What Is The Outlook
With treatment, most people with autoimmune hepatitis have a normal life expectancy and feel well most of the time. The treatment used for autoimmune hepatitis has improved the outlook tremendously. It is very important that you do not stop your treatment too early without your doctors knowledge, as your hepatitis may return. Although the condition usually returns at some point after stopping treatment, it can usually be treated again by quickly going back on medication.
There is a very small increased risk of developing liver cancer, especially if you also have scarring of the liver due to your autoimmune hepatitis. Some doctors recommend a blood test and an ultrasound scan of your liver every so often to screen for this.
Darkening Color Of Urine And Light
The dark, brownish color of the urine and light-colored stools are among the side effects of how the liver is not able to filter wastes and excess in the body anymore. Usually, this problem is present in hepatitis B, and C. Furthermore, common symptoms can include dehydration, bleeding, or swelling of the private parts.
The Impact Of Immunosuppressant Therapy On Prognosis
Prior to the 1970s, most individuals diagnosed with autoimmune hepatitis died from their disease. Multiple studies in the early 1970s demonstrated the positive impact of corticosteroid therapy on disease outcomes. Sherlock and colleagues looked at the long-term impact of prednisolone therapy on survival and found that 63% of treated patients were alive at 10 years compared with only 27% of untreated patients in the control group . The median survival in the treatment group was 12.2 years versus 3.3 years in the control group.
More recent literature described markedly improved outcomes with immunosuppressive treatment. Czaja and colleagues reported a 90% transplant-free survival at 10 years for patients without cirrhosis at presentation and 89% for patients with cirrhosis at presentation. These survival rates were similar to those of the general population.
Studies utilizing serial liver biopsies have demonstrated how successful immunosuppressive therapy can improve both liver inflammation and fibrosis, potentially preventing the development of cirrhosis.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Antibody Test Results
Is It Contagious Or Hereditary
It is absolutely not contagious. It is generally not considered an inherited disease but a tendency to autoimmune diseases may run in some families. That is, children of patients with autoimmune hepatitis may be at slightly increased risk of developing autoimmune diseases of the thyroid or liver or arthritis. The risk, however, is only slightly greater than the normal population and thus genetic counselling is not necessary.
Symptoms Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
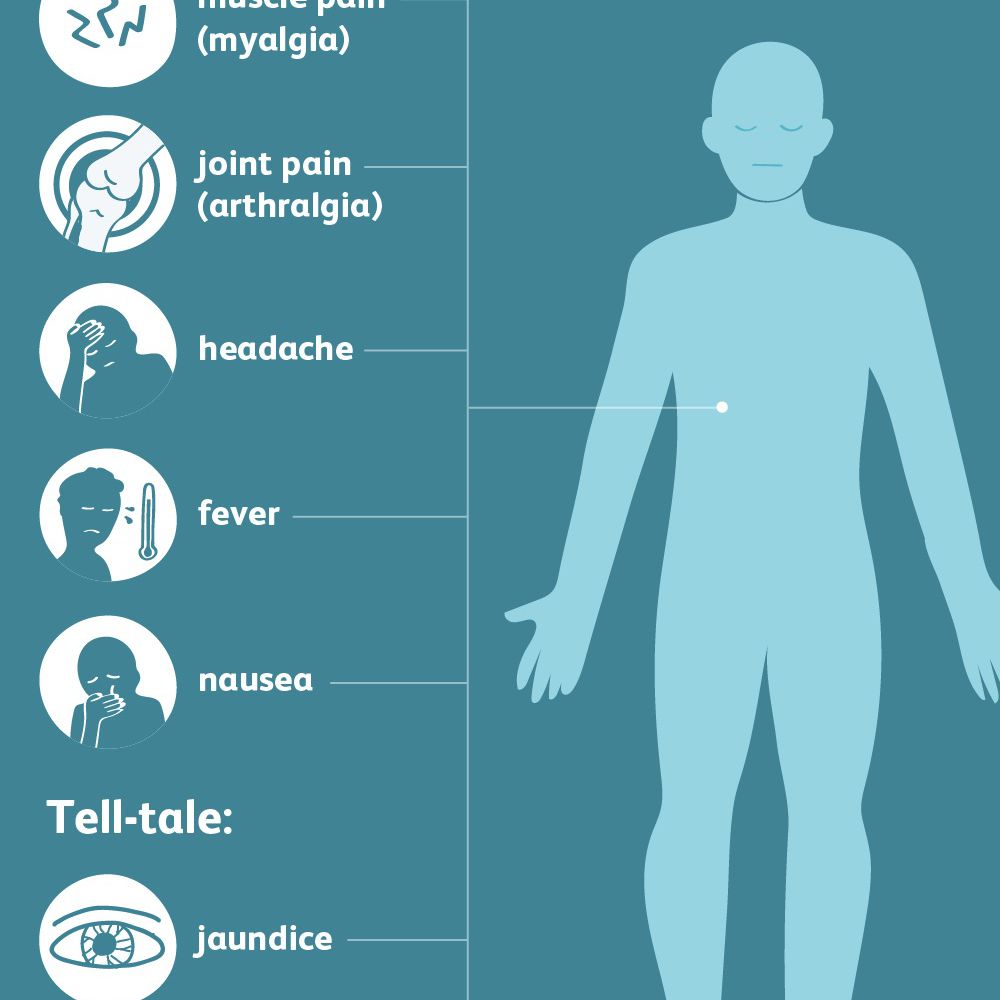
There are two forms of autoimmune hepatitis: type 1 and type 2. The majority of patients have type 1, which typically begins in adolescence or young adulthood. Almost half of individuals with type 1 disease also have other autoimmune disorders, including:
