What Makes Yale Medicine’s Approach To Treating Hepatitis B And C Unique
The Viral Hepatitis Program at Yale Medicine represents one of the leading viral hepatitis treatment programs in the country and is engaged in innovative research focused on advancing the care of patients with chronic hepatitis B, C and D infections.
A multidisciplinary team of faculty physicians and mid-level providers offer a coordinated approach to preparing patients for success. Services include structured hepatitis patient education classes, mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques , a formal physician-guided weight-loss program and access to clinical trials evaluating current and new therapies that are not available in routine clinical practice.
Our program is a core member of several national and international observational cohort studies which contributes to the advancement of science of hepatitis treatment around the world.
“Our team at Yale Medicine is uniquely equipped to serve patients with viral hepatitis from Connecticut and beyond and aims to offer outstanding, individualized, patient-centered care to help educate and guide patients through their treatment,” says Dr. Lim. We have specialists who have nationally recognized expertise in the management of viral hepatitis in special populations, including HCV-HIV coinfection, end-stage renal disease, cirrhosis/liver failure, post-liver transplant, and prior failure to respond to all-oral direct acting antivirals .
What Are The Common Types Of Viral Hepatitis
Although the most common types of viral hepatitis are HAV, HBV, and HCV, some clinicians had previously considered the acute and chronic phases of hepatic infections as “types” of viral hepatitis. HAV was considered to be acute viral hepatitis because the HAV infections seldom caused permanent liver damage that led to hepatic failure. HBV and HCV produced chronic viral hepatitis. However, these terms are outdated and not currently used as frequently because all of the viruses that cause hepatitis may have acute phase symptoms . Prevention techniques and vaccinations have markedly reduced the current incidence of common viral hepatitis infections however, there remains a population of about 1 to 2 million people in the U.S. with chronic HBV, and about 3.5 million with chronic HCV according to the CDC. Statistics are incomplete for determining how many new infections occur each year the CDC documented infections but then goes on to estimate the actual numbers by further estimating the number of unreported infections .
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C
Types D, E, and G Hepatitis
Individuals who already have chronic HBV infection can acquire HDV infection at the same time as they acquire the HBV infection, or at a later time. Those with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HDV develop cirrhosis rapidly. Moreover, the combination of HDV and HBV virus infection is very difficult to treat.
Finding Help For Hepatitis
If youve been diagnosed with viral hepatitis, there are a variety of resources that are available to help you. Lets explore a few of them below:
- Your doctor. Your doctor is a great first point of contact for questions and concerns. They can help you to better understand the type of hepatitis you have, as well as how it will be treated.
- American Liver Foundation . ALF is dedicated to ending liver disease through education, research, and advocacy. Their site has educational material about viral hepatitis, as well as ways to find doctors, support groups, and clinical trials in your area.
- Patient assistance programs. If you have hepatitis C, the cost of antiviral drugs can be high. The good news is that many drug manufacturers have patient assistance programs that can help you pay for these medications.
The chart below is an at-a-glance summary of some of the key differences between hepatitis A, B, and C.
| Hepatitis A |
|---|
Read Also: How Can You Spread Hepatitis C
What Is Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is a condition that causes inflammation of your liver. When a hepatitis virus enters your body, it travels to the liver. It can then enter liver cells and begin to replicate, making more of itself.
The activity of the virus can cause damage to your liver cells. Immune cells begin to travel to your liver to fight the infection. This can also contribute to inflammation.
