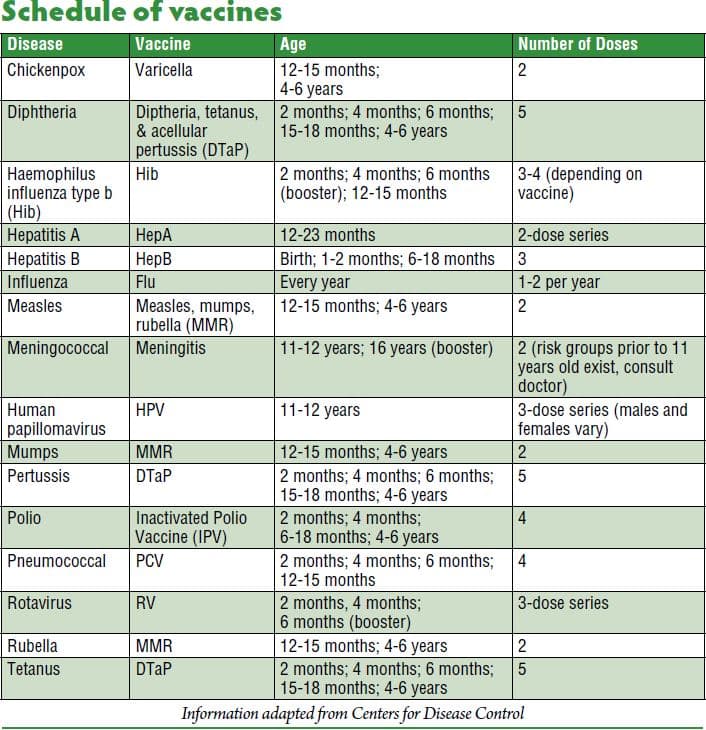
General Information About Vaccination Outside The Us
In developing countries, the pentavalent vaccine, a combination 5-in-one vaccine that protects against five diseases, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, Hib and hepatitis B, may be given to babies more than 6 weeks of age, and can be given up to 1 year of age. The first dose is given at 6 weeks, and the second and third doses are given at 10 and 14 weeks of age. The pentavalent vaccine may be made available free of charge with the support of GAVI, the vaccine alliance. Check the GAVI country hub to see the resources and immunizations that may be available:
For babies born to mothers with hepatitis B, waiting for the first dose of the pentavalent vaccine is too late and will NOT protect the baby from vertical or horizontal transmission of hepatitis B. Babies born to a mother with hepatitis B have a greater than 90% chance of developing chronic hepatitis B if they are not properly treated at birth.
WHO recommends the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth for ALL babies. Plan ahead and inquire about the availability and cost of the monovalent , birth dose of the vaccine, as it is not a GAVI provided immunization. This is particularly important to women who are positive for hepatitis B.
If you are unsure of your hepatitis B status, please be sure your doctor tests you for hepatitis B!
*WHO does not recommend a birth dose of HBIG, which may not be available in all countries. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Page updated September 2022.
What Are The Side Effects Of Hepatitis B Adult Vaccine
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction or a severe skin reaction .
You should not receive a booster vaccine if you had a life-threatening allergic reaction after the first shot.
Keep track of any and all side effects you have after receiving this vaccine. When you receive a booster dose, you will need to tell the doctor if the previous shot caused any side effects.
- a light-headed feeling, like you might pass out
- seizure-like muscle movements or
Common side effects may include:
- redness, pain, swelling, or a lump where the shot was given.
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report vaccine side effects to the US Department of Health and Human Services at 1-800-822-7967.
Babies And Hepatitis B Vaccination
Pregnant women have a routine blood test for hepatitis B as part of their antenatal care.
Babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B need to be given a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of their birth, followed by further doses at 4, 8, 12 and 16 weeks of age, plus a final dose when they’re 1 year old.
Babies of mothers identified by the blood test as particularly infectious might also be given an injection of HBIG at birth on top of the hepatitis B vaccination to give them rapid protection against infection.
All babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B should be tested at 1 year of age to check if they have become infected with the virus.
Also Check: Blood Work For Hepatitis B
For Adults And Children
This vaccine schedule involves three doses within 2 months, followed by a booster dose at 1 year.