- Type 1 diabetes
- Ulcerative colitis
Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic disorder with symptoms that can worsen over time if not treated. Symptoms include:
Recommended Reading: If You Have Hepatitis C Can It Go Away
Willowbrook State School Experiments
A New York University researcher named Saul Krugman continued this research into the 1950s and 1960s, most infamously with his experiments on mentally disabled children at the Willowbrook State School in New York, a crowded urban facility where hepatitis infections were highly endemic to the student body. Krugman injected students with gamma globulin, a type of antibody. After observing the temporary protection against infection this antibody provided, he then tried injected live hepatitis virus into students. Krugman also controversially took feces from infected students, blended it into milkshakes, and fed it to newly admitted children.
What Are The Risk Factors For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Several factors seem to increase the risk of developing autoimmune hepatitis. You may be at a slightly higher risk if you are a girl or young woman, if you have a relative with any autoimmune disorder, or if you already have an autoimmune disorder. Not all people with risk factors will get autoimmune hepatitis. Risk factors for autoimmune hepatitis can include:
-
Family history of an autoimmune disorder
Your risk of autoimmune hepatitis is also increased if you have another autoimmune disease including:
Dont Miss: Hepatitis E Causes And Treatment
Also Check: Chronic Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma Hcc
Hepatitis Cases In Children
The number of cases of hepatitis in children has increased recently. Public health doctors and scientists are looking into what could be causing this.
See a GP if your child has symptoms of hepatitis, including yellowing of the eyes and skin .
Good hygiene, including supervising hand washing in young children, can help to prevent infections that can cause hepatitis.
What Causes Autoimmune Hepatitis In Children
It is not known exactly why the immune system begins attacking liver cells in children with autoimmune hepatitis.
Experts are looking at a number of possible causes, including:
- Genetics. Physical traits passed down from parents
- Environment. Causes of disease from outside the body, such as toxic substances, certain medicines, or germs
- Problems with the immune system. For example, in patients with autoimmune hepatitis, it seems that some cells that regulate the immune system are fewer or weaker, while other cells that make the immune system attack are more frequent or more active.
Inside the Liver Center: Meet Dr. Weymann
Dr. Weymann leads a team of highly skilled specialists dedicated to caring for children suffering from a wide range of liver diseases. Named to the Best Doctors in America list, Dr. Weymann understands that liver problems can be life-threatening and life-changing. Quick evaluation, correct diagnosis and early treatment can impact long-term health.
