What Are The Chances Of Persons With Hcv Infection Developing Long Term Infection Chronic Liver Disease Cirrhosis Liver Cancer Or Dying As A Result Of Hepatitis C
Of every 100 persons infected with HCV about:
-
75 to 85 persons may develop long-term infection
-
70 persons may develop chronic liver disease
-
15 persons may develop cirrhosis over a period of 20 to 30 years
-
Less than 3% of persons may die from the consequences of long term infection
-
Hepatitis C is a leading indication for liver transplants.
What Are The Recommendations For Follow
Anti-viral agents or immune globulin should not be used for postexposure prophylaxis.
For the source, baseline testing for anti-HCV.
For the person exposed to an HCV-positive source, baseline and follow-up testing including baseline testing for anti-HCV and ALT activity and follow-up testing for anti-HCV and ALT activity.
Also Check: Autoimmune Hepatitis Flare Up Symptoms
Hepatitis C Virus Genotyping
Hepatitis C viruses are not all the same. Certainly, they are all identified as hepatitis C viruses and they all can cause acute and chronic hepatitis C infection, but they are not exactly genetically alike. They have slightly different genetic variations and are grouped into different genotypes .
Knowing your genotype can significantly alter the duration of your treatment because your healthcare provider can select the right treatment for the type of HCV you have.
Genotypes are important because hepatitis C viruses with different genetic variations require different treatment approaches. Healthcare providers determine your HCV genotype with a laboratory test that uses a method called reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction . This test analyzes the genetic material of the virus to determine its sequence, which identifies the virus’s genotype.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vs Hepatitis C
Similar Articles Being Viewed By Others
Carousel with three slides shown at a time. Use the Previous and Next buttons to navigate three slides at a time, or the slide dot buttons at the end to jump three slides at a time.
23 March 2021
Christos Fotis, Nikolaos Meimetis, Leonidas G. Alexopoulos
21 July 2021
Essam H. Ibrahim, Hamed A. Ghramh & Mona Kilany
02 January 2023
Poramed Winichakoon, Jiraprapa Wipasa, Romanee Chaiwarith
02 February 2021
Allison N. Grossberg, Lilia A. Koza, Daniel A. Linseman
20 June 2022
Lorena O. Fernandes-Siqueira, Fabiana A. P. Ferreira, Andrea T. Da Poian
volume 11, Article number: 8689
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patientâs vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Also Check: How Can Hepatitis C Be Transmitted
You May Like: How Is Hepatitis B Transferred
Who Should Get Tested Or Hepatitis C
-
All Baby-Boomers need to be tested for hepatitis C. These are individuals born between 1945-1965. You need to get tested regardless of risk factors.
-
Persons who ever injected illegal drugs, including those who injected once or twice many years ago
-
Persons who were treated for clotting problems with a blood product made before 1992 when more advanced methods for manufacturing the products were developed
-
Persons who were notified that they received blood from a donor who later tested positive for hepatitis C
-
Persons who received a blood transfusion or solid organ transplant before July 1992 when better testing of blood donors became available
-
Long-term hemodialysis patients
-
Persons who have signs or symptoms of liver disease
-
Healthcare workers after exposures to HCV positive blood on the job
-
Children born to HCV-positive women
-
Homosexual men or women
- New recommendations from the Centers for Disease control state that all “Baby Boomers” get tested, regardless of their HCV risk factors. Baby Boomers were born between 1945-1965. Baby Boomers, as a group, are five times more likely to have HCV. Many have no symptoms, so they need to ask to be tested for HCV-do not assume you will be tested by your physician.
- This video by Dr. Galati outlines some of the Baby Boomer issues related to HCV.
Finding The Cause Of A False
Since there are various reasons for false-positive results, individuals should speak with a doctor about the probable cause. Some may be due to human error, such as a technical or clerical oversight.
However, a false-positive result can also result from another condition, such as an STI or an autoimmune disorder. Autoimmune disorders that may cause false-positive results include lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
Donât Miss: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Sex
You May Like: How Do You Contact Hepatitis
Enzyme Immunoassays For Detection Of Hepatitis C Antibody
The HCV Ab test is used for initial screening for hepatitis C. The test is performed by enzyme immunoassays , which detect the presence of hepatitis C antibodies in serum. The result of the test is reported as positive or negative. Third-generation EIAs have a sensitivity/specificity of approximately 99%. However, the presence of HCV Ab does not indicate whether the infection is acute, chronic, or resolved. A positive antibody test result should be followed up with an HCV RNA test to confirm that viremia is present.
How Hepatitis C Virus Is Diagnosed
Hepatitis C virus is usually diagnosed with blood tests. An antibody test can detect whether your body has had to fight off HCV infection. A blood test which measures the virus in your blood confirms the diagnosis, but results take longer. Sometimes, liver function tests, imaging studies, or a biopsy can support or confirm the diagnosis as well.