The initial accelerated doses provide immediate protection from HBV, and the booster dose helps provide long-term protection.
Below is the accelerated vaccination schedule approved for both adults and children:
| Vaccine series | |
|---|---|
| 2 months after the first dose | 1 year after the first dose |
Are Hepatitis B Virus Infections Easily Avoided
Large quantities of hepatitis B virus are present in the blood of people with hepatitis B in fact, as many as one billion infectious viruses can be found in a milliliter of blood from an infected individual. Therefore, hepatitis B virus is transmitted in the blood of infected individuals during activities that could result in exposure to blood, such as intravenous drug use, tattooing, or sex with people who are infected. However, it is also possible to catch hepatitis B virus through more casual contact, such as sharing washcloths, toothbrushes or razors. In each of these cases, unseen amounts of blood can contain enough viral particles to cause infection. In addition, because many people who are infected don’t know that they are infected, it is very hard to avoid the chance of getting infected with hepatitis B virus.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Treatment Antiviral Drugs
Who Should Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
All infants should get their first dose of hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth and will usually complete the series at 6 months of age.
All unvaccinated children and adolescents younger than 19 years of age should also get vaccinated.
All adults 19 through 59 years of age are recommended to get vaccinated.
Adults 60 years and older with risk factors should get vaccinated. Risk factors include:
- People whose sex partners have hepatitis B
- People who live with someone with hepatitis B
- Sexually active people who are not in a long-term relationship
- People getting evaluated or treated for a sexually transmitted infection
- Men who have sex with men
- People who share needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment
- Health care and public safety workers at risk for exposure to blood or body fluids
- People with chronic liver disease, who are on dialysis, have HIV infection, or hepatitis C infection
- People with diabetes
- Developmentally disabled persons in long-term care facilities
- People in prison or jail
- Travelers to areas with high rates of hepatitis B
A Look At Each Vaccine: Hepatitis B Vaccine
View larger image The hepatitis B vaccine is given to prevent the severe liver disease that can develop when children or adults are infected with hepatitis B virus. The hepatitis B vaccine is given as a series of three shots. The first dose is given within 24 hours of birth. The second dose is given one to two months after the first dose, and the third dose is given between 6 months and 18 months of age. The vaccine is also recommended for those up to 60 years of age who have not previously received it and those 60 years and older who are at increased risk or who simply want the protection afforded by vaccination.
You May Like: Chronic Viral Hepatitis B Without Delta Agent And Without Coma
Hepatitis B Vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide
For health professionals
Last partial content update : May 2022
The footnotes in and the accompanying text description for the figure have been revised to align with the corresponding figure in Protocole dimmunisation du Québec, 5e édition from which it was adapted.
Last complete chapter revision :
You May Like: How Is Hepatitis B Transferred
How And When Do Doctors Give Vaccines
For the hepatitis A vaccine:
You should get two doses, given as shots, 6 months apart for complete protection. The virus in the vaccine is killed .
Children should get the first dose between 12 and 23 months of age. Children older than age 2 can get the first dose at their next doctorâs visit.
If you need the vaccine because of upcoming travel, get it at least 1 month before you go.
For the hepatitis B vaccine:
For long-lasting immunity, you need three to four doses, depending on which type of vaccine is used. You get them as shots.
Children should get their first dose at birth and complete the series by age 6 months. Usually, the baby would get a second dose at 1 month old and the third dose at 6 months.
Babies born to women who have hepatitis B need a shot of hep B antibodies, as well as their first hep B vaccine shot, when theyâre born. They will also need follow-up blood tests to make sure theyâre OK.
Catch-up vaccinations are recommended for children and teens who were never vaccinated or who did not get all three shots.
If you’re an adult who wants to be vaccinated, you should talk about it with your doctor or pharmacist. If you are considering both vaccines, ask your doctor about vaccines that combine hep A and B.
Show Sources
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Contagious Through Urine
What Hepatitis B Immunisation Involves
Full protection involves having 3 injections of the hepatitis B vaccine at the recommended intervals.
Babies born to mothers with hepatitis B infection will be given 6 doses of hepatitis B-containing vaccine to ensure long-lasting protection.
