Safe Food And Water Precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater , particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Risk
To protect against cholera, all travellers should practise safe food and water precautions.
Travellers at higher risk of getting cholera include those:
- visiting, working or living in areas with limited access to safe food, water and proper sanitation
- visiting areas where outbreaks are occurring
Vaccination may be recommended for high-risk travellers, and should be discussed with a health care professional.
Travellers’ diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers’ diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers’ diarrhea is rehydration . Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Design And Data Sources
In this cross-sectional study, records from the hospital Discharge Abstract Database were linked to the Immigrant Landing File data at Statistics Canada, using previously described methods.Note 23 Essentially, the Immigrant Landing File data were linked to the DAD via a central depository called the Derived Record Depository within the Social Data Linkage Environment at Statistics Canada. The DRD is a national dynamic relational database containing only basic personal identifiers, and was created by linking selected Statistics Canada source index files, including tax,birth and death data, to produce a list of unique individuals. The linkage was approved by Statistics Canadas Executive Management Board,Note 24 and the use and privacy of the data are governed by the Directive on Microdata Linkage.Note 25
The DAD, from which the study population was constructed, contains demographic, administrative and clinical data for all acute care and some psychiatric, chronic rehabilitation, and day surgery discharges for all provinces excluding Quebec.Note 26 Hospital discharges occurring between April 1, 1994, and March 31, 2015, were eligible for linkage in the present study . The linkage used a deterministic approach .Note 27
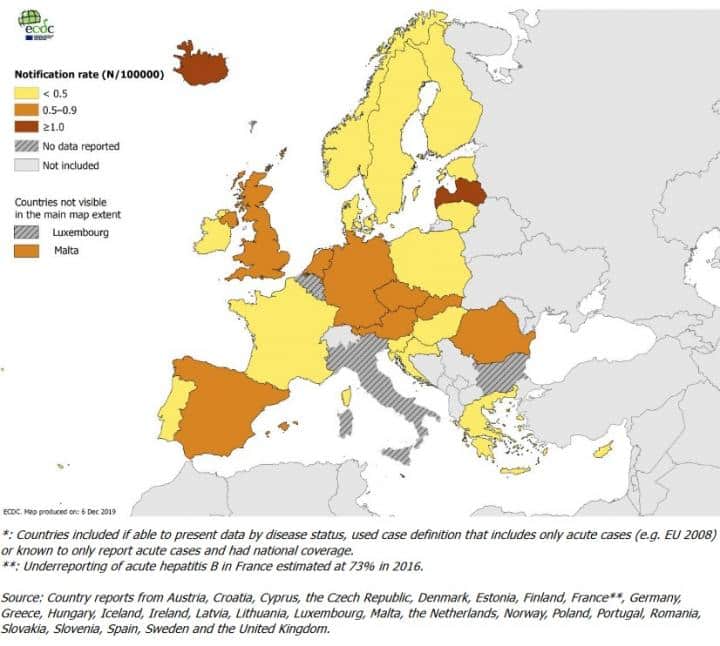
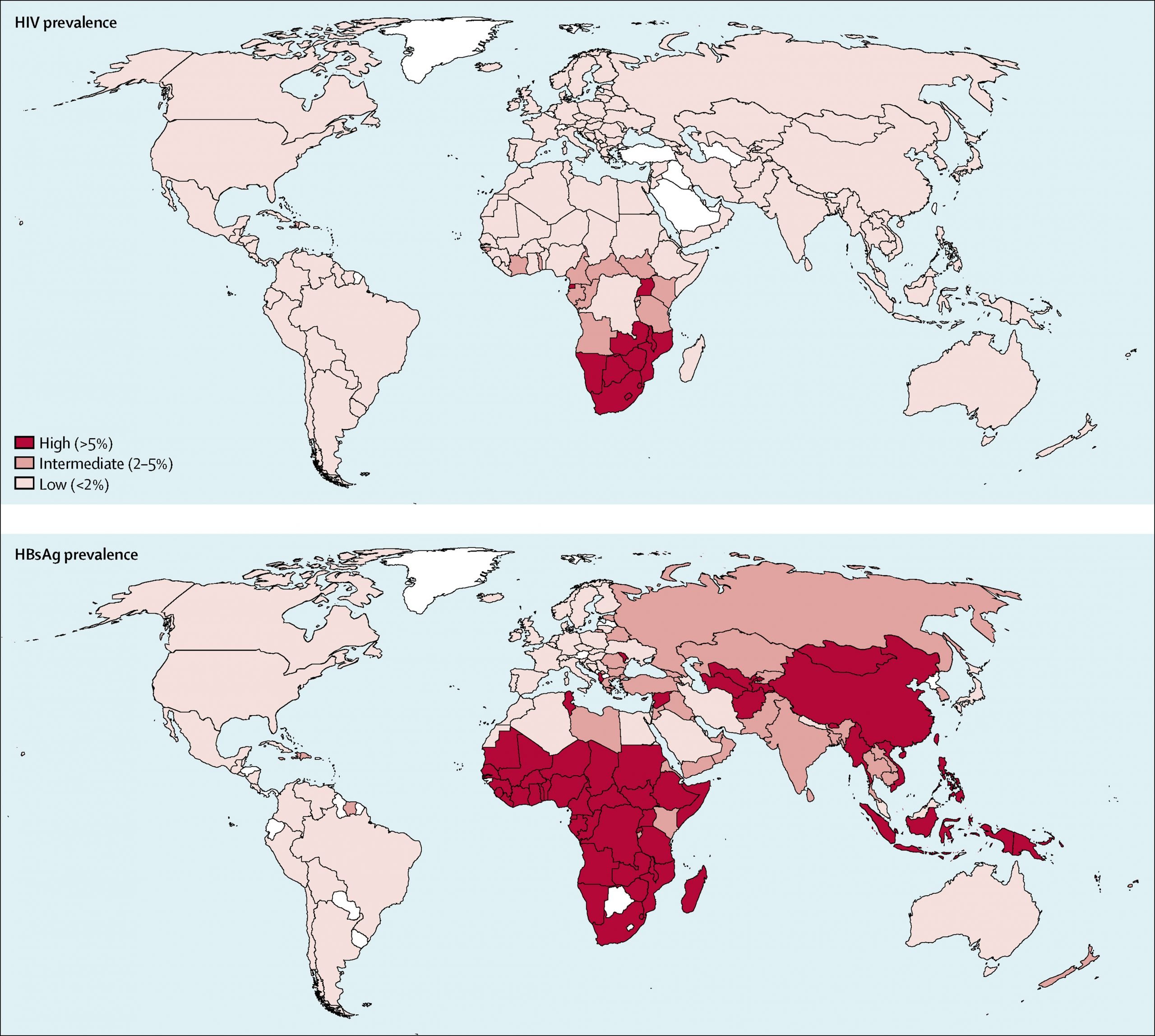
Hepatitis B Around The World
Hepatitis B is a contagious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus and is the leading cause of liver cancer.
Hepatitis B transmission from mother to child is the leading cause of chronic infection.
If not vaccinated, 9 in 10 children infected with HBV at birth will progress to chronic infections.
The percentage of newborns given the shot of Hepatitis B vaccine at birth in each region in 2020:
- South East Asia 51%
- Western Pacific 84%
The African Region has the highest number of hepatitis B infections in children and the fewest newborn given the hepatitis B vaccine at birth.
The key to eliminating HBV infection?
Vaccinating babies within 24 hours of birth followed by 2-3 vaccinations within 6 months is the key to eliminating HBV infections.
