Infectious Diseases That Spread Through Saliva
If you’ve ever heard of “mono,” then you know of at least one “kissing disease.” Mononucleosis is probably one of the most well-known infectious diseases among adolescents. While many people know that they can acquire a sexually transmitted disease from intercourse, there are also many infections that can be spread through mere kissing alone.
How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis B
Signs and symptoms can vary, in particular by the age of the individual. Many individuals may not show symptoms . When symptoms develop, they include fever, joint pain, abdominal pain, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, dark urine, clay-coloured bowel movements, or jaundice.
Most infections are asymptomatic or mild. Occasionally, people with serious cases of hepatitis B require hospitalization. A very small proportion of these patients develop a critical form of the disease called “fulminant” hepatitis B. This condition results from a sudden breakdown of liver function.
Good Nutrition And Rest
- All family members should eat a well-balanced diet that includes foods shown in the graphic MyPlate . You can find more information about balanced nutrition on the website ChooseMyPlate.gov .
- All family members should get at least 8 hours of sleep each night.
- Young children who are ill should rest during the day when possible.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Hepatitis Vaccine Last
What Occupations Have Increased Risk Of Hepatitis B
In general, occupational groups with increased risk include:
- Health-care workers repeatedly exposed to blood or blood products or those who are at risk of needlestick injury.
- Pathologists, laboratory personnel, or embalmers.
- Dentists, dental assistants, and dental hygienists.
- Certain staff members of institutions for the developmentally handicapped.
- Staff of institutions where workers may be exposed to aggressive, biting residents.
Travellers to regions with intermediate or high rates of endemic HBV infection may also consider being vaccinated.
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
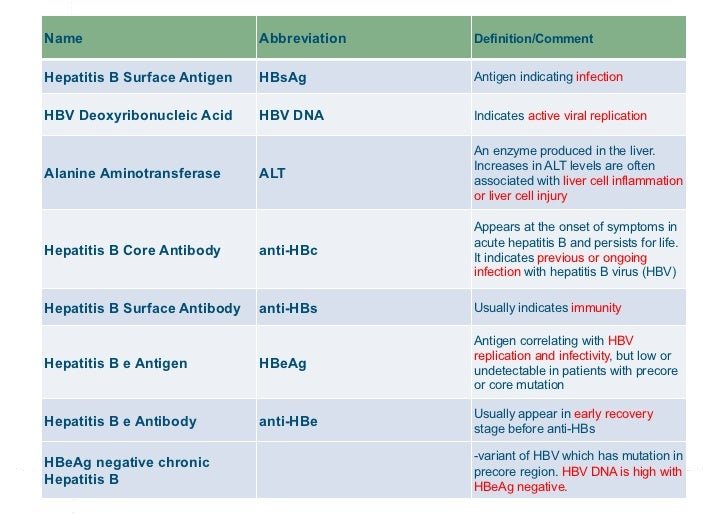
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if you have an active infection. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can transmit the virus to others. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B.
This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the state of a hepatitis B infection.
Read Also: Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis B
Immunohistological Analysis Of Liver Tissue For Hbv Antigens
Immunohistochemical staining was performed on a liver specimen from the mouse with HBV viremia . The hepatocytes were positive for HBsAg and HBcAg . These findings indicated that HBV transmission from tears could be replicated in a human liver chimeric mouse model.
Immunohistological staining for liver tissue with antibodies to hepatitis B virus surface antigen and HBV core antigen . A, HBsAg was expressed on cytoplasmic membrane . B, HBcAg were expressed in nuclei of hepatocytes . Arrows indicate the nuclei of HBcAg-positive staining.
When To Call The Doctor
- The child has not felt hungry or wanted to eat in the past 24 hours.
- Your childs fever is over 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit for more than 2 days.
- Your child has a stomachache.
- Your child vomits more than 2 times in an hour.
- Your child’s skin or the white part of the eyes turns yellow.
- Your child is overly tired for more than 2 days.