If youre a healthcare worker or you have kidney failure, youll have a follow-up appointment to see if you have responded to the vaccine.
If you have been vaccinated by your employers occupational health service, you can request a blood test to see if you have responded to the vaccine.
Pregnant Women At Risk For Infection Or An Adverse Infection
Lin and Vickery searched for large, high-quality studies related to hepatitis B screening in pregnancy that have been published since the 2004 USPSTF recommendation. English-language studies indexed in PubMed and the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews and published between January 1, 2001 and March 5, 2008 were included in this study. For benefits of screening and newborn prophylaxis, these investigators included systematic reviews meta-analyses and RCTs. For harms of screening, they included systematic reviews meta-analyses RCTs cohort studies case-control studies and case series of large, multi-site databases. Abstracts and full articles were independently reviewed for inclusion by both reviewers. Data on the benefits of screening, including benefits of hepatitis B immune globulin and hepatitis B vaccine prophylaxis of newborns of HBsAg-positive mothers, were extracted by 1 reviewer. No new studies met inclusion criteria. A 2006 systematic review of RCTs found that newborn prophylaxis reduced peri-natal transmission of HBV infection all relevant trials were published in 1996 or earlier. The authors concluded that no new evidence was found on the benefits or harms of screening for HBV infection in pregnant women. Previously published RCTs support the 2004 USPSTF recommendation for screening.
Read Also: Which Hepatitis Is Not Curable
Can Hepatitis B Become Negative
It can happen, especially in older adults after a long period of âinactiveâ hepatitis B infection. About 1 to 3 percent of people with chronic hepatitis B lose HBsAg each year, and about half of all people with chronic infections who live up to age 75 will lose HBsAg, depending on the amount of HBV DNA in their blood.
Hepatitis B Vaccine On The Nhs
A hepatitis B-containing vaccine is provided for all babies born in the UK on or after 1 August 2017. This is given as part of the 6-in-1 vaccine.
Hospitals, GP surgeries and sexual health or GUM clinics usually provide the hepatitis B vaccination free of charge for anyone at risk of infection.
GPs are not obliged to provide the hepatitis B vaccine on the NHS if you’re not thought to be at risk.
GPs may charge for the hepatitis B vaccine if you want it as a travel vaccine, or they may refer you to a travel clinic for a private vaccination. The current cost of the vaccine is around £50 a dose.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Antiviral Drugs Cost
The Centers For Disease Control And Prevention Universally Recommends The Hepatitis B Vaccine For All Adults Up To Age 59 And For Adults 60 And Over At High
The new recommendation simplifies the previously complex guidelines by eliminating the need to screen for risk factors. Read the full recommendation and clinical guidance here.
The CDC recommends three actions that healthcare providers should take to implement the new universal recommendation:
-
Offer hepatitis B vaccination to all adults aged 1959 years who have not previously completed vaccination, as well as adults > 60 years with risk factors for hepatitis B or without identified risk factors but seeking protection.
-
Implement standing orders to administer the hepatitis B vaccine as part of routine services to adults who have not completed the vaccine series.
-
Offer hepatitis B vaccination, when feasible, in outreach and other settings in which services are provided to persons at risk for HBV infection .
Available Hepatitis B Vaccines for Adults
In the U.S., there are now five vaccines approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use in adults.
3-dose Vaccine Brands
Key Messaging to Promote Universal Adult Hepatitis B Vaccination
The CDC has shared key messages about why universal adult hepatitis B vaccination is important. The messages listed below can be used to promote the new recommendation among the medical community.
-
Disparities can be reduced with increases in vaccination facilitated by a universal adult recommendation.
This Vaccine Side Effects
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction or a severe skin reaction .
You should not receive a booster vaccine if you had a life-threatening allergic reaction after the first shot.
Keep track of any and all side effects you have after receiving this vaccine. When you receive a booster dose, you will need to tell the doctor if the previous shot caused any side effects.
Hepatitis B adult vaccine may cause serious side effects. Call your doctor at once if you have:
-
a light-headed feeling, like you might pass out
-
seizure-like muscle movements or
-
redness, pain, swelling, or a lump where the shot was given.
