Counseling Practices That Educate Support And Motivate Clients Undergoing Screening
Clients might need help deciding whether to get screened, understanding the test results, and determining their next steps. Even when services offered through the substance abuse treatment program are limited, discussing testing with clients presents an opportunity for counselors to motivate clients for change by confronting substance use and by making choices that improve their overall health. However, this may also be true when services are offered on-site through substance abuse treatment programs. A study at one methadone clinic that offered hepatitis screening and vaccination revealed that although the majority of clients completed screening , only 54.7 percent of clients who lacked for hepatitis A received vaccinations and only 2.9 percent of clients who lacked immunity for received vaccinations .
The Consensus Panel makes the following general recommendations while recognizing that, in some programs, the counselors role may be limited:
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B Caused By
Preparing Clients For Screening
Once clients are comfortable talking about viral , they might be more willing to undergo screening. However, clients might be anxious about the test itself a reassurance that testing is a simple procedure can help allay these concerns. Many substance use treatment facilities do not offer screening, and clients might need to be referred elsewhere. The following strategies can enhance the discussion of the hepatitis screening process and hepatitis prevention:
Recommended Reading: What Is Chronic Hepatitis B
Why It Is Done
Hepatitis B testing is done to:
- Find the type of infection and see if an infection has occurred recently or in the past.
- Screen people who have a higher chance of getting or spreading hepatitis B. This includes doctors, dentists, and nurses.
- Screen blood donors and donor organs to prevent the spread of hepatitis B.
- Find out if a person has antibodies after getting a hepatitis B vaccination. Having antibodies means the vaccine worked.
- Find out if hepatitis B is the cause of abnormal liver function tests.
- See how well treatment of chronic hepatitis B is working.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis And How Do You Get It
Read Also: Latest Treatment Of Hepatitis C
Is Hepatitis B Curable
Theres currently no known cure for hepatitis B, but there are many ways you can prevent infection and avoid transmitting the virus to others.
The most effective and safe way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated. You can also use barrier methods, like condoms, when having sex and avoid sharing needles.
Provides Information To Assist In Interpretation Of The Test Results
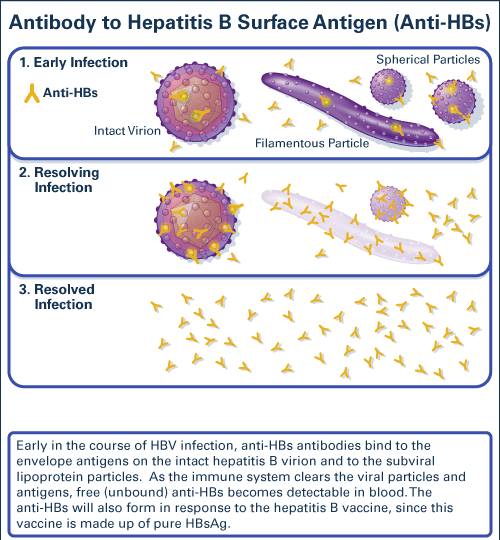
A positive result indicates recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection or acquired immunity from HBV vaccination. This assay does not differentiate between a vaccine-induced immune response and an immune response induced by infection with HBV. A positive total antihepatitis B core result would indicate that the hepatitis B surface antibody response is due to past HBV infection.
Per assay manufacturers instructions for use, positive results, defined as anti-HBs levels of 12.0 mIU/mL or greater, indicate adequate immunity to hepatitis B from past hepatitis B or HBV vaccination. However, per current CDC guidance, individuals with anti-HBs levels greater than 10 mIU/mL after completing an HBV vaccination series are considered protected from hepatitis B.
Negative results, defined as anti-HBs levels of less than 5.0 mIU/mL, indicate a lack of recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B or inadequate immune response to HBV vaccination. The US Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices does not recommend more than 2 HBV vaccine series in nonresponders.
Indeterminate results, defined as anti-HBs levels in the range from 5 to 11.9 mIU/mL, indicate inability to determine if anti-HBs is present at levels consistent with recovery or immunity. Repeat testing is recommended in 1 to 3 months.
