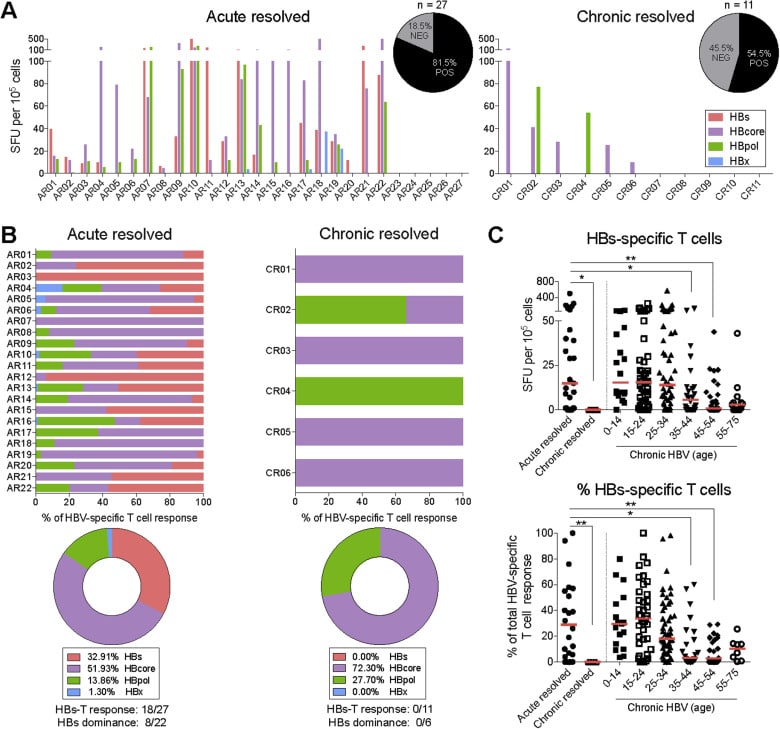
What Happens After A Hepatitis B Infection
Some people carry the virus in their bodies and are contagious for the rest of their lives. They should not drink alcohol, and should check with their doctor before taking any medicines to make sure these won’t cause more liver damage.
Anyone who has ever tested positive for hepatitis B cannot be a blood donor.
Chronic Hepatitis B Complications
Chronic hepatitis B can lead to
- cirrhosis, a condition in which scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue and prevents your liver from working normally. Scar tissue also partly blocks the flow of blood through the liver. As cirrhosis gets worse, the liver begins to fail.
- liver failure, in which your liver is badly damaged and stops working. Liver failure is also called end-stage liver disease. People with liver failure may require a liver transplant.
- liver cancer. Your doctor may suggest blood tests and an ultrasound or another type of imaging test to check for liver cancer. Finding cancer at an early stage improves the chance of curing the cancer.
How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis B
Signs and symptoms can vary, in particular by the age of the individual. Many individuals may not show symptoms . When symptoms develop, they include fever, joint pain, abdominal pain, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, dark urine, clay-coloured bowel movements, or jaundice.
Most infections are asymptomatic or mild. Occasionally, people with serious cases of hepatitis B require hospitalization. A very small proportion of these patients develop a critical form of the disease called “fulminant” hepatitis B. This condition results from a sudden breakdown of liver function.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Antibody Reactive Means
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. Its transmitted through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not transmitted through sharing utensils or kissing. Its also not transmitted through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure. Symptoms can last for several weeks.
But even without symptoms, you can still transmit the infection to others. The virus can live outside the body and remains infectious for at least
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious condition. Its associated with many serious complications, some of which can be life threatening.
But there are many treatment options available and multiple ways you can prevent infection, including getting vaccinated.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a doctor to prevent infection and determine the best course of treatment for you.
Who Should Be Vaccinated
Preventing hepatitis B is important because of the high risk oflifelong infection leading to serious liver problems. The followingpersons should be vaccinated against hepatitis B:
- All babies, beginning at birth.
- Adolescents who have sex or inject drugs .
- Persons who engage in any of the high-risk behaviors listed in thispamphlet.
- Persons whose jobs expose them to human blood.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis B Bacterial Or Viral
Who Should Get The Hbv Vaccine
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that all children and adults up to age 59 should receive the hepatitis B vaccine.
Infants should get their first hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth and complete their doses by age 6 to 18 months.
