Progression Of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease can progress and develop into more severe forms of liver disease. The first step in the progression of fatty liver disease is nonalcoholic steatohepatitis . Steatohepatitis indicates that fatty liver disease is now causing inflammation within your liver. If your liver is inflamed, this means that the livers cellular processes are not operating as smoothly as usual. The tissues are irritated, and liver processes are essentially clogged.
The progression of liver steatosis tends to be more rapid if you also have other conditions like hepatitis C or iron deposition in the liver.
What is the NASH liver disease life expectancy? Generally, if diet and lifestyle changes are made and recommended medical interventions are followed, an individual with NASH can live a long healthy life.
If NASH is left untreated, it can lead to liver fibrosis, also known as hepatic fibrosis. Fibrosis describes the development of scar tissue in the liver. Over time, fibrosis can lead to liver cirrhosis. Liver cirrhosis describes the significant scarring of the liver and impeded liver functions. Over time, liver cirrhosis can lead to liver cancer or liver failure.
Liver Biopsy And Histopathologic Examination
Liver biopsy and histopathologic examination are important components of the diagnostic evaluation in patients with suspected alcoholic liver disease . They are the most sensitive and specific means of evaluating the degree of liver cell injury and hepatic fibrosis. Several reasons justify obtaining a liver biopsy in patients with ALD, including the following:
-
Confirming the diagnosis
-
Excluding other unsuspected causes of liver disease
-
Assessing the extent of liver damage
-
Defining the prognosis
In making the decision on whether to perform a biopsy, it is important to consider the strength of the clinical diagnosis and the role that the biopsy findings would have in guiding therapeutic options. For patients who are unlikely to receive specific treatments or who have conditions that make a biopsy unsafe, the 2018 ALD guideline recommends including procedure risk in the biopsy decision.
A liver biopsy and histopathologic examination are required to establish the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease . The diagnosis should be considered in all patients with unexplained elevations in serum aminotransferases . It should also be considered in patients with NAFLD who are at increased risk of having steatohepatitis and/or advanced fibrosis. The Brunt classification is the standard used to report NAFLD and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis biopsy specimens.
Also Check: What Are The Symptoms To Hepatitis C
The Typical Treatments What Does Mild Diffuse Hepatic Steatosis Mean
The primary treatment for fatty liver disease is surgery. This involves removing or dissolving the fatty liver cell. Surgery can be used for treating both severe and moderate cases. But the downside to surgery is that it can leave you with scarring that could impede your progress in losing weight and even your ability to stand up.
A more common way to diagnose fatty liver disease is through the use of liver function tests called a CT scan and an MRI. These tests will show whether or not your liver is functioning to its fullest capacity. If it shows signs of inflammation then your doctor may want to prescribe medication that will reduce inflammation. If there is fluid buildup in your abdomen, then your doctor may use a procedure called a liposuction to remove some of the fluid and reduce the swelling in the abdominal area.
===> How To Cure A Fatty Liver In Just Days < < <
The diagnosis of fatty liver is a little more tricky. A biopsy of your liver from the abdominal area will reveal inflammation, but it might not be fatty liver. It could be something else like hepatitis B or C, or even HIV if it is contained in its early stages. If the biopsy indicates the presence of fatty liver, then your doctor will conduct a trial of anti viral medication to make sure that the hepatitis does not develop into cirrhosis of the liver which would be very serious.
Read Also: What Kind Of Doctor Treats Hepatitis B
Diagnosis Of Liver Cirrhosis And Dyslipidemia
Liver cirrhosis was diagnosed based on ultrasonographic findings. These included findings such as altered parenchymal echogenicity with coarsened echotexture and surface nodularity, caudate hypertrophy, splenomegaly, and slow portal vein mean flow velocity.23,24 A diagnosis of dyslipidemia was made when low-density lipoprotein cholesterol was â¥160 mg/dL, total cholesterol was â¥240 mg/dL, or total triglyceride was â¥200 mg/dL.25
What Causes Fatty Liver Disease
Some people get fatty liver disease without having any pre-existing conditions. But these risk factors make you more likely to develop it:
- Having Type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance.
