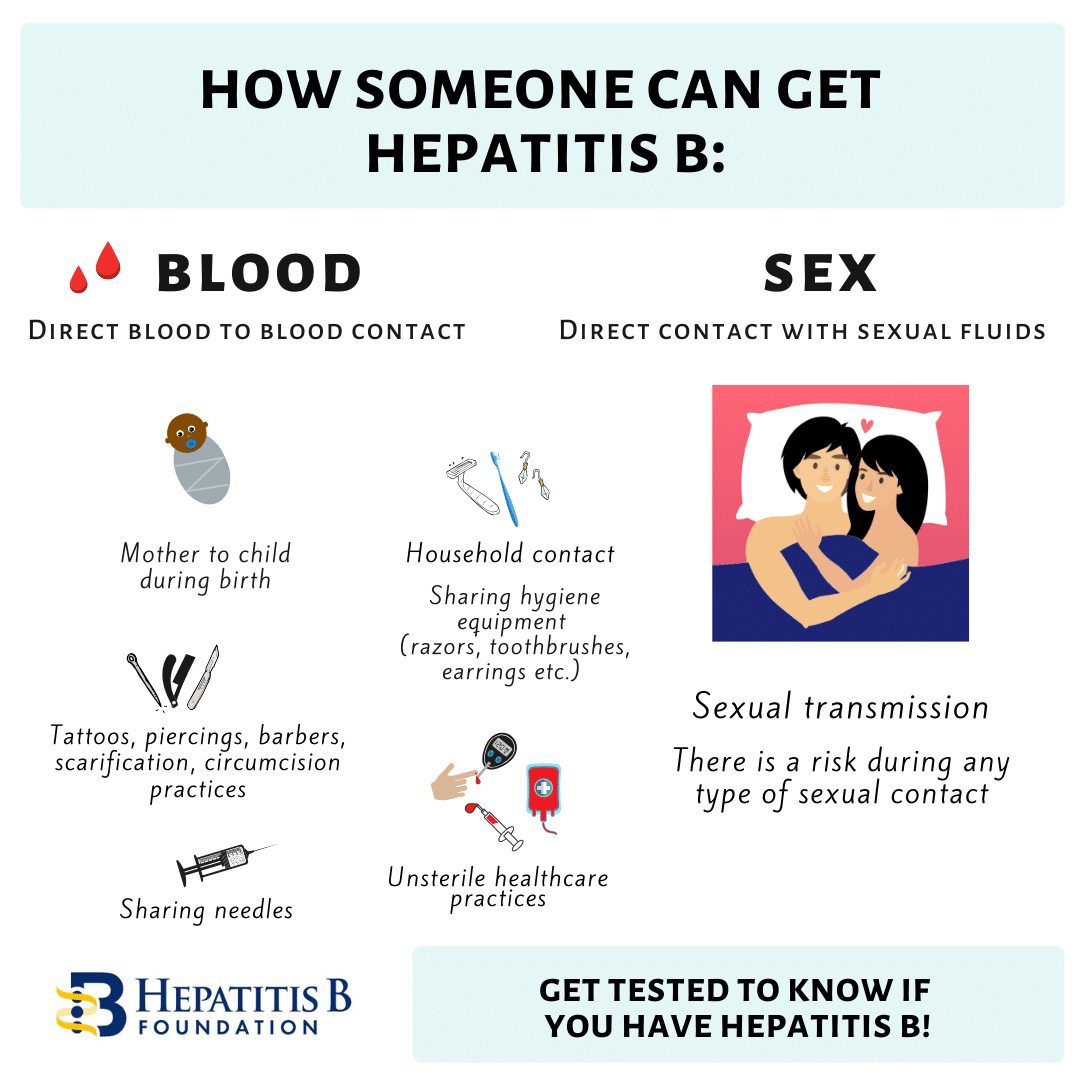
How Do You Get Hepatitis B
-
sharing toothbrushes and razors
-
sharing needles for shooting drugs, piercings, tattoos, etc.
