Reduce Your Chance Of Infection
You can reduce your chance of hepatitis B infection by
- not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- wearing gloves if you have to touch another persons blood or open sores
- making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools
- not sharing personal items, such as toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- using a latex or polyurethane condom during sex
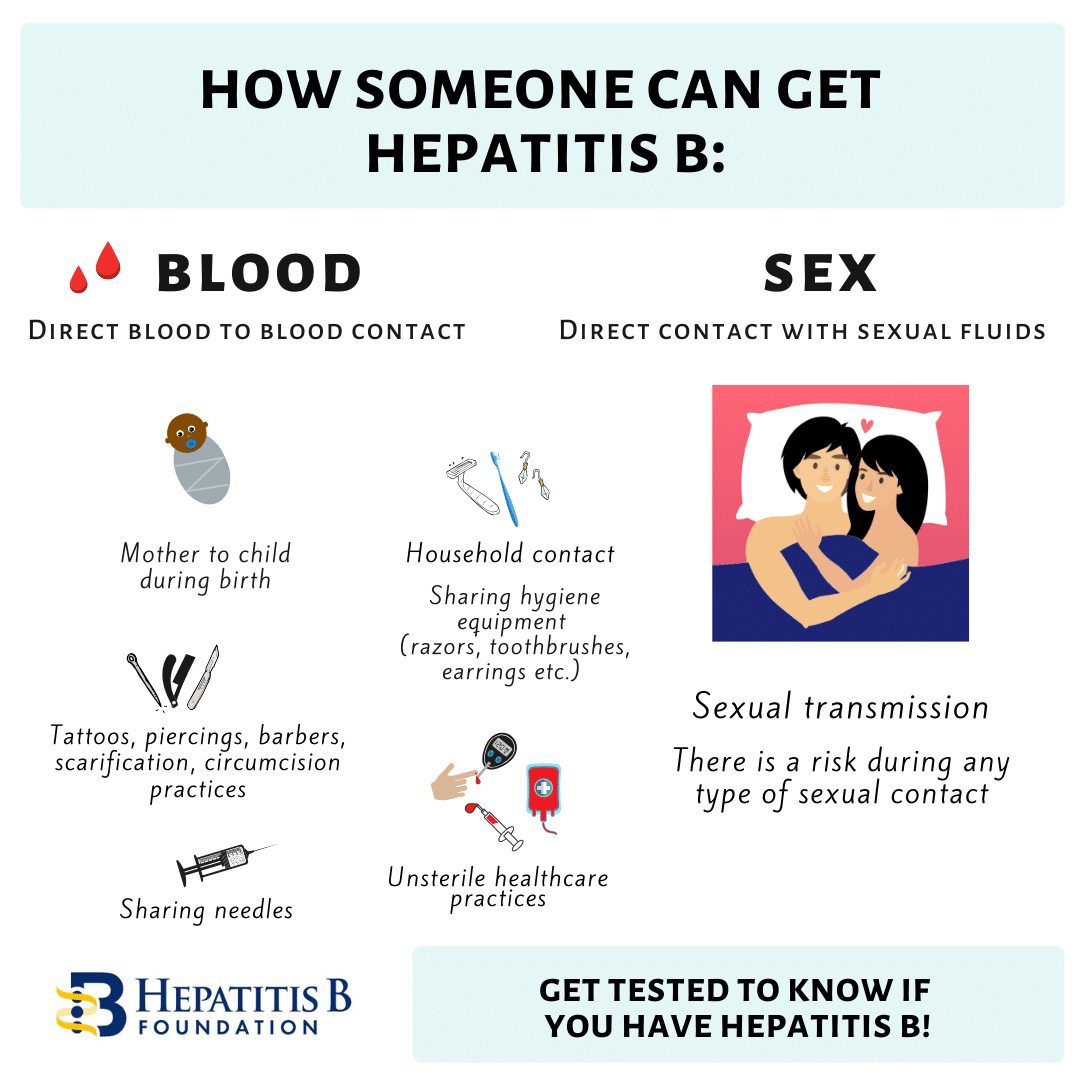
How Can I Contract Hepatitis B
You can contract hepatitis B by coming into contact with the bodily fluids of an infected person.