- Having metabolic syndrome .
- Taking certain prescription medications, such as amiodarone , diltiazem , tamoxifen or steroids.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis B A Virus
Greens To Prevent Fat Buildup
Compounds found in spinach and other leafy greens may help fight fatty liver disease.
A 2021 study found that eating spinach specifically lowered the risk of NAFLD, possibly due to the nitrate and distinct polyphenols found in the leafy green. Interestingly enough, the study focused on raw spinach, as cooked spinach did not have the same strong results. This could be because cooking spinach may result in lowered polyphenolic content and antioxidant activity.
Signs And Symptoms Of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Initially, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease may have no symptoms at all. However, as the condition progresses, it may start to exhibit symptoms. Here are a few signs and symptoms of fatty liver disease:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Pain in the upper right quadrant of your abdomen
If nonalcoholic liver disease progresses to more serious conditions, it can cause more severe symptoms like ascites, jaundice, muscle wasting, and hepatic encephalopathy.
Keep in mind that fatty liver disease rarely occurs in isolation. Metabolic conditions are significant risk factors for developing fatty liver disease. Metabolic syndrome includes conditions like insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, elevated triglycerides, and high cholesterol. Fatty liver disease is also correlated with obesity and hypertension.
You May Like: How Do You Get Hepatitis Of The Liver
Diagnostic Accuracy Of Hsi And Other Variables In The Diagnosis Of Fatty Liver
The diagnostic accuracy of the HSI was assessed in each subgroup . In NAFLD group, platelet count had the highest AUROC value in the diagnosis of fatty liver , followed by the HSI . In CHB group, AUROC value of platelet count was also highest , and that of HSI was second , but the difference of both values was less than that in NAFLD group.
When patients with CHB were divided into two groups with or without AVT, the AUROC of the HSI in diagnosing fatty liver was increased in patients not receiving AVT , whereas it was decreased in patients receiving AVT , when compared to the overall AUROC of all patients with CHB .
Types Of Fatty Liver Disease
Health care providers divide fatty liver disease into two types. If you just have fat but no damage to your liver, the disease is called nonalcoholic fatty liver disease . If you have fat in your liver plus signs of inflammation and liver cell damage, the disease is called nonalcoholic steatohepatitis .
About 10% to 20% of Americans have NAFLD. About 2% to 5% have NASH.
You May Like: How Do You Get Autoimmune Hepatitis
Is Mild Hepatomegaly Dangerous
The extent to which a slightly enlarged liver is dangerous depends on the reason for the enlargement.
For people with NAFLD, a slightly enlarged liver is unlikely to pose a major threat to health. However, it could be an indication that a person should consider making some lifestyle changes.
That said, certain conditions can cause a slightly enlarged liver to become a significantly enlarged and damaged liver without treatment. Such conditions include:
- alcohol use disorder
- hepatitis B, C, and D
In general, mild hepatomegaly indicates that it is time to visit a doctor for a full physical evaluation.
Hepatomegaly usually does not cause any symptoms. In fact, the liver conditions that lead to hepatomegaly can progress significantly without causing any symptoms at all.
Because of this, a person should see a doctor if they:
- experience any symptoms of an enlarged liver
- develop any other symptoms of liver disease
- have any conditions that increase their risk of developing liver disease
The outlook for people with hepatomegaly depends on the cause of the hepatomegaly and the extent of the liver damage.
People with hepatitis A and acute hepatitis B usually recover without treatment.
People with the early stages of NAFLD may also have a positive outlook. A mildly damaged liver can often repair itself if a person makes the necessary lifestyle changes early on.
People who have other forms of liver damage will need to ask their doctor about their individual outlook.
What Gets Stored In A Cookie
This site stores nothing other than an automatically generated session ID in the cookie no other information is captured.
In general, only the information that you provide, or the choices you make while visiting a web site, can be stored in a cookie. For example, the site cannot determine your email name unless you choose to type it. Allowing a website to create a cookie does not give that or any other site access to the rest of your computer, and only the site that created the cookie can read it.