-
getting stuck with a needle that has the Hep B virus on it.
Hepatitis B can also be passed to babies during birth if their mother has it.
Hepatitis B isnt spread through saliva , so you CANT get hepatitis B from sharing food or drinks or using the same fork or spoon. Hepatitis B is also not spread through kissing, hugging, holding hands, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding.
Urgent Advice: Contact Your Gp If:
- you have any persistent or troublesome symptoms that you think could be caused by hepatitis
- your child develops any symptoms of hepatitis, such as yellowing of the eyes and skin
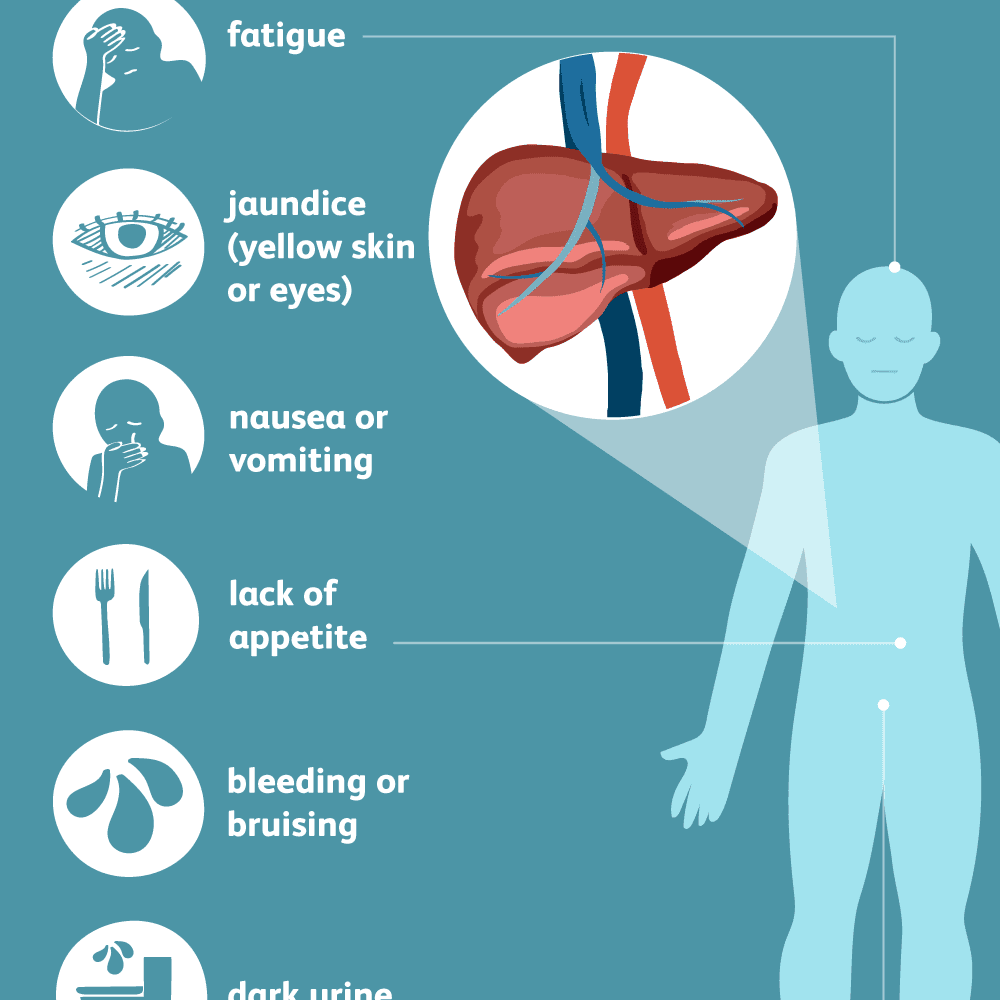
Long-term hepatitis also may not have any obvious symptoms until the liver stops working . Routine blood tests can help diagnose hepatitis.