Learn more about CDCs global immunization efforts: www.cdc.gov/globalhealth/immunization/
Get CDCs free global health newsletter each week! Enter your email address:
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website’s privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
CDC.gov Privacy Settings
Read Also: Interferon Treatment For Hepatitis C
Vital Information About Entering France And Obtaining Visas
Prior to traveling to France for the 2022 HBV Meeting, please review to clarify your Visa requirements. The Conference Organizers recommend that if required, you apply for a visa as soon as your attendance is confirmed, as visa requests can often take months to process.
To apply for a visa please visit:
Visa processing times vary depending on the nationality of the applicant, the purpose of the stay and the local visa issuing conditions.
To apply for a short-stay visa, the application must be submitted at least two weeks prior to your planned visit however, it can not be submitted more than 6 months prior to your planned visit. It is the responsibility of the applicant to take the necessary precautions in terms of respecting deadlines when an appointment system is in place.
Certain types of visa require special checks or consulting different French authorities, which may extend the processing time.
How Is It Transmitted
Hepatitis B is highly infectious, and is spread from one person to another through exposure to infected blood and body fluids . It can be spread through:
- blood transfusions or organ transplantation in countries where blood or blood products have not been properly screened for hepatitis B and other viruses transmitted through blood
- unprotected sex with an infected person
- sharing needles or equipment for injecting drugs
- unsterilized medical/dental equipment and shared/contaminated materials or equipment used for tattooing, body piercing or acupuncture
- sharing toothbrushes or razors
- household contact between family members
Also Check: Can Hepatitis C Be Transmitted Via Saliva
How Do Mandatory Vaccination Policies Vary By Region
We found that assessing policies across WHO regions European, Americas, Western Pacific, African, and Eastern Mediterranean was a useful way to break down our analysis of policies worldwide.
In the chart you see a breakdown of the number of countries with a given policy mandate. You can view this by region by using the Change region toggle on the interactive chart.
Europe has a mixture of mandatory and recommended policies. But most European countries 16 out of 28 do not have mandatory vaccination. European countries were among the first to introduce mandatory vaccination for smallpox in the early 19th century, which also led to early push-back. The early introduction and early push-back, along with present-day approaches to foster mutual trust and responsibility between citizens and the health authorities, may be part of the reason why vaccination is often recommended rather than mandated in many European countries.52 Countries of the former-USSR or under the influence of the Eastern Bloc previously had mandatory vaccination, and many kept this policy in the post-USSR era.
Most countries in the Americas 29 out of 35 have mandatory vaccinations. In the USA, vaccination is regulated by individual states though it is mandatory for school entry in all of them. In Canada, only three provinces have legislated mandatory vaccination policies that apply to children enrolling in school.
Can I Prevent Getting Hepatitis B
You can take the following precautions to help reduce your risk of infection:
Don’t Miss: Echogenic Liver Consistent With Hepatic Steatosis
What Is Already Known On This Subject
- Since viral hepatitis is an important global public health problem, there are international commitments that have prioritized the elimination of hepatitis.
- Chronic viral hepatitis can lead to significant morbidity and mortality, but early detection through screening can help mitigate the risk of clinical deterioration.
- Canada receives over 350,000 immigrants each year, with the numbers expected to grow.
- Patterns of migration have changed over time.
- For admissibility purposes, Canadian immigrants are medically screened for selected diseases to mitigate impacts on Canadian health and social services.
Diphtheria Tetanus And Pertussis Vaccine
Diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis are all bacterial diseases and a combination vaccine against all three diseases is commonly used.
- Diphtheria primarily infects the throat and upper airways and is fatal in 5 10% of cases.
- Tetanus is not passed person-to-person but through spores of a bacteria living in soil and animal intestinal tracts. These bacteria enter the body through wounds and release a toxin that affects the nerves, which causes muscle stiffness and spasms.
- Pertussis is a highly contagious disease of the respiratory tract, commonly known as whooping cough. Children who contract pertussis tend to have coughing spells that last four to eight weeks, but the highest fatality is in young infants. Vaccinating health workers and pregnant women is the most effective strategy for preventing disease in infants too young to be vaccinated.