Liver damage and inflammation can affect your livers ability to function, which can in turn affect your overall health. This is because your liver has several important functions for your body, including:
- breaking down or filtering various substances in the body, such as drugs and toxins
- producing bile, which is important for digestion
- making important blood proteins, including those that help your blood to clot
- storing additional blood sugar as glycogen, which can be used for energy later
- synthesizing immune system factors that are important for fighting infections
How Serious Is It
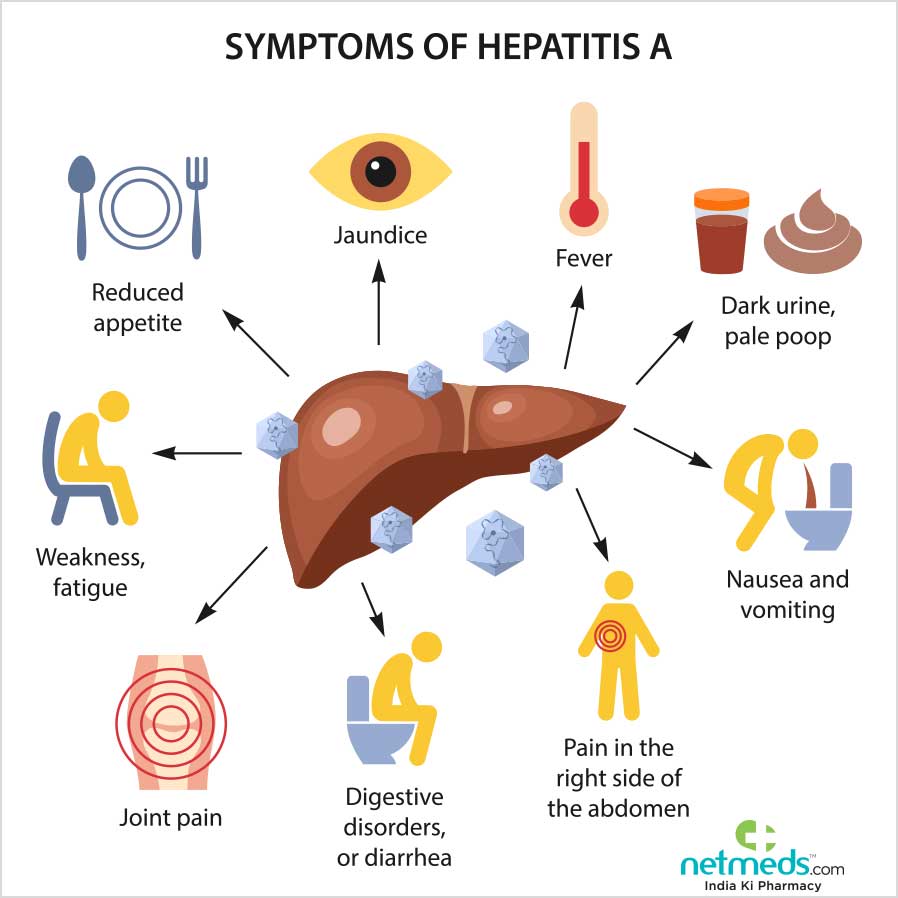
- People can be sick for a few weeks to a few months
- Most recover with no lasting liver damage
- Although very rare, death can occur
- 15%25% of chronically infected people develop chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer
- More than 50% of people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop a chronic infection
- 5%-25% of people with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis over 1020 years
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis A Vaccine A Live Virus
How One Black Man Was Cured Of Hep C Despite Racial Bias
According to the CDC, approximately 10 to 20 percent of people with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis over a period of two to three decades.
People with cirrhosis have a 1 to 5 percent annual risk of developing liver cancer and a 3 to 6 percent risk of hepatic decompensation . Theres a 15 to 20 percent risk of death in the year following the development of decompensation.
Age and gender have been shown to affect how chronic hepatitis C progresses, warns Adalja. It doesnt advance to cirrhosis and liver cancer as quickly in premenopausal women as it does in men, according to a report published in July 2013 inSouthern Medical Journal.
Adalja notes that other factors that may accelerate chronic hepatitis C progression, increasing the risk of liver damage. These include HIV or hepatitis B coinfection, alcohol overuse, and cigarette smoking. The symptoms of chronic hepatitis C vary depending on the type of liver damage.
