What To Do If You Miss A Scheduled Dose
The recommended schedule for the HBV vaccine follows a three-dose pattern, with all doses complete within 6 months. The good news is that if you miss a dose, you dont need to start the series of shots all over.
If you missed getting the second dose 1 month after the first, make an appointment as soon as possible. If you miss the third dose, you should also try to get it as quickly as possible. Keep in mind that the second and third doses
Who Should Not Receive The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Talk to your healthcare provider before getting the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- You have had a severe allergic reaction to the hepatitis B vaccine or any of its ingredients in the past.
- You have had an allergic reaction to yeast in the past.
- You are moderately or severely ill.
- You are currently taking immunosuppressive medications.
In addition, pregnant people should not receive the Heplisav-B or PreHevbrio vaccines until more safety information is available.
Recommended Vaccines For Healthcare Workers
Healthcare workers are at risk for exposure to serious, and sometimes deadly, diseases. If you work directly with patients or handle material that could spread infection, you should get appropriate vaccines to reduce the chance that you will get or spread vaccine-preventable diseases. Protect yourself, your patients, and your family members. Make sure you are up-to-date with recommended vaccines.
Healthcare workers include physicians, nurses, emergency medical personnel, dental professionals and students, medical and nursing students, laboratory technicians, pharmacists, hospital volunteers, and administrative staff.
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis A Be Transmitted Sexually
Complications Of Hepatitis B Infection In Infants And Children
Mothers who are infected with hepatitis B can pass the virus to their baby at the time of birth. Hepatitis B virus can also be spread through exposure of broken skin or mucous membranes to the blood or other body fluids of an infected person.
Babies born to mothers with hepatitis B are recommended a dose of hepatitis B vaccine within 12 hours of birth as well as another medicine called hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These 2 injections provide extra protection for babies born to women living with hepatitis B.
Many people who are infected with hepatitis B have no symptoms. Babies and children who are infected with hepatitis B are less likely than adults to have symptoms of infection, but are more likely to develop chronic hepatitis B.
Symptoms of hepatitis B include:
- Yellow skin and eyes
- Aching muscles or joints arthritis.
A child who contracts chronic hepatitis B has an increased risk of developing chronic liver disease and cancer later in life. A small proportion of adults who become infected with the hepatitis B virus develop chronic hepatitis B infection.
Immunisation Against Hepatitis B For People At Risk
In Victoria free hepatitis B vaccine is provided for people who are at increased risk, including:
- Men who have sex with men.
- People living with HIV.
- People living with hepatitis C.
- People no longer in a custodial setting who commenced, but did not complete, a free vaccine course while in custody.
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people.
- People born in priority hepatitis B endemic countries who arrived in Australia in the last 10 years priority countries include China, Philippines, Malaysia, Vietnam, Afghanistan, Thailand, South Korea, Myanmar , Indonesia, Singapore, Hong Kong, Taiwan and Cambodia.
- Vulnerable citizens people who have experienced hardship that prevented them from accessing the vaccine earlier. Vulnerable citizens are vaccinated based on an individual assessment by an immunisation provider.
Immunisation is also recommended, but not free, for people who are at increased risk including:
If you think you have been exposed to hepatitis B, see a doctor immediately. Your doctor can give you treatment that, in some instances, can greatly reduce your risk of infection with hepatitis B.
Remember that being immunised against hepatitis B does not protect you against HIV, hepatitis C or other diseases spread by blood or bodily fluids. It is important that you take precautions to make sure you are not exposed to these diseases.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Viral Load Test
Concurrent Administration Of Vaccines
HB-containing vaccines may be administered concomitantly with other vaccines or with HBIg. Different injection sites and separate needles and syringes must be used for concurrent parenteral injections.
Refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1 for additional information about concurrent administration of vaccines.