Also Check: Symptoms Of Hepatitis C In Females
What Are The Stages Of Liver Fibrosis
There are several different scales of liver fibrosis staging, where a doctor determines the degree of liver damage. Since staging can be subjective, each scale has its own limitations. One doctor may think a liver is slightly more scarred than another. However, doctors will usually assign a stage to liver fibrosis because it helps the patient and other doctors understand the degree to which a persons liver is affected.
One of the more popular scoring systems is the METAVIR scoring system. This system assigns a score for activity or the prediction of how fibrosis is progressing, and for the fibrosis level itself. Doctors can usually assign this score only after taking a biopsy or tissue sample of a piece of the liver. The activity grades range from A0 to A3:
- A0: no activity
Therefore, a person with the most severe disease form would have an A3, F4 METAVIR score.
Another scoring system is Batts and Ludwig, which grades fibrosis on a scale of grade 1 to grade 4, with grade 4 being the most severe. The International Association of the Study of the Liver also has a scoring system with four categories that range from minimal chronic hepatitis to severe chronic hepatitis.
Doctors dont often diagnose liver fibrosis in its mild to moderate stages. This is because liver fibrosis doesnt usually cause symptoms until more of the liver is damaged.
When a person does progress in their liver disease, they may experience symptoms that include:
Computed Tomography And Magnetic Resonance Imaging Of Diffuse Liver Disease: A Multiparametric Predictive Modelling Algorithm Can Aid Categorization Of Liver Parenchyma
Ricardo Donners1, Carmen Zaugg1, Julian E. Gehweiler1, Tuyana Boldanova2,3, Markus H. Heim2,3, Luigi M. Terracciano4, Daniel T. Boll1
1 Department of Radiology, University Hospital Basel , Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology , , Switzerland
Contributions: Conception and design: R Donners, C Zaugg, JE Gehweiler, DT Boll Administrative support: R Donners, MH Heim, LM Terracciano, DT Boll Provision of study materials or patients: R Donners, T Boldanova, MH Heim, LM Terracciano, DT Boll Collection and assembly of data: R Donners, C Zaugg, T Boldanova Data analysis and interpretation: R Donners, C Zaugg, JE Gehweiler, LM Terracciano Manuscript writing: All authors Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Correspondence to:
Background: Liver steatosis is common and tracking disease evolution to steatohepatitis and cirrhosis is essential for risk stratification and resultant patient management. Consequently, diagnostic tools allowing categorization of liver parenchyma based on routine imaging are desirable. The study objective was to compare established mono-factorial, dynamic single parameter and iterative multiparametric routine computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging analyses to distinguish between liver steatosis, steatohepatitis, cirrhosis and normal liver parenchyma.
Keywords: Liver fatty liver liver cirrhosis diagnostic imaging decision-support
Submitted Apr 07, 2021. Accepted for publication Sep 06, 2021.
doi: 10.21037/qims-21-384
Read Also: Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Positive Means
Complications Of Fatty Liver Disease
The main complication for all these conditions is cirrhosis, or scarring of your liver. As your liver tries to stop the inflammation that comes with these conditions, it creates areas of scars. As inflammation spreads, so do the scars, and eventually, your liver canât do its job. That can result in:
- Fluid buildup in your abdomen
- Swollen veins in your esophagus that can burst and bleed
- Confusion and drowsiness
What Are The Forms Of Fatty Liver Disease
There are two main forms of fatty liver disease:
Alcohol-induced fatty liver disease
Alcohol-induced fatty liver disease is caused by heavy drinking. About 5% of people in the U.S. have this form of liver disease.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease occurs in people who arent heavy drinkers. The condition affects one in three adults and one in 10 children in the United States. Researchers havent found the exact cause of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Several factors, such as obesity and diabetes, can increase your risk.
