What Can Happen If Viral Hepatitis Is Not Treated
Most people recover from hepatitis A with no treatment or long-lasting health problems.
Chronic hepatitis B and C can lead to serious health problems, such as:
- , or scarring of the liver
People with liver failure may need a liver transplant to survive. In the United States, cirrhosis caused by chronic hepatitis C is currently the most common reason for needing a liver transplant. Viral hepatitis is also the most common cause of liver cancer.
Who Should Be Tested
Testing for hepatitis A is not routinely recommended.
CDC recommends hepatitis B testing for:
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household and sexual contacts of people with hepatitis B
- People requiring immunosuppressive therapy
- People with end-stage renal disease
- People with hepatitis C
- People with elevated ALT levels
- Infants born to HBV-infected mothers
CDC recommends hepatitis C testing for:
- All adults aged 18 years and older
- All pregnant women during each pregnancy
- About 24,900 new infections each year
- About 22,600 new infections in 2018
- Estimated 862,000 people living with hepatitis B
- About 50,300 new infections in 2018
- Estimated 2.4 million people living with hepatitis C
Complementary Or Alternative Medicine
Clients might turn to complementary or alternative medicine , believing it will bolster nutrition, attack the , protect or strengthen the liver, or mitigate side effects of viral hepatitis treatment. As many as 20 percent of people who have liver disease use herbal remedies. No conclusive scientific evidence supports the use of CAM for herbal treatments, dietary supplements, alternative medicines, and acupuncture have not been proven to cure or relieve symptoms of hepatitis C . In addition, some herbal treatments might harm the liver, further damaging an already compromised organ. Plants and alternative treatments that can harm the liver are provided in .
Read Also: Hiv And Hepatitis B And C Are Incurable Bloodborne Pathogens
Is There A Vaccine For Hepatitis
There are vaccines for hepatitis A and hepatitis B that are available in the U.S. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. Since you can only get hepatitis D if you have hepatitis B, getting the vaccine against B should protect you against hepatitis D. There is no FDA approved vaccine against hepatitis E, but vaccines against hepatitis E exist overseas .
Also Check: How Do You Get Hepatitis A B C
What Is The Outlook For Hepatitis
Hepatitis A and E usually only cause short-term infections that your body can overcome. The others can also cause acute infections, but might also cause chronic infections. The chronic forms are more dangerous. Hepatitis non-E is usually acute, but can become chronic.
Most people recover fully from hepatitis even though it might take several months for the liver to heal. To help improve your health and to help speed up your recovery:
- Practice good nutrition.
- If you feel sick, rest.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about your medicines, even over-the-counter drugs or vitamins and supplements, to know which ones you should take and which to avoid until you are recovered.
With hepatitis, your healthcare provider will also be looking for long-term damage to the liver in the forms of cirrhosis or liver failure. You may be asked to take other types of tests, such as liver function tests, imaging tests or possibly a liver biopsy.
If you have questions, new symptoms, or worsening of any existing symptoms, you should call the office of your healthcare provider.
In the U.S., A, B and C are the most common viral forms of hepatitis. It doesnt matter how you were infectedwhat matters is taking care of yourself once you have been diagnosed and taking care not to spread the infection to anyone else.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 01/06/2020.
References
Also Check: How Do People Get Hepatitis C
Spontaneous Clearance Of Hcv Following Acute Infection
Following acquisition of hepatitis C, an estimated 25 to 35% of persons will have spontaneous clearance of HCV 12 months after HCV acquisition. Studies have shown that if spontaneous clearance occurs, most do so within 12 months of acquiring HCV failure to clear HCV by 12 months is a strong predictor of developing chronic HCV infection. Investigators have identified several factors that predict a higher likelihood of spontaneous clearance: host IL28B CC genotype, female sex, and infection with HCV genotype 1. In contrast, lower rates of spontaneous clearance occur in males, Black persons, and those with HIV coinfection.