In the later stages it can cause:
- swelling in the legs, ankles and feet
- blood in your poo or vomit
Hepatitis A: How Does It Spread
It usually spreads through food or water. Food can be tainted when it’s touched by a person with hepatitis who did not wash their hands after using the bathroom. This transfers tiny amounts of infected stool to the food. Raw shellfish, fruits, vegetables, and undercooked foods are common culprits in hepatitis A outbreaks. The virus can also spread in daycare centers if employees aren’t careful about washing hands after changing diapers.
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis Transmitted From Person To Person
Hepatitis B: How Does It Spread
You can get it through contact with the blood or body fluids of an infected person. In the U.S., it’s most often spread through unprotected sex. It’s also possible to get hepatitis B by sharing an infected person’s needles, razors, or toothbrush. And an infected mother can pass the virus to their baby during childbirth. Hepatitis B is not spread by hugging, sharing food, or coughing.
Parenteral Routes: Transmission Of Hepatitis B Hepatitis D And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B, C, and D viruses are all transmitted by what is known as the parenteral route. Parenteral simply means that these viruses can be introduced by all routes except through the intestinal tract, which leaves the door wide open in terms of possible exposure. Let’s look at the possible transmission routes for each of these types of hepatitis virus more closely.
Don’t Miss: What Type Of Hepatitis Can Be Cured
How Is Niaid Addressing This Critical Topic
NIAID supports and conducts research on each of the five known hepatitis virusesA, B, C, D, and E. During the past 60 years, NIAID-supported investigators have been involved in many important advances in hepatitis research, including:
- Discovery of the hepatitis A and E viruses
- Development of one of the first diagnostic tests for hepatitis A
- Studies that led to the creation of the hepatitis A vaccine
- Studies that laid the foundation for advanced development of a hepatitis E vaccine.
NIAIDs research program emphasizes the study of hepatitis B and C viruses due to the large magnitude of medical burdens that they impose. Studies focus on understanding the immune response to infection, the course of disease development, and developing new therapeutics and vaccines for these viruses.
To learn about risk factors for hepatitis and current prevention and treatment strategies visit the MedlinePlus hepatitis site.
Can Hepatitis Be Treated
There are no treatments to cure hepatitis A, aside from carefully monitoring liver function. If you know you have hepatitis A early enough, you might be able to stop the infection if you get a dose of the hepatitis A vaccine or something called hepatitis A immune globulin.
Hepatitis B, when chronic, can often be treated successfully. The most commonly used drugs to treat chronic hepatitis B are:
For hepatitis C, the following drugs are used:
- Sofosbuvir sofusbuvir/velpatasvir sofusbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir ledipasvir/sofosbuvir .
- Ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir/dasabuvir .
- Elbasivir/grazoprevir .
- Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir .
These new drugs are sometimes given with older drugs like ribavirin and peginterferon alfa-2a and peginterferon-2b. You might have to take these medicines for some time, even as long as six months.
If you have chronic hepatitis D, your doctor may prescribe drugs with interferons and might also add medicines for hepatitis B. Hepatitis E treatments include peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin.
Also Check: What Are The Effects Of Hepatitis C
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
Learn More About Hepatitis
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is contagious, and usually spreads through food, drink, or objects contaminated by feces containing the hepatitis A virus. The hepatitis A vaccine has made the infection less common in the United States and other developed countries.
This virus can cause severe symptoms, but unlike some other hepatitis viruses, it rarely leads to long-lasting liver damage. People recover from hepatitis A have immunity to the virus and won’t get it again.
Read more about hepatitis A.