Also Check: What Is The Schedule For Hepatitis B Vaccine For Adults
Drug Induced Liver Injury
Drug induced liver injury represents the most challenging differential diagnosis, not only because it can mimic the clinical, biochemical, serological and morphological phenotype of AIH , but also because drugs may trigger latent or induce a de novo AIH . The distinction between DILI and AIH by histology can be extremely difficult , due to the absence of histological features pathognomonic of either DILI or AIH. Severe portal plasma cell-rich inflammation, prominent intralobular plasmacells and eosinophils, rosette formation, absence of cholestasis and presence of fibrosis have been suggested as features that are in favor of the diagnosis of AIH . The absence of cirrhosis, or advanced fibrosis, at presentation mainly suggests AIH-like DILI. A detailed clinical information is crucial, and the patients history should focus on recent exposure to drugs that can induce AIH-DILI. Fortunately, AIH-DILI usually responds to high doses of steroids as severe AIH usually does, but differently from true AIH that always relapses, steroid treatment can be discontinued without a DILI relapse .
How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Treated
Treatment works best when autoimmune hepatitis is found early. The goal of treatment is to control the disease and to reduce or get rid of any symptoms .
To do this, medicines are used to help slow down or suppress your overactive immune system. They also stop your body from attacking your liver.
Once you have started treatment, it can take 6 months to a few years for the disease to go into remission. Some people can stop taking medicine, but often the disease comes back. You may need treatment now and then for the rest of your life. Some people need to remain on treatment if they have relapsed many times or if their disease is severe.
In some cases autoimmune hepatitis may go away without taking any medicines. But for most people, autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic disease.
It can lead to scarring of the liver . The liver can become so badly damaged that it no longer works. This is called liver failure.
If you have liver failure, a liver transplant may be needed.
Be sure to ask your healthcare provider about recommended vaccines. These include vaccines for viruses that can cause liver disease.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Ql Meaning
Autoimmune Hepatitis Causes And Risk Factors
Doctors aren’t sure exactly what causes your immune system to turn against your liver. Your genes may have something to do with it, since AIH can run in families.
But genes aren’t the whole story. Something you come into contact with may trigger your genes to set autoimmune hepatitis in motion. This could include:
- Medicines such as statins and hydralazine or antibiotics like nitrofurantoin and minocycline
- Infections such as viral hepatitis, herpes, Epstein-Barr, and measles
Early Symptoms Of Autoimmune Hepatitis:
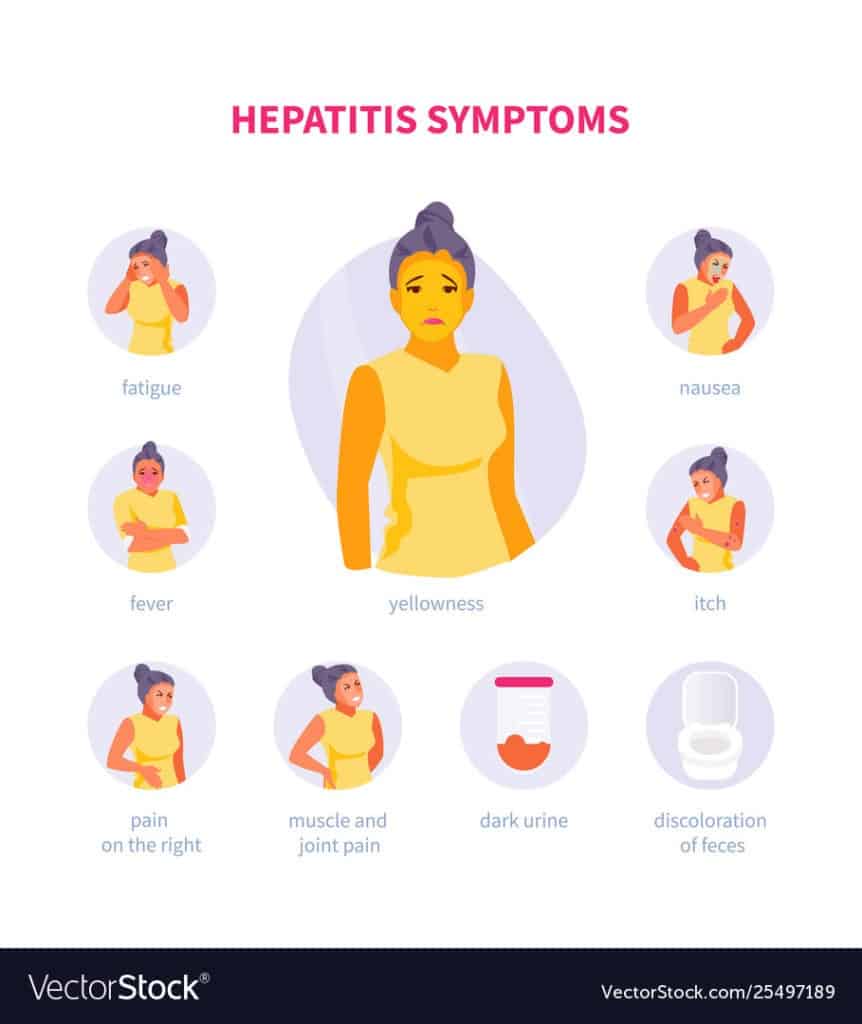
While acquired liver disease like viral hepatitis infection is possible through unsanitary food or unhygienic practices, autoimmune hepatitis can have unknown reasons. That said, you may want to get your doctors advice if you see any of these early symptoms. Disorders in the immune system are always chronic. So, people who want to know the type of hepatitis may do some tests for the right diagnosis as soon as possible.