Resort activities that may put you at risk for hepatitis B include:
Getting a manicure, pedicure, tattoo, piercing, or acupuncture with improperly sterilized tools
Having sexual contact with an infected partner
Giving first aid to, or receiving it from, an infected person
Receiving a medical or dental procedure with contaminated equipment
Sharing personal grooming items with an infected person
How Can I Pay For My Medication
Private health insurance or drug plansIf you have private health insurance or a drug plan at work, you may be able to have the medication paid through your plan. Please consult your private health insurance or drug plan provider to see if your drug is covered.
Publicly funded drug plansEach province and territory has their own rules. Some provincial drug plans provide coverage for individuals 65 and older, or those on social assistance. Some provinces provide special support to low-income individuals. Please call your Provincial Ministry or Department of Health to get more information about the terms of the publicly funded drug plan in your province.
Quebec public drug programIn Quebec, everyone must be covered by prescription drug insurance either through private or publicly funded plans.
Each provincial and territorial government offers a drug benefit plan for eligible groups. Some are income-based universal programs. Most have specific programs for population groups that may require more enhanced coverage for high drug costs. These groups include seniors, recipients of social assistance, and individuals with diseases or conditions that are associated with high drug costs. For more details, please contact your provincial or territorial health care ministry, or click on the appropriate link below.
Yukon
Available Patient Assistance Program for Hepatitis B treatment VEMLIDY
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B Surface Ab
How Many People Have Hepatitis B
In the United States, an estimated 880,000 to 1.89 million people are chronically infected with HBV. New cases of HBV infection in the United States had been decreasing until 2012. Since that time, reported cases of acute hepatitis B have been fluctuating around 3,000 cases per year. In 2020, 2,157 cases of acute hepatitis B were reported however, because of low case detection and reporting, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that there were 14,000 acute hepatitis B infections. The rate of acute cases of HBV decreased by 32% after 2019 which may be related to the disruptions of the COVID-19 pandemic. For the most recent surveillance data visit CDC Viral Hepatitis Surveillance.
Globally, HBV is the most common blood-borne infection with an estimated 296 million people infected according to the World Health Organization .
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis B

People are more likely to get hepatitis B if they are born to a mother who has hepatitis B. The virus can spread from mother to child during birth. For this reason, people are more likely to have hepatitis B if they
- were born in a part of the world where 2 percent or more of the population has hepatitis B infection
- were born in the United States, didnt receive the hepatitis B vaccine as an infant, and have parents who were born in an area where 8 percent or more of the population had hepatitis B infection
People are also more likely to have hepatitis B if they
- are infected with HIV, because hepatitis B and HIV spread in similar ways
- have lived with or had sex with someone who has hepatitis B
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have sex with men
- are injection drug users
- work in a profession, such as health care, in which they have contact with blood, needles, or body fluids at work
- live or work in a care facility for people with developmental disabilities
- have been on kidney dialysis
- live or work in a prison
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before the mid-1980s
In the United States, hepatitis B spreads among adults mainly through contact with infected blood through the skin, such as during injection drug use, and through sexual contact.12
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis Contracted And Prevented
What Are My Next Steps Once I Get My Results
It can be difficult to understand what the results of your test mean. A healthcare provider can help you interpret your results and decide whether you need to take further action:
- If your results suggest that youre already immune to hepatitis B and arent contagious, you likely wont need to do anything.
- If your results suggest that youre not immune, a doctor may recommend vaccination, especially if youre somebody whos at a high risk of infection.
You may also need additional testing if more information is needed to interpret your results.
Check If You Have Hepatitis B
Symptoms of hepatitis B infection include:
- a high temperature
- pain in your upper tummy
- feeling sick or being sick
- patches of raised skin that may be itchy
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes
The infection usually lasts for 1 to 3 months and most people either have no symptoms or mild symptoms. If the infection lasts longer than 6 months it is called chronic hepatitis B.
Also Check: Hiv And Hepatitis Both Have What Symptoms
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis B
Doctors typically dont treat hepatitis B unless it becomes chronic. Doctors may treat chronic hepatitis B with antiviral medicines that attack the virus.
Not everyone with chronic hepatitis B needs treatment. If blood tests show that hepatitis B could be damaging a persons liver, a doctor may prescribe antiviral medicines to lower the chances of liver damage and complications.
Medicines that you take by mouth include
A medicine that doctors can give as a shot is peginterferon alfa-2a .