Dont Miss: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
You May Like: How To Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Is There Anything Else I Should Know
Even if you donât have symptoms, an HBV infection can damage your liver and you can spread the infection to others. For this reason, it is important to get tested if you think you have been exposed to HBV.
Blood banks screen all donated blood for the hepatitis B virus , hepatitis B surface antigen , and hepatitis B core antibody . Donors are notified of any confirmed positive reactions. People who receive a notice regarding possible infection with hepatitis B after donating should visit their healthcare provider for further testing. The healthcare practitioner will order additional tests to make a proper diagnosis and determine if treatment is necessary.
If exposed to HBV and you havenât been vaccinated, an infection can be avoided by getting a shot of hepatitis B immune globulin within 24 hours and typically you will also be given the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine.
A test is available to determine the specific type of hepatitis B virus that is causing a personâs infection. This is called HBV genotyping. However, this testing is currently mainly used in research settings and not for clinical purposes.
What Does It Mean When Hepatitis Is Reactive
A reactive or positive antibody test means you have been infected with the hepatitis C virus at some point in time. Once people have been infected, they will always have antibodies in their blood. This is true if they have cleared the virus, have been cured, or still have the virus in their blood.
What does it mean if hepatitis B surface antibody is non reactive?
Normal results are negative or nonreactive, meaning that no hepatitis B surface antigen was found. If your test is positive or reactive, it may mean you are actively infected with HBV. In most cases this means that you will recover within 6 months.
What is the difference between Hep B surface antigen and antibody?
The basic blood test for hepatitis B consists of three screening tests: a hepatitis B surface antigen test, which determines whether a person currently has the infection a hepatitis B core antibody test, which determines whether a person has ever been infected and a hepatitis B surface antibody test, which determines
Dont Miss: How Contagious Is Hepatitis A
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C And Sexuality Activity
What Does It Mean If Your Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Is Negative
Your test results may not mean you have a problem. Ask your healthcare provider what your test results mean for you. Normal results are negative or nonreactive, meaning that no hepatitis B surface antigen was found. If your test is positive or reactive, it may mean you are actively infected with HBV.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis B Cause Meningitis
Educating Clients About Viral Hepatitis
Clients may believe they know about viral , but their understanding of the disease may not be accurate. It is easy to confuse the three main types of viral , B, and C. Clients may have formed impressions based on limited or incorrect information. Counselors should briefly describe hepatitis A, B, and C, including their prevalence, , and relationship to drug use, as well as to other infections, such as HIV and sexually transmitted diseases. Specific strategies for speaking with clients include:
- Speak clearly and keep the message simple, focused, and brief.
- Use language, examples, and concepts that the client understands.
- Use appropriate visual aids.
- Frame numerical statements in terms that are easy to visualize. Say 5 out of 100 people rather than 5 percent of the population say more than half instead of the majority.
- Repeat the information at different times in different ways. The average client retains only approximately one-third of what he or she is told. Summarize essential points.
- Pay attention to a clients response to the information. For example, if a client stiffens his or her posture, consider saying, I notice that this topic seems to make you uncomfortable. It does for a lot of people. Please tell me what youre feeling right now. Id really like to help you with this.
- Use the opportunity to describe the potential detrimental effects of alcohol and other substance use on the liver of a person who is infected with HCV.