Hepatitis B
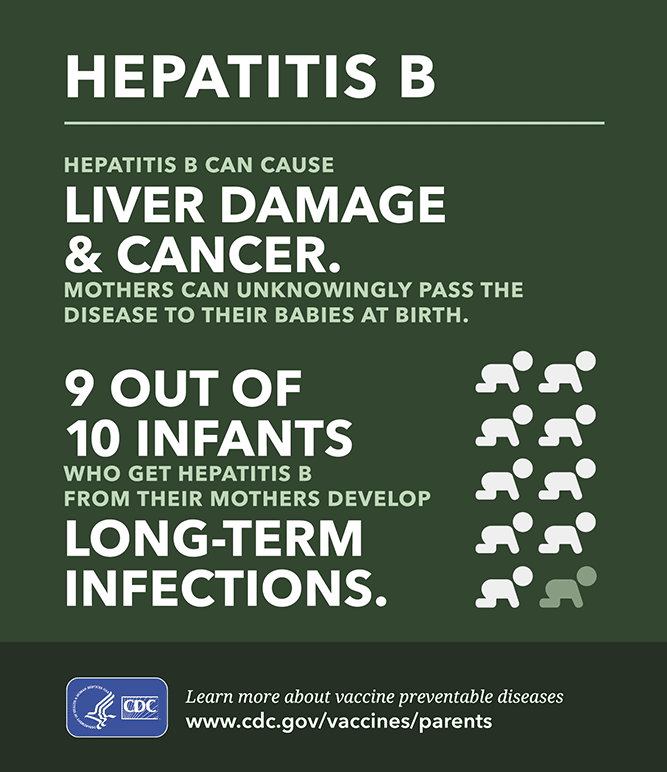
Hepatitis B is a more serious infection. It can lead to cirrhosis of the liver, liver failure, or liver cancer, causing severe illness and even death.
The hepatitis B virus spreads from person to person through blood or other body fluids. In the United States, this most commonly happens through unprotected sex with someone who’s infected or from injecting drugs with shared needles that aren’t sterilized. It also can pass from an infected mother to her unborn baby.
Read more about hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus spreads from person to person through blood or other body fluids, and can lead to cirrhosis or liver cancer. The most common way people become infected is by sharing drug equipment such as needles and straws. People also can get hepatitis C from unprotected sex with an infected partner. And it can pass from an infected mother to her unborn baby.
Also Check: What Hepatitis Is Caused By Alcohol
Who Should Get The Hepatitis A Vaccine
The CDC recommends that all children between ages 12 months and 23 months get this vaccine as well as for any infant aged 6 to 11 months who is traveling internationally.
The following people are also at risk for the disease and should be vaccinated:
- Children and teens through age 18 who live in states or communities that have made this vaccination routine because of a high rate of disease
- Men who have sex with men
- Anyone who uses illegal drugs
- People with chronic liver disease
- Anyone treated with blood clotting drugs, such as people with hemophilia
- People who work with HAV-infected primates or in HAV research laboratories.
- Travelers to countries where hepatitis A is common. A good source to check is the CDCâs travelersâ health website, which you can search by the country youâre going to.
- People adopting or close to a child adopted from a country where hepatitis A is common
You should not get the vaccine if youâre allergic to any ingredients in it or if you had a severe allergic reaction to an earlier dose of it. Tell your doctor or pharmacist about any allergies you have.
If youâre pregnant, let your doctor know. The safety of this vaccine for pregnant women is unknown, although the risk is considered to be very low.
Persons With Inadequate Immunization Records
Evidence of long term protection against HB has only been demonstrated in individuals who have been vaccinated according to a recommended immunization schedule. Independent of their anti-HBs titres, children and adults lacking adequate documentation of immunization should be considered susceptible and started on an immunization schedule appropriate for their age and risk factors. Refer to Immunization of Persons with Inadequate Immunization Records in Part 3 for additional information.