The length of treatment varies. Hepatitis B medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Tell your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, you also should talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Who Is Most Affected
In the United States, rates of new HBV infections are highest among adults aged 30-59 years, reflecting low hepatitis B vaccination coverage among adults at risk. The most common risk factor among people with new HBV infections is injecting drugs, related to the opioid crisis and other drug use.
The highest rates of chronic hepatitis B infection in the United States occur among foreign-born individuals, especially people born in Asia, the Pacific Islands, and Africa. Approximately 70% of cases in the United States are among people who were born outside of the United States. CDC developed this map of the geographic distribution of hepatitis B around the world – PDF. Other groups who have higher rates of chronic HBV infection include people who inject drugs and men who have sex with men.
Also Check: How To Treat Hepatitis C
How Long Does It Last
According to the World Health Organization , the complete vaccine series induces protective antibody levels in of the infants, children, and adolescents who receive it.
Immune memory induced by the HBV vaccine can last for in healthy people. That said, studies into the duration of the protection that the vaccine offers are ongoing.
Prevent Hepatitis B Infections In Newborns
If you are pregnant and have hepatitis B, talk with your doctor about lowering the risk that the infection will spread to your baby. Your doctor will check your virus levels during pregnancy. If virus levels are high, your doctor may recommend treatment during pregnancy to lower virus levels and reduce the chance that hepatitis B will spread to your baby. Your doctor may refer you to a liver specialist to find out if you need hepatitis B treatment and to check for liver damage.
When it is time to give birth, tell the doctor and staff who deliver your baby that you have hepatitis B. A health care professional should give your baby the hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG right after birth. The vaccine and HBIG will greatly reduce the chance of your baby getting the infection.
You May Like: Hepatic Metastasis From Colorectal Cancer
How Can You Prevent Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B: Vaccination is the best way to prevent all the ways that hepatitis B is transmitted. People with HIV who do not have active HBV infection should be vaccinated against it. The hepatitis B vaccine is now recommended for all infants, children and adults ages 19-59, as well as adults ages 60+ at high risk for infection. There is a 3-dose series of hepatitis B vaccine given over 6 months, and a 2-dose series given over 1 month. Additionally, there is a 2-dose combination vaccine that protects against both hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C: No vaccine exists for HCV and no effective pre- or post-exposure prophylaxis is available. Injection drug use is one of the risk factors for hepatitis C. For people who inject drugs, the best way to prevent hepatitis C infection is to always use new, sterile needles or syringes, and never reuse or share needles or syringes, water, or other drug preparation equipment. Community-based prevention programs, such as medication-assisted treatment and syringe services programs provide support and services aimed at preventing and reducing the transmission of HCV. Although the risk of sexual transmission of HCV is considered to be low, avoiding unprotected sexual exposure by using condoms has been shown to reduce the chance of sexually transmitted infections.
How Is It Treated
Acute hepatitis B: There are no drugs to treat acutehepatitis B. Doctors usually suggest rest, goodnutrition, and fluids. Some people may need to be inthe hospital.
Chronic hepatitis B: People with chronic hepatitis Bvirus infection should receive care from a provider whohas experience treating hepatitis B. These providerscan be:
- Some internists or family medicine providers
- Infection specialists
- Gastroenterologists
If you have chronic hepatitis B, get checked regularlyfor signs of liver disease. Discuss treatment with yourhealth care provider. Not every person with chronichepatitis B needs treatment. If you show no signs ofliver damage, your provider will continue to check youfor liver disease.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Antigens And Antibodies
If I Have Hepatitis B And Feel Healthy Do I Need To Keep Going To My Doctor
Chronic hepatitis B is a silent disease because often no symptoms appear until your liver is severely damaged. Although many people with chronic hepatitis B have an inactive disease and will remain healthy, about one in four will have an active disease that may lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer.
Because hepatitis B has no symptoms until your liver is badly damaged, a blood test is the only way for your doctor to find out if your hepatitis B is active or inactive, and to offer treatment, if needed. To help your doctor monitor how your disease behaves over time, you will need lifelong repeat blood tests every six to 12 months. Some tests, such as HBV DNA may need to be done more frequently . No treatment is required while the virus is inactive, but you should continue to get regular blood tests from your doctor to monitor your liver disease.
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B
Prevