Easy Bleeding And Bruising
If you see someone with lots of bruising, it means there is a problem with blood clotting, says Eugene R Schiff, M.D., the executive director of the Schiff Center for Liver Diseases at the University of Miami Health System. Part of your livers job is to regulate the production of new blood platelets via a hormone called thrombopoietin. When the liver is damaged or scarred, as in the case of cirrhosis, thrombopoietin production slows, leading to a lower platelet count, according to research in the journal Hematology. Without these platelets to help with blood clotting, research shows that you are at greater risk for an increase in bleeding, both internally and externally.
Related: The Very Best Foods for Your Liver
Hepatitis C And Injecting Drugs
If you inject drugs, avoid sharing needles, syringes or other equipment such as tourniquets, spoons, swabs or water.
Where possible, always use sterile needles and syringes. These are available free of charge from needle and syringe programs and some pharmacists. To find out where you can obtain free needles, syringes and other injecting equipment, contact DirectLine
Try to wash your hands before and after injecting. If you cant do this, use hand sanitiser or alcohol swabs from a needle and syringe program service.
Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis
If you are living with a chronic form of hepatitis, like hepatitis B and C, you may not show symptoms until the damage affects liver function. By contrast, people with acute hepatitis may present with symptoms shortly after contracting a hepatitis virus.
Common symptoms of infectious hepatitis include:
It is crucial to understand what is causing hepatitis in order to treat it correctly. Doctors will progress through a series of tests to accurately diagnose your condition.
You May Like: Hepatitis A Causes Symptoms Treatment
What Makes Yale Medicine’s Approach To Treating Hepatitis B And C Unique
The Viral Hepatitis Program at Yale Medicine represents one of the leading viral hepatitis treatment programs in the country and is engaged in innovative research focused on advancing the care of patients with chronic hepatitis B, C and D infections.
A multidisciplinary team of faculty physicians and mid-level providers offer a coordinated approach to preparing patients for success. Services include structured hepatitis patient education classes, mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques , a formal physician-guided weight-loss program and access to clinical trials evaluating current and new therapies that are not available in routine clinical practice.
Our program is a core member of several national and international observational cohort studies which contributes to the advancement of science of hepatitis treatment around the world.
“Our team at Yale Medicine is uniquely equipped to serve patients with viral hepatitis from Connecticut and beyond and aims to offer outstanding, individualized, patient-centered care to help educate and guide patients through their treatment,” says Dr. Lim. We have specialists who have nationally recognized expertise in the management of viral hepatitis in special populations, including HCV-HIV coinfection, end-stage renal disease, cirrhosis/liver failure, post-liver transplant, and prior failure to respond to all-oral direct acting antivirals .
Late Signs Of Liver Disease
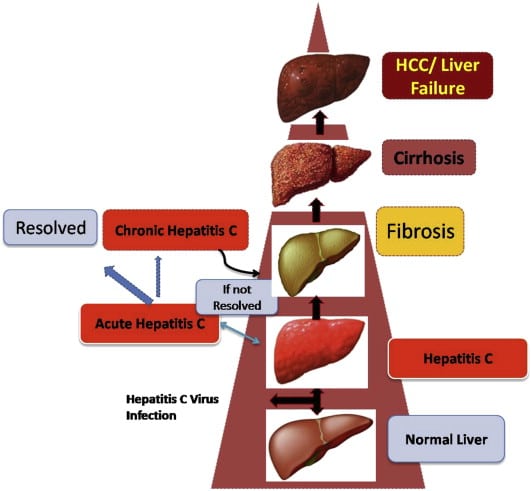
If you dont notice or experience any early signs, it can take as long as 15 years for symptoms of hepatitis C-liver disease to emerge. The damage to your liver starts off as a slow, simmering inflammation that, over time, can progress to scarring , liver failure, liver cancer, and the need for a liver transplant. Hepatitis C is the leading cause of cirrhosis and liver cancer and the most common reason for liver transplantation in the United States.
Symptoms of end-stage liver disease are far less innocuous than the early signs of an acute infection. They may include easy bleeding or bruising, persistent or recurring jaundice, intense itching, loss of appetite, and nausea. Swelling in your abdomen and legs due to fluid buildup, liver cancer, and problems with concentration and memory may also occur.
If you develop cirrhosis, your liver can fail. Other signs of cirrhosis are bleeding of the digestive tract caused by enlarged veins in the esophagus connecting the throat and stomach. Another consequence of cirrhosis is brain and nervous system damage due to the buildup of toxins in your blood, which occurs when the failing liver can no longer clean and detoxify your blood.
The good news is that today hepatitis C is curable, and knowing what to look out for can help you and your doctor diagnose it early, and potentially stave off some of the end-stage symptoms.
Read Also: When To Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Can Hepatitis C Be Prevented
There is no vaccine against hepatitis C. The only way to prevent infection is to avoid contact with infected blood.
Hepatitis C cannot be spread by coughing, sneezing or sharing eating utensils. People should not be kept away from school, work, or other social settings because they have hepatitis C.