- Yellowish of skin or whites of the eyes
One of the most common symptoms of this immune system problem is jaundice or yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes. The yellow color is caused by the unfiltered overproduction of the chemical, bilirubin. This chemical is present when red blood cells break down frequently. But, the damage in the liver may not handle the abnormal immune system condition.
- Recurring Fatigue, Nausea, and Diarrhea
Tiredness, lethargy, and fatigue include nausea and diarrhea when there is liver failure. Acute hepatitis with mild problems can affect the bodys overall wellness. Notably, the immune system may feel restless with its unending autoimmune attacks.
- Loss Of Appetite
People with an immune system issue also lose their appetite. Depending on the types of hepatitis, the patient may also suffer from digestive system disorders, as mentioned previously. The abdominal pain may also increase depending on the stages of the symptoms.
Read Also: How Do Most People Get Hepatitis C
What Is The Treatment For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Treatment is almost always needed. Early treatment can improve symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and also greatly improve your outlook . Treatment aims to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system with immunosuppressant medicines:
- Steroid medication is the usual first treatment. Steroids are good at reducing inflammation. A high dose is usually needed at first. The dose is then gradually reduced over a few weeks. The aim is to find the lowest dose needed to control the inflammation. The dose needed varies from person to person. See the separate leaflet called Oral Steroids for more detail.
- Azathioprine is an immunosuppressant medicine that works in a different way to steroids. It is usually used in addition to the steroid. A steroid plus azathioprine tends to work better than either alone. Also, the dose of steroid needed is usually less if you also take azathioprine. This means that any side-effects from steroids may be less severe.
Treatment works well in most cases. Usually, the inflammation settles and symptoms improve within a few months of starting treatment. However, it may take a year or more to get the disease totally under control. Azathioprine is usually taken for at least two years.
For some people a liver transplant may be an option for example:
- In the few people who do not respond to treatment with the medicines mentioned above or
- In people diagnosed in the late stage of the disease with severe scarring of the liver or liver failure.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
This article discusses hepatitis, which is a complex disease and requires an interprofessional approach from healthcare providers to tackle it. The article discusses strategies to prevent hepatitis through patient education and vaccination and the importance of closer monitoring for disease progression and complications. These strategies require significant interprofessional communication and care coordination by physicians, including primary care physicians and specialists, nurses, pharmacists, and other health professionals, to enhance patient-centered care. Nursing needs to work closely with the patient to ensure they understand their disease, are compliant with medications and vaccines, and note progress or lack thereof. Pharmacists are crucial to ensuring the proper medications at the correct dose are in the therapy regimen, and that there are no interactions. Any issues noted by any member of the interprofessional healthcare team need to be shared and charted, so everyone operates from the same data. These measures can help improve the outcomes and aid to patient safety and can also help enhance team performance.
Also Check: How Can Hepatitis C Be Transmitted Sexually
You May Like: Is Hepatitis C An Autoimmune Disease
What Is The Right Therapy For A Patient With Autoimmune Hepatitis
AIH can be treated very effectively with immunosuppressive agents. The gold standard is the treatment with prednisone alone or in combination with azathioprine.