As of March 2020, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends HCV screening for all adults ages 18 to 79. The CDC also updated their guidelines in April 2020, recommending screening for all adults and pregnant women.
Read Also: How Long Is Hepatitis B Treatment
Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
The CDC recommends that you get tested at least once no matter what. Definitely get screened if any of these things apply to you:
- You were born between 1945 and 1965.
- You use or inject drugs.
- You have ever injected drugs â even if it was just once or a long time ago.
Read Also: What Does Hepatitis C Ab Non Reactive Mean
Hepatitis B Blood Tests
The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
Read Also: What Do You Do If You Have Hepatitis C
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose Schedule
Search Strategy And Identification Of Studies
Search strategies were developed by a medical librarian with expertise in designing systematic review searches. Our search algorithm consisted of the following components: hepatitis C, diagnostic tests, and diagnostic accuracy. We searched MEDLINE , EMBASE , the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials , Science Citation Index Expanded , Conference Proceedings Citation Index-Science , SCOPUS , Literatura Latino-Americana e do Caribe em Ciências da Saúde and WHO Global Index Medicus. The search was supplemented by searching for ongoing studies in WHOs International Clinical Trials Registry. The literature search was limited to English language and human subjects that available until April 30th, 2015. In addition to searching databases, we contacted individual researchers and authors of major trials to address whether any relevant manuscripts are in preparation or in press. The references of published articles found in the above databases were searched for additional pertinent materials.
Study selection proceeded in three stages: 1) titles/abstracts were screened by a single reviewer according to standard inclusion and exclusion criteria 2) full manuscripts were obtained and evaluated by two independent reviewers to include or not 3) two independent reviewers extracted all data. Differences were resolved by a third independent reviewer.
Dont Miss: Can Hepatic Steatosis Be Reversed
Hepatitis C Antibody Test
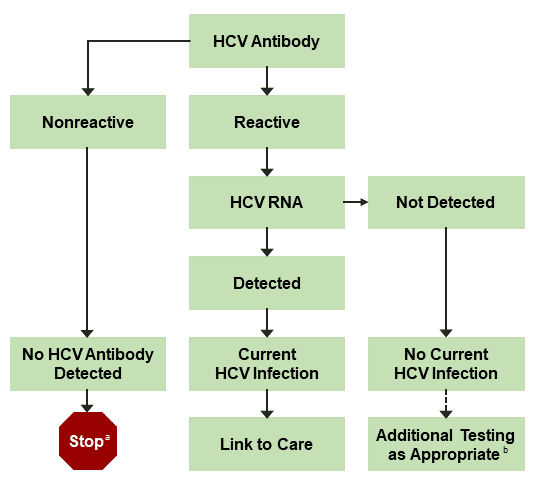
Initially, doctors use the anti-HCV test. It detects antibodies that the immune system produces to fight the HCV.
However, the anti-HCV test cannot tell whether the antibodies are present because a person currently has an active hepatitis C infection or whether they have had this infection in the past.
The antibodies can remain, even if a person has had successful treatment, or if their body has cleared the virus on its own.
A negative result is interpreted as no HCV infection, assuming one has not had recent exposure to HCV. If one has had recent exposure to HCV in the last 6 months, anti-HCV testing will need to be repeated in the future.
Anyone who receives a positive result on an anti-HCV test will require further testing.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Viral Rna Quantitative Real Time Pcr
Cases And Clusters Of Potential Public Health Importance
Jurisdictions should review and analyze hepatitis B data regularly to identify cases and clusters of hepatitis B that merit further investigation. When resources are limited, these should be prioritized for investigation based on the degree of public health importance. The following are examples of high priority cases and clusters:
- People of childbearing age who are or have the potential to become pregnant, indicating the potential for perinatal transmission
- Children 24 months of age to detect perinatal transmission
- People in age and demographic groups for whom infection may be acute due to recent transmission, including those
- 70 years of age
Can You Have A False Positive Anti
Yes. A false positive test means the test looks as if it is positive, but it is really negative. This happens more often in persons who have a low risk for the disease for which they are being tested. For example, false positive anti-HCV tests happen more often in persons such as blood donors who are at low risk for hepatitis C. Therefore, it is important to confirm a positive anti-HCV test with a supplemental test as most false positive anti- HCV tests are reported as negative on supplemental testing. There are certain situations where individuals with autoimmune disorders, such as Lupus, may have a false positive HCV antibody test. Confirming this with a HCV-RNA will usually be negative-indicating no active hepatitis C.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Can You Get It From Intercourse
What Can Persons With Hcv Infection Do To Protect Their Liver
-
Stop using alcohol.