All unvaccinated children and adults through age 59 should receive the vaccine. Also, unvaccinated adults over the age 60 who are at risk of hepatitis B should get the vaccine.
Adults over age 60 who are not at risk of hepatitis B may also choose to get the shot.
Several types of the HBV vaccine are also safe to administer to pregnant women.
- people who have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months
- men who have sex with men
- people seeking treatment for a sexually transmitted infection
- people whose partners or household members have hepatitis B
- people who inject drugs
- people who live or work in care facilities
- people who are on dialysis
- travelers to countries where hepatitis B is common
- people with chronic liver disease, HIV, or hepatitis C
- people who are in jail or prison
People who have diabetes should talk with a healthcare professional about their risk for contracting hepatitis B.
What Occupations Have Increased Risk Of Hepatitis B
In general, occupational groups with increased risk include:
- Health-care workers repeatedly exposed to blood or blood products or those who are at risk of needlestick injury.
- Pathologists, laboratory personnel, or embalmers.
- Dentists, dental assistants, and dental hygienists.
- Certain staff members of institutions for the developmentally handicapped.
- Staff of institutions where workers may be exposed to aggressive, biting residents.
Travellers to regions with intermediate or high rates of endemic HBV infection may also consider being vaccinated.
Read Also: Does Hepatitis Cause Stomach Pain
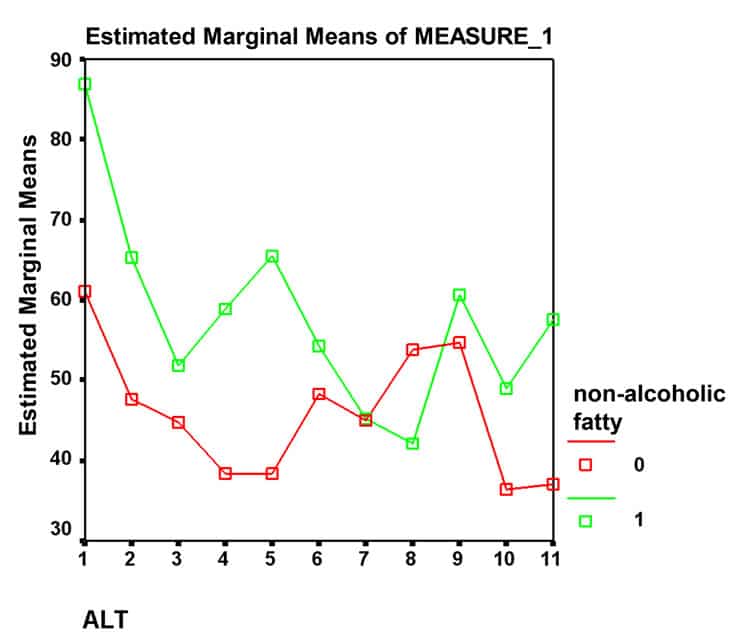
How Common Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is fairly common in Africa and the western Pacific region. Throughout the world, there are about 292 million people who are infected with chronic hepatitis B. In the U.S., the figure exceeds 2 million people.
The number of infections had been falling in the U.S., but fewer vaccinations among adults combined with the onset of the opioid crisis and injected drug usage has resulted in the numbers rising again. Infected women can pass the infection on to their babies. Children who are infected before age 5 are more likely to have chronic infection than those infected later in life.
How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Most people who contract hepatitis B during adulthood fully recover within 1 to 3 months.
People with chronic hepatitis B may have a higher risk of developing long-term liver problems, like cirrhosis or liver cancer, which require treatment and may be life threatening.
Keep in mind that the risk of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for babies and children, especially if they have not been vaccinated against the virus.
Also Check: How Do You Get Hepatitis Of The Liver
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
There are three main ways to diagnose HBV infection. They include:
- Blood tests: Tests of the blood serum shows how your bodys immune system is responding to the virus. A blood test can also tell you if you are immune to HBV.
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to show the size and shape of your liver and how well the blood flows through it.
- Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis.
The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit. Often, people whove become infected first learn they have hepatitis B when they go to donate blood. Blood donations are routinely scanned for the infection.
The virus can be detected within 30 to 60 days of infection. About 70% of adults with hepatitis B develop symptoms, which tend to appear an average of 90 days after initial exposure to the virus.