Cirrhosis can produce a variety of symptoms:
Overview Of Hepatitis And Its Different Types
- Test – Back End Blogs Articles
- Overview of Hepatitis and its different types
If you have been diagnosed with Hepatitis, you may be feeling overwhelmed. It’s a serious condition, and it’s important to understand both the diagnosis and your treatment plan in order to get better. In this blog post, we will provide an overview of Hepatitis, discuss its different types and offer suggestions on how to successfully manage the disease. Understanding what hepatitis is can help you stay informed about your medical care and make sure that you are taking all the necessary steps towards a healthier life.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Ab With Reflex To Hcv Pcr
How Is Hepatitis A Transmitted
Hepatitis A infection is usually spread through contaminated food and water. However, there are many other ways through which HAV spreads. The following are major ways:
Cross References To Published Guidelines
The following published guidelines were reviewed and cross referenced with the recommendations made in this guideline.
- Brook MG. European guideline for the management of hepatitis B and C virus infections. Int J STD AIDS 2001 12:4857
- Brook MG. National guideline for the management of the viral hepatitides A, B and C. www.mssvd.org.uk/CEG/ceguidelines.htm.
- Cramp M, Rosenberg W. Guidance on the treatment of hepatitis C incorporating the use of pegylated interferons. www.bsg.org.uk/clinical_prac/guidelines/pegylated.htm).
Recommended Reading: Cvs Hepatitis B Vaccine Appointment
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis A B And C
Hepatitis is the combination of two words, Hepa or Hepatic means related to the Liver, and itis means infection. There are five main strains of hepatitis, namely, A, B, C, D, and E, with different etiologies. While some are caused by ingestion of contaminated food, some are caused by blood-to-blood or body fluids contact. According to WHO, 354 million people globally live with a hepatitis B or C infection. In the WHO European Region, an estimated 13.3 million people live with chronic hepatitis B and an estimated 15 million people with hepatitis C.
Adding to the alarming stats, as per the CDC , since the outbreaks were first identified in 2016, 37 states have publicly reported 44,241 cases, 27,029 hospitalizations, and 420 deaths as of May 6, 2022.
Even though the prevalence of Hepatitis is high, not many people know about the difference in the strains of Hepatitis viruses and their transmission route. Here, we have highlighted the main differences in hepatitis A, B, and C and how is it caused?
LetsLets begin by talking about,
You May Like: Royal Canin Hepatic Dog Food Canned
How Can I Protect Myself Against Viral Hepatitis
There are many ways you can reduce your chances of getting hepatitis:
- Get the vaccines for hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
- Use a condom during sex.