Donât Miss: Is There A Vaccine For Hepatitis A
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis A B C Difference
What Is The Risk
Because universal vaccination of newborns has been recommended since 1991, rates of Hepatitis B in the United States have been going down. But certain groups are still at higher risk, including:
- Infants born to mothers with hepatitis B
- People born outside the United States, or those who travel to areas like Asia or sub-Saharan Africa, where hepatitis B is more common
- Sexual partners of people with hepatitis B
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs and share needles or syringes
- People who live with someone who has hepatitis B
- Abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting
Role In Human Disease
Examples of common human diseases caused by viruses include the , , , and . Many serious diseases such as , , , , and are caused by viruses. The relative ability of viruses to cause disease is described in terms of . Other diseases are under investigation to discover if they have a virus as the causative agent, such as the possible connection between and neurological diseases such as and . There is controversy over whether the , previously thought to cause diseases in horses, could be responsible for illnesses in humans.
Viruses have different mechanisms by which they produce disease in an organism, which depends largely on the viral species. Mechanisms at the cellular level primarily include cell lysis, the breaking open and subsequent death of the cell. In , if enough cells die, the whole organism will start to suffer the effects. Although viruses cause disruption of healthy , resulting in disease, they may exist relatively harmlessly within an organism. An example would include the ability of the , which causes cold sores, to remain in a dormant state within the human body. This is called latency and is a characteristic of the herpes viruses, including EpsteinâBarr virus, which causes glandular fever, and , which causes chickenpox and . Most people have been infected with at least one of these types of herpes virus. These latent viruses might sometimes be beneficial, as the presence of the virus can increase immunity against bacterial pathogens, such as .
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Can Transmitted Through Saliva
What Is The Most Common Way To Get Hepatitis A
The hepatitis A virus is transmitted primarily by the faecal-oral route that is when an uninfected person ingests food or water that has been contaminated with the faeces of an infected person. In families, this may happen though dirty hands when an infected person prepares food for family members.
How Do I Avoid Getting Hepatitis A
Hand hygiene is the gold standard for preventing the spread of hepatitis A. Use soap and water to wash your hands after using the toilet or changing nappies, before and after preparing food and before eating.
A vaccine is available for people at risk of infection, but it is not funded. It is recommended more than one vaccination is needed. For more information please see your family doctor.
Recommended Reading: Non Reactive Test Result For Hepatitis
How To Get Vaccinated Against Hepatitis B
All babies in the UK born on or after 1 August 2017 are given 3 doses of hepatitis B-containing vaccine as part of the NHS routine vaccination schedule.
These doses are given at 8, 12 and 16 weeks of age.
Babies at high risk of developing hepatitis B infection from infected mothers are given extra doses of the hepatitis B vaccine at birth, 4 weeks and 1 year of age.
If you think youâre at risk and need the hepatitis B vaccine, ask your GP to vaccinate you, or visit any sexual health or genitourinary medicine clinic.
If your job places you at risk of hepatitis B infection, itâs your employerâs responsibility to arrange vaccination for you, rather than your GP. Contact your occupational health department.
Hepatitis A And B Vaccines
There are vaccines to protect against hepatitis A and B. The CDC recommends hepatitis A vaccination for all children ages 12 to 23 months and for adults who plan to travel or work in areas with hepatitis A outbreaks or who have other risk factors. People with chronic hepatitis B or C should also get the hepatitis A vaccine if they don’t already have immunity to the disease. The hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for all infants at birth and for adults who have any of the risk factors we discussed earlier. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C.
Also Check: Hiv And Hepatitis B And C Are Incurable Bloodborne Pathogens
How Is Hepatitis A Spread
Hepatitis A
The hepatitis A virus is usually spread by putting something in your mouth that is contaminated with the virus. The virus is found in the stool of people with hepatitis A and is spread when someone’s stool accidentally contaminates food or water. This can happen when an infected person does not adequately wash their hands after using the bathroom then touches other things such as food. When other people eat that food, they can get infected with hepatitis A. Usually the transmission is between people in very close personal contact.
