccine A Live Virus
Quality Of Life With Hepatitis C And Interferon Treatment
Several studies have shown that patients with chronic hepatitis C have a reduced quality of life . Reduction in quality of life is not associated with how the infection is acquired or with the severity of the liver disease . Although a history of intravenous drug use is independently associated with reduced quality of life, patients without a history of drug use still show a reduction in quality of life. Quality of life for patients with chronic hepatitis C appears to be worse than for patients with hypertension and comparable to that for patients with type II diabetes .
The impact of IFN- treatment is less clear. Hunt et al. prospectively followed patients with hepatitis C who were treated with IFN- and found that the health status of these patients was similar to that of the general U.S. population and did not change during IFN- therapy. In contrast, Bonkovsky et al. , in a much larger study, showed that successful therapy with IFN- improves quality of life and that the degree of improvement is related to sustained virological or biochemical response to treatment. However, the patients were not blinded to their state of infection. Further study is needed to establish whether eradication of hepatitis C improves quality of life.
Effects Of Antiviral Therapy
Until recently, INF and pegylated INF have been the only effective treatments for HCV infection as modulators of the immune response, showing a sustained virological response of up to 50%-80% when combined with ribavirin.
This therapy is associated with a high prevalence of neuropsychiatric disorders, which affect up to 70% of subjects. Predominant symptoms are mood disorders such as anxiety and depression, psychosis and manic agitation, suicidal ideation and cognitive decline. These disorders disappear at the end of therapy and can be attributed to numerous pathophysiological complications associated with treatment such as alteration of monoamine metabolism, increase in apoptosis, reduction in cerebral neurotrophic factor, alteration of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and alteration of frontal-subcortical circuits. Co-factors for the development of this disorder during antiviral therapy are low education, a known history of psychiatric disease and high serum concentrations of IL-6. In subjects infected with HCV and treated with INF, PET studies with 18-FDG have shown a reduction of metabolic activity in the prefrontal cortex which agrees with a depressive state.
HCV infection treatment has been radically changed since the introduction of direct-acting antivirals . INF-free regimens are better tolerated and are highly effective, reaching an SVR greater than 95% furthermore, the simplicity of dosage and their safety profile guarantee good compliance.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Mode Of Transmission
Inclusion And Exclusion Criteria
Prospective observational and retrospective cross-sectional studies that assessed HCV prevalence in adults with SMI aged18 years were systematically reviewed. HCV prevalence was determined based on International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision coded data as well as seroprevalence data. Many of the extracted articles did not elucidate a specific definition for SMI in the recruitment strategy however, data were included if SMI, severe psychiatric illnesses, or an enduring mental illness with functional impairment was clearly stipulated as an inclusion criterion.
The Role Of Primary Care Physicians And Psychiatrists In Screening For Hcv
Despite the association between HCV and psychiatric illness, screening for HCV has not been a routine practice in patients with psychiatric illness. These patients are at risk for contracting HCV by engaging in risky sexual behaviors and intranasal drug use but may not be forthcoming about these activities.65 Therefore, the only reliable way to rule out HCV infection would be to screen these at-risk populations. The CDC has recommended routine screening of incarcerated individuals in correctional facilities for HCV.66 Routine HCV screening is also recommended for all patients who are found to be infected with HIV.65 The Department of Veterans Affairs conducts routine HCV screening for all veterans being treated at Veterans Affairs hospitals.31,67,68
However, the US Preventive Services Task Force in 2004 recommended against routine screening for HCV in high-risk individuals because it found no data to support the efficacy of interferon alfa and ribavirin treatment in reducing morbidity and mortality from HCV infection despite 2 decades of research on the utility of interferon alfabased therapies in achieving viral clearance.69 Therefore, interferon alfa and ribavirin treatment for patients with HCV infection continues to be considered a therapeutic modality with an intuitive value but no evidence-based efficacy in reducing the overall morbidity and mortality associated with HCV.70
Also Check: Royal Canin Hepatic Wet Food
Can Hep C Make You Delusional
It is also worth noting that while pegylated interferon alpha-2b therapy is effective in treating chronic hepatitis C patients, delusional parasitosis can occur. During the course of a medication discontinuation, an entire and sustained remission can be observed without the use of any psychopharmacologic medications.
Also Check: How Does Hepatitis Affect The Body
Psychosocial And Neurocognitive Factors Associated With Hepatitis C Implications For Future Health And Wellbeing
- 1Clínica Universitária de Psiquiatria e Psicologia Médica, Faculdade de Medicina, Universidade de Lisboa, Serviço de Gastrenterologia e Hepatologia, Centro Hospitalar Lisboa Norte-Hospital de Santa Maria, Lisbon, Portugal
- 2Faculdade de Medicina, Universidade de Lisboa, Serviço de Gastrenterologia e Hepatologia, Centro Hospitalar Lisboa Norte-Hospital de Santa Maria, Lisbon, Portugal
- 3Laboratório de Genética, Faculdade de Medicina, Instituto de Saúde Ambiental, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal
- 4Assertive Outreach Team, Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust, Brighton and Hove, United Kingdom
- 5Clínica Universitária de Psiquiatria e Psicologia Médica, Faculdade de Medicina, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal
Background: Hepatitis C virus infection involves changes not only from the point of view of physical health, but also emotional, and social that have a significant impact on the quality of life of these patients. According to the literature review, it seems that there is an important association between psychosocial factors, in particular on a cognitive level and disease progression. The aim of this mini-review is to summarize recent literature looking at the associations between psychosocial and neurocognitive factors and HCV.
Methods: PubMed/Medline was systematically searched for psychosocial and neurocognitive factors associated with hepatitis C, treatment adherence, and patient wellbeing.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis A Vaccine
Rationale For Bbv Screening In Smi And Barriers To Care
We show that BBV screening delivered through population-based programs has high acceptability among people with SMI. Nonetheless, real-world data suggest that people within mental health services are underserved from an HCV screening perspective. In a cross-sectional analysis of 57,170 SMI outpatients, 4.7% were screened for HCV over a 12-month period as compared to 12.4% in a general population comparator cohort, with the strongest predictor of HCV screening in the SMI group being non-psychiatric health care utilization.64 Importantly, person-centered blood-borne virus screening delivered through collocated specialist services has been shown to significantly bolster HCV screening rates in community-managed individuals with SMI.65 However, even with positive case identification, significant attrition in follow-up and treatment is commonly encountered.6567 Few publications in this systematic review addressed linkage to care in HCV-positive individuals however, known barriers exist as a composite of complex patient-related, clinician, and health system factors.8,10,66 For example, issues pertaining to access and retention within traditional specialist health care models may be experienced at a patient level. This may be compounded by perceived or actual stigma.66 From a clinician perspective, legacy concerns stemming from interferon-era therapies coupled with competing mental health care priorities may hinder advocacy and referral to HCV treatment services.66,68