Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis
If you are living with a chronic form of hepatitis, like hepatitis B and C, you may not show symptoms until the damage affects liver function. By contrast, people with acute hepatitis may present with symptoms shortly after contracting a hepatitis virus.
Common symptoms of infectious hepatitis include:
It is crucial to understand what is causing hepatitis in order to treat it correctly. Doctors will progress through a series of tests to accurately diagnose your condition.
Causes And Risk Factors Of Hepatitis D
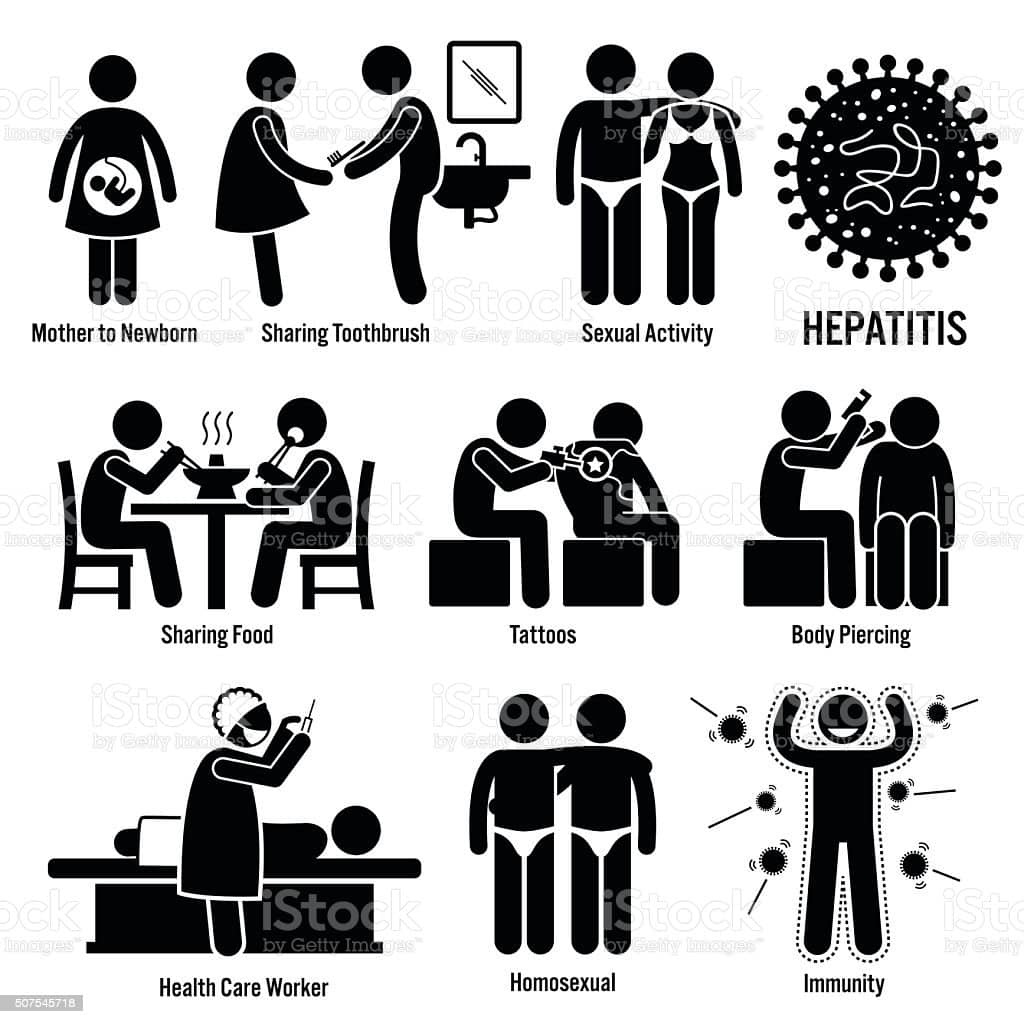
The primary route of transmission for hepatitis D is contact with infected blood or other bodily fluids. This can happen through sharing needles or drug materials with an infected person or having unprotected sex with an infected person.
Although it is rare, hepatitis D can be passed from mother to child during birth.
People cant get hepatitis D through everyday close contact that doesnt involve blood or bodily fluids.
How Is Hepatitis D Diagnosed
Doctors may suspect a person has hepatitis D when the symptoms of acute hepatitis B are unusually severe, chronic hepatitis B gets worse much faster than usual, or when chronic hepatitis B suddenly gets much worse, which would indicate a superinfection.
If hepatitis D is suspected, the doctor will take a medical history to understand factors that may have led to the infection. A physical exam will look for signs of liver damage, which could include jaundice, swelling in the feet or ankles, and swelling or tenderness in the abdomen.
If its suspected that a person may have hepatitis D, a blood test that confirms the presence of the antibodies that are produced in response to the infection is required to confirm the diagnosis.
There may be additional tests to determine if there is liver damage as a result of hepatitis B and hepatitis D. The tests can include the following:
- An elastography, a special ultrasound that can measure the stiffness of the liver
- A liver biopsy, in which a long needle is used to take a small piece of tissue that will be examined under a microscope to look for signs of disease or damage
- A blood test to measure liver enzyme levels, elevated levels of which often indicate inflammation or damage to the liver cells
Read Also: Hepatitis C Is Caused By
What Causes Hepatitis D
The hepatitis D virus causes hepatitis D. The hepatitis D virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood or other body fluids. Contact can occur by
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
The hepatitis D virus rarely spreads from mother to child during birth.
You cant get hepatitis D from
- being coughed on or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking water or eating food
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis D
People who have acute hepatitis D usually have symptoms, which can include the following:
- Fatigue and lethargy
- Jaundice, which causes a yellowish tint to the whites of the eyes and skin
- Discolored stools and urine
- Pain over the liver, in the upper part of the abdomen
In contrast, the majority of people with chronic hepatitis D will have few symptoms until complications develop. This could be several years after the initial infection. These symptoms can include the following:
- Weakness and fatigue
- Swelling of the ankles and abdomen
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Genotype 4 Treatment
Causes Of Noninfectious Hepatitis
Although hepatitis is most commonly the result of an infection, other factors can cause the condition.
Alcohol and other toxins
Excess alcohol consumption can cause liver damage and inflammation. This may also be referred to as alcoholic hepatitis.
The alcohol directly injures the cells of your liver. Over time, it can cause permanent damage and lead to thickening or scarring of liver tissue and liver failure.
Other toxic causes of hepatitis include misuse of medications and exposure to toxins.
Autoimmune system response
In some cases, the immune system mistakes the liver as harmful and attacks it. This causes ongoing inflammation that can range from mild to severe, often hindering liver function. Itâs three times more common in women than in men.
Viral Structure And Life Cycle
Hepatitis D virus viral life cycle and sites of drug target. 1. Hepatitis D virus virion attaches to the hepatocyte via interaction between hepatitis B surface antigen proteins and the sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide , a multiple transmembrane transporter. 2. HDV ribonucleoprotein is translocated to nucleus mediated by the hepatitis D antigen . 3. HDV genome replication occurs via a rolling-circle mechanism. 4. HDV antigenome is transported out of the nucleus to the endoplasmic reticulum . 5. HDV antigenome is translated in the ER into small HDAg and large HDAg . 6. L-HDAg undergoes prenylation prior to assembly. 7. S-HDAg is transported back to the nucleus where it supports HDV replication. 8. New HDAg molecules are associated with new transcripts of genomic RNA to form new RNPs that are exported to the cytoplasm. 9. New HDV RNP associates with hepatitis B virus envelop proteins and assembled into HDV virions. 10. Completed HDV virions are released from the hepatocyte via the trans-Golgi network.
Finally, once the RNP interacts with the envelop protein of HBV and the HDV is assembled, the HDV virion is now ready for release. The HDV virion is released via the trans-Golgi network, where it can go on to infect other hepatocytes. However, the exact mechanism of HDV-virion release remains unknown .
Don’t Miss: Who Needs Hepatitis C Screening
Research And Statistics: How Many People Have Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D was first identified as a distinct form of hepatitis in 1977. A systematic review and meta-analysis published on April 23, 2020, in the Journal of Hepatology estimated its worldwide prevalence at 12 million people. 30220-8/fulltext” rel=”nofollow”> 14)
Hepatitis D is rare in the United States, and most cases occur among people who migrate or travel to the United States from countries that have a higher rate of HDV.
Hepatitis D is not a nationally notifiable condition, so the actual number of people who have it is unknown.
Study results published in Clinical Infectious Diseases found that approximately 0.11 percent of the more than 21,000 subjects had antibodies, which would indicate they had hepatitis D infection. That would correspond to approximately 357,000 people in the United States with a past or ongoing HDV infection.
The researchers found that the prevalence of hepatitis D is highest in Asian Americans and people born outside the United States.
Prevention Of Hepatitis D
Although there is no vaccine for hepatitis D, an effective vaccine does exist for hepatitis B. Since hepatitis D cannot survive without hepatitis B, a vaccination against hepatitis B will protect you from both strains.
Its important to note that the hepatitis B vaccine is only effective at preventing coinfection, not superinfection.
