Causes And Risk Factors Of Hepatitis D
The primary route of transmission for hepatitis D is contact with infected blood or other bodily fluids. This can happen through sharing needles or drug materials with an infected person or having unprotected sex with an infected person.
Although it is rare, hepatitis D can be passed from mother to child during birth.
People cant get hepatitis D through everyday close contact that doesnt involve blood or bodily fluids.
Prevention Of Hepatitis D
Avoiding high-risk behavior helps prevent people from getting hepatitis B and thus from getting hepatitis D.
There is no vaccine for hepatitis D. But if people do not already have hepatitis B, they can be vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine Hepatitis B Vaccine The hepatitis B vaccine helps protect against hepatitis B and its complications . Generally, hepatitis B is more serious than hepatitis A and… read more , which can prevent hepatitis D as well as hepatitis B.
What Is Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the blood, and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis. However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Hepatitis C Screening
Enteric Routes: Transmission Of Hepatitis A And Hepatitis E
The Hepatitis A and hepatitis E viruses are both transmitted by enteric, that is digestive or by fecal, routes. This is also known as the fecal-oral route. To be exposed to these viruses, you must ingest fecal matter that is infected with the virus. While there are several ways in which this fecal-oral route can be established, poor hygiene and poor sanitary conditions in some countries lead to higher rates of infection of these viruses.
As a result, some areas of the world, like India, Bangladesh, and Central and South America, are particularly prone to the hepatitis E virus. About one-third of people in the United States have been exposed to the hepatitis A virus.
It is believed that the hepatitis F virus may also be spread by enteric routes.
When To See A Healthcare Provider
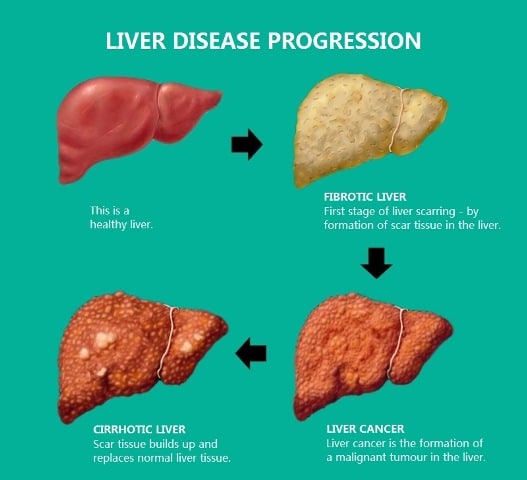
Recognizing the signs of infection is crucial in diagnosing hepatitis D and avoiding any serious complications.
If you notice symptoms such as fever, fatigue, nausea, pain in the upper abdomen, dark-colored urine, or jaundice, its important to contact a healthcare professional as soon as possible and accessible. Theyll be able to run blood tests to determine the diagnosis.
Also Check: Can You Get Hepatitis A After Vaccination
Interfering With Viral Replication
Viral targets
In contrast to other RNA viruses that encode RNA-dependent RNA-polymerases for replication and mRNA synthesis, HDV recruits and reprogrammes the cellular Pol II to achieve these goals. Accordingly, an important viral drug target is lacking. Nevertheless, crucial steps in the viral life cycle like the ribozyme-mediated self-cleavage of genomic and antigenomic RNA oligomers or the HDAg-dependent regulation of RNA replication and mRNA synthesis are attractive viral structures suitable for drug targeting. Inactivation of the S-HDAg could induce a selective shut down of RNA synthesis . Alternatively, abolition of the interaction of the prenylated C-terminus of L-HDAg with the cytosolic loop in the HBV S-domain by small molecules would inhibit virus release similar to LNF, which targets the corresponding host enzyme . No such drugs have been identified so far, however applying the new replication systems mentioned above will facilitate screening approaches and drug candidate identification in the future.
Cellular targets
Beside these well-characterised host factors additional approaches using siRNA or drug libraries in susceptible cell lines will allow to identify novel host factors in the future and it will be a challenging task to identify those that allow intervention and are tolerable regarding side effects.
