Considerations For Hepatitis C Cases Who Were Transplant Recipients
With the availability of curative treatment for HCV infection, an increasing number of transplant recipients are receiving organs from anti-HCV and HCV-RNA positive donors . This can result in transmission of hepatitis C to the recipient, which is then treated with DAA agents . In some jurisdictions, these expected donor-derived HCV transmissions might represent a significant proportion of new acute HCV infections therefore, jurisdictions are encouraged to reach out to transplant facilities and discuss public health reporting of expected donor-derived HCV infections.
A listing of transplant facilities in the United States, including facility location and phone number, can be found on the OPTN websiteexternal icon . As these patients are already linked to testing and treatment, the infections should be notified to CDC as new acute cases. However, the jurisdiction need not investigate beyond indicating that the infection was donor-derived.
Typically, there are two outstanding questions that only the public health jurisdiction can answer: 1) Did the recipient have any behavioral or other risks for hepatitis C and 2) Does the jurisdiction have any ongoing investigations of health care-associated hepatitis C that might be related to this investigation?
Table 4-3. Considerations for hepatitis C cases who were organ transplant recipients*
| Organ Recipient Pre-transplant |
|---|
Dont Miss: Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
Im A Health Care Worker Who Was Recently Exposed To Hcv Is There Post
No. Immune globulin is not recommended for postexposure prophylaxis against HCV, and prophylactic antiviral therapy is also not recommended. However, following exposure, a health care worker should be tested for HCV antibody right away and at 6 months so that early HCV infection can be identified. Several studies suggest that interferon treatment begun early in the course of HCV infection is associated with a higher rate of cure however, further studies are needed to confirm this. There is no hepatitis C vaccine.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms Of Having Hepatitis C
What Causes Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus causes hepatitis C. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood. Contact can occur by
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not kept sterilefree from all viruses and other microorganismsand were used on an infected person before they were used on you
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
- being born to a mother with hepatitis C
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
You cant get hepatitis C from
- being coughed or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking water or eating food
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
A baby cant get hepatitis C from breast milk.18
Read Also: How Deadly Is Hepatitis C
What Use Of These Terms Means For Your Health
Broadly speaking, acute conditions occur suddenly, have immediate or rapidly developing symptoms, and are limited in their duration . Chronic conditions, on the other hand, are long-lasting. They develop and potentially worsen over time .
These descriptions can vary somewhat, though, depending on who you speak to or what sources you reference. While the terms may apply in specific circumstances, they dont always, and they often fall short in describing what you may be faced with if given an acute or chronic diagnosis.
Read Also: How Do You Contract Hepatitis A
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Each patient with hepatitis C is important to us at Health Services of North Texas. Symptoms can be subtle, but over time, the hepatitis C virus can destruct and damage the liver. Some of the most commons symptoms that your body is fighting the hepatitis C virus are:
-
Pain in the abdomen, usually the upper right side
-
Jaundice in the whites of eyes and skin
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis B Or C
Recommended Regimens For Patients With Acute Hcv Infection
RECOMMENDED RATING Owing to high efficacy and safety, the same regimens that are recommended for chronic HCV infection are recommended for acute infection. IIa, C
A number of studies have evaluated DAA treatment of acute HCV infection. Small single-arm, uncontrolled studies have evaluated 6 or 8 weeks of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir. One such study demonstrated 100% SVR with 8 weeks of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir among 27 men with acute HCV and HIV-coinfection . Investigators conducting another study evaluated 6 weeks of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir in a similar cohort . Among participants with genotype 1 infection, 79% achieved SVR12 71% of those with genotype 4 infection achieved SVR12 with this shortened regimen. Among the 6 individuals whose treatment did not lead to SVR12, there were 3 relapses . Three participants achieved SVR4 but were lost to follow-up . A phase 2 study followed a similar treatment protocol among 20 individuals with genotype 1 HCV monoinfection, all of whom achieved SVR12 .
An open-label, single-arm, multicenter pilot study evaluated the efficacy of 6 weeks of the pangenotypic regimen glecaprevir/pibrentasvir among persons with acute/recent HCV infection . SVR12 was 90% a single virological failure occurred in a man with genotype 1a, HIV coinfection, and a viral load of 7.7 log10 IU/mL. This patient was successfully retreated .
- Related References
Recommended Reading: Most Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
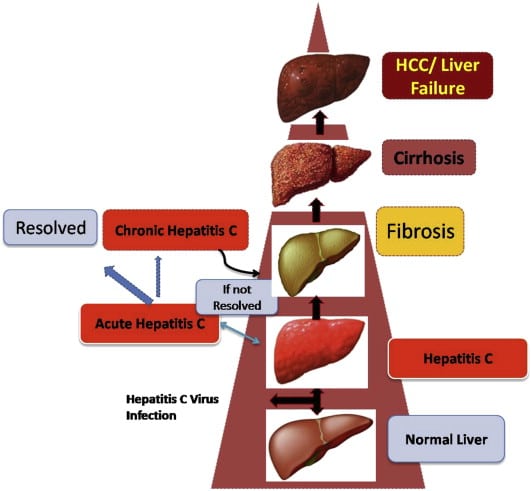
Acute Vs Chronic Hepatitis C: Whats The Difference
Without treatment, acute hepatitis C could become chronic.
Without treatment, chronic hepatitis C can cause damage to the liver over time. Scarring on the liver increases the risk of liver cancer and liver failure. Unfortunately, many people do not catch hepatitis C when its in the acute stage when its easier to treat.
Also Check: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Recommended Reading: Unspecified Viral Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma
Appropriate Uses Of The Hcv Rna Test
There are 4 major reasons that HCV RNA tests are used:
More rarely, HCV RNA is used when either very acute HCV infection is suspected or a false HCV Ab is suspected.
It would not be appropriate to repeatedly order HCV RNA viral load screening for a patient who is not on or was recently on HCV treatment, or to use the HCV viral load to determine the severity of the patient’s infection or the patient’s risk of developing significant liver disease.
Time For Processing Hcv Ab Test Results
The turnaround time for 3rd-generation EIAs is at least 1 day. Many labs do not perform the tests on site and must send specimens to another lab for processing, which may further increase the turnaround time.
A point-of-care test is also available. The OraQuick® HCV Rapid Antibody Test is an FDA-approved test that can be performed with a fingerstick . It is also a CLIA-waived test and therefore can be used in clinic offices and outreach facilities. Results are reported as reactive or nonreactive within 20 minutes. Just as for the standard HCV Ab test done in the lab, a positive OraQuick® test must be confirmed by an HCV RNA test. The sensitivity and specificity of the test is similar to that of the laboratory-based assays.
Read Also: What Is The Cure Of Hepatitis B
Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis B
Doctors may recommend antiviral medication for people with chronic hepatitis B, which occurs when the virus stays in your body for more than six months.
Antiviral medication prevents the virus from replicating, or creating copies of itself, and may prevent progressive liver damage. Currently available medications can treat hepatitis B with a low risk of serious side effects.
NYU Langone hepatologists and infectious disease specialists prescribe medication when they have determined that without treatment, the hepatitis B virus is very likely to damage the liver over time. People with chronic hepatitis B may need to take antiviral medication for the rest of their lives to prevent liver damage.
There are many different types of antiviral medications available, and your doctor recommends the right type for you based on your symptoms, your overall health, and the results of diagnostic tests. A doctor may take a wait-and-see approach with a person who has a healthy liver and whose blood tests indicate a low viral load, the number of copies of the hepatitis B virus in your bloodstream.
Someone with HIV infection or AIDS may have a weakened immune system and is therefore more likely to develop liver damage. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention strongly recommends that people with HIV infection who are diagnosed with hepatitis B immediately begin treatment with antiviral medication.
The Acute Phase Of Hepatitis C
The term Acute Phase can be confusing. This is because it only refers to the 6 month period of time after the virus has first entered your body. It bears no relation to the acuteness of the symptoms or the severity of the disease.Antibodies to the virus are produced by your immune system when it reacts to the presence of the virus and are detectable in the blood from between 3 to 12 weeks after initial infection. Depending on how long it takes for the virus to take hold in the body, different immune systems will take different amounts of time to create antibodies. This is called the window period. Because it can take up to 3 months for the antibodies to show up in a blood test, if you suspect you have recently been infected, it is important to wait this long before having a test. If the antibody test is positive you will be offered a PCR or RNA test.
Symptoms during the Acute Phase
During the acute phase most people do not seem to experience any noticeable symptoms. For the 25-35% of people who do, the symptoms are normally vague and non-specific. They can include low-grade fever, fatigue, appetite loss, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. About 20% of the people who develop symptoms contract jaundice. This can be seen in the yellowing of the skin and eyes. This is a sign of the livers functions being affected as bilirubin begins to build up in the body. Jaundice is a recognised sign of liver problems and may lead to a test for hepatitis C being suggested.
Read Also: Natural Cure For Hepatitis A
How Is Hepatitis C Infection Prevented
Unfortunately, there is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To reduce your risk of getting hepatitis C:
- Injection drug use is the most common way people get hepatitis C. Avoid injecting drugs to reduce your risk. If you do inject drugs, use sterile injection equipment. Avoid reusing or sharing.
- Avoid sharing personal care items that might have blood on them
- If you are a health care or public safety worker, follow universal blood/body fluid precautions and safely handle needles and other sharps
- Consider the risks if you are thinking about tattooing, body piercing, or acupuncture are the instruments properly sterilized?