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus . The infection can range in severity from mild to acute. It may last just a few weeks or become a serious, chronic, and potentially fatal health condition.
The best way to prevent this infection is to get the hepatitis B vaccine. Heres what you need to know.
Also Check: Does Hepatitis Cause Back Pain
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B And C
In most patients, hepatitis B develops slowly over the course of several decades, and thus most patients have no symptoms. People who have advanced liver disease such as cirrhosis of the liver may experience complications and symptoms that reflect liver failure. Other symptoms include:
- A buildup of fluid within the abdominal cavity
- Confusion and tremors , which are complications due to the inability of the liver to filter out toxins that are normally cleaned out by a healthy liver
- Vomiting of blood, or blood within the stool . This is a complication in which enlarged veins within the esophagus or stomach bleed as a consequence of increased pressure around the diseased liver.
Most patients with chronic hepatitis C infection report no symptoms. But some patients may have very nonspecific symptoms related to fatigue and discomfort on the right side of the abdomen. Often, symptoms that lead to a diagnosis of hepatitis C are noticeable only at the end stage of liver disease, when the patient has developed liver cirrhosis and liver failure.
Because hepatitis B and C typically have no specific symptoms, many people who have the viruses dont even know it.
What Makes Yale Medicine’s Approach To Treating Hepatitis B And C Unique
The Viral Hepatitis Program at Yale Medicine represents one of the leading viral hepatitis treatment programs in the country and is engaged in innovative research focused on advancing the care of patients with chronic hepatitis B, C and D infections.
A multidisciplinary team of faculty physicians and mid-level providers offer a coordinated approach to preparing patients for success. Services include structured hepatitis patient education classes, mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques , a formal physician-guided weight-loss program and access to clinical trials evaluating current and new therapies that are not available in routine clinical practice.
Our program is a core member of several national and international observational cohort studies which contributes to the advancement of science of hepatitis treatment around the world.
“Our team at Yale Medicine is uniquely equipped to serve patients with viral hepatitis from Connecticut and beyond and aims to offer outstanding, individualized, patient-centered care to help educate and guide patients through their treatment,” says Dr. Lim. We have specialists who have nationally recognized expertise in the management of viral hepatitis in special populations, including HCV-HIV coinfection, end-stage renal disease, cirrhosis/liver failure, post-liver transplant, and prior failure to respond to all-oral direct acting antivirals .
Read Also: Does Hepatitis C Cause Liver Damage
Complications Of Hepatitis B
Most people do not have any lasting problems after having a hepatitis B infection.
If left untreated, chronic hepatitis B can cause liver damage and increase your risk of getting liver cancer.
It is important to take any medicine you have been prescribed and go for regular check-ups to make sure your liver is working properly.
Page last reviewed: 01 July 2022 Next review due: 01 July 2025
Who Is Most Affected
In the United States, rates of new HBV infections are highest among adults aged 30-59 years, reflecting low hepatitis B vaccination coverage among adults at risk. The most common risk factor among people with new HBV infections is injecting drugs, related to the opioid crisis and other drug use.
The highest rates of chronic hepatitis B infection in the United States occur among foreign-born individuals, especially people born in Asia, the Pacific Islands, and Africa. Approximately 70% of cases in the United States are among people who were born outside of the United States. CDC developed this map of the geographic distribution of hepatitis B around the world – PDF. Other groups who have higher rates of chronic HBV infection include people who inject drugs and men who have sex with men.
Read Also: What Are The Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Why Is Hepatitis B So Serious In Pregnant Women
Pregnant women who are infected with hepatitis B virus frequentlytransmit the disease to their babies. Many of these babies developlifelong infections, cirrhosis of the liver, and liver cancer. Allpregnant women should be tested early in pregnancy to determine if they areinfected with hepatitis B virus. If the blood test is positive, the babyshould be vaccinated at birth and in the first year of life.
Treatment For Acute Hepatitis B
If you’re diagnosed with hepatitis B, your GP will usually refer you to a specialist, such as a hepatologist .
Many people don’t have any troublesome symptoms, but if you do feel unwell, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter painkillers, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen, for abdominal pain
- maintain a cool, well-ventilated environment, wear loose clothing, and avoid hot baths or showers if itching is a problem
- take medication such as metoclopramide to stop you feeling sick and chlorphenamine to reduce itching your doctor can give you a prescription for these if necessary
Most people recover completely in a couple of months, but you’ll be advised to have regular blood tests to check that you’re free of the virus and haven’t developed chronic hepatitis B.