The indication for starting an immunosuppressive treatment has to be evaluated, and the treatment strategy must be adjusted to the patients individual risk for developing adverse events of either corticosteroids or azathioprine. For instance, in obese patients, patients with osteoporosis, or patients with brittle diabetes, the steroid dose should be as low as possible, whereas in patients with cytopenia, azathioprine should be avoided .
Patients with refractory disease and burned out cirrhosis may be candidates for liver transplantation. Alternative immunosuppressive agents are not well established in AIH, but the promising agents with the most empiric use are mycophenolate mofetil and cyclosporine.
Indications for treatment of AIH
Absolute indication for starting an immunosuppressive treatment in patients with AIH include the following:
-
An elevation of ALT > 10 fold ULN
-
A more than 5-fold ULN elevated ALT in conjunction with a more than twofold-elevated gamma globulin
-
Bridging necrosis or multiacinar necrosis in the histological picture
-
Cases of severe and intolerable symptoms
Patients with absolute indications for treatment have a poor prognosis without immunosuppressive therapy.
Relative indication for starting an immunosuppressive treatment include the following:
Instrtion
Is There Anything I Can Do To Help My Liver Heal Itself
No, not directly. However, you can help by giving your liver favourable working conditions, by eating a healthy well-balanced diet, not smoking, and drinking alcohol only in modest amounts or abstaining altogether. Obesity may result in fat deposits in the liver and increases the surgical risk with transplantation. Therefore, if you are overweight, strive for a gradual and sustained weight loss. Introduce exercise into your routine: you can enjoy walking, swimming, gardening, stretching. Please remember that a healthy diet and exercise are important components of any weight-loss regimen.
Read Also: Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
Who Is At Risk For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis affects one in every 100,000 people. The disease is more common in women than in men, and women are typically diagnosed in their 40s or 50s. Girls between two and 14 years old may also get the disease.
Those who may suffer from other autoimmune conditions, such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid disease and celiac disease, are also at risk to develop autoimmune hepatitis .
A person who has a family history of autoimmune hepatitis also has a higher risk of developing the disease.
How Is It Spread
Hepatitis A is spread when a person ingests fecal mattereven in microscopic amountsfrom contact with objects, food, or drinks contaminated by feces or stool from an infected person.
- Birth to an infected mother
- Sex with an infected person
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles, syringes, and even medical equipment, such as glucose monitors
- Sharing personal items such as toothbrushes or razors
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
Hepatitis C is spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus even in microscopic amounts enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis C virus can also be transmitted from:
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles and syringes
- Receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
- Birth to an infected mother
Recommended Reading: Can You Give Plasma If You Have Hepatitis C
What Are The Symptoms And Complications Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Often, the symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis are minor. When symptoms do occur, the most common are fatigue, abdominal discomfort, aching joints, itching, jaundice , enlarged liver, nausea and spider angiomas on the skin. Other symptoms may include dark urine, loss of appetite, pale stools and absence of menstruation. More severe complications can include ascites and mental confusion. In 10%-20% of cases, autoimmune hepatitis may present with symptoms like an acute hepatitis.
Warning Signs & Symptoms Of Hepatitis You Should Not Ignore

Hepatitis is the inflammation of the liver, which is triggered by different causes. One of the most common causes of hepatitis is one of five different viruses, known as Hepatitis A, B, C, D, or E. They are viruses with varying disease mechanisms, but they all cause a liver disease known as viral hepatitis.
Other types of hepatitis can be triggered by alcohol, toxic substances, and autoimmune disease. Most of them have similar symptoms, but the diseases development is very different from one another, and sometimes the infection is asymptomatic until it causes liver cancer or cirrhosis.
In this article, were covering the signs and symptoms commonly shared by most viral hepatitis, and then were going through specific symptoms triggered by individual hepatitis viruses.
First of all, it is vital to recognize those symptoms shared by most types of hepatitis:
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Non-reactive
What Causes Autoimmune Hepatitis
Experts dont know what causes autoimmune hepatitis, but it is more likely to show up in people with other autoimmune conditions, including:
- Fluid buildup in the belly
- Rectal bleeding or vomiting blood
The symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis may look like other health problems. Always see your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.