Acute Hepatitis C Vs Chronic Hepatitis C
Acute and chronic hepatitis C are caused by the same virus.
Acute hepatitis C develops after initial infection with the HCV. This stage can last up to 6 months. Many people have no symptoms during the acute stage and never find out that they have the infection.
According to the CDC, of people with acute hepatitis C develop chronic hepatitis C.
The World Health Organization states that 15 to 45 percent of people with acute hepatitis C spontaneously clear the virus within 6 months. This means that the virus goes away even though it hasnt been treated.
The 55 to 85 percent of people who dont clear the virus will develop a chronic HCV infection.
Chronic hepatitis C can be managed with medications and even cured, but its still a serious condition. According to the CDC,
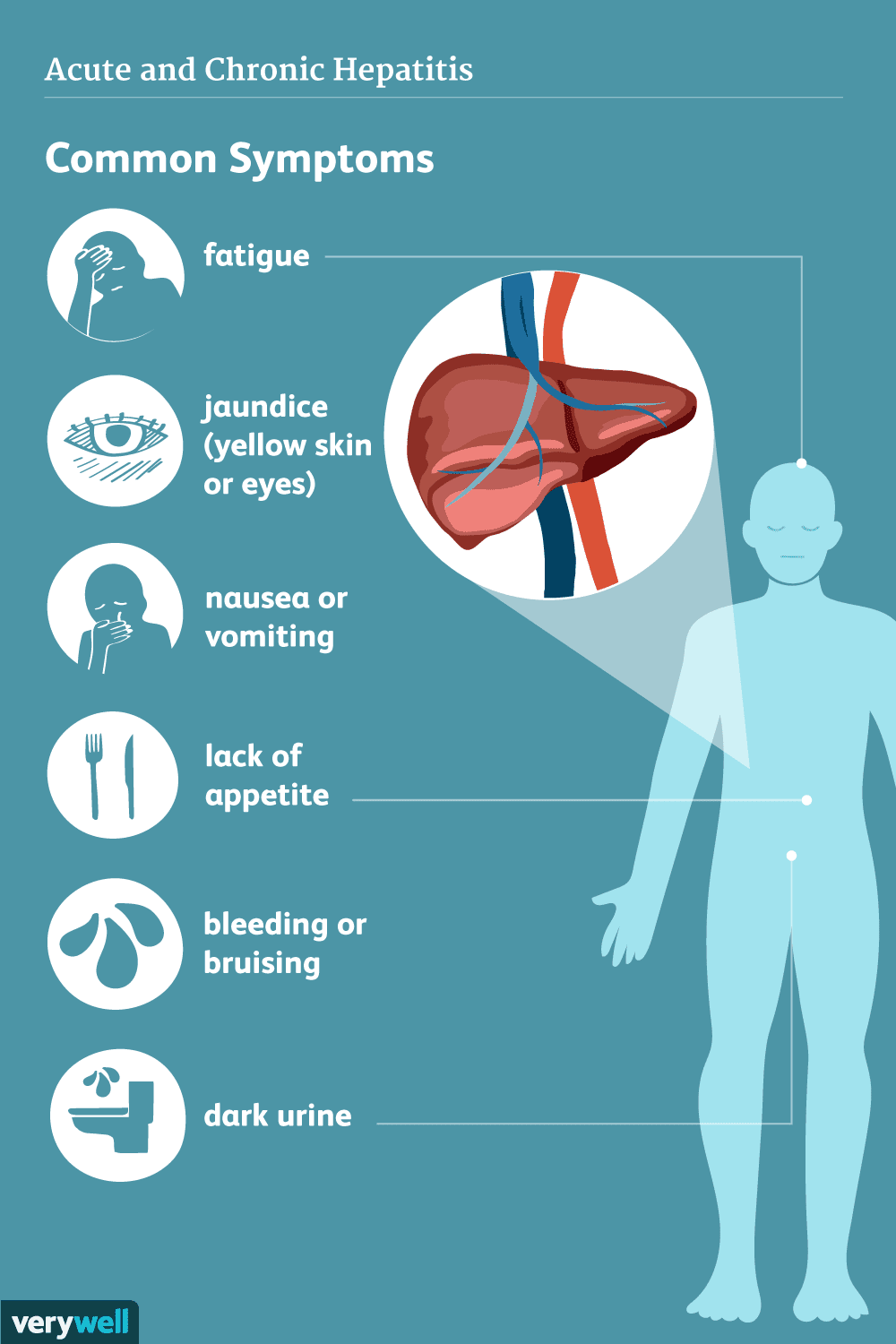
Frequent Hepatitis C Symptoms
The symptoms of liver failure include generalized flu-like symptoms, as well as more specific signs of liver involvement because the virus targets the liver. Common hepatitis C symptoms that occur in both the acute and chronic phase of HCV infection generally last longer and are more severe during the chronic stage of the infection.