Here are some precautions that may prevent the spread of hepatitis C:
- Do not share personal care items, such as toothbrushes or razors, with others.
- Practice safe sex by using condoms.
- Dont share needles or syringes.
- Wear gloves when handling another persons blood.
- Use sterile equipment for body piercings or tattoos.
- If you are a healthcare worker, follow recommended safety measures.
People who are at greater risk for contracting hepatitis C should have their blood tested. The Centers for Disease Control recommends that Americans born between 1945 and 1965 be screened at least once for the disease.
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
You are more likely to get hepatitis C if you:
- Have injected drugs
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you probably will not have symptoms until it causes complications. This can happen decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
The Challenges Of Early Diagnosis
HCV infection can be difficult to detect, for several reasons.
Many early symptoms of HCV infection, such as fatigue and joint pain, are non specific and may not catch the attention of patients or their doctors. Furthermore, Lok adds, most patients with hepatitis C do not have any symptoms until they have cirrhosis and even when they have early cirrhosis, they may not have symptoms.
As a result, many individuals with HCV infection dont even know they are infected. Dr. Lok adds that screening for high-risk groups in particular needs to be improved, so they can benefit from new treatments.
One of Dr. Loks current research projects addresses this very issue. Working with MiChart,the University of Michigans electronic health record system, Dr. Loks team placed electronic alerts indicating the need for HCV testing in all patients born between 1945 and 1965 a group that is five times more likely to be infected who have never been tested. The alert links to an order set and provides educational information on HCV infection for primary care physicians, medical staff and patients.
We just completed the pilot phase of this study, and we observed a marked increase in screening rates, Dr. Lok says.
Hepatitis C With Compensating Cirrhosis
Oral antiviral medications, which remove the virus from a persons blood, are the primary treatment for hepatitis C. The aim is to make the virus undetectable in the blood, which shows that the medication is working. Doctors refer to this as a virologic response.
If this response lasts for 12 weeks or more after finishing treatment, the person has achieved a sustained virologic response . Around 99 percent of people who have an SVR remain virus-free for the rest of their lives.
Although antiviral treatment is generally more successful when liver fibrosis has a METAVIR score of F2 or below, people with stage F3 or even stage F4 fibrosis can reach SVR.
After achieving an SVR, the hepatitis C infection will not cause further liver damage. However, people with advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis may continue to experience complications as a result of the existing liver damage.
Don’t Miss: Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
What Are The Risk Factors For Hepatitis B And C
Hepatitis B: Although most commonly acquired early in life, adults can also contract it. Hepatitis B is largely transmitted through bodily fluids. It can be passed at birth from a hepatitis B-infected mother or through exposure in early childhood to body fluids, blood or contaminated medical instruments. Hepatitis B can also be transmitted through intranasal and injection drug use as well as infected tools used during tattooing and body piercing.
Hepatitis C: The key risk factors are also intranasal and injection drug use, tattoos and body piercings, high-risk sexual contact, blood transfusions before 1992 and organ transplantation.
Another key risk factor for hepatitis C is being born from 1945 to 1965, during the baby-boom years. Eighty percent of all people who currently have hepatitis C in the United States were born in that timeframe.
Although the reasons that baby boomers are more likely to have hepatitis C than others arent entirely understood, its believed that most were infected in the 1970s and 1980s, when rates of hepatitis C were at their peak.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend that all U.S. adults born from 1945 to 1965 undergo a one-time screening test for hepatitis C. Connecticut is one of several states that has written this recommendation into law. In Connecticut ,the law requires that primary care clinicians screen all adults born within those years.
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Don’t Miss: Can You Transmit Hepatitis Sexually
The Search For A Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are research studies that test how well new medical approaches work in people. Before an experimental treatment can be tested on human subjects in a clinical trial, it must have shown benefit in laboratory testing or animal research studies. The most promising treatments are then moved into clinical trials, with the goal of identifying new ways to safely and effectively prevent, screen for, diagnose, or treat a disease.
Speak with your doctor about the ongoing progress and results of these trials to get the most up-to-date information on new treatments. Participating in a clinical trial is a great way to contribute to curing, preventing and treating liver disease and its complications.
Start your search here to find clinical trials that need people like you.
Importance Of Understanding And Acting On The Early Signs Of Hepatitis
Should you discover that you are a carrier, it is vital that you take the necessary steps to prevent the disease from spreading. If you have recently acquired the disease, treatments are available. However, time is of the essence if you wait too long, you may suffer liver damage or even develop liver cancer. If you discover that you have a form of hepatitis that has progressed to the chronic stage, it is important that you learn how to manage the disease.
You could unknowingly be participating in activities that exacerbate some of the effects of the disease. For instance, persons who have hepatitis should avoid alcohol, because it can damage the liver and make it harder for a persons body to fight the infection. Poor diets can also have a negative impact.
Should you discover that you have hepatitis, though, you can begin to adopt a diet and lifestyle that is beneficial to counteract the effects of the disease.