A Look At Each Vaccine: Hepatitis B Vaccine
View larger image The hepatitis B vaccine is given to prevent the severe liver disease that can develop when children or adults are infected with hepatitis B virus. The hepatitis B vaccine is given as a series of three shots. The first dose is given within 24 hours of birth. The second dose is given one to two months after the first dose, and the third dose is given between 6 months and 18 months of age. The vaccine is also recommended for those up to 60 years of age who have not previously received it and those 60 years and older who are at increased risk or who simply want the protection afforded by vaccination.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis Cause Low Platelets
Us Children And Adult Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
The hepatitis B vaccine is an injection that is generally given in the arm as a three-dose series on a 0, 1, and 6-month schedule. Alternative schedules may be considered, noting that a third dose at 6 months, meeting minimum intervals between doses, is needed for maximum, long-term protection. Completing the hepatitis B vaccine series, preferably beginning at birth, will ensure protection against hepatitis B, hepatitis delta and lower the lifetime risk of liver cancer. Greater than 90% of babies and up to 50% of young children who are not vaccinated and are infected with hepatitis B will have lifelong infection, which makes the birth dose essential to their protection.
There are four, 3-dose vaccine brands approved in the U.S.
- PreHevbrio PreHevbrio is only approved for adults age 18 and over.
2-Dose Vaccine Series
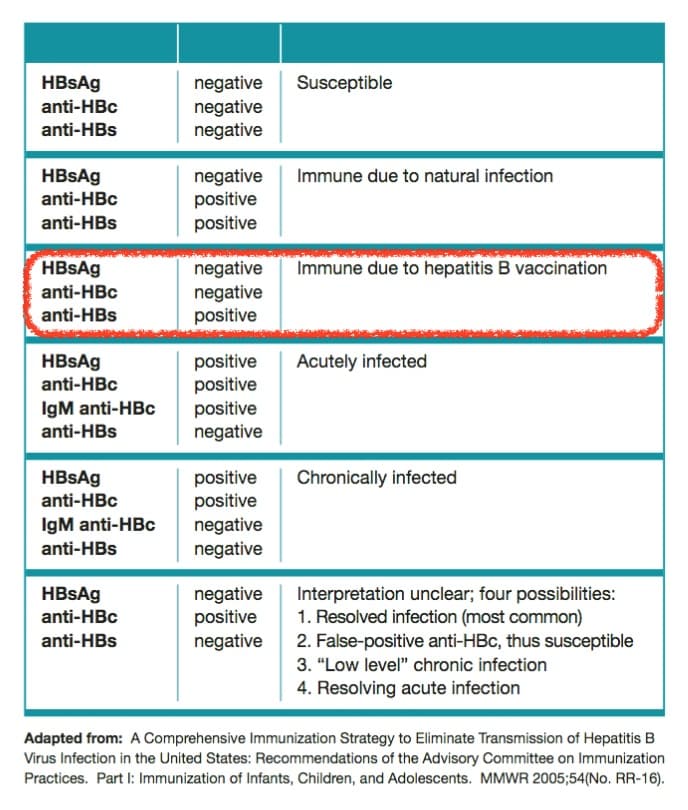
What Do The Results Mean
A hepatitis B blood panel consists of three tests that can be done with just one blood sample:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen . A positive test indicates that youre infected with hepatitis B and that you can spread it to other people. Further tests are needed to see if you have an acute or chronic infection.
- Hepatitis B core antibody . A positive result can indicate a past or current hepatitis B infection, but doesnt mean youre immune. A positive result needs to be interpreted by a doctor by examining the results of the other two tests.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody . A positive test indicates that youre protected from hepatitis B either through previous infection or vaccination .
The combination of these tests can indicate your hepatitis B status and whether you need to be vaccinated. Your test will give a negative or positive result for each category depending on whether your results are above or below the cutoff value.
Most peoples test results fall into the following categories. But its possible to have a result that doesnt fall into one of these groups. If youre reading your results yourself, be careful not to confuse HBsAb with HBcAb.
| HBsAG |
is associated with hepatitis B immunity after vaccination. But research has found that anti-HBs decline over time.