Populations At Higher Risk
Given the way it is spread, almost anyone can become infected with hepatitis A. However, certain people are at higher risk of contracting the disease than others. These include people who:
- Travel to countries where hepatitis A is common
- Are male and have sexual contact with other males
- Are illegal drug users
- Have blood clotting issues such as hemophilia
- Live with another person who is infected with hepatitis A
Recommended Reading: How Hepatitis B And C Are Transmitted
Why Understanding The Numbers Matters
Scientist testing samples
With the development of new therapies for hepatitis D, knowing how many people are infected is necessary to properly target and fund meaningful interventions that help save lives and prevent people from developing life-threatening conditions, such as cancer, caused by hepatitis. These interventions include a new drug, bulevirtide, that is showing promise in treating Hepatitis D and for which approval is being sought in North America.
The screening and testing of hepatitis D infected populations is crucial to ensuring physicians can provide appropriate treatment, care and support, says Dr. Carla Osiowy, Chief, Viral Hepatitis and Bloodborne Pathogens at the NML. Increased awareness also means physicians can provide information to patients such as how to protect themselves from being infected or how to prevent further transmission to other people.
What Are The Complications Of Chronic Hepatitis D
Chronic hepatitis D may lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer. People who have chronic hepatitis B and D are more likely to develop these complications than people who have chronic hepatitis B alone.20 Early diagnosis and treatment of chronic hepatitis B and D can lower your chances of developing serious health problems.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C And Hair Loss
Home Remedies And Lifestyle
Healthcare and sanitation workers who have a higher chance of exposure to needle pricks should take additional precautions to prevent the accidental spread of infection. If you use injection drugs or live with someone who does, seek help immediately to reduce your exposure to long-term consequences.
Getting a hepatitis B vaccination can protect you against contracting hepatitis D, so talk to your doctor if you believe youre at risk.
Abstaining from alcohol will minimize strain on your liver. If you choose to drink, its essential to drink responsibly. Health authorities define responsible drinking as no more than one drink per day for women and no more than two drinks per day for men.
Binge drinking is harmful, especially when your liver function is already compromised from hepatitis.
Following safe sex practices will keep you from contracting additional infections and help keep your partner from getting hepatitis D. Safe sex to prevent the spread of hepatitis D is particularly important for men who have sex with other men.
Sexual Transmission And Viral Hepatitis
Certain adults who are sexually active should be vaccinated against hepatitis B.
CDC and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommend hepatitis B vaccination for
- sexually active people with more than one sex partner during the previous 6 months
- people seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually transmitted disease
- sex partners of people with hepatitis B and
- men who have sex with men .
CDC recommends one-time hepatitis C testing of all adults and regular testing for people with risk factors.
Recommended Reading: Difference Between Hepatitis B And C Symptoms
What Is Hepatitis D Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment And Prevention
Hepatitis D, also known as delta hepatitis affects only those who have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus if you contract both, the one-two punch can cause serious liver problems.
The hepatitis D virus depends on another virus, namely the one that causes hepatitis B, to reproduce itself. This means hepatitis D can only infect people who are already infected with the hepatitis B virus, or who are exposed to hepatitis B at the same time theyre exposed to hepatitis D.
When you are infected with hepatitis B and D at the same time, its called coinfection.
If you already have chronic hepatitis B and are then exposed to the hepatitis D virus, its called a superinfection. In either case, this double whammy can lead to serious problems.
Hepatitis D can cause significant liver damage and even death, so prevention of this dual infection is crucial.
Hepatitis D can cause an acute or chronic infection, or both. The acute infection lasts a short time, and the chronic infection lasts longer than six months.
Prognosis Of Hepatitis D
Your health outlook depends on whether you were coinfected or superinfected with hepatitis D the prognosis is better for people who were coinfected.
The vast majority of coinfected people experience only the acute phase of the disease most of these people will get better over two to three weeks. Liver enzyme levels typically return to normal within four months.
About 10 percent of people infected with hepatitis D develop a chronic liver infection.
Chronic hepatitis D leads to cirrhosis, or scarring of the liver, in about 70 to 80 percent of cases. Once a person has cirrhosis, the disease may remain stable for as long as 10 years, although a high percentage of people with chronic hepatitis D and cirrhosis eventually die of acute liver failure or liver cancer unless they get a liver transplant.
