What Causes Hepatitis B
- being born to a mother with hepatitis B
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools that were used on an infected person and werent properly sterilized, or cleaned in a way that destroys all viruses and other microbes
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
You cant get hepatitis B from
- being coughed on or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking unclean water or untreated water that has not been boiled
- eating food that is unclean or has not been properly cooked
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
Mothers who have hepatitis B can safely breastfeed their babies. If a baby receives hepatitis B immune globulin and starts receiving the hepatitis B vaccine to prevent hepatitis B infection shortly after birth, hepatitis B is unlikely to spread from mother to child through breastfeeding.15
What Should I Do If I Am Exposed To The Hepatitis B Virus
If you know you were recently exposed to the hepatitis B virus, you may get protection from an injection of hepatitis B immunoglobulin , which is different from the hepatitis B vaccine.
HBIG is given only when it is suspected or known that someone has been infected with hepatitis B, and it is given within 24 hours after the exposure.Unlike the vaccine, which is not given after exposure, HBIG is given before a potential exposure. HBIG will protect you for 3 to 6 months, but it is strongly recommended that you also begin the 3-shot hepatitis B vaccination series within 7 days of your exposure.
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
Read Also: What Does Hepatitis C Antibody Non Reactive Mean
Who Should Be Vaccinated For Hepatitis B
All newborns should be vaccinated. Also, people who are under 18 who were not vaccinated at birth should also get the vaccine. Other groups who should be sure to be vaccinated are those in certain high-risk categories, such as:
- People who have more than one sexual partner.
- Men who have sex with men.
- Adults with diabetes.
- Sexual partners of infected people and people who share households with infected individuals.
- People who are exposed to blood and other bodily fluids, including healthcare and public safety professionals, and people who work in jails and other places taking care of people who cant take care of themselves.
Causes Of Noninfectious Hepatitis
Although hepatitis is most commonly the result of an infection, other factors can cause the condition.
Alcohol and other toxins
Excess alcohol consumption can cause liver damage and inflammation. This may also be referred to as alcoholic hepatitis.
The alcohol directly injures the cells of your liver. Over time, it can cause permanent damage and lead to thickening or scarring of liver tissue and liver failure.
Other toxic causes of hepatitis include misuse of medications and exposure to toxins.
Autoimmune system response
In some cases, the immune system mistakes the liver as harmful and attacks it. This causes ongoing inflammation that can range from mild to severe, often hindering liver function. Itâs three times more common in women than in men.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Antigens And Antibodies
Injections: Interferon And Pegylated Interferon
Pegylated interferon is given as an injection once per week. It can be used alone or with an oral hepatitis B medication. Patients with both chronic hepatitis B and hepatitis D infection may need pegylated interferon alone or combined with an oral hepatitis B pill.
- Pegylated interferon therapy is usually given for 48 weeks.
- Pegylated interferon may cause many side effects, such as flu-like symptoms, rashes, irritability, and depression.
- Side effects to interferon require close monitoring with routine blood tests.
What Other Problems Can Hepatitis B Cause
In rare cases, acute hepatitis B can cause liver failure.
Chronic hepatitis B can develop into a serious disease that causes long-term health problems such as cirrhosis , liver cancer, and liver failure.
If you have ever had hepatitis B, the virus may become active again, or reactivated, later in life. This could start to damage the liver and cause symptoms.
Read Also: How Much Does Hepatitis C Medicine Cost
Potential Triggers Of Chb
The potential triggers of CHB-ACLF were widely researched. Bacterial infections and alcoholism were found to be the two major identifiable factors in the CANONIC study, while hepatitis B relapse was found to be the predominant factor followed by bacterial infections in studies conducted in China . The CANONIC criteria primarily identified hepatic-ACLF triggers categorized as liver toxins and extrahepatic-ACLF triggers . Despite exhaustive examination, the trigger for CHB-ACLF remains unknown in 2045% of cases, particularly for cases in China . We speculate that the potential triggers among these CHB-ACLF patients are related to HBV characteristics such as HBV genotype and mutations .
Table 2. Potential triggers of HBV-ACLF.