If you already have hepatitis B, other prevention strategies will help you avoid hepatitis D.
You can prevent hepatitis D and other bloodborne illnesses like hepatitis C and HIV by avoiding these high-risk behaviors:
- Sharing intravenous drug paraphernalia
- Having unprotected sex
- Sharing personal-care items with a person who has hepatitis D, especially those items that may have trace amounts of blood on them, such as razors or toothbrushes.
If you have hepatitis D you shouldnt donate blood or blood products, sperm, organs, or tissue.
Read Also: How Can Hepatitis B And C Be Transmitted
Treatment Of Hepatitis D
-
Supportive care
No treatments attenuate acute viral hepatitis, including hepatitis D. Alcohol should be avoided because it can increase liver damage. Restrictions on diet or activity, including commonly prescribed bed rest, have no scientific basis.
The only drug widely recommended for treatment of chronic hepatitis D is interferon-alfa, although pegylated interferon-alpha is likely equally effective. Treatment for 1 year is recommended, although whether longer treatment courses are more effective has not been established. Bulevirtide is available for treatment of hepatitis D in Europe. Hepatitis D is also treated in the context of clinical trials.
What Is Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D is a viral infection that causes liver inflammation and damage. Inflammation is swelling that occurs when tissues of the body become injured or infected. Inflammation can damage organs.
Viruses invade normal cells in your body. Many viruses cause infections that can spread from person to person.
The hepatitis D virus is unusual because it can only infect you when you also have a hepatitis B virus infection. In this way, hepatitis D is a double infection. You can protect yourself from hepatitis D by protecting yourself from hepatitis B by getting the hepatitis B vaccine.
Hepatitis D spreads the same way that hepatitis B spreads, through contact with an infected persons blood or other body fluids.
The hepatitis D virus can cause an acute or chronic infection, or both.
Recommended Reading: What Symptoms Does Hepatitis C Have
Hispanic Americans And Hepatitis B
Adult Hispanic Americans have a low rate of chronic hepatitis B infection, according to CDC statistics, and they die from hepatitis Brelated causes at the same rate as adult white Americans. Among adults ages 19 to 49, vaccination coverage was lower for Hispanic than for white Americans in 2015, but among Hispanic and white adolescents ages 1317 years and children age 19 to 35 months, it was the same in 2016.
Home Remedies And Lifestyle

Healthcare and sanitation workers who have a higher chance of exposure to needle pricks should take additional precautions to prevent the accidental spread of infection. If you use injection drugs or live with someone who does, seek help immediately to reduce your exposure to long-term consequences.
Getting a hepatitis B vaccination can protect you against contracting hepatitis D, so talk to your doctor if you believe youre at risk.
Abstaining from alcohol will minimize strain on your liver. If you choose to drink, its essential to drink responsibly. Health authorities define responsible drinking as no more than one drink per day for women and no more than two drinks per day for men.
Binge drinking is harmful, especially when your liver function is already compromised from hepatitis.
Following safe sex practices will keep you from contracting additional infections and help keep your partner from getting hepatitis D. Safe sex to prevent the spread of hepatitis D is particularly important for men who have sex with other men.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Infection
Cirrhosis Of The Liver
Chronic hepatitis D can lead to cirrhosis, which is when the liver slowly breaks down. Scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue, which blocks the flow of blood. Gradually, the liver is able to function less and less.
If cirrhosis is diagnosed early and the underlying cause is treated, the damage can be halted and in some rare cases, reversed.
Hepatitis D Questions And Answers For The Public
What is hepatitis D?Hepatitis D is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis D virus. Only people infected with the hepatitis B virus can get hepatitis D. They can become infected with both viruses at the same time or get hepatitis D after first being infected with hepatitis B virus . Hepatitis D can cause severe symptoms and serious illness that can lead to life-long liver damage and even death.
What is hepatitis B/hepatitis D coinfection?People who get infected with both hepatitis B and hepatitis D at the same time are considered to be coinfected. Coinfection with hepatitis B and hepatitis D can cause serious, short-term health problems and even liver failure, but it usually does not lead to life-long illness.
What is hepatitis D superinfection?Superinfection happens when people get hepatitis D after having been first infected with the hepatitis B virus. This type of infection is more likely to result in long-term illness, including rapid development of liver fibrosis, liver failure, and even death.
How common is hepatitis D in the United States?Hepatitis D is considered to be uncommon in the United States. However, the number of people with hepatitis D is unknown, because this infection is not tracked by public health departments or by CDC.