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report vaccine side effects to the US Department of Health and Human Services at 1-800-822-7967.
Recommended Reading: Early Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Persons New To Canada
Health care providers who see persons newly arrived in Canada should review the immunization status and update immunization for these individuals, as necessary. In many countries outside of Canada, HB vaccine is in limited use.
All persons from a country that is endemic for HB should be assessed and vaccinated against HB if not immune and not infected. Individuals born in developing countries are more likely to be carriers of HB, necessitating vaccination of their sexual and household contacts based on review of their serologic test results. HB vaccine is recommended for all household contacts whose families have immigrated to Canada from areas in which there is a high prevalence of HB and who may be exposed to HB carriers through their extended families or when visiting their country of origin.
Children adopted from countries in which there is a high prevalence of HB infection should be screened for HBsAg and, if positive, household or close contacts in the adopting family should be immunized before adoption or as soon as possible thereafter. Adults going to pick-up children from these countries should be vaccinated before departure. Refer to Immunization of Persons New to Canada in Part 3 for additional information.
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
The CDC recommends it for all babies, who should get their first dose as newborns.
Other people who need it include:
- People younger than age 19 who haven’t been vaccinated
- Anyone who has a sex partner with hepatitis B
- People who are sexually active but arenât in a long-term relationship in which both partners are monogamous
- Anyone being evaluated or treated for an STD
- Men who have sex with men
- People who share needles used to inject drugs
- Anyone who lives with someone who has hep B
- Anyone whose job routinely puts them at risk for coming in contact with blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- People with end-stage kidney disease
- People who live and work in facilities for people who are developmentally disabled
- Travelers to regions with moderate to high rates of hepatitis B
- People with chronic liver disease
- People with HIV infections
You should not get the vaccine if you had a severe allergic reaction to an earlier dose or are allergic to yeast, because yeast is used to make the vaccine.
Also Check: New Treatments For Hepatitis C
What Is A Hepatitis B Vaccine
A hepatitis B vaccine prevents hepatitis B virus infection . Engerix-B, Heplisav-B, and Recombivax HB are examples of hepatitis B vaccines approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration . Engerix-B and Recombivax HB are both approved for use in people of all ages. Heplisav-B is approved for use in adults 18 years of age and older.HBV can be an opportunistic infection of HIV. An OI is an infection that occurs more frequently or is more severe in people with weakened immune systemssuch as people with HIVthan in people with healthy immune systems. To learn more about OIs, read the HIVinfo What is an Opportunistic Infection? fact sheet. To learn how HIV and HBV infection are connected, read the HIVinfo HIV and Hepatitis B fact sheet.
Who Should Not Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B is a safe vaccine that does not contain a live virus.
However, there are some circumstances in which doctors advise against getting the HBV vaccine.
You should not receive the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- youve had a serious allergic reaction to a previous dose of the hepatitis B vaccine
- you have a history of hypersensitivity to yeast or any other HBV vaccine components
Read Also: Should I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
The Hepatitis B Vaccine
The hepatitis B vaccine is used to prevent hepatitis B. Its usually provided in three doses.
The first dose can be taken on a date you choose. The second dose must be taken 1 month later. The third and final dose must be taken 6 months after the first dose.
Some people may need two or four doses of this vaccine.
There is also a newer hepatitis B vaccine thats offered in two doses.
Hepatitis B Adult Vaccine Dosing Information
Usual Adult Dose for Hepatitis B Prophylaxis:
Primary Vaccination:Engerix-B:19 years and younger: Three doses intramuscularly on a 0, 1, and 6 month schedule20 years and older: Three doses intramuscularly on a 0, 1, and 6 month scheduleHeplisav-B: Two doses intramuscularly one month apartRecombivax-HB: 19 years and younger: Three doses intramuscularly on a 0, 1, and 6 month schedule 20 years and older: Three doses intramuscularly on a 0, 1, and 6 month schedule Known or Presumed Hepatitis B Exposure:Engerix-B : Use recommended doses of on a 0, 1, and 6 month schedule OR a 0, 1, 2, and 12 month schedule.Recombivax-HB: Refer to recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B How To Get It