- Don’t share needles to take drugs.
- Practice good personal hygiene such as thorough hand-washing with soap and water.
- Don’t use an infected person’s personal items.
- Take precautions when getting any tattoos or body piercings.
- Take precaution when traveling to areas of the world with poor sanitation.
- Drink bottled water when traveling.
It is very important that you take these preventive measures if you participate in risky behaviors. Take preventive steps, too, if you work in places like a nursing homes, dormitories, daycare centers, or restaurants where there you have extended contact with other people and a risk of coming into contact with the disease.
You May Like: Autoimmune Hepatitis Signs And Symptoms
How Is Hepatitis B Virus Transmitted
The hepatitis B virus transmits through the following:
How Does It Affect The Body
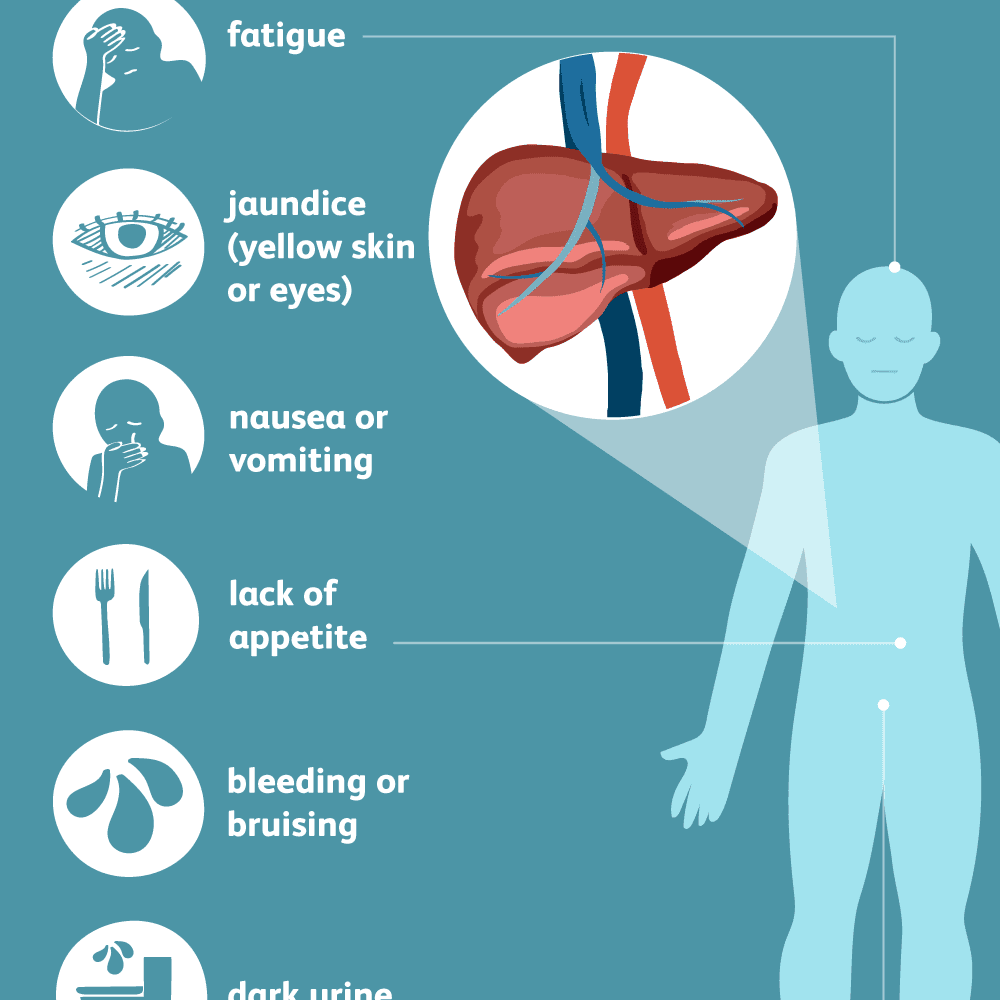
The incubation period for hepatitis B can range from . However, not everyone who has acute hepatitis B will experience symptoms.
About 95 percent of adults completely recover from hepatitis B. However, hepatitis B can also become chronic.
The risk of chronic hepatitis B is greatest in those who were exposed to HBV as young children. Many people with chronic hepatitis B dont have symptoms until significant liver damage has occurred.
In some people whove had hepatitis B, the virus can reactivate later on. When this happens, symptoms and liver damage may occur. People with a weakened immune system and those being treated for hepatitis C are at a higher risk for HBV reactivation.
Also Check: Differences Between Hepatitis B And C
How Do You Contract Each Type Of Hepatitis Virus
It is important to avoid sharing needles and to practice safe sex when engaging in intercourse to minimize the potential risk of contracting this virus. Lastly, Hepatitis C spreads by direct contact with infected blood usually through intravenous drug use or sharing of equipment used for tattoos or piercings. It is best to practice safety when considering such activities and follow safety protocols established by health organizations.
Vaccination Is The Best Way To Prevent Hepatitis A And B Infection
Narrator: ÂYou are a traveller…Â .
Narrator: …and you are already dreaming of your next getaway. .
Disclaimer on-screen reads: TWINRIX is a combined hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccine used in adults, adolescents, children, and infants over the age of 1 year to prevent hepatitis A and hepatitis B diseases
Narrator: ÂWhile your travel plans probably donÂt include hepatitis A or hepatitis B…Â .
Disclaimer reads: 100% protection cannot be guaranteed and booster doses may be required.
Narrator: Â…you know that many common travel activities can put you at risk of acquiring these two serious liver diseases…Â .
Disclaimer reads: TWINRIX does not protect against hepatitis C or E, and is not indicated to treat or reduce the severity of hepatitis A or B infections. .