Foods themselves can be contaminated with hepatitis A virus, such as raw oysters harvested from sewage-contaminated water. When people eat food contaminated with hepatitis A virus, they can get infected with the virus.
Hepatitis A is usually spread through:
- household contact with an infected person
- sexual contact with an infected person
- eating or drinking contaminated food or water
- sharing eating utensils that are contaminated
- touching contaminated surfaces and then placing your hands near or in the mouth
Unregulated Tattoos And Body Piercings
Tattoos and body piercings use needles that pierce through your skin. Each piercing brings more opportunities for the needle to come in contact with infected blood. If you get a tattoo or body piercing using the same needle that’s been exposed to infected blood, it puts you at greater risk of contracting hepatitis C.
Read Also: Hepatitis B And Liver Cancer
For Adults And Children
This vaccine schedule involves three doses within 2 months, followed by a booster dose at 1 year.
The initial accelerated doses provide immediate protection from HBV, and the booster dose helps provide long-term protection.
Below is the accelerated vaccination schedule approved for both adults and children:
| Vaccine series | |
|---|---|
| 2 months after the first dose | 1 year after the first dose |
What Causes Hepatitis
There are different types of hepatitis, with different causes:
- Viral hepatitis is the most common type. It is caused by one of several viruses — hepatitis viruses A, B, C, D, and E. In the United States, A, B, and C are the most common.
- Alcoholic hepatitis is caused by heavy alcohol use
- Toxic hepatitis can be caused by certain poisons, chemicals, medicines, or supplements
- Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic type in which your body’s immune system attacks your liver. The cause is not known, but genetics and your environment may play a role.
Read Also: Can Hepatitis C Be Contracted Sexually
How Long Does It Last
Hepatitis A can last from a few weeks to several months.
Hepatitis B can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long condition. More than 90% of unimmunized infants who get infected develop a chronic infection, but 6%10% of older children and adults who get infected develop chronic hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long infection. Most people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop chronic hepatitis C.
Who Should Be Tested
Testing for hepatitis A is not routinely recommended.
CDC recommends hepatitis B testing for:
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household and sexual contacts of people with hepatitis B
- People requiring immunosuppressive therapy
- People with end-stage renal disease
- People with hepatitis C
- People with elevated ALT levels
- Infants born to HBV-infected mothers
CDC recommends hepatitis C testing for:
- All adults aged 18 years and older
- All pregnant women during each pregnancy
- About 24,900 new infections each year
- About 22,600 new infections in 2018
- Estimated 862,000 people living with hepatitis B
- About 50,300 new infections in 2018
- Estimated 2.4 million people living with hepatitis C
Read Also: How Do People Catch Hepatitis B
Indications For Hepatitis B Vaccine
HepB vaccine is a routine childhood vaccination .
HepB vaccine also is indicated for adults who have not been previously vaccinated when any of the following is present:
-
A desire for protection from hepatitis B in people who have not been previously vaccinated
-
A sexually active lifestyle in people who are not in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship
-
Need for evaluation or treatment of a sexually transmitted infection
-
Current or recent use of illicit injection drugs
-
Sex between men
-
Employment in which workers may be exposed to blood or other potentially infectious body fluids
-
Diabetes in people < 60 years and sometimes in those 60 years
-
End-stage renal disease
-
Household contact and/or sexual contact with people who are positive for hepatitis B surface antigen
-
Travel to endemic areas
-
Time spent in correctional facilities or in facilities that provide sexually transmitted infection treatment, HIV testing and treatment, drug abuse treatment and prevention services, services to injection-drug users or men who have sex with men, or care for patients with developmental disabilities or with end-stage renal disease
-
Pregnant women if at risk of infection or severe outcome resulting from infection during pregnancy
The combination HepA and HepB vaccine can be used in people 18 years who have indications for either hepatitis A or hepatitis B vaccine and who have not been previously vaccinated with one of the vaccine components.