The chart shows the progress over time of DTP3 immunization coverage of children around the world. By clicking on any country you can see the change in that country over time.
The WHO reports in 2017 that 85% of infants worldwide received 3 doses of diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis vaccine . Also in 2016 130 countries had reached at least 90% coverage with the DTP3 vaccine.58
If we look at the change over time by world region it is South Asia in particular that stands out. While 85% of one-year-olds today are immunized, that same figure was as low 6% in 1980.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Shots How Often
New And Current Treatment Options For Hepatitis B
The search for new treatments for hepatitis B has been ongoing for decades. While effective at suppressing the virus, current treatments, which include antivirals, cannot eliminate it from the liver.
Hepatitis B is a liver infection that results from the hepatitis B virus. People acquire it through contact with the bodily fluids of someone with the virus. The liver cleanses the body of waste, and the disruption to its processes can make a person seriously ill.
This article will outline the current treatment options for HBV. It will also discuss new treatments in development that may lead to a cure for HBV.
Initial infection with HBV is an acute infection. Most healthy people with infection with this virus will not have symptoms and can shed the virus easily. If tests show that a person still has the virus 6 months after contracting it, they have a chronic, long-term infection. Doctors use blood tests to diagnose and monitor the condition.
Treatment whether a person has acute or chronic hepatitis B.
What Drives The Introduction Of Mandatory Vaccinations
Overall, we found that the occurrence of recent outbreaks is a major factor in the introduction of mandatory vaccination, particularly for high and upper-middle-income countries in Europe. Germany, for example, made measles vaccination mandatory for school and day-care attendance in 2020 following large outbreaks.54 Similarly, Serbia tightened mandatory vaccination laws following a measles outbreak in 2014 to 2015 by introducing harsher penalties.55 Trends of reported cases of measles can be explored in detail here.
Secondly, many low- and lower-middle-income countries have resorted to mandatory vaccination policies because of a lack of other policy options. Nonetheless, many have still missed their target vaccination rates due to problems with vaccine supply, delivery, and access. In Guyana for example, vaccination is mandatory, yet vaccination coverage is hindered by the management of the supply chain in keeping storage temperatures consistent and the distribution of freeze-sensitive vaccines.56 In Nigeria, vaccination is mandatory, and several states have enacted legislation criminalising vaccine refusal. Yet as Onyemelukwe argues, there are structural, logistical, political, systemic, religious and cultural obstacles to the effective distribution and uptake of vaccines, ranging from cold chain issues, to corruption and security issues.57 There is thus often variation between vaccination in policy compared to in practice.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Reactive What Does It Mean
Global Immunization Strategic Framework 2021
In 2021, CDC released the Global Immunization Strategic Framework 2021-2030, which provides a roadmap to achieving progress toward a world where everyone is protected from vaccine-preventable diseases , such as hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
Three Goals are core immunization program capacities that CDC seeks to strengthen:
-
Prevent VPDs by strengthening immunization services.
-
Detect VPDs by supporting and improving disease surveillance systems.
-
Respond to and prepare for VPD outbreaks.
Two Goals are cross-cutting capacities:
-
Sustain immunization program capacities over time.
-
Innovate to increase immunization program impact through research and evaluation.
Which Countries Include Vaccines In Their Immunization Schedules
Several vaccines, including rubella, mumps, and rotavirus, are included in immunization schedules in many countries around the world. This means these vaccines are provided and recommended through routine services.
This doesnt necessarily tell us how many children receive these vaccines in each country. The vaccines may or may not be mandatory and their coverage rates may vary widely. Similarly, when countries do not have a vaccine in their schedule, this does not mean that the vaccine is completely unavailable in those countries, as it may be optional or available commercially.
In the chart you can see which countries include rubella vaccines in their national immunization schedules. Rubella vaccines became available for the first time in 1969, starting in the United States, where it was developed.46 It was included in the schedules of the United States and most European countries as early as 1994 . Over time, more countries included it in their schedule.
But this took many years for some countries: for example, it took until 2018 for it to be included in countries such as Uganda and Congo.
As of 2021 some countries, such as Nigeria and South Africa, still do not include it in their schedules.47
In the links below, you can see these charts for other vaccines.
Read Also: Information About Hepatitis B Vaccine
Does Vaccine Skepticism Affect Immunization Coverage
The crucial question to ask when considering the importance of vaccine skepticism is: does it actually have an effect on behaviour? Does it really affect the share of children who are vaccinated?
In the chart we see the comparison of vaccination rates here as the share of children who were immunized against diphtheria, pertussis and tetanus in 2015, the latest year available to the share of respondents in a given country who disagreed that vaccines are safe.
You can also see this relationship for measles vaccine coverage.
Overall we see that widespread public concern for vaccine safety does not appear to be strongly correlated with vaccination rates. While one-third of the French public disagrees with their safety, 97% of children in France are vaccinated.
There are numerous other reasons, however, why vaccination rates in some countries are low: in low-to-middle income countries the availability, affordability and access to vaccines can be poor. Having low coverage rates often doesnt reflect the populations view of them. As the chart shows, in many poor countries the situation is the opposite as in France: the vast majority of the population considers vaccine safe, but only about every second child receives the DTP vaccine.
One country which stands out is Ukraine: there we see that vaccination rates are uncharacteristically low for its income level less than 1-in-4 children receive the DTP vaccine. Skepticism of vaccine safety in Ukraine is high at 15%.
Cdcs Viral Hepatitis Program Collaborates Worldwide
CDC assists with the implementation of strategiesexternal icon to achieve progress toward global viral hepatitis elimination goals in countries around the world. Collaborative work with partners, including in-country CDC offices, Ministries of Health, the World Health Organization , international public health professionals, and foreign government officials, focuses on efforts to develop, implement, monitor, and evaluate viral hepatitis-related guidelines, policies, plans, and programs. For example, CDC helped implement the country of Georgias Hepatitis C Elimination Program, the first program of its kind, and is continuing to provide technical assistance to Georgia as the program progresses toward elimination. Additionally, CDC assisted in the implementation of a pilot program to eliminate hepatitis B and hepatitis C in Uzbekistan using an innovative funding approach tailored to the needs of low- and middle-income countries . International collaborations not only help the host country but can help reduce the risk for disease among U.S. travelers abroad and reduce the likelihood that people coming to the United States are infected.
Learn more about World Hepatitis Day, how viral hepatitis impacts millions of people worldwide, and CDCs efforts to combat viral hepatitis globally.
A partial list of countries* with whom CDC collaborated to enhance viral hepatitis prevention and control efforts
Read Also: Homeopathic Medicine For Hepatitis C
How Many People Support Vaccination Across The World
The London-based research charity The Wellcome Trust published their Wellcome Global Monitor in 2019 on attitudes to science and major health challenges. It is the worlds largest study of its kind, surveying over 140,000 people from over 140 countries. As part of the Gallup World Poll, the 30-question survey ran during 2018.26
The Wellcome Trust survey asked three core questions related to attitudes to vaccines: do people think that vaccines are important for children to have do they think vaccines are safe and do they believe vaccines are effective.
Most people in the world think vaccines are important for children to have
More than 9-in-10 people in the world think that vaccines are important for children to have.
How support varies across the world is shown in the map. We see high support for vaccination across almost all countries. In most countries over 80% of respondents think child vaccination is important, in many countries it is over 90% who think so.
There is a visible North-South divide in attitudes: support is highest across South Asia at 98% 97% in South America 94% in Northern Africa and 92% in Southern Africa. Support is still high, but lower across North America Western Europe and Eastern Europe .
Of those surveyed in Venezuela, Palestine, Ethiopia and Northern Cyprus thought vaccines were most important: 100% were in favour.27
Most people in the world think vaccines are safe, but mistrust is high in some countries