- If youre having sex with more than one partner, use latex condoms correctly and every time to prevent the spread of sexually transmitted diseases, including hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Steatosis is a hallmark of genotype 3 HCV liver injury. Studies directly comparing genotype-specific injuries are rare, although genotype differences have been studied in the setting of definite hepatic steatosis and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis . Gene expression profiling has identified genotype 3-specific genes SOCS1 and IFITM1, and genotype 1-specific genes CCL3, CCL4, IFNAR, and PRKRIR . Importantly, fibrotic injury did not have a genotype-specific signature . Unique HCV-associated fibrosis signatures have been identified and have led to the correlation of the corresponding proteins of three of these genes inter- inhibitor H1, serpin peptidase inhibitor clade F member 2, and transthyretin being correlated with stages of fibrosis development . Clearly, such proteins may well be useful biomarkers of HCV fibrosis development in the future.
Grzegorz W. Telega, in, 2018
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis C Transmission Mayo Clinic
Diagnosis Of Acute Hcv
In the United States, the gold standard for the laboratory diagnosis of acute HCV is an HCV antibody seroconversion , combined with a positive HCV RNA test and elevated ALT. In clinical practice, many patients do not present early enough after a potential exposure and so it is not always possible to demonstrate an initial negative antibody followed by a positive antibody. Thus, a probable diagnosis of acute HCV is made when an individual has a positive HCV RNA and evidence of a negative HCV antibody in the prior 6 months. It can be challenging to differentiate an acute infection from chronic infection in patients who have not previously undergone HCV antibody testing.
Potential Missed Diagnosis of Acute HCV with HCV Reflex Testing Protocol
Laboratory Testing Following Known Exposure to HCV
In situations where patients have encountered high-risk exposures, follow-up with serial laboratory testing is the key to promptly establishing the diagnosis of acute HCV infection. The following briefly outlines the recommended laboratory testing following a known exposure to hepatitis C virus :
- At Initial Presentation: HCV antibody, HCV RNA, and ALT
- At 4 Weeks from Time of Suspected Exposure: HCV RNA and ALT
- At 12 Weeks from Time of Suspected Exposure: HCV antibody, HCV RNA, and ALT
- At 24 Weeks from Time of Suspected Exposure: HCV antibody and HCV RNA
How Common Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is fairly common in Africa and the western Pacific region. Throughout the world, there are about 292 million people who are infected with chronic hepatitis B. In the U.S., the figure exceeds 2 million people.
The number of infections had been falling in the U.S., but fewer vaccinations among adults combined with the onset of the opioid crisis and injected drug usage has resulted in the numbers rising again. Infected women can pass the infection on to their babies. Children who are infected before age 5 are more likely to have chronic infection than those infected later in life.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Also Check: How Contagious Is Hepatitis B
What Makes Yale Medicines Approach To Treating Hepatitis B And C Unique
The Viral Hepatitis Program at Yale Medicine represents one of the leading viral hepatitis treatment programs in the country and is engaged in innovative research focused on advancing the care of patients with chronic hepatitis B, C and D infections.
A multidisciplinary team of faculty physicians and mid-level providers offer a coordinated approach to preparing patients for success. Services include structured hepatitis patient education classes, mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques , a formal physician-guided weight-loss program and access to clinical trials evaluating current and new therapies that are not available in routine clinical practice.
Our program is a core member of several national and international observational cohort studies which contributes to the advancement of science of hepatitis treatment around the world.
Our team at Yale Medicine is uniquely equipped to serve patients with viral hepatitis from Connecticut and beyond and aims to offer outstanding, individualized, patient-centered care to help educate and guide patients through their treatment, says Dr. Lim. We have specialists who have nationally recognized expertise in the management of viral hepatitis in special populations, including HCV-HIV coinfection, end-stage renal disease, cirrhosis/liver failure, post-liver transplant, and prior failure to respond to all-oral direct acting antivirals .
Dont Miss: Hepatitis C Antibody With Reflex To Hcv Rna
Treatment For Chronic Hbv Infection
For chronic HBV infection, antiviral medications are available.
This is not a cure for chronic HBV. However, it can stop the virus from replicating and prevent its progression into advanced liver disease.
A person with a chronic HBV infection can develop cirrhosis or liver cancer rapidly and without warning. If a person does not have access to adequate treatment or facilities, liver cancer can be fatal within months of diagnosis.
People with a chronic HBV infection require ongoing medical evaluation and an ultrasound of the liver
You May Like: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
I’m A Health Care Worker Who Was Recently Exposed To Hcv Is There Post
No. Immune globulin is not recommended for postexposure prophylaxis against HCV, and prophylactic antiviral therapy is also not recommended. However, following exposure, a health care worker should be tested for HCV antibody right away and at 6 months so that early HCV infection can be identified. Several studies suggest that interferon treatment begun early in the course of HCV infection is associated with a higher rate of cure however, further studies are needed to confirm this. There is no hepatitis C vaccine.
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis Cause Heart Problems
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Currently inject drugs
You May Like: Combined Hepatitis A And B Vaccine