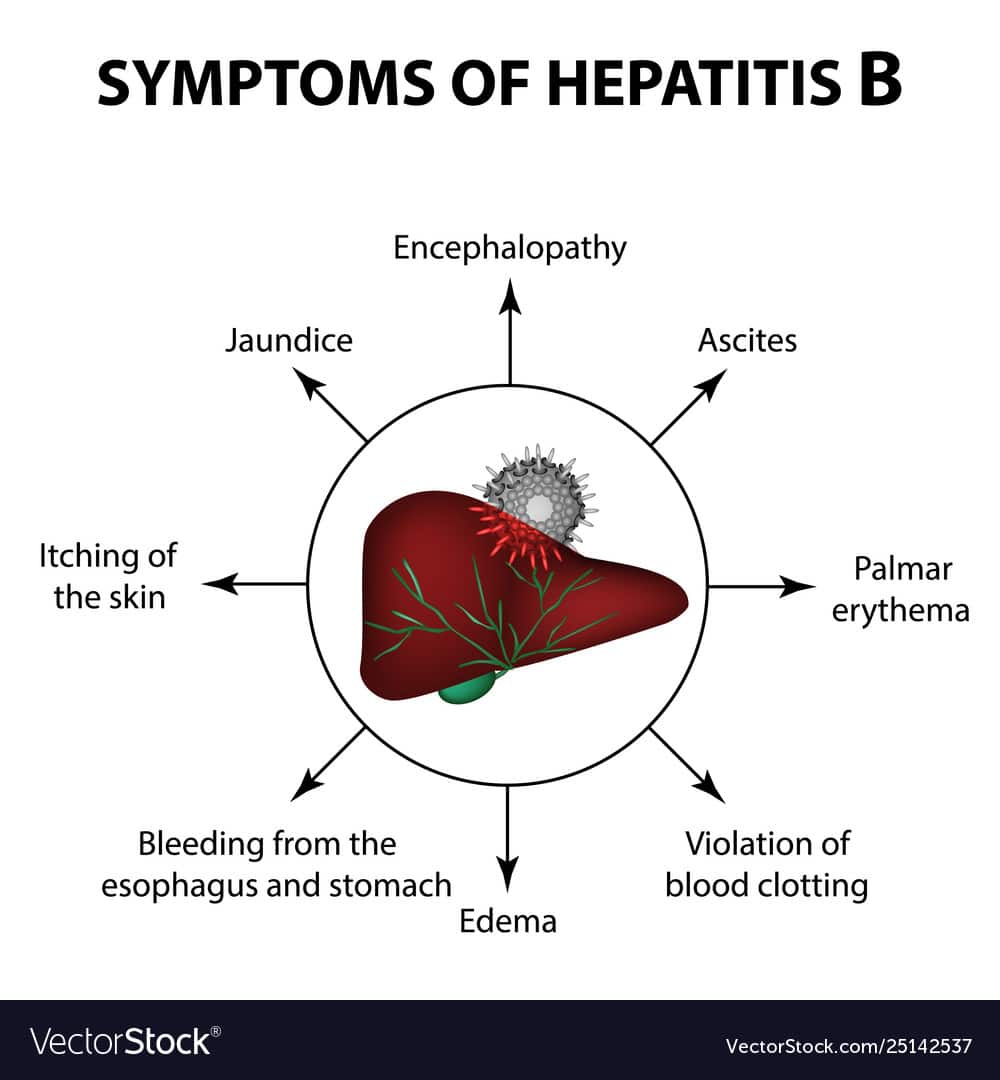
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B has a wide range of symptoms. It may be mild, without symptoms, or it may cause chronic hepatitis. In some cases, hepatitis B can lead to full-blown liver failure and death. The following are the most common symptoms of hepatitis B. However, each individual may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include:
-
Loss of appetite
-
Clay colored or light colored stools
Read Also: July 28 World Hepatitis Day
What Is Involved In A Liver Transplant
A liver transplant is considered necessary when the liver is damaged and cannot function or in some cases of liver cancer. Your liver is very important. It is responsible for many functions related to making sure that your body stays healthy and is able to digest foods.
You may be eligible for a transplant if you have chronic hepatitis B infection or some of the diseases that may result from it, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. You will have to complete testing and be evaluated before being approved for a transplant. It is likely that you will be placed on a waiting list while an appropriate organ is found.
Donated livers come from two types of donors: living and deceased. Because the liver can regenerate, it is possible to use part of a liver for transplant. The remaining sections in both the donor and the receiver will grow into livers of adequate size.
People who get liver transplants must take anti-rejection drugs for the rest of their lives. These drugs make you more susceptible to infection. However, liver transplants have become more successful over time and continue to improve.
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Ql Reactive Meaning
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
If youâre pregnant, you might pass the virus to your baby at birth.
If your baby gets the virus and isnât treated, they could have long-term liver problems. All newborns with infected mothers should get hepatitis B immune globulin and the vaccine for hepatitis at birth and during their first year of life.
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- What kinds of therapy are possible to reduce my viral load?
- Are there clinical trials looking at curing Hepatitis B?
- Do I have liver damage?
- Will I need a liver transplant?
- Does my family need a booster vaccination?
- What are the potential risks at infecting my partner with Hepatitis B?
- How can I make my friends and family aware of what my condition is?
- Should I be re-vaccinated for Hepatitis A?
Also Check: Interferon Treatment For Hepatitis B
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis B
There are two types of hepatitis B infection: acute and chronic.
Acute
An acute infection happens at the beginning, when you first get infected with hepatitis B. Many people are able to clear it from their bodies and recover. In fact, this is true of about 4 in 5 adults who are infected.
Chronic
If you are not able to clear the infection within six months or longer, you have chronic hepatitis B. It is chronic hepatitis B that leads to inflammation and the serious, and possibly fatal, illnesses of cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer. Treatment can slow disease progress, reduce the chance of liver cancer and increase your chances of surviving.
Hepatitis B: Know The Risks And Symptoms
This is part one of a two part story on hepatitis B. Visit the OSF Newsroom next week to learn about treatment and prevention of the disease.
The average person may think about things like the flu or common cold, especially during winter. Wash your hands and dont cough or sneeze into the open air, were constantly told.But when it comes to hepatitis B, experts say its not a disease we need to think about daily.David Rzepczynski, MD, a gastroenterologist at OSF HealthCare in Urbana, Illinois, explains that while there are many types of hepatitis A, B, C, D and E they all describe inflammation of the liver.
How its spread
Dr. Rzepczynski says hepatitis B is most commonly spread through bodily fluids like blood, saliva and fluids from the genital area.A common scenario, he says, is young adults spreading the disease by sharing needles to inject drugs. Sexual relations between people who are infected can also result in the spread.And there are everyday scenarios. Someone may share a toothbrush or a shaving razor with a person close to them. Children may be roughhousing outside and get a cut, exposing their blood to others.
Symptoms
Not all people who get hepatitis B show symptoms. But those who get an acute, sudden infection may experience fatigue, nausea, loss of appetite, pain in the upper right abdomen and for smokers less desire to light up.
Also Check: Can Hepatitis C Cause Mental Illness
Coordinated Care In One Medical Center
Infection with the hepatitis B virus is one of the most common causes of hepatitis worldwide. Chronic hepatitis B can lead to cirrhosis , liver cancer, liver failure, and death. NewYork-Presbyterians liver specialists are experts in the care of people with hepatitis B, offering the latest medications and monitoring techniques. We are experienced in liver transplantation for people whose hepatitis B becomes life-threatening, with more clinical experience caring for these patients than most hospitals.
Is Innate Immune Recognition The Original Trigger
Early pathogen detection generally occurs via the recognition of Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns by Pathogen Recognition Receptors . The known PRRs include nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein -like, retinoic acid-inducible gene I -like, toll-like receptor , DNA-sensing receptors and C-type Lectin . These immunity sensors are distributed across various liver cell types and intrahepatic liver endothelial cells . After PAMP recognition by their corresponding PRRs, downstream signaling pathways are sequentially activated involving the expression of various adaptor molecules , kinase activation or phosphorylation . Thereafter, transcription factors are expressed . This process ultimately leads to effector gene expression including interferon-stimulated-genes , NF-B-inducible genes, and pro-inflammatory genes .
The hypothesis that TLR recognition initiates the transition from CHB to ACLF has been refuted due to the lack of a defined turning point from chronicity to the acute exacerbation phase of CHB-ACLF and the limited observations regarding the relationship between TLR recognition, the IFN response, and the prognosis of CHB-ACLF patients.
You May Like: How Often Do You Need Hepatitis Vaccine
How Can I Avoid Getting Hepatitis B
There is a safe and effective vaccine that can protect you from getting hepatitis B. The vaccine is usually given in three doses over a six month period. The vaccine will give you long-lasting protection. A combined vaccine for hepatitis A and hepatitis B is also available.
Other ways to protect yourself or your loved ones include:
- Adopt safe sex practices.
- Avoid sharing personal hygiene items
- If you have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus , an injection of hepatitis B immune globulin may help protect you.