Recommended Reading: Doctors And Medical Specialists For Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
The hepatitis B vaccine is considered a very safe and effective vaccine. Its made with an inactivated virus, so most types of the vaccine are even safe for pregnant people.
The hepatitis B vaccine may cause some mild side effects. The most common symptom is redness, swelling, or soreness where the injection was given. Some people also experience headache or fever. These effects usually last a day or two .
Rarely, some people have a serious and potentially life threatening allergic reaction to the vaccine. Call 911 or get to a hospital immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms after vaccination:
Symptoms Of Chronic Hepatitis B
Symptoms of chronic hepatitis B vary depending on how badly the liver is damaged.
Many people with chronic hepatitis B, particularly children, have no symptoms. People who have symptoms usually feel generally ill and tired and lose their appetite. Some people have a low-grade fever and vague discomfort in the upper abdomen.
Often, the first specific symptoms occur when the liver disease has progressed and there is evidence of cirrhosis. Symptoms can include
-
An enlarged spleen
-
Deterioration of brain function due to malfunction of the liver
Brain function deteriorates because toxic substances build up in the blood and reach the brain. The liver normally removes them from the blood, breaks them down, then excretes them as harmless by-products into the bile or blood. The badly damaged liver is less able to remove them.
People have a tendency to bleed because the damaged liver can no longer synthesize enough of the proteins that help blood clot.
Read Also: Confirmatory Test For Hepatitis C
How Many People Have Hepatitis B
In the United States, an estimated 880,000 to 1.89 million people are chronically infected with HBV. New cases of HBV infection in the United States had been decreasing until 2012. Since that time, reported cases of acute hepatitis B have been fluctuating around 3,000 cases per year. In 2020, 2,157 cases of acute hepatitis B were reported however, because of low case detection and reporting, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that there were 14,000 acute hepatitis B infections. The rate of acute cases of HBV decreased by 32% after 2019 which may be related to the disruptions of the COVID-19 pandemic. For the most recent surveillance data visit CDC Viral Hepatitis Surveillance.
Globally, HBV is the most common blood-borne infection with an estimated 296 million people infected according to the World Health Organization .
Treatment For Chronic Hepatitis B
If blood tests show that you still have hepatitis B after 6 months, your doctor may recommend medication to reduce the risk of complications of hepatitis B and regular tests to assess the health of your liver.