A found that more than 95 percent of people had anti-HBs levels greater than 10IU/L two years after vaccination. But this rate decreased to 70 percent after eight years.
Don’t Miss: What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Of The Liver
Why Do You Need A Hepatitis B Shot
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that cant be transferred person-to-person unless you have contact with an infected persons bodily fluids. Annual infection rates of HBV are going down in the United States thanks to vaccines. So you might be wondering if you or your child needs a shot to protect against hepatitis B.
What Are The Stages Of Hepatitis B
The entire illness of acute hepatitis B sequentially passes through three phases, namely prodromal phase, icteric phase and convalescence phase. The prodromal phase is characterized by MARKED LOSS OF APPETITE, and other fluâlike symptoms such as lowâgrade fever, nausea and vomiting, and lasts for a few days.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Is It Sexually Transmitted
Persons With Chronic Diseases
Refer to Immunization of Persons with Chronic Diseases in Part 3 for additional general information about vaccination of people with chronic diseases.
Chronic renal disease and patients on dialysis
People with chronic renal disease may respond sub-optimally to HB vaccine and experience more rapid decline of anti-HBs titres, and are therefore recommended immunization with a higher vaccine dose. Individuals undergoing chronic dialysis are also at increased risk for HB infection. In people with chronic renal disease anti-HBs titre should be evaluated annually and booster doses using a higher vaccine dose should be given as necessary.
Neurologic disorders
People with conditions such as autism spectrum disorders or demyelinating disorders should receive all routinely recommended immunizations, including HB-containing vaccine.
Chronic liver disease
HB immunization is recommended for non-immune persons with chronic liver disease, including those infected with hepatitis C, because they are at risk of more severe disease if infection occurs. Vaccination should be completed early in the course of the disease, as the immune response to vaccine is suboptimal in advanced liver disease. Post-immunization serologic testing may be used to confirm vaccine response.
Non-malignant hematologic disorders
Persons with bleeding disorders and other people receiving repeated infusions of blood or blood products are considered to be at higher risk of contracting HB and should be offered HB vaccine.
Us Infant Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
Since 1991, ALL medically stable infants with a birth weight of at least 2,000 g in the U.S. are recommended to receive the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth. The additional 2 doses are given at 1 month and 6 months of age.
4-Dose Vaccine Combination Series for Infants
Combination vaccines, such as the pentavalent and hexavalent vaccines, include protection against 5 or 6 diseases, including hepatitis B. The first shot is usually given at 6 weeks of age, but in order to protect infants from hepatitis B beginning at birth, a monovalent or single dose of the hepatitis B vaccine is also recommended within 24 hours of birth. The hepatitis B vaccine series can then be completed with the pentavalent or hexavalent vaccine with the recommended schedule.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Side Effects Of Hepatitis B
If I Already Have Hepatitis B Can The Vaccine Treat It
No. The hepatitis vaccine prevents hepatitis, but doesnt cure it if you already have it. If you have hepatitis B, there are other treatment options.
However, if you recently got exposed to the hepatitis B virus and you havent had the vaccine yet, tell your doctor right away. The vaccine and possibly other treatment can reduce your chances of getting hepatitis B if you get it within 2 weeks after you came into contact with the virus. The sooner you seek care after being exposed to hepatitis B, the better, so try to get there right away.
Can Hepatitis B Become Negative
It can happen, especially in older adults after a long period of âinactiveâ hepatitis B infection. About 1 to 3 percent of people with chronic hepatitis B lose HBsAg each year, and about half of all people with chronic infections who live up to age 75 will lose HBsAg, depending on the amount of HBV DNA in their blood.
Also Check: Will Hepatitis C Go Away
Emergency Hepatitis B Vaccination
If you have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and have not been vaccinated before, you should get immediate medical advice, as you may benefit from having the hepatitis B vaccine.