The overall mortality rate of hepatitis D is unclear, with estimates placing it between 2 and 20 percent. As with most forms of hepatitis, prevention is the best strategy.
You May Like: Can You Transmit Hepatitis Sexually
Symptoms Of Hepatitis D
Coinfection with hepatitis D usually makes the hepatitis B infection more severe.
Coinfection with hepatitis B and D can lead to fulminant hepatitis Symptoms . Fulminant hepatitis can progress very quickly. Toxic substances normally removed by the liver build up in the blood and reach the brain, causing hepatic encephalopathy Hepatic Encephalopathy Hepatic encephalopathy is deterioration of brain function that occurs in people with severe liver disease because toxic substances normally removed by the liver build up in the blood and reach… read more . People may lapse into a coma within days to weeks. Fulminant hepatitis may be fatal, especially in adults.
Open Questions And Future Directions
-
Can hepatitis D virus establish transcriptionally silenced but reactivatable episomes in hepatocytes as an additional mechanism of persistence?
-
To what extent do the eight HDV genotypes differ in replication efficacy and sensitivity against the upcoming novel treatments?
-
Do HDV-targeted therapies lead to a restoration of HDV-specific immunity?
-
Are these restored immune responses required for treatment response? Are they required for prevention of viral relapse? Of note, there may be differences in treatment regimens that are associated with alanine aminotransferase flares combination therapy) compared with treatment regimens without ALT flares .
-
How can a synergistic potential of antiviral drugs and immune-modulators be translated into curative regimens?
-
Are there baseline or on-treatment predictors to sustained HDV virological response for the different treatment strategies?
-
Is a sustained HDV virological response without hepatitis B surface antigen loss a realistic and achievable aim for treatment regimens without IFNs?
-
Are drugs aiming at HBsAg loss effective and safe in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus/HDV coinfection?
-
Last but not least, since HDV is prevalent in low-income countries and migrant populations, it will be important to establish new concepts to foster diagnosis and access to care.
Recommended Reading: What Blood Test Checks For Hepatitis C
How Hepatitis D Is Spread
Hepatitis D is spread when infectious body fluids come into contact with body tissues beneath the skin or mucous membranes . In Australia most infections are associated with:
- immigration from a country where hepatitis D is relatively common
- sharing injecting equipment
- mother-to-baby transmission of hepatitis D virus at or around the time of birth can occur, although this is uncommon.
Who Should Be Vaccinated
Children
- All children aged 1223 months
- All children and adolescents 218 years of age who have not previously received hepatitis A vaccine
People at increased risk for hepatitis A
- International travelers
- Men who have sex with men
- People who use or inject drugs
- People with occupational risk for exposure
- People who anticipate close personal contact with an international adoptee
- People experiencing homelessness
People at increased risk for severe disease from hepatitis A infection
- People with chronic liver disease, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C
- People with HIV
Other people recommended for vaccination
- Pregnant women at risk for hepatitis A or risk for severe outcome from hepatitis A infection
Any person who requests vaccination
There is no vaccine available for hepatitis C.
You May Like: Hepatitis B And C Home Test Kit
Parenteral Routes: Transmission Of Hepatitis B Hepatitis D And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B, C, and D viruses are all transmitted by what is known as the parenteral route. Parenteral simply means that these viruses can be introduced by all routes except through the intestinal tract, which leaves the door wide open in terms of possible exposure. Let’s look at the possible transmission routes for each of these types of hepatitis virus more closely.
How Long Does It Last
Hepatitis A can last from a few weeks to several months.
Hepatitis B can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long condition. More than 90% of unimmunized infants who get infected develop a chronic infection, but 6%10% of older children and adults who get infected develop chronic hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long infection. Most people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop chronic hepatitis C.
Read Also: Is Hepatitis C Related To Aids
Immune Response To Hdv
Mechanisms of HDV-specific CD8+ Tcell failure. HDV-specific CD8+ T cells targeting viral epitopes with wild-type sequence display a chronically activated phenotype and are functionally partially exhausted , HDV-specific CD8+ T cells targeting viral epitopes with sequence variations do not recognise the antigen anymore and display a memory-like phenotype . HDV, hepatitis D virus.