Also Check: Cure For Chronic Hepatitis B
Read Also: Which Statement Is True About The Hepatitis C Virus
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
Don’t Miss: Does Hepatitis B Have A Vaccine
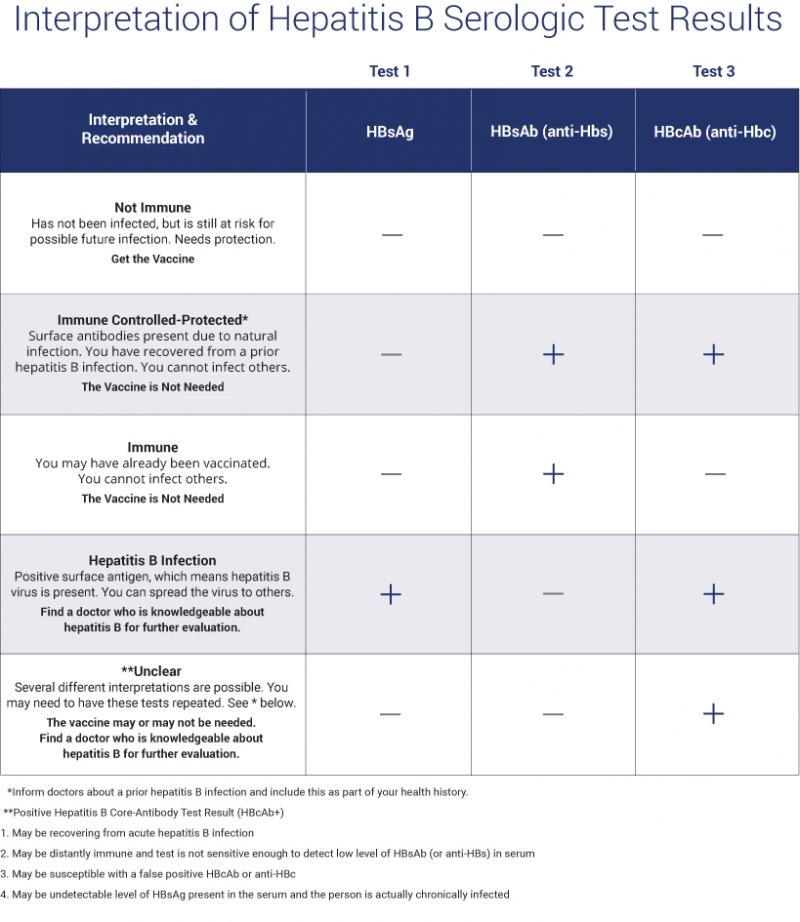
Understanding Your Test Results
Understanding your hepatitis B blood tests can be confusing. It is important to talk to your health care provider so you understand your test results and your hepatitis B status. Are you infected? Protected? Or at risk? The Hepatitis B Panel of blood tests includes 3 tests and all three results must be known in order to confirm your status.
Below is a chart with the most common explanation of the test results, but unusual test results can occur. Please note that this chart is not intended as medical advice, so be sure to talk to your health care provider for a full explanation and obtain a printed copy of your test results. In some cases, a person could be referred to a liver specialist for further evaluation.
More Detailed Information About Hepatitis B Blood Tests
An acute hepatitis B infection follows a relatively long incubation period – from 60 to 150 days with an average of 90 days. It can take up to six months, however, for a person to get rid of the hepatitis B virus. And it can take up to six months for a hepatitis B blood test to show whether as person has recovered from an acute infection or has become chronically infected .
The following graphic from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention represents the typical course of an acute hepatitis B infection from first exposure to recovery.
According to the CDC, a hepatitis B blood test result varies depending on whether the infection is a new acute infection or a chronic infection.
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if youre contagious. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can spread the virus. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B. This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the .
Also Check: How Much Is A Hepatitis C Test
Question 1 What Is The Clinical Indication For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitation
Hepatitis B surface antibody quantitation is used to determine hepatitis B immune status, ie, to determine if the patient has developed immunity against the hepatitis B virus. Such immunity may develop following exposure to the hepatitis B virus or its vaccine.
Patients at higher risk of exposure to the virus include:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- Sex partners of infected persons
- People with more than 1 sex partner in the last 6 months
- People with a history of sexually transmitted infection
- Men who have sex with men
- Injection drug users
- Household contacts of an infected person
- Healthcare and safety workers who have contact with blood and body fluids
- People who have lived or traveled in an area in which hepatitis B is common
- People who live or work in a prison
Testing is not recommended routinely following vaccination. It is advised only for people whose subsequent clinical management depends on knowledge of their immune status. These people include:
- Chronic hemodialysis patients
- Immunocompromised people, including those with HIV infection, hematopoietic stem-cell transplant recipients, and people receiving chemotherapy
- Infants born to women who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Sex partners of people who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Healthcare and public safety workers who have contact with blood or body fluids
Identifying Patterns Of Risky Behavior
Screening is an opportunity to draw attention to the clients behaviors that put him or her at risk for contracting :
- Ask for the clients perception of his or her risk for having contracted : How likely do you think it is that the test will be positive?
- Listen for and identify behaviors that put the client at risk for contracting , B, and C and HIV, especially unprotected sex and sharing injection drug paraphernalia.