Is Interferon An Option
There is evidence for an overwhelming immune response in the pathogenesis of fulminant hepatitis B therefore, an immune-stimulant such as interferon- could be dangerous. However, it was explored as an option for acute hepatitis B in the past, without obvious deleterious effects, but also without evidence of benefit . Still interferon might be an option for cases that are not too severe, but prolonged without significant HBsAg decline during the early weeks of infection. Such patients could be more likely to benefit from an immune-stimulating agent in order to achieve HBsAg seroconversion. HBsAg seroconversion during chronic HBV infection is more frequently observed with interferon than with direct antivirals.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Antigens And Antibodies
Vaccines And Immune Globulin
Vaccines to prevent hepatitis A and hepatitis B are available in the United States. A vaccine for hepatitis E is currently available only in China. No vaccines against hepatitis C or D virus are available. However, vaccination against hepatitis B virus also reduces the risk of infection with hepatitis D virus. Hepatitis vaccines are given by injection into muscle.
) and for adults at high risk of getting hepatitis .
As with most vaccines, protection requires allowing a number of weeks for the vaccine to reach its full effect as the immune system gradually creates antibodies against the particular virus.
If people who have not been vaccinated are exposed to hepatitis A virus, they are given a single dose of hepatitis A vaccine or an injection of standard immune globulin, depending on their age and health. Standard immune globulin contains antibodies obtained from blood collected from a large group of people who have a normal immune system. Immune globulin prevents infection or decreases its severity. However, the amount of protection it provides varies, and the protection is only temporary.
Babies born to mothers with hepatitis B are given hepatitis B immune globulin and hepatitis B vaccine.
Medical Treatment Of Acute Hepatitis B Virus Infection
Background
Hepatitis B virus is a virus that affects the liver. It is usually transmitted by injectable drug abuse, transfusion of infected blood, unhygienic tattooing practices, coming into contact with blood infected with HBV, or by unprotected sex. Acute HBV infection is the period that covers the period immediately after HBV infection. Most people are asymptomatic. About 5% to 40% of people with acute HBV develop symptoms such as jaundice , tummy pain, tiredness, nausea, and vomiting. While most people clear the virus after acute HBV infection, the virus remains in others and causes major health problems . Occasionally, people with acute HBV may develop immediate liver failure . The best way to treat acute HBV is not clear. We sought to resolve this issue by performing this review. We included all randomised clinical trials published to August 2016. We included only trials in which participants with acute HBV infection had not undergone liver transplantation previously and did not have liver disease due to other viral infections. Apart from using standard Cochrane methods which allow comparison of only two treatments at a time , we planned to use an advanced method which allows comparison of the many different treatments individually which are compared in the trials . However, because of the nature of the information available, we could not determine whether the network meta-analysis results were reliable. So, we used standard Cochrane methodology.
Study characteristics
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Hepatitis A
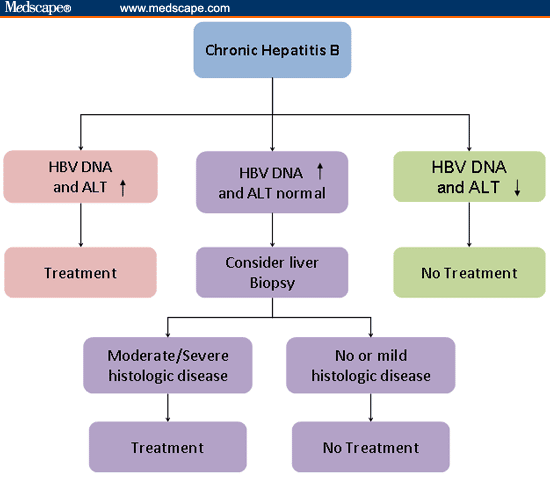
Hepatitis B Treatment Guidance Recommendations
Several leading organizations have addressed guidance for treatment of chronic HBV, including when to initiate treatment. The following summary is intended to provide a succinct description of the indications for initiating HBV treatment in persons with chronic HBV, as outlined by the different organizational guidelines. The reader is encouraged to access these documents for additional details, descriptions, and discussion. The following summaries do not include guidance for the treatment of HBV in special situations or circumstances, such as reactivation of HBV, pre- or post-liver transplantation, treatment of HBV in persons who have coinfection , or treatment of HBV reactivation in persons undergoing immunosuppressive or cytotoxic therapy. These issues are addressed later in this topic review.
Can Hepatitis Be Treated
There are no treatments to cure hepatitis A, aside from carefully monitoring liver function. If you know you have hepatitis A early enough, you might be able to stop the infection if you get a dose of the hepatitis A vaccine or something called hepatitis A immune globulin.
Hepatitis B, when chronic, can often be treated successfully. The most commonly used drugs to treat chronic hepatitis B are:
For hepatitis C, the following drugs are used:
- Sofosbuvir sofusbuvir/velpatasvir sofusbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir ledipasvir/sofosbuvir .
- Ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir/dasabuvir .
- Elbasivir/grazoprevir .
- Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir .
These new drugs are sometimes given with older drugs like ribavirin and peginterferon alfa-2a and peginterferon-2b. You might have to take these medicines for some time, even as long as six months.
If you have chronic hepatitis D, your doctor may prescribe drugs with interferons and might also add medicines for hepatitis B. Hepatitis E treatments include peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Cost Walmart
When And How To Treat Acute Hepatitis C
- Anna LicataAffiliationsCattedra di Gastroenterologia, Istituto di Clinica Medica I, University of Palermo, Piazza delle Cliniche, 2, 90127 Palermo, Italy
- Danilo Di BonaAffiliationsCattedra di Gastroenterologia, Istituto di Clinica Medica I, University of Palermo, Piazza delle Cliniche, 2, 90127 Palermo, Italy
- Antonio CraxAffiliationsCattedra di Gastroenterologia, Istituto di Clinica Medica I, University of Palermo, Piazza delle Cliniche, 2, 90127 Palermo, Italy
- ContactAffiliationsCattedra di Gastroenterologia, Istituto di Clinica Medica I, University of Palermo, Piazza delle Cliniche, 2, 90127 Palermo, ItalyIBIM, Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche, Palermo, Italy
Treatment Of Acute Viral Hepatitis
-
Supportive care
-
Antiviral drugs for acute hepatitis C
For most people with acute viral hepatitis, special treatment is not necessary. However, people with severe acute hepatitis may require hospitalization so that symptoms can be treated. If doctors suspect that fulminant hepatitis is developing, the person is hospitalized so that mental status can be monitored, liver tests can be done, and doctors can determine whether liver transplantation is needed.
After the first several days, appetite usually returns and people do not need to stay in bed. Severe restrictions of diet or activity are unnecessary, and vitamin supplements are not required. Most people can safely return to work after the jaundice clears, even if their liver test results are not quite normal.
People with hepatitis should not drink alcohol until they have fully recovered.
The infected liver may not process drugs normally. So a doctor may need to stop a drug or reduce the dosage of a drug that could accumulate to harmful levels in the body . Thus, people with hepatitis should tell their doctor all the drugs they are taking , so that the dosage of the drug can be adjusted if necessary.
If itching occurs, cholestyramine, taken by mouth, is often effective.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis And Hiv The Same
Injections: Interferon And Pegylated Interferon
Pegylated interferon is given as an injection once per week. It can be used alone or with an oral hepatitis B medication. Patients with both chronic hepatitis B and hepatitis D infection may need pegylated interferon alone or combined with an oral hepatitis B pill.
- Pegylated interferon therapy is usually given for 48 weeks.
- Pegylated interferon may cause many side effects, such as flu-like symptoms, rashes, irritability, and depression.
- Side effects to interferon require close monitoring with routine blood tests.
Whats The Prognosis For Hepatitis B
Your doctor will know youâve recovered when you no longer have symptoms and blood tests show:
- Your liver is working normally.
- You have hepatitis B surface antibody.
But some people don’t get rid of the infection. If you have it for more than 6 months, youâre whatâs called a carrier, even if you donât have symptoms. This means you can give the disease to someone else through:
- Unprotected sex
- Contact with your blood or an open sore
- Sharing needles or syringes
Doctors donât know why, but the disease does go away in a small number of carriers. For others, it becomes whatâs known as chronic. That means you have an ongoing liver infection. It can lead to cirrhosis, or hardening of the organ. It scars over and stops working. Some people also get liver cancer.
If youâre a carrier or are infected with hepatitis B, donât donate blood, plasma, body organs, tissue, or sperm. Tell anyone you could infect — whether itâs a sex partner, your doctor, or your dentist — that you have it.
Show Sources
CDC: âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for Health Professionals,â âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Mayo Clinic: âHepatitis B.â
UpToDate: âHepatitis B virus: Screening and diagnosis.â
CDC.