Sexual Transmission And Hepatitis A
Transmission of hepatitis A virus can occur from any sexual activity with an infected person and is not limited to fecal-oral contact. People who are sexually active are considered at risk for hepatitis A if they are MSM, live with or are having sex with an infected person, or inject drugs. Vaccination is the most effective means of preventing hepatitis A transmission among people at risk for infection. CDC has published recommendations for prevention of hepatitis A that identify all groups recommended for vaccination, including hepatitis A vaccination for MSM.
Don’t Miss: Different Types Of Hepatitis C
What Can You Do To Prevent Hepatitis D
One of the best ways to prevent hepatitis D is by getting a hepatitis B vaccination. Since its impossible to contract hepatitis D without hepatitis B, avoiding hepatitis B in the first place is the best-case scenario.
If you already have hepatitis B, you can still prevent hepatitis D by abstaining from risky behaviors, such as unprotected sex and injection drug use. If you need help to develop safer habits, talk to your healthcare professional for a referral to a social worker, therapist, or treatment program.
The Types Of Viral Hepatitis
There are five main types of viral hepatitis known as hepatitis A , hepatitis B , hepatitis C , hepatitis D , and hepatitis E . That said, there have been cases of acute hepatitis that could not be attributed to one of these five types of hepatitis viruses, alcohol, drugs, or autoimmune disease, which lead researchers to try to find another cause.
Though the etiology of these viruses have not yet been fully established, researchers have identified three other types of viral hepatitis , which they have named hepatitis F , hepatitis G , and transfusions transmitted virus . As relatively new diseases and viral discoveries, information about them and how they work is relatively scarce. We do know, however, that cases of TTV have only been associated with hepatitis in people who have had a blood transfusion.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis Vaccine For Adults Schedule
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis D
-
Chronic hepatitis B Hepatitis B, Chronic Chronic hepatitis B is inflammation of the liver that is caused by the hepatitis B virus and that has lasted more than 6 months. Most people with chronic hepatitis B have no symptoms, but some… read more suddenly becomes much worse in people who are chronically infected with hepatitis B.
-
Chronic hepatitis B progresses more rapidly than it typically does.
If hepatitis D is suspected, a blood test to detect antibodies produced by the person’s immune system in response to the hepatitis virus D is done to confirm the diagnosis.
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis
Each type of hepatitis is treated differently.
Hepatitis A often goes away on its own and home treatment is all that is needed to help the liver recover, such as:
- Avoiding alcohol
- Avoiding certain medicines that can be harmful to the liver
Hepatitis B often goes away on its own in about 6 months, and can also be treated at home with the above remedies. Other treatments for hepatitis B include:
- Antiviral medications
- Liver transplant in severe cases
Treatment for hepatitis C is effective on certain forms of the hepatitis C virus. The choice of medications depends on the type of hepatitis C you have, whether you have been treated for the illness before, how much liver damage has occurred, any other underlying medical issues, and other medicines you take. Treatment for hepatitis C usually involves 8 to 12 weeks of oral antiviral medications, such as:
- Elbasvir-grazoprevir
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine Cost Without Insurance
How Is Hepatitis D Diagnosed
Doctors may suspect a person has hepatitis D when the symptoms of acute hepatitis B are unusually severe, chronic hepatitis B gets worse much faster than usual, or when chronic hepatitis B suddenly gets much worse, which would indicate a superinfection.
If hepatitis D is suspected, the doctor will take a medical history to understand factors that may have led to the infection. A physical exam will look for signs of liver damage, which could include jaundice, swelling in the feet or ankles, and swelling or tenderness in the abdomen.
If its suspected that a person may have hepatitis D, a blood test that confirms the presence of the antibodies that are produced in response to the infection is required to confirm the diagnosis.
There may be additional tests to determine if there is liver damage as a result of hepatitis B and hepatitis D. The tests can include the following:
- An elastography, a special ultrasound that can measure the stiffness of the liver
- A liver biopsy, in which a long needle is used to take a small piece of tissue that will be examined under a microscope to look for signs of disease or damage
- A blood test to measure liver enzyme levels, elevated levels of which often indicate inflammation or damage to the liver cells