The most common hepatitis C symptoms include symptoms that are not specific to hepatitis and occur with most infections. These symptoms are largely due to the activity of the body’s own immune system as it fights the virus.
The most common symptoms of acute and chronic HCV include:
- Joint pain
- Muscle Pain
Some of the symptoms of acute and chronic stage HCV are similar to the symptoms of any liver disease.
- Bleeding and Bruising: The liver plays a role in producing proteins that aid in blood clotting, which is part of healing from an injury. Bleeding and bruising can be signs of liver dysfunction, resulting from the viral attack on the liver, as well as the body’s inflammatory response to the virus.
- Dark-colored urine: The build-up of bilirubin, which is produced when the liver is infected or impaired, can cause jaundice, as well as the dark coloring of the urine , and pale or chalky stools.
- Pale or chalky stools
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis C
Drugs are licensed for treatment of persons with chronic hepatitis C. Combination drug therapy, using pegylated interferon and ribavirin, can get rid of the virus in up to five out of ten of persons with genotype 1, the most common genotype in the U.S. and eight out of ten persons with genotype 2 or 3. It is important to know that not everyone will need treatment. The decision to treat hepatitis C is complex and is best made by a physician experienced in treating the disease.
Recommended Reading: How Hepatitis C Virus Spread
Hiv And Hepatitis C Coinfection
HCV infection is common among people with HIV who also inject drugs. Nearly 75% of people living with HIV who report a history of injection drug use are co-infected with HCV. All people who are diagnosed with HIV are recommended to be tested for HCV at least once. People living with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HCV infection. Fortunately, direct acting antivirals that are used to treat HCV work equally well in people with and without HIV infection. For more information about HIV and HCV coinfection, visit the HIV.govs pages about hepatitis C and HIV coinfection.
What Is The Treatment For People With Acute Hepatitis C Infection
When people first get hepatitis C, the infection is said to be acute. Most people with acute hepatitis C do not have symptoms so they are not recognized as being infected. However, some have low-grade fever, fatigue or other symptoms that lead to an early diagnosis. Others who become infected and have a known exposure to an infected source, such as a needlestick injury, are monitored closely.
Treatment decisions should be made on a case-by-case basis. Response to treatment is higher in acute hepatitis infection than chronic infection. However, many experts prefer to hold off treatment for 8-12 weeks to see whether the patient naturally eliminates the virus without treatment. Approaches to treatment are evolving. Patients with acute hepatitis C infection should discuss treatment options with a health care professional who is experienced in treating the disease. There is no established treatment regimen at this time.
How effective is hepatitis C treatment? Is hepatitis C curable?
If the hepatitis C RNA remains undetectable at the end of the treatment and follow-up period, this is called a sustained virologic response and is considered a cure. Over 90% of people treated with DAAs are cured. These people have significantly reduced liver inflammation, and liver scarring may even be reversed.
About 5% of people who are treated for HCV infection are not cured by some of the older regimens. These people may still have options for cure with the newer regimens.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis B Be Transmitted Through Sweat
Can Hepatitis C Be Treated
Yes, since 2010 enormous progress has been made in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are pills that act on the virus itself to eradicate it from the body, unlike older medicines like interferon injections which work by stimulating an immune response. These new treatments are very effective and can achieve cure rates of over 90%. In most situations now, there is no need for interferon, which was responsible for many of the side effects previously associated with HCV treatment. The new treatment combinations require shorter treatment durations , have reduced side effects and appear to be effective at all stages of the disease.
Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Your primary care physician may refer you to a specialist to determine whether you are eligible for treatment. A specialist will help you decide which drug therapy is best for you based on the severity of your liver disease, your virus genotype and whether or not you have been treated in the past.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C In Females: Different Signs In Men And Women
Four million Americans have been infected by Hepatitis C. The main culprit of this disease is the Hepatitis C virus which is a blood-borne virus. Unlike HIV, more people are ending their lives due to this malady. Although HCV has the same effects on each gender, females react differently to it. Therefore, we will discuss the symptoms of hep C in females and how these symptoms differ from the signs of males hep c. In addition, this gender-blind virus is also blind in age and race. So, we will discuss the main factors which differentiate the Hepatitis symptoms in males and females.
The first thing which we should keep under consideration that how Hepatitis C transmitted from one person to another.
-
Blood Transfusion: As I mentioned earlier that HCV is a blood-borne virus and it can only transmit through blood contact.
-
Needles of Syringe: If a person is using needles of an infected person, he/she are at high risk.
-
Tattoo: During getting tattoos on the body, tattoo maker cannot discriminate the person with HCV and chances get higher to be infected with tattoos.
Ordinarily, you cannot diagnose Hep c by symptoms because of late indication of its symptoms. The most affected organ is liver by it. Moreover, it can be prognosticated by a blood test. However, there are several symptoms which may appear with this chronic disease.
Bad Coagulation: Blood clotting becomes difficult in this illness and bleeding becomes easier due to this chronic disease.
Also Check: Gilead Sciences Hepatitis C Cure
Hepatitis C And Injecting Drugs
If you inject drugs, avoid sharing needles, syringes or other equipment such as tourniquets, spoons, swabs or water.
Where possible, always use sterile needles and syringes. These are available free of charge from needle and syringe programs and some pharmacists. To find out where you can obtain free needles, syringes and other injecting equipment, contact DirectLine
Try to wash your hands before and after injecting. If you cant do this, use hand sanitiser or alcohol swabs from a needle and syringe program service.
What Does A Reactive Hcv Antibody Test Result Mean
A reactive or positive antibody test means you have been infected with the hepatitis C virus at some point in time.
Once people have been infected, they will always have antibodies in their blood. This is true if they have cleared the virus, have been cured, or still have the virus in their blood.
A reactive antibody test does not necessarily mean that you currently have hepatitis C and a follow-up test is needed.
You May Like: Where To Get Tested For Hepatitis
How Do Women Get Liver Disease C
Liver disease C spreads out from person-to-person through contact with infected blood. If you work in a market where you might come in contact with blood, theres a small risk of exposure. This consists of personal care such as:
- manicurists
- house cleaning
- nursing
To protect yourself, prevent contact with cuts or open sores on patients and clients. Use non reusable latex or non-latex gloves and sterilize equipment after each use . If you operate in the janitorial or housekeeping market, wear gloves to prevent contact with blood from feminine health products.
Liver disease C can likewise be spread to a sexual partner during a menstruation .
Numerous women with the virus are able to have a healthy baby. However, there is a small risk that the infection will be transferred to a baby during pregnancy. If you have hepatitis C and give birth, your baby will be checked for the infection at around 18 months.
How Is It Treated
Hepatitis A is treated using supportive methods. These can include things like rest, fluids, and healthy foods. Medications can also help to ease some symptoms like fever, aches, and pains.
Theres a vaccine available to protect against infection with HAV. This is typically recommended for children as well as for people at an increased risk for contracting the virus.
Also, receiving a single dose of the hepatitis A vaccine may prevent you from becoming ill if youve been exposed to HAV. For it to be effective, the vaccine needs to be given of exposure.
Recommended Reading: Can You Treat Hepatitis C
Spread Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is spread through blood-to-blood contact when blood from a person with hepatitis C enters another persons bloodstream.
The most common way people become infected with hepatitis C in Australia is by sharing injecting equipment such as needles, syringes, spoons and tourniquets. It is possible to be infected with hepatitis C after only one risk event.
Hepatitis C may also be spread through:
- tattooing and body piercing with equipment that has not been properly cleaned, disinfected or sterilised such as backyard tattoos’. Registered parlours with appropriate infection control procedures are not a risk
- needlestick injuries in a healthcare setting
- receiving blood transfusions in Australia prior to 1990 before hepatitis C virus testing of blood donations was introduced
- medical procedures, blood transfusions or blood products and mass immunisation programs provided in a country other than Australia
- pregnancy or childbirth there is a 5% chance of a mother with chronic hepatitis C infection passing on the virus to her baby during pregnancy or childbirth.
Breastfeeding is safe, however if nipples are cracked or bleeding cease breastfeeding until they have healed.