You May Like: Can You Die From Hepatitis B
What Laboratory Tests Are Available For Hepatitis B
Tests are available to detect the types of antigens used to identify the hepatitis B virus. The tests determine if the virus is present in the body tissue or blood. The amount of each type of antigen present indicates how advanced the disease is and how infective the individual has become.
Other tests are available to detect the body’s reaction to the viral infection or the body’s reaction to vaccination against the virus. These tests work by measuring the number of antibodies present in the blood.
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious liver disease. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus . Infections of hepatitis B occur only if the virus is able to enter the blood stream and reach the liver. Once in the liver, the virus reproduces and releases large numbers of new viruses into the bloodstream.
To combat the disease, the body has several defenses. White blood cells, which protect the body from infections, attack and destroy the infected liver cells. The body also produces antibodies which circulate in the blood to destroy the virus and protect against future infections of hepatitis B. During the infection and recovery process, the liver may not function normally causing illness that affects the entire body.
For reasons that are not completely understood, 10 percent of people who develop hepatitis B become carriers of the disease. Their blood remains infected for months, years, sometimes for life. Seventy percent of carriers develop chronic persistent hepatitis B. Most do not appear to be ill. The remaining 30 percent of carriers experience continuous liver disease. This condition often progresses to cirrhosis and then, after 30 to 40 years, possibly to liver cancer. At present, there is no way of curing carriers. The risk of becoming a chronic carrier is related inversely with a person’s age when infected. For example, the risk of an infant becoming a carrier is 90-95% whereas the risk of an adult becoming a carrier is 3-10%.
Read Also: How Contagious Is Hepatitis A
Groups At High Risk Of Hep B Transmission
Hep B can only be passed on through blood-to-blood contact, unprotected sex or during birth so you might be at risk of having hep B if you:
- have moved to Australia from a country where hep C is widespread
- were born to a mother who was hep B positive during her pregnancy
- live or have lived with someone with hep B
- have or have had a sexual partner who has hep B
- have ever injected drugs or steroids
- are in prison or have ever been in prison
- have had blood transfusions, blood products or organ transplant in Australia before February 1990
- are of Aboriginal ancestry
- have had unsterile cosmetic or medical procedures.
- have had unsterile tattooing or piercing
- have ever taken part in unsterile traditional practices such as traditional tattooing, circumcision, initiation rituals involving blood, and scarification
- do not meet the above profiles but have abnormal liver function tests or experience hep B symptoms
The Types Of Viral Hepatitis
There are five main types of viral hepatitis known as hepatitis A , hepatitis B , hepatitis C , hepatitis D , and hepatitis E . That said, there have been cases of acute hepatitis that could not be attributed to one of these five types of hepatitis viruses, alcohol, drugs, or autoimmune disease, which lead researchers to try to find another cause.
Though the etiology of these viruses have not yet been fully established, researchers have identified three other types of viral hepatitis , which they have named hepatitis F , hepatitis G , and transfusions transmitted virus . As relatively new diseases and viral discoveries, information about them and how they work is relatively scarce. We do know, however, that cases of TTV have only been associated with hepatitis in people who have had a blood transfusion.
Don’t Miss: Nofx The Hepatitis Bathtub And Other Stories Audiobook
Kissing And Risk Of Hepatitis: Should You Be Worried
Angela Underwood’s extensive local, state, and federal healthcare and environmental news coverage includes 911 first-responder compensation policy to the Ciba-Geigy water contamination case in Toms River, NJ. Her additional health-related coverage includes death and dying, skin care, and autism spectrum disorder.
It’s been said that when you kiss someone, you kiss everyone that person has kissed before. I’ll leave it to doctors to debate the truth of that claim, but a point worth noting is that sometimes kissing can be very intimate and, unfortunately, an opportunity to spread infection. Is viral hepatitis one of those infections?
How Can I Catch Hbv
Hepatitis B virus is transmitted between people by contact with the blood or other body fluids of an infected person. In Africa the virus is mainly transmitted early in life, from mother-to-child or between children. HBV is spread through a break in the skin , or through sexual intercourse. HBV is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV. Unlike HIV, HBV can survive outside the body for at least 7 days. During that time, the virus can still cause infection if it enters the body of a person who is not infected.