HealthyPeople.gov: âHepatitis B in Pregnant Women: Screening.â
Annals of Internal Medicine: âScreening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.â
You May Like: What Medication Treats Hepatitis C
How Is Acute Hepatitis C Treated
Acute hepatitis C is typically monitored and not treated. Treatment during the acute stage doesnt change the risk that the disease will progress to the chronic form. An acute infection may resolve on its own without treatment. The following treatment may be all thats necessary:
- adequate fluids
Some people may need treatment with prescription medication. Your doctor will be able to work with you about what treatment options may be best for you.
Those most at risk for acute and chronic hepatitis C are people who use or share contaminated needles. Mothers can transmit HCV to their babies during childbirth, but not through breastfeeding. Other risk factors for transmission of HCV include:
- healthcare work, especially work around needles
- getting a tattoo or body piercing with unsterile equipment
- undergoing hemodialysis
- living in a household with someone with HCV
- sharing personal hygiene products, such as razors or toothbrushes
- engaging in sexual activity with multiple partners without condoms or dental dams
- having a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992 or receiving clotting factors before 1987
The most serious long-term risk of acute hepatitis C is developing chronic hepatitis C, which can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. In 75 to 85 percent of those with acute hepatitis C, the disease will progress to the more serious chronic hepatitis C.
Chronic Hepatitis B Treatment
The aim of treatment in patients with hepatitis B is to prevent progression to liver cirrhosis, liver failure and liver cancer and to prevent transmission of the disease to others. People with chronic hepatitis B should maintain a healthy diet and avoid alcohol and unnecessary medications.
Regular blood tests to monitor the health of the liver will be recommended. Biopsies of the liver may also be recommended to monitor the seriousness of any liver damage over time.
The serious liver complications of chronic hepatitis B can be prevented if the disease is detected and treated in its early stages. Chronic hepatitis B is treated with antiviral medication that reduces the viral load on the body and allows the immune system to keep infection in check.
The main medications used in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B are:
Liver transplantation may be a treatment option for some patients with liver cancer or liver failure. Hepatitis B-specific immune globulin and antiviral medication is usually used before and after the transplant procedure to prevent recurrence of the hepatitis B virus.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine For Newborns
Recommended Reading: What Does Chronic Hepatitis C Mean
Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis
If you are living with a chronic form of hepatitis, like hepatitis B and C, you may not show symptoms until the damage affects liver function. By contrast, people with acute hepatitis may present with symptoms shortly after contracting a hepatitis virus.
Common symptoms of infectious hepatitis include:
It is crucial to understand what is causing hepatitis in order to treat it correctly. Doctors will progress through a series of tests to accurately diagnose your condition.
What Is Chronic Viral Hepatitis
Patients infected with HBV and HCV can develop chronic hepatitis. Doctors define chronic hepatitis as hepatitis that lasts longer than 6 months. In chronic hepatitis, the viruses live and multiply in the liver for years or decades. For unknown reasons, these patients’ immune systems are unable to eradicate the viruses, and the viruses cause chronic inflammation of the liver.
Chronic hepatitis can lead to the development over time of extensive liver scarring , liver failure, and liver cancer. Liver failure from chronic hepatitis C infection is the most common reason for liver transplantation in the U.S. Patients with chronic viral hepatitis can transmit the infection to others with blood or body fluids as well as infrequently by transmission from mother to newborn.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Antibody Test Positive
Treatment For Hepatitis A
Because is always acute, its treatment is generally limited to addressing symptoms, monitoring liver health, and letting the run its course. Clients recently exposed to hepatitis A virus might be advised by their medical care providers to receive the HAV vaccination or injection to reduce the likelihood of becoming ill .
In rare cases, leads to severe liver problems that require medication, hospitalization, or transplantation. If left untreated, liver problems can lead to life-threatening conditions. Therefore, a client who might have been infected with HAV should seek the care of a medical care provider.
Suggestions for counseling clients who have include the following:
- Assure clients that their symptoms are temporary.
- Reinforce prevention with messages such as, You will recover from lets talk about what you can do to make sure you never get the more serious types. A vaccine against can protect you, and there are ways to reduce the risk of getting .
- Encourage clients to take care of themselves. Say, for example, Your body is working hard to fight off the . It is very important that you take care of yourself now.
- Reinforce the importance of maintaining SUD recovery activities. Say, Your liver is injured. If you drink or use drugs, you could make it worse. Lets talk about everything youre doing to stay free of alcohol and other substances.