Treatment is usually offered if:
- your immune system is unable to control the hepatitis B by itself
- there’s evidence of ongoing liver damage
Hepatitis B medications can help keep the virus under control and stop it damaging your liver, although they won’t necessarily cure the infection and some people need lifelong treatment.
The main medicines for chronic hepatitis B are outlined below.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Is For What
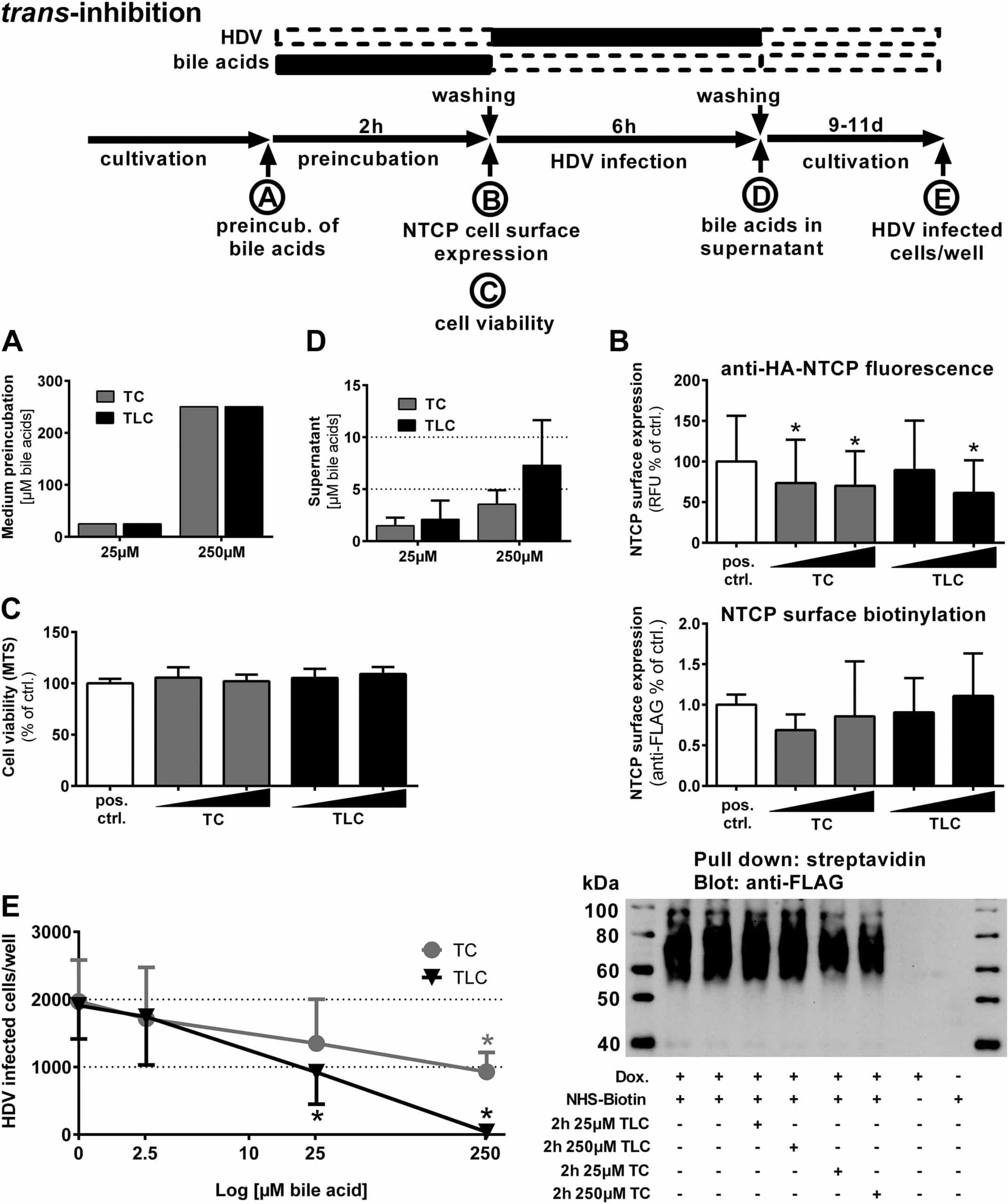
Prevent Infection After Contact With The Virus
If you think you have been in contact with the hepatitis B virus, see your doctor right away. Doctors typically recommend a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine to prevent infection. In some cases, doctors may also recommend a medicine called hepatitis B immune globulin to help prevent infection. You must get the vaccine dose and, if needed, HBIG shortly after coming into contact with the virus, preferably within 24 hours.
How Is Hepatitis B Virus Spread
Hepatitis B virus is found in the blood and body fluids of personswith hepatitis B. Contact with even small amounts of infected blood cancause infection. You can get hepatitis B by direct contact with the bloodor body fluids of an infected person, for example, by sharing needles or byhaving sex with an infected person. A baby can get hepatitis B from aninfected mother during childbirth.
Also Check: Do They Have A Cure For Hepatitis C
How Can I Pay For My Medication
Private health insurance or drug plansIf you have private health insurance or a drug plan at work, you may be able to have the medication paid through your plan. Please consult your private health insurance or drug plan provider to see if your drug is covered.
Publicly funded drug plansEach province and territory has their own rules. Some provincial drug plans provide coverage for individuals 65 and older, or those on social assistance. Some provinces provide special support to low-income individuals. Please call your Provincial Ministry or Department of Health to get more information about the terms of the publicly funded drug plan in your province.
Quebec public drug programIn Quebec, everyone must be covered by prescription drug insurance either through private or publicly funded plans.
Each provincial and territorial government offers a drug benefit plan for eligible groups. Some are income-based universal programs. Most have specific programs for population groups that may require more enhanced coverage for high drug costs. These groups include seniors, recipients of social assistance, and individuals with diseases or conditions that are associated with high drug costs. For more details, please contact your provincial or territorial health care ministry, or click on the appropriate link below.
Yukon
Available Patient Assistance Program for Hepatitis B treatment VEMLIDY