Less likely possible routes of transmission of hepatitis C include:
Hepatitis C cannot be transmitted by:
- kissing
- sharing food, cups or cutlery
- shaking hands or day-to-day physical contact.
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis C
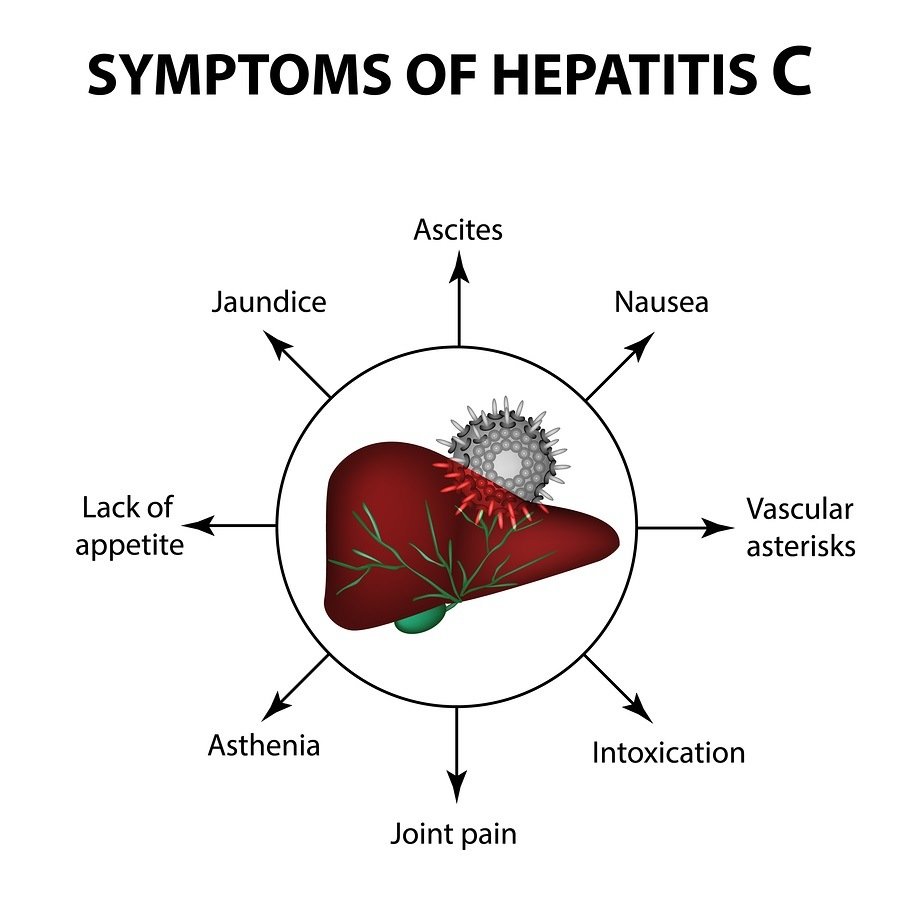
Numerous studies have established that you may not show the symptoms if affected by the hep C virus. Undertaking the following testing and diagnosis will help protect you and your family from the long-term effects of the virus.
- Anti-HCV antibodies: This test determines the number of antibodies produced by your body to fight against the HCV virus. It is usually conducted 12 weeks after the infection. It is the period when your immune system detects the HCV virus in your blood and produces proteins to fight against them. Generally, the results are out within 24 hours and will either be negative meaning your blood does not have any HCV antibodies and you have not contracted the virus, or positive meaning you have been affected by the virus.
- HCV RNA testing: HCV RNA is a blood test that measures the viral load of the HCV virus in your bloodstream and accurately detects the presence of the virus a few weeks after the exposure. A negative test report indicates that you have not been affected, and a positive test report indicates that you are currently infected with hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: Hepatic Wet Food For Cats
Who Gets Hepatitis C
Persons at highest risk for HCV infection include:
- persons who ever injected illegal drugs, including those who injected once or a few times many years ago,
- people who had blood transfusions, blood products or organ donations before June 1992, when sensitive tests for HCV were introduced for blood screening, and
- persons who received clotting factors made before 1987.