- Assess the clients alcohol consumption.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C An Std
Read Also: How Long Does It Take To Treat Hepatitis B
Transmission Symptoms And Treatment
How is HBV transmitted?
HBV is transmitted through activities that involve percutaneous or mucosal contact with infectious blood or body fluids , including
- sex with a partner who has HBV infection
- injection drug use that involves sharing needles, syringes, or drug-preparation equipment
- birth to a person who has HBV infection
- contact with blood from or open sores on a person who has HBV infection
- exposures to needle sticks or sharp instruments and
- sharing certain items with a person who has HBV infection that can break the skin or mucous membranes , potentially resulting in exposure to blood.
How long does HBV survive outside the body?
HBV can survive outside the body and remains infectious for at least 7 days .
What should be used to clean environmental surfaces potentially contaminated with HBV?
Any blood spills should be disinfected using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 9 parts water. Gloves should be worn when cleaning up any blood spills.
Who is at risk for HBV infection?
The following populations are at increased risk for becoming infected with HBV:
- Infants born to people with HBV infection
- Sex partners of people with HBV infection
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household contacts or sexual partners of known people with chronic HBV infection
- Health care and public safety workers at risk for occupational exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Patients on hemodialysis
Who should be screened for HBV?
Cautions Discusses Conditions That May Cause Diagnostic Confusion Including Improper Specimen Collection And Handling Inappropriate Test Selection And Interfering Substances
Positive screen results without need for confirmation testing should be interpreted in conjunction with test results of other hepatitis B virus serologic markers .
Positive hepatitis B surface antigen test results should be reported by the health care provider to the State Department of Health, as required by law in some states.
Individuals, especially neonates and children, who recently received hepatitis B vaccination may have transient positive HBsAg test results because of the large dose of HBsAg used in the vaccine relative to the individualâs body mass.
Performance characteristics have not been established for the following specimen characteristics:
-Grossly icteric
-Containing particulate matter
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C And Herpes The Same Thing
About The Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus is a small DNA virus that belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family. Related viruses in this family are also found in woodchucks, ground squirrels, tree squirrels, Peking ducks, and herons.
Structure of the Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus contains an outer envelope and an inner core.
- The outer envelope of the virus is composed of a surface protein called the hepatitis B surface antigen or HBsAg. The HBsAg can be detected by a simple blood test and a positive test result indicates a person is infected with the hepatitis B virus.
- The inner core of the virus is a protein shell referred to as the hepatitis B core antigen or HBcAg, which contains the hepatitis B virus DNA and enzymes used in viral replication.
Life Cycle of the Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus has a complex life cycle. The virus enters the host liver cell and is transported into the nucleus of the liver cell. Once inside the nucleus, the viral DNA is transformed into a covalently closed circular DNA , which serves as a template for viral replication . New HBV virus is packaged and leaves the liver cell, with the stable viral cccDNA remaining in the nucleus where it can integrate into the DNA of the host liver cell, as well as continue to create new hepatitis B virus. Although the life cycle is not completely understood, parts of this replicative process are error prone, which accounts for different genotypes or genetic codes of the hepatitis B virus.
Igg Subclass Profiles Of Anti
Since anti-HBs in most of the infants was higher than that in their mothers , and IgG1 is the most efficiently transplacentally transported subclass , we attempted to clarify which subclass of anti-HBs IgG was predominant in the infants. We selected 20 paired mother-infant sera and analyzed the anti-HBs IgG subclasses. Anti-HBs IgG1 subclass was predominant in all these samples, regardless of the antibody induced by vaccination or by resolved HBV infection, and three other IgG subclasses accounted for minor portion of the total anti-HBs. Figure 3 shows the representative results of the four paired sera.
Anti-HBs IgG subclasses in paired mother-infant sera.
1, 2, 3, and 4 under the X axial indicate the subclasses IgG1, G2, G3, and G4, respectively. Sera 018 and 020 were from mothers recovered from natural HBV infection, while sera 141 and 166 were from vaccinated mothers. The data from 4 paired sera were used to represent anti-HBs IgG subclasses distribution in 20 paired mother/infant sera.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis B Contagious Through Saliva