Unless vaccinated at the time of birth, these babies can become chronic carriers, which means they are infected with the virus for life. Of children who become infected with the virus between one and five years of age, 30-50 percent become carriers.
In many developed countries , patterns of transmission are different than those mentioned above. Today, the majority of infections in these countries are transmitted during young adulthood by sexual activity and injecting drug use. HBV is a major infectious occupational hazard of health workers.
HBV is not spread by contaminated food or water, and cannot be spread casually in the workplace.
The virus incubation period is 90 days on average, but can vary from about 30 to 180 days. HBV may be detected 30 to 60 days after infection and persist for widely variable periods of time.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Non Reactive Test Result
Where Is The Hepatitis B Virus Found And How Is It Transmitted
Blood is the major source of the hepatitis B virus in the workplace. It can also be found in other tissues and body fluids, but in much lower concentrations. The risk of transmission varies according to the specific source. The virus can survive outside the body for at least 7 days and still be able to cause infection.
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B
Prevention is recommended by receiving a vaccine for HBV.
Receiving an injection of the hepatitis B immune globulin within 12 hours of coming in contact with the virus may help prevent the development of the disease.
At present, there is no specific treatment for patients with acute hepatitis B. Acute infection is usually short and will often resolve on its own. Your health care provider may recommend rest, and adequate nutrition and fluids to help your body fight the infection. Hospitalization may be required for patients who suffer from severe vomiting and who are unable to maintain adequate nutritional levels. It may also be required to prevent the development of complications.
While chronic infection cannot be cured, there are two standard treatments in Canada that may control the virus and prevent further damage to the liver.
- Antiviral medications can fight the virus and slow damage to the liver.
- Interferon which may be given for short periods and if effective, results in suppression of the virus.
Don’t Miss: Foods To Eat When You Have Hepatitis
Who Is Most At Risk For Chronic Disease
The likelihood that an HBV infection will become chronic depends upon the age at which a person becomes infected, with young children who become infected with HBV being the most likely to develop chronic infections.
About 90% of infants infected during the first year of life develop chronic infections 30% to 50% of children infected between one to four years of age develop chronic infections. About 25% of adults who become chronically infected during childhood die from HBV-related liver cancer or cirrhosis. About 90% of healthy adults who are infected with HBV will recover and be completely rid of the virus within six months.
How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Most people who contract hepatitis B during adulthood fully recover within 1 to 3 months.
People with chronic hepatitis B may have a higher risk of developing long-term liver problems, like cirrhosis or liver cancer, which require treatment and may be life threatening.
Keep in mind that the risk of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for babies and children, especially if they have not been vaccinated against the virus.
Also Check: Why Does Hepatitis Cause Joint Pain
Key Facts About Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis B is a viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic liver disease, including cancer.
- The virus is transmitted through contact with the blood or other body fluids of an infected person.
- About 2 billion people worldwide have been infected with the virus and about 370 million live with chronic infection and liver damage.
- Two thirds of those infected with HBV are unaware of their infection
- An estimated 800 000 people die each year due to HBV induced liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Despite there being a vaccine, globally HBV kills one person every minute
- About 25% of adults who become chronically infected during childhood later die from liver cancer or cirrhosis caused by the chronic infection.
- The hepatitis B virus is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV.
- Hepatitis B is preventable with a safe and effective vaccine.
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
Hepatitis B can be transmitted from a birthing parent to a newborn infant. This is because the newborn is exposed to blood and bodily fluids during delivery.
In fact, 90% of mothers with an acute hepatitis B infection and 10% to 20% of mothers with chronic hepatitis B will transmit the virus to their newborn, estimates the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
For this reason, birthing parents are routinely screened for hepatitis B during each pregnancy.
Additionally, the hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin are both administered to infants with an HBV-positive birthing parent within of birth to prevent infection.