Read Also: Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Symptoms Of Hepatic Steatosis
Most people have no symptoms until the disease progresses to cirrhosis of the liver. Symptoms may include:
- Abdominal pain or a feeling of fullness in the upper right side of the abdomen
- Nausea, loss of appetite, or weight loss
- Swollen abdomen and legs
- Yellowish skin and whites of the eyes
- Extreme fatigue or mental confusion
Focal Fat Deposition And Focal Fatty Sparing
Focal fat deposition is slightly less common and can mimic other hepatic benign or malignant lesions on ultrasound and CT . MRI is very useful for making the diagnosis of focal hepatic steatosis, which appears isointense or hyperintense to liver on in-phase images and loses signal on out-of-phase images. Fat accumulation does not show diffusion restriction, which may also be useful to differentiate steatosis from other liver abnormalities. Moreover, focal fat accumulation tends to show wedgeshaped margins, no mass effect on adjacent blood vessels or the biliary tree, sharp boundaries, and lobar or segmental distribution .
Fig. 4
Focal fatty liver deposition. a CT, axial contrast-enhanced portal phase image in a 58-year-old woman shows a hypodense, mildly heterogeneous, cuneiform lesion in the posterior aspect of segment IV. MRI, b axial T1-weighted in-phase and c out-of-phase images show a signal drop within this lesion on the opposed-phase image
Fig. 5
ad Perivesicular fatty sparing. a Ultrasound image in a 77-year-old woman who had nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma shows a hyperechoic liver with hypoechoic perivesicular foci. b CT, axial contrast-enhanced portal phase image shows a diffusely hypodense liver in comparison with the spleen with a perivesicular spared zone . MRI, c axial T1-weighted in-phase and d out-of-phase images show an important signal drop of the liver on the opposed-phase image with the exception of a perivesicular spared zone