In some situations, you may also need to have an injection of antibodies, called specific hepatitis B immunoglobulin , along with the hepatitis B vaccine.
HBIG should ideally be given within 48 hours, but you can still have it up to a week after exposure.
Whats The Procedure For A Hepatitis B Titer Test
A hepatitis titer test requires a healthcare professional to draw a small amount of blood for testing.
No special preparation is needed beforehand. If needles or the sight of blood make you anxious, you may want to arrange a drive ahead of time in case you feel faint.
Heres what will typically happen during this test:
Home tests that require a fingerpick are also available. The results of your tests are generally available within 3 days.
You May Like: Which Hepatitis Causes Liver Cancer
How Do You Catch Hepatitis B Virus
Blood from a person infected with hepatitis B virus is heavily contaminated with the virus. As a result, contact with blood is the most likely way to catch hepatitis B. Even casual contact with the blood of someone who is infected can cause infection.
Healthcare workers are at high risk of catching the disease, as are intravenous drug users and newborns of mothers infected with the virus. Sexual contact can also expose people to infection. The virus is also present in low levels in saliva.
What If My Baby Is Premature
Premature babies are more at risk of developing infections and should be immunised at the recommended time. Babies born less than 32 weeks gestation or weighing less than 2,000 grams at birth will need an extra dose of the vaccine at 12 months of age. Your doctor or nurse should tell you if your baby will need an extra dose of hepatitis B vaccine.
Also Check: What Causes Hepatitis C Infection
How And When Do Doctors Give Vaccines
For the hepatitis A vaccine:
You should get two doses, given as shots, 6 months apart for complete protection. The virus in the vaccine is killed .
Children should get the first dose between 12 and 23 months of age. Children older than age 2 can get the first dose at their next doctorâs visit.
If you need the vaccine because of upcoming travel, get it at least 1 month before you go.
For the hepatitis B vaccine:
For long-lasting immunity, you need three to four doses, depending on which type of vaccine is used. You get them as shots.
Children should get their first dose at birth and complete the series by age 6 months. Usually, the baby would get a second dose at 1 month old and the third dose at 6 months.
Babies born to women who have hepatitis B need a shot of hep B antibodies, as well as their first hep B vaccine shot, when theyâre born. They will also need follow-up blood tests to make sure theyâre OK.
Catch-up vaccinations are recommended for children and teens who were never vaccinated or who did not get all three shots.
If you’re an adult who wants to be vaccinated, you should talk about it with your doctor or pharmacist. If you are considering both vaccines, ask your doctor about vaccines that combine hep A and B.
Show Sources
General Information About Vaccination Outside The Us

In developing countries, the pentavalent vaccine, a combination 5-in-one vaccine that protects against five diseases, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, Hib and hepatitis B, may be given to babies more than 6 weeks of age, and can be given up to 1 year of age. The first dose is given at 6 weeks, and the second and third doses are given at 10 and 14 weeks of age. The pentavalent vaccine may be made available free of charge with the support of GAVI, the vaccine alliance. Check the GAVI country hub to see the resources and immunizations that may be available:
For babies born to mothers with hepatitis B, waiting for the first dose of the pentavalent vaccine is too late and will NOT protect the baby from vertical or horizontal transmission of hepatitis B. Babies born to a mother with hepatitis B have a greater than 90% chance of developing chronic hepatitis B if they are not properly treated at birth.
WHO recommends the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth for ALL babies. Plan ahead and inquire about the availability and cost of the monovalent , birth dose of the vaccine, as it is not a GAVI provided immunization. This is particularly important to women who are positive for hepatitis B.
If you are unsure of your hepatitis B status, please be sure your doctor tests you for hepatitis B!
*WHO does not recommend a birth dose of HBIG, which may not be available in all countries. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Page updated September 2022.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Hepatitis Panel