- If you are pregnant, make sure you are screened for hepatitis B. If the test result shows that you have the virus, make sure your baby receives the free hepatitis B vaccine. If you have hepatitis B, breastfeeding is safe if the baby has received both protective antibody called immune globulin, and the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine within the first 12 hours of life. Talk to your doctor about having your newborn immunized .
- If you decide to have a tattoo, piercing, manicure or pedicure, ensure that the facility uses single-use needles and inks and/or follows proper sterilization procedures.
Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis B
Currently, there is no complete cure for hepatitis B. But when managed properly, those living with the virus can expect to live a normal life. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding beverages that contain alochol and tobacco products are crucial components in managing the disease.
You should also visit a doctor familiar with hepatitis B at least annually though twice a year might be best to monitor your liver through blood tests and medical imaging. As with most diseases, detecting it early leads to a better outcome. If youre exposed to the virus, you should get an antibody injection within 12 hours of exposure.
Read Also: Cdc Hepatitis B Vaccination Schedule
Chronic Hepatitis B Complications
Chronic hepatitis B can lead to
- cirrhosis, a condition in which scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue and prevents your liver from working normally. Scar tissue also partly blocks the flow of blood through the liver. As cirrhosis gets worse, the liver begins to fail.
- liver failure, in which your liver is badly damaged and stops working. Liver failure is also called end-stage liver disease. People with liver failure may require a liver transplant.
- liver cancer. Your doctor may suggest blood tests and an ultrasound or another type of imaging test to check for liver cancer. Finding cancer at an early stage improves the chance of curing the cancer.
Hepatitis B And Your Liver
The liver is such an important organ that we can survive only one or two days if it completely shuts down – if the liver fails, your body will fail, too. Fortunately, the liver can function even when up to 80% of it is diseased or removed. This is because it has the amazing ability to regenerate – or create – itself from healthy liver cells that still exist.
If your body were an automobile, your liver would be considered the engine. It does hundreds of vital things to make sure everything runs smoothly:
- Stores vitamins, sugar and iron to help give your body energy
- Controls the production and removal of cholesterol
- Clears your blood of waste products, drugs and other poisonous substances
- Makes clotting factors to stop excessive bleeding after cuts or injuries
- Produces immune factors and removes bacteria from the bloodstream to combat infection
- Releases a substance called “bile” to help digest food and absorb important nutrients
The word hepatitis actually means inflammation of the liver. Thus, hepatitis B refers to inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus. With early detection and appropriate follow-up medical care, people living with a chronic hepatitis B infection can expect to enjoy a long and healthy life.
Recommended Reading: Can You Have Hepatitis C And Not Know It
Can Hepatitis B Be Prevented
The hepatitis B vaccine is one of the best ways to control the disease. It is safe, effective and widely available. More than one billion doses of the vaccine have been administered globally since 1982. The World Health Organization says the vaccine is 98-100% effective in guarding against the virus. Newborns should be vaccinated.
The disease has also been more widely prevented thanks to:
- Widespread global adoption of safe blood-handling practices. WHO says 97% of the blood donated around the world is now screened for HBV and other diseases.
- Safer blood injection practices, using clean needles.
- Safe-sex practices.
You can help prevent hepatitis B infections by:
- Practicing safe sex .
- Never sharing personal care items like toothbrushes or razors.
- Getting tattoos or piercings only at shops that employ safe hygiene practices.
- Not sharing needles to use drugs.
- Asking your healthcare provider for blood tests to determine if you have HBV or if you are immune.
What Is The Outlook For People With Hepatitis B
The outlook for people with HBV is better now than ever before. You are certainly able to live a full life and help yourself stay healthy. You should make sure to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider who is qualified to treat hepatitis B, possibly a liver doctor.
Make sure you are vaccinated against hepatitis A. Check with your healthcare provider or pharmacist before taking other medications or over-the-counter products, including supplements and natural products. These could interfere with your medication or damage your liver. For instance, taking acetaminophen in large doses may harm your liver.
Follow the usual guidelines for living a healthy life:
- Eat nutritious foods, choosing from a variety of vegetables, fruits and healthy proteins. It is said that cruciferous vegetables are especially good at protecting the liver.
- Exercise regularly.
- Dont smoke and dont drink. Both tobacco and alcohol are bad for your liver.
- Do things that help you cope with stress, like journaling, talking with others, meditating and doing yoga.
- Avoid inhaling toxic fumes.
Also Check: Diagnosis Of Chronic Hepatitis B