Narrator: Â…which is why you plan on talking to your doctor about TWINRIX, right? … Of course, right…Â Â…because you are a traveller.Â
Video concludes with TWINRIX logo, GSK logo, You are a traveller slogan, and safety information: Very commonly reported adverse events in adults were pain or discomfort, redness at the infection site, headache, and tiredness. Common adverse events were swelling at the injection site, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, and generally feeling unwell. Allergic reactions may also occur. Full product information can be found on Twinrix.ca. If you need to report an adverse event, please call 1-800-387-7374.
Twinrix.ca
Don’t Miss: Dental Management Of Hepatitis Patient Ppt
Hepatitis And Liver Transplant
Any form of hepatitis can cause liver damage. If the liver becomes severely damaged, a liver transplant is necessary.
With more than 14,000 Americans on the waiting list for a liver transplant, patients often wait years for a transplant. Living donor transplantation allows a transplant to take place before the disease progresses further.
To reduce time on the transplant waiting list, you can choose to find a living donor. During a living-donor liver transplant, the surgeon takes a small part of the donors healthy liver and transplants it into the recipient. This process is possible because of the livers unique ability to regenerate, or regrow.
Hepatitis C: Who Is At Risk
People who have injected illegal drugs at any time, even one time, many years ago, could be walking around with chronic hepatitis C. Because there are often no symptoms, many former drug users may not realize they have the infection. People who received a blood transfusion before 1992 also have a higher risk. Before that year, donated blood was not screened for the hepatitis C virus.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis B And Hiv The Same
What If You Test Positive
If a test says you have viral hepatitis, you can take steps to protect the ones you love. For hepatitis A, wash hands frequently. For hepatitis B and C, avoid sharing nail clippers, razors, or toothbrushes. Hepatitis B, and sometimes hepatitis C, can be passed through sexual contact. Make sure everyone in your household gets the hepatitis B vaccine. An important step is to see a specialist to discuss treatment options.
Hepatitis B: What Happens
Many adults who get hepatitis B have mild symptoms for a short time and then get better on their own. But some people are not able to clear the virus from the body, which causes a long-term infection. Nearly 90% of infants who get the virus will carry it for life. Over time, hepatitis B can lead to serious problems, such as liver damage, liver failure, and liver cancer.