Also Check: How Do People Get Hepatitis
Get A Subspecialty Second Opinion Today
The DocPanel platform enables people all over the world to get an expert second opinion in as little as 24 72 hours.
An easy 3-step process instantly upload your scans, select an expert subspecialty radiologist , and submit your request. Upon uploading your scans, youll also have the opportunity to ask any questions you might have about your case.Not sure what a subspecialist is? Learn more with our in-depth article on the importance of getting a second opinion from a subspecialty radiologist.
What Does Diagnosis Look Like
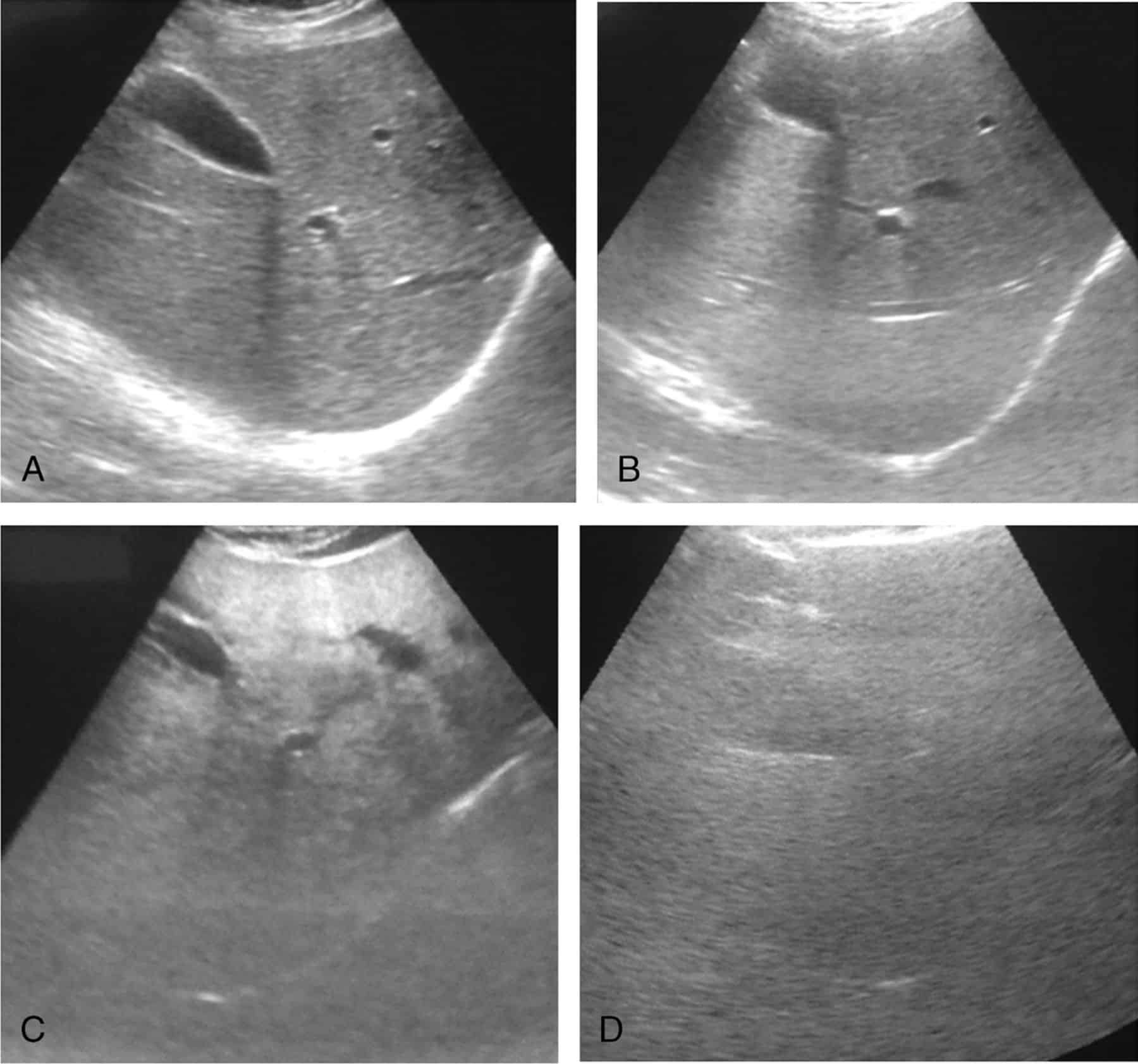
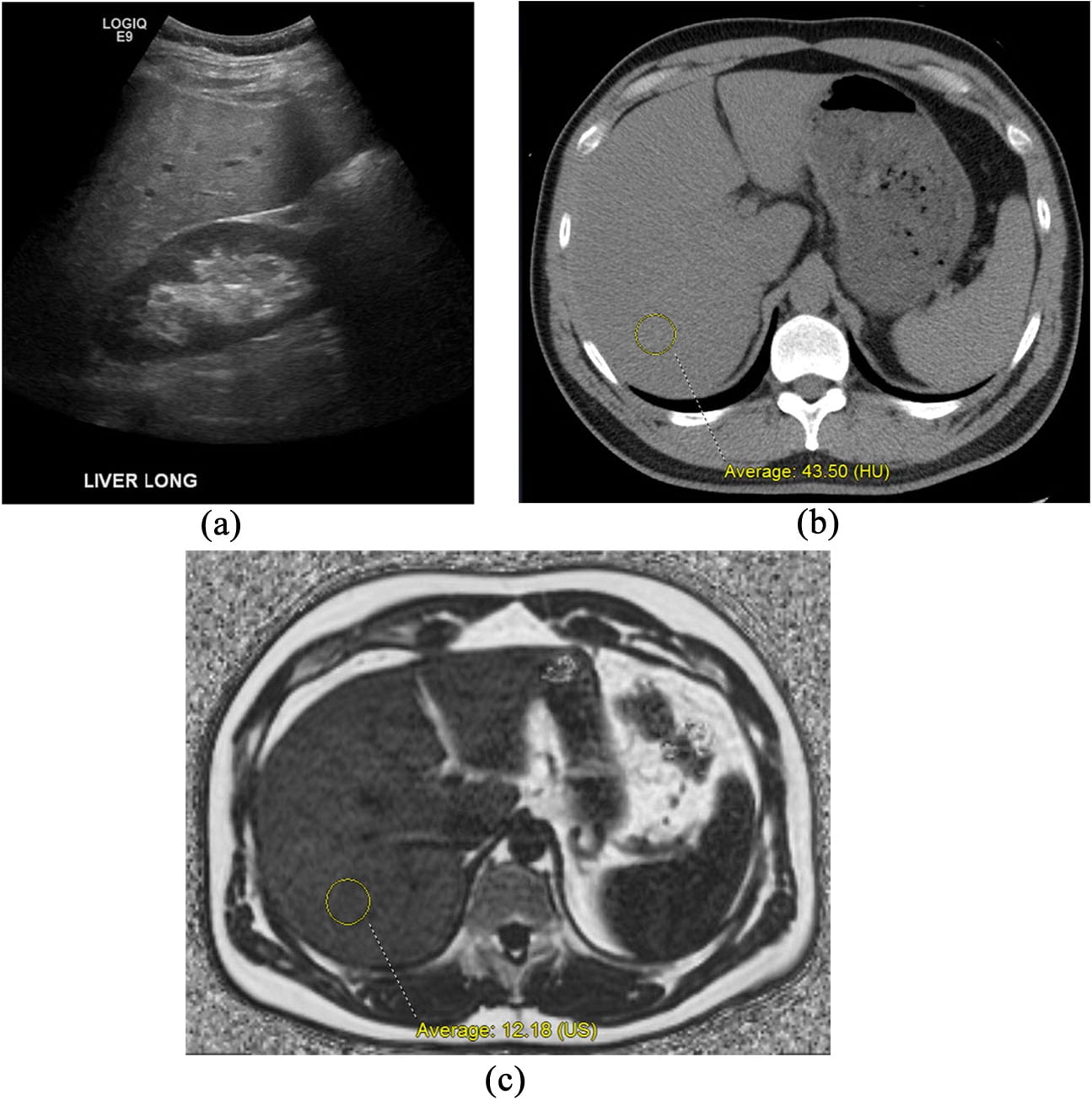
Hepatic steatosis can often be diagnosed by imaging techniques, such as ultrasound, computed tomography scan, or magnetic resonance imaging . All types of medical imaging can reveal diffuse fat content in the liver. This finding may also be described as lower liver attenuation, which means that healthy tissue is interrupted by fatty deposits. Imaging tests are performed by radiology specialists and interpreted by radiologists.
Ultrasound imaging is a type of sonography that is useful for detecting fat within the liver. Ultrasound technology utilizes sound waves to detect variations in structures and composition within body tissues. A higher measure of echogenicity will also accompany fat deposits in the liver parenchyma, which is the part of the liver responsible for carrying out the organs processes. Higher echogenicity means that sound waves more readily bounce off fat tissue and echo back to their source. An MRI might reveal a chemical shift that signifies the presence of fat within the liver.
Another type of imaging is called elastography. Elastography can reveal if soft tissue has hardened, indicating damage. For example, normally functioning liver tissue is soft in texture. Scarred or damaged liver becomes harder in texture.
One of the most definitive ways to detect and diagnose fatty liver disease is through a liver biopsy. A liver biopsy requires taking a tiny sample of your liver and analyzing it for the presence of fat cells, lesions, and other abnormalities.
Read Also: Chronic Hepatitis B Without Delta Agent
Prevention Of Hepatic Steatosis
A negative by-product of our modern civilization is little need for physical activity and an increased risk of chronic disease, such as heart disease, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and NAFLD. Physical inactivity is one of the causes of these associated metabolic disorders and is an actual known leading cause of death in the United States.-
Recommended Reading: How Hepatitis C Is Transmitted Sexually
Steatosis And Fibrosis Progression In Hcv
High levels of TNF- have also been observed in human chronic hepatitis C patients. TNF- has been shown to induce IR in experimental animals and cultured cells. Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS 1 and 2 may be one of the mechanisms by which a high level of TNF- causes IR. Administration of an anti-TNF- antibody restores insulin sensitivity. These results provide direct experimental evidence for the contribution of HCV in the development of IR. There are experimental arguments for a direct role of insulin in fibrosis progression in HCV infection.
Epidemiological studies indicating that the state of IR now associated with NASH is also associated with an increased risk of HCC. It is worth mentioning that diabetes increases the risk of chronic liver disease and HCC.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis C Antibody Test