How is hepatitis D spread?You can only get hepatitis D after coming into contact with the blood or body fluids of someone who is infected with the hepatitis D virus. This can happen through
Read Also: Signs Of Hepatitis C Getting Worse
Immunizations: Hepatitis D Virus
Hepatitis D is a serious liver disease. It is caused by an infection from the hepatitis D virus . Hepatitis D is also known as delta hepatitis.
The illness can be acute or chronic. That means the illness can either cause serious short-term health problems or could cause life-long illness that affects you for the rest of your life. Hepatitis D cases are rare in the United States.
Hepatitis D is an incomplete virus. It needs help from the hepatitis B virus to infect people. Hepatitis D only infects people who have the hepatitis B virus.
Treatment And Medication Options For Hepatitis D
Medications are not effective against acute hepatitis D, but fortunately, the acute infection tends to subside on its own.
As for chronic hepatitis D, appropriate treatment depends on the phase of the disease and how severe the infection is.
If a persons liver is severely damaged, a liver transplant may become necessary.
While treatment options for hepatitis D are limited, new medications are being studied.
Read Also: What Do You Get Hepatitis From
How You Can Get Hepatitis B
You can contract hepatitis B by:
- Sharing needles while doing drugs, or being tattooed by a needle that isn’t clean
- Having unprotected sex
- At birth, if the mother has hepatitis B
- Sharing items like razors, nail clippers, or toothbrushes with someone who has hepatitis B
You can’t contract hepatitis B from casual contact, including:
- Hugging someone with the virus
- Using the same toilet as someone with the virus
- Being in the same space as someone with the virus
How Is It Spread
Hepatitis A is spread when a person ingests fecal mattereven in microscopic amountsfrom contact with objects, food, or drinks contaminated by feces or stool from an infected person.
- Birth to an infected mother
- Sex with an infected person
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles, syringes, and even medical equipment, such as glucose monitors
- Sharing personal items such as toothbrushes or razors
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
Hepatitis C is spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus even in microscopic amounts enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis C virus can also be transmitted from:
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles and syringes
- Receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
- Birth to an infected mother
Recommended Reading: Cost Of Hepatitis C Test
What Can You Do To Prevent Hepatitis D
One of the best ways to prevent hepatitis D is by getting a hepatitis B vaccination. Since its impossible to contract hepatitis D without hepatitis B, avoiding hepatitis B in the first place is the best-case scenario.
If you already have hepatitis B, you can still prevent hepatitis D by abstaining from risky behaviors, such as unprotected sex and injection drug use. If you need help to develop safer habits, talk to your healthcare professional for a referral to a social worker, therapist, or treatment program.
What Is Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the blood, and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis. However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
Recommended Reading: Is Hiv Easier To Transmit Than Hepatitis B
Complementary And Alternative Medicine
Several supplements are marketed to promote liver health or even repair a damaged liver, but you should never rely on them to treat hepatitis D. Common ingredients in these products include milk thistle or turmeric, which may have some potential for liver health but fall short of any proven benefits for hepatitis.
Furthermore, since dietary supplements are not regulated by the Food and Drug Administration, its impossible to know if what youre buying actually contains the ingredients written on the label. Several herbal supplements and vitamins are known to be toxic to the liver, so its best not to take your chances with a potentially harmful product.
Discuss any herb or supplement you are thinking of taking with your healthcare professional so they can advise you on whether it may be harmful to your condition.
When To See A Healthcare Provider
Recognizing the signs of infection is crucial in diagnosing hepatitis D and avoiding any serious complications.
If you notice symptoms such as fever, fatigue, nausea, pain in the upper abdomen, dark-colored urine, or jaundice, its important to contact a healthcare professional as soon as possible and accessible. Theyll be able to run blood tests to determine the diagnosis.
Recommended Reading: Is Viral Hepatitis C Contagious
Epidemiology And Risk Factors
The seroprevalence of HDV among HBsAg-positive carriers has substantial variations worldwide. These are depicted in . Interestingly, more recent data have shown that 8% of the general Mongolian population is estimated to be positive for HDV . Notably, in the USA, the prevalence of HDV among HBV carriers has been reported to range from 2% to 50%, depending on the patient population . A large study of the US Veterans Affairs medical system more recently reported an HDV seroprevalence of 3.4% among patients with chronic HBV who are tested for HDV . A study using the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey reported a HDV seroprevalence of 42% among HBV carriers . Finally, the highest estimation of HDV seroprevalence came from a study of HBV-positive intravenous drug users , which showed that the seroprevalence of HDV increased from 29% in 19881989 to 50% in 20052006 . However, a general lack of HDV RNA validation in these studies prevents estimation of true HDV prevalence.