Don’t Miss: New Treatments For Hepatitis B
How To Prevent Hepatitis A Disease
The following measures can prevent the hepatitis A virus from entering the body:
Hepatitis A: Who Is At Risk
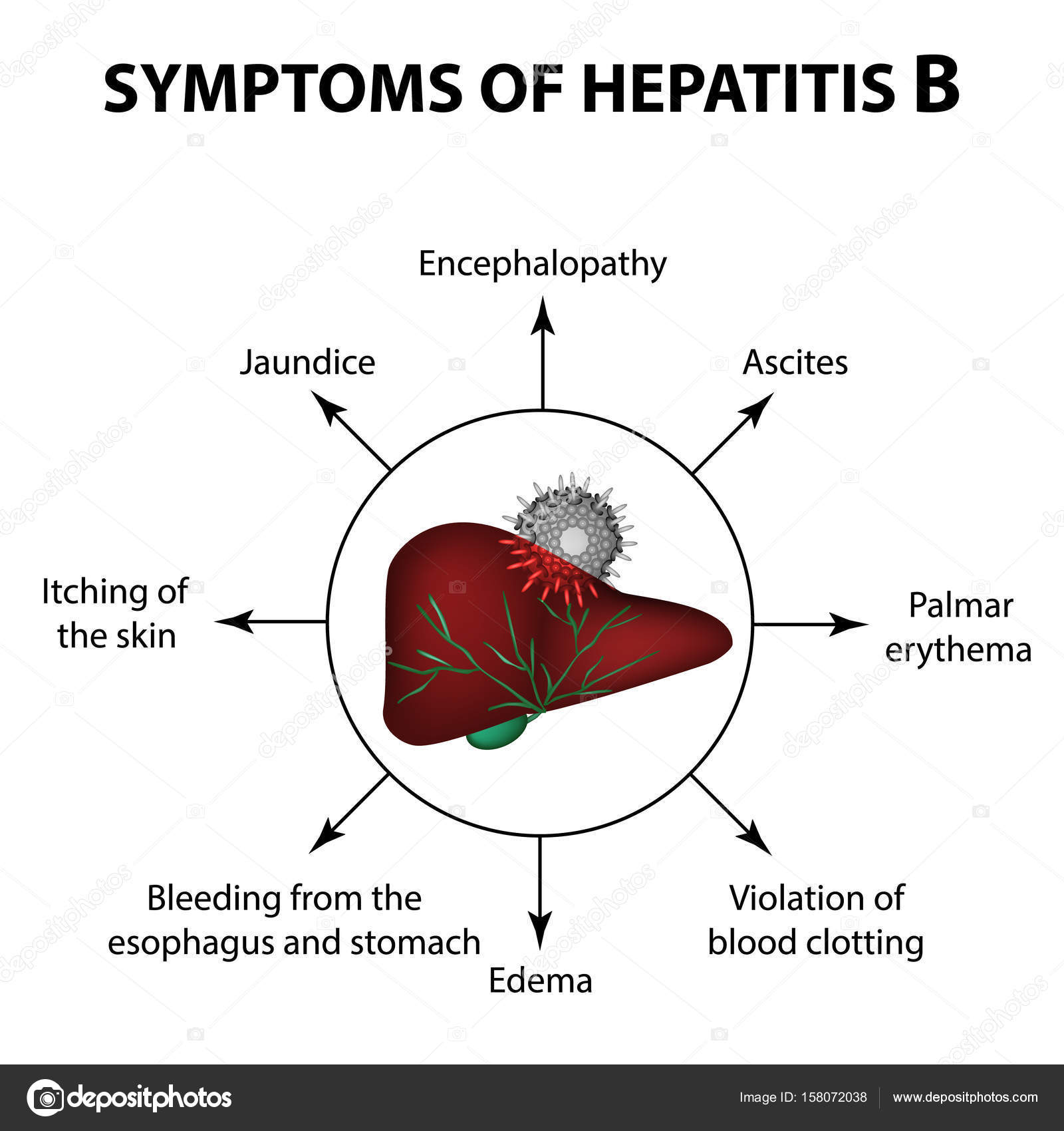
A prime risk factor for hepatitis A is traveling to or living in a country with high infection rates. You can check the CDC’s travel advisories to learn about recent outbreaks. Eating raw foods or drinking tap water can raise your risk while traveling. Children who attend daycare centers also have a higher risk of getting hepatitis A.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine Antibody Test
What Is The Outlook For Hepatitis
Hepatitis A and E usually only cause short-term infections that your body can overcome. The others can also cause acute infections, but might also cause chronic infections. The chronic forms are more dangerous. Hepatitis non-E is usually acute, but can become chronic.
Most people recover fully from hepatitis even though it might take several months for the liver to heal. To help improve your health and to help speed up your recovery:
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a virus that affects the liver. Someone can live with hepatitis C for a long time before they start to develop any symptoms, feel sick, or see any sign of liver damage. Without testing, treatment, or follow-up from a provider, the liver can become scarred and cause people to become ill. Hepatitis C can be very common in certain parts of the world, such as Central, East, and South Asia, Australia and Oceania, Eastern Europe, sub Saharan Africa, North Africa, and the Middle East.
What are the symptoms?
Most people have no signs or symptoms of hepatitis C. People who have hepatitis C may have some or all of the following symptoms:
- Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, poor appetite
How does someone get Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is passed through blood-to blood-contact with someone who has the virus.
The main ways that hepatitis C is passed between people are:
- Sharing needles/syringes or other equipment used to inject drugs, such as cookers, filters, stems, bills/straws, etc.
- Having received blood and/or blood products, or immunoglobulin before 1992
- Tattoos, body piercing/modifications, acupuncture, manicures, or pedicures where non-sterile equipment is used
- Sharing personal hygiene items such as razors, toothbrushes, or nail clippers
- Maternal transmission
How do I get tested for Hepatitis C?
What happens if I have a positive RNA result?
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Banned Countries List 2021