Recommended Reading: How Does Someone Get Hepatitis B
Also Check: New Drugs For Hepatitis C
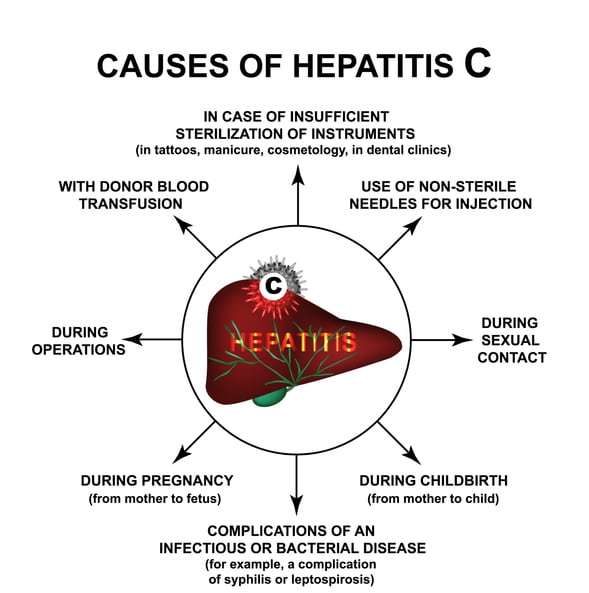
Causes Of Hepatitis C
You can become infected with hepatitis C if you come into contact with the blood of an infected person.
Other bodily fluids can also contain the virus, but blood contains the highest level of it. Just a small trace of blood can cause an infection. At room temperature, it’s thought the virus may be able survive outside the body in patches of dried blood on surfaces for up to several weeks.
The main ways you can become infected with the hepatitis C virus are described below.
When To Seek Medical Advice
See your GP if you persistently have any of the later symptoms listed, or if they keep returning. They may recommend having a blood test that can check for hepatitis C.
Read more about diagnosing hepatitis C
None of these symptoms mean you definitely have hepatitis C, but its important to get them checked out.
You should also speak to your GP about getting tested if theres a risk youre infected, even if you dont have any symptoms. This particularly includes people who inject drugs or have done so in the past.
Read about the causes of hepatitis C for more information about whos at risk of having the infection.
Page last reviewed: 27 October 2021 Next review due: 27 October 2024
Also Check: Is Hepatitis B And Hiv The Same
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
There are three main ways to diagnose HBV infection. They include:
- Blood tests: Tests of the blood serum shows how your bodys immune system is responding to the virus. A blood test can also tell you if you are immune to HBV.
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to show the size and shape of your liver and how well the blood flows through it.
- Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis.
The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit. Often, people whove become infected first learn they have hepatitis B when they go to donate blood. Blood donations are routinely scanned for the infection.
The virus can be detected within 30 to 60 days of infection. About 70% of adults with hepatitis B develop symptoms, which tend to appear an average of 90 days after initial exposure to the virus.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Antibody Reactive Means
Hepatitis C With Decompensating Cirrhosis
Until recently, doctors considered a liver transplant to be the only effective treatment for decompensating cirrhosis.
However, a recent small-scale study found that a course of direct-acting antiviral medication may improve some peoples liver function enough to take them off the waiting list for a liver transplant. People with liver disease that was less severe had a higher likelihood of removal from the list.
However, recent Canadian guidelines warn that certain antiviral drugs may potentially be dangerous for people with severe decompensating cirrhosis. This is because the liver is less able to filter out toxic waste, meaning that the antiviral drugs could accumulate to toxic levels. Doctors must weigh up the benefits against the risks.
When a person is waiting for a liver transplant, a doctor will assess whether or not to pause antiviral treatment.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis C Genotype 1a
How Is It Spread
Hepatitis A is spread when a person ingests fecal mattereven in microscopic amountsfrom contact with objects, food, or drinks contaminated by feces or stool from an infected person.
- Birth to an infected mother
- Sex with an infected person
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles, syringes, and even medical equipment, such as glucose monitors
- Sharing personal items such as toothbrushes or razors
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
Hepatitis C is spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus even in microscopic amounts enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis C virus can also be transmitted from:
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles and syringes
- Receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
- Birth to an infected mother
Also Check: What Are The Ways You Can Get Hepatitis C
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis C
Doctors treat hepatitis C with antiviral medicines that attack the virus and can cure the disease in most cases.
Several newer medicines, called direct-acting antiviral medicines, have been approved to treat hepatitis C since 2013. Studies show that these medicines can cure chronic hepatitis C in most people with this disease. These medicines can also cure acute hepatitis C. In some cases, doctors recommend waiting to see if an acute infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
Your doctor may prescribe one or more of these newer, direct-acting antiviral medicines to treat hepatitis C:
You may need to take medicines for 8 to 24 weeks to cure hepatitis C. Your doctor will prescribe medicines and recommend a length of treatment based on
- which hepatitis C genotype you have
- how much liver damage you have
- whether you have been treated for hepatitis C in the past
Your doctor may order blood tests during and after your treatment. Blood tests can show whether the treatment is working. Hepatitis C medicines cure the infection in most people who complete treatment.
Hepatitis C medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Check with your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Also Check: How To Know If I Have Hepatitis C