- Keep your weight in the normal weight. Fatty liver, related to obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrom increases your risk of liver damage and cirrhosis in hepatitis C.
-
See your doctor regularly.
-
Don’t start any new medicines or use over-the-counter, herbal, and other medicines without a physician’s knowledge.
-
Get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B
Why A False Positive Happens
A doctor will consider two factors when reviewing the accuracy of a test result. These two factors are the tests specificity and sensitivity.
Specificity refers to the ability of a test to correctly identify those who do not have a disease. This is called the true negative rate.
Sensitivity reflects the ability of a test to correctly identify those who do have a disease. This is called the true positive rate.
According to a , third-generation anti-HCV tests have an average specificity of 97.5% to 99.7%. The sensitivity of these tests varies from 61.0% to 81.8%.
These findings indicate that anti-HCV tests detect true negatives more accurately than true positives .
A person may receive a false-positive test result if they have HCV antibodies from a previous active infection. They may have received successful treatment for this infection, or their body may have cleared it without treatment.
In either case, the antibodies from the previous infection can remain in the body and lead to positive results on anti-HCV tests.
False-positive results can also occur in children who had HCV transmitted to them during birth from a mother with hepatitis C virus infection.
Ultimately, a person who receives a positive result from an anti-HCV test may not have an active hepatitis C infection. This is why a doctor then typically performs another test the HCV RNA RT-PCR test before making a definitive diagnosis.
People who do not have hepatitis C can often prevent exposure to it by:
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Adults Missed Dose
Other Hepatitis C Tests
After an individual has received a reactive or positive result from a hepatitis C antibody test, they will need to have two follow-up tests.
The first test checks to see whether a person still has the virus the other measures the amount of the virus in the blood.
The first test is the hep C RNA qualitative test, also known as the PCR test. A positive result means that a person has the hepatitis C virus. A negative result means that the body has cleared the virus without treatment.
The second test is the hep C RNA quantitative test. The result of this test is given as a number rather than a positive or negative. This is because the test compares the amount of the virus in the body before, during, and after treatment.
The number given as a result of this test is known as the viral load. The lower amount of the hepatitis C virus in the blood, the better the chances that a person can eliminate the virus from their body.
After hepatitis C virus is diagnosed, other tests may be needed:
Certain behaviors, experiences, and medical procedures increase the risk of getting the hepatitis C virus, which is transmitted by contact with blood.
The following are risk factors for contracting the virus:
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advise all baby boomers get tested for hepatitis C. Baby boomers are people born between 1945 and 1965. They are five times more likely to have the virus than other adults.
You May Like: Titer Test Hepatitis B Vaccine
Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
AIDS is caused by 2 known types of HIV. HIV type 1 is found in patients with AIDS or AIDS-related complex and in asymptomatic infected individuals at high risk for AIDS. The virus is transmitted by sexual contact, by exposure to infected blood or blood products, or from an infected mother to her fetus or infant. HIV type 2 infection is endemic only in West Africa, and it has been identified in individuals who had sexual relations with individuals from that geographic region. HIV-2 is similar to HIV-1 in viral morphology, overall genomic structure, and its ability to cause AIDS.
Antibodies against HIV-1 and HIV-2 are usually not detectable until 6 to 12 weeks following exposure and are almost always detectable by 12 months. They may fall to undetectable levels in the terminal stage of AIDS when the patients immune system is severely depressed.
Routine serologic screening of patients at risk for HIV-1 or HIV-2 infection usually begins with a HIV-1/-2 antigen and/or antibody screening test, which may be performed by various FDA-approved assay methods, including rapid HIV antibody tests, enzyme immunoassays, and chemiluminescent immunoassays. In testing algorithms that begin with these methods, supplemental or confirmatory testing should be requested only for specimens that are repeatedly reactive by these methods according to assay manufacturers instructions for use.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis B Core Antibody
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a liver disease caused by the hepatitis C virus , which is found in the blood of persons who have this disease. HCV is spread by contact with the blood of an infected person. Once exposed, 85% of these individuals become chronically infected, with a 15% chance of developing cirrhosis, which is scarring of the liver, over a 25 year time frame.
What Is The Risk That Hcv Infected Women Will Spread Hcv To Their Newborn Infants
About 5 out of every 100 infants born to HCV infected women become infected. This occurs at the time of birth, and there is no treatment that can prevent this from happening. Most infants infected with HCV at the time of birth have no symptoms and do well during childhood. More studies are needed to find out if these children will have problems from the infection as they grow older. There are no treatments or guidelines for the treatment of infants or children infected with HCV. Children with elevated ALT levels should be referred for evaluation to a specialist familiar with the management of children with HCV-related disease.
Recommended Reading: What Does It Mean To Have Antibodies For Hepatitis C