According to the
- people with hepatitis C infection
- men who have sex with men
- people with multiple sexual partners
- people who are seeking treatment for a sexually transmitted infections
- people with current or recent injection drug use
- family members or sexual partners of those with hepatitis B
- people with chronic liver disease
- people traveling to areas with high rates of hepatitis B
- people on maintenance dialysis
- people who are incarcerated
The hepatitis B vaccine is usually administered in three shots, given 1 month and 6 months after the first dose. Another recently approved vaccine is completed in two doses spaced 1 month apart.
Also Check: How To Get Checked For Hepatitis
Hepatitis A: What Happens
Hepatitis A is highly contagious and can spread from person to person in many different settings. It typically causes only a mild illness, and many people who are infected may never realize they’re sick at all. The virus almost always goes away on its own and does not cause long-term liver damage.
Is Hepatitis B Contagious

Hepatitis B is highly contagious. Its transmitted through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not transmitted through sharing utensils or kissing. Its also not transmitted through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure. Symptoms can last for several weeks.
But even without symptoms, you can still transmit the infection to others. The virus can live outside the body and remains infectious for at least
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious condition. Its associated with many serious complications, some of which can be life threatening.
But there are many treatment options available and multiple ways you can prevent infection, including getting vaccinated.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a doctor to prevent infection and determine the best course of treatment for you.
Also Check: How To Prevent Hepatitis A
Hepatitis C: What Happens
About 25% of people who get hepatitis C defeat the virus after a short-term infection. The rest will carry the virus in their body for the long term. Chronic hepatitis C can cause very serious complications, including liver failure and liver cancer. There are effective treatments for the virus, though.
Why It’s Important To Get Tested
Because hepatitis C is a highly infectious virus, the CDC recommends that adults 18 years or older get tested for hepatitis C at least once in their lifetime. This is also true for pregnant people during each pregnancy.
To test whether you have a hepatitis C infection, your healthcare provider will perform a hepatitis C antibody test to determine whether you have antibodies that were created in response to the infection.
If your test is positive, your healthcare provider will also perform a hepatitis C RNA test, which accurately determines whether you have a current infection.
Once it is determined you have an HCV infection, your healthcare provider will recommend the best course of treatment. For most people, treatment with antiviral drugs will be started. There are effective treatments that can cure HCV and prevent liver damage.
Read Also: How Do You Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis A: How Does It Spread
It usually spreads through food or water. Food can be tainted when it’s touched by a person with hepatitis who did not wash their hands after using the bathroom. This transfers tiny amounts of infected stool to the food. Raw shellfish, fruits, vegetables, and undercooked foods are common culprits in hepatitis A outbreaks. The virus can also spread in daycare centers if employees aren’t careful about washing hands after changing diapers.
Infectious Diseases From Mouth Sores
Certain infections causing ulcerations in the mouth can also be spread through kissing. These include cold sores and hand, foot, and mouth disease.
Cold sores are caused by the herpes virus, usually herpes simplex virus-1 . While related, this is different from herpes simplex virus-2 , which is more generally associated with genital herpes.
In contrast to infections spread through the saliva, HSV-1 is spread through open cold sores on the lips or near the mouth. Although the infection is contagious through all stages of a cold sore, the infection is most contagious when the sore is open and leaking fluid.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease, caused by the Coxsackievirus, is another infectious disease that is spread through open sores in the mouth. This is a type of enterovirus, which is a common infection that has multiple strains that we all often are exposed to. This particular infection is common in kids, especially those in daycare or preschool settings.
It spreads by breathing the air after the sick person coughs or sneezes, touching or close contact such as kissing or sharing utensils and cups, through touching a sick person’s feces such as when changing a diaper, or from touching the eyes, nose, or mouth after contact with surfaces that have been contaminated such as doorknobs or toys.
In contrast to cold sores and coxsackievirus blisters, canker sores have no infectious disease origin and cannot be spread through saliva or kissing.
You May Like: How To Prevent Hepatitis C