Other persons at risk for hepatitis C include:
- long-term kidney dialysis patients,
- health care workers after exposures to the blood of an infected person while on the job,
- infants born to HCV-infected mothers,
- people with high-risk sexual behavior, multiple partners and sexually transmitted diseases,
- people who snort cocaine using shared equipment, and
- people who have shared toothbrushes, razors and other personal items with a family member who is HCV-infected.
In Case You Feel You Have Hepatitis A Then What To Do
If you are experiencing some of the symptoms of Hepatitis A, the first thing you should do is to get tested for Hepatitis A.
A small blood sample is required for Hepatitis A testing. You can book a test online with us. We offer confidential STD testing services in NYC.
Knowing is better than ignoring. Dont ignore your health. Stay informed, get tested today.
STDTestingNYC.Net is a leading online STD Testing website in New York. We offer a wide range of STD tests at an affordable price including the panel test and HIV early detection test.
Get in Touch
You May Like: Does Hepatitis Affect The Liver
Other Risks Can Include:
- Sharing personal care items that may have come in contact with another persons blood, such as razors, toothbrushes or nail clippers
- Inoculation practices involving multiple use needles or immunization air guns
- Exposure of broken skin to HCV infected blood
- HIV infected persons
People with current or past risk behaviors should consider HCV testing and consult with a physician. HCV testing is currently not available at most public health clinics in Missouri. For information about HCV testing that is available, call the HCV Program Coordinator at 573-751-6439.
How Do You Prevent Hepatitis C
Researchers have yet to develop a vaccine that prevents hepatitis C .
Just as you might not know you have hepatitis C, other people with the condition may not know they have it, either. But you can take a few key precautions to avoid contracting it:
- Avoid sharing needles.
- When getting piercings or tattoos, check to make sure the piercer or tattoo artist uses only sterile, unopened needles and ink.
- Avoid sharing nail clippers, razors, and toothbrushes.
- Use sterile gloves when caring for someone elses wound.
Since hepatitis C is transmitted through blood, you wont get it by sharing food and drinks with someone who has the condition or by hugging, touching, or holding hands.
Hepatitis C is not commonly transmitted through sexual contact. But using a condom or another barrier method when having sex can always help lower your chances of contracting a sexually transmitted infection.
Keep in mind that you can contract hepatitis C again, even if youve had it already.
Read Also: What Is The Definition Of Hepatitis B
Stages Of Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus affects people in different ways and has several stages:
- Incubation period. This is the time between first exposure to the start of the disease. It can last anywhere from 14 to 80 days, but the average is 45
- Acute hepatitis C. This is a short-term illness that lasts for the first 6 months after the virus enters your body. After that, some people who have it will get rid of, or clear, the virus on their own.
- Chronic hepatitis C. For most people who get hepatitis C — up to 85% — the illness moves into a long-lasting stage . This is called a chronic hepatitis C infection and can lead to serious health problems like liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis. This disease leads to inflammation that, over time, replaces your healthy liver cells with scar tissue. It usually takes about 20 to 30 years for this to happen, though it can be faster if you drink alcohol or have HIV.
- Liver cancer. Cirrhosis makes liver cancer more likely. Your doctor will make sure you get regular tests because there are usually no symptoms in the early stages.
Learn more about the stages and progression of hepatitis C.
Who Is At High Risk And Should Be Tested For Hepatitis C Infection
The U.S. Preventive Health Services task force recommends that all adults born between 1945 and 1965 be tested once routinely for hepatitis C, regardless of whether risk factors for hepatitis C are present. One-time testing also is recommended for:
- People who currently inject drugs or snort drugs, or ever did so, even once many years previously
- People with persistently elevated alanine aminotransferase level, a liver enzyme found in blood
- People who have HIV infection
- Children born to HCV- or HIV-infected mothers
- People who were ever on long-term hemodialysis
- People who got a tattoo in an unregulated setting, such as prison or by an unlicensed person
- People who received clotting factor produced before 1987
- People who received transfusions or organ transplants before July 1992, or who were notified that they received blood from a donor who later tested positive for hepatitis C infection
- Health care, emergency medical, and public safety workers after a needlestick, eye or mouth exposure to hepatitis C-infected blood
People who may have been exposed to hepatitis C in the previous 6 months should be tested for viral RNA load rather than anti-HCV antibody, because antibody may not be present for up to 12 weeks or longer after infection, although HCV RNA may be detectable in blood as soon as 2-3 weeks after infection.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Early Signs Of Hepatitis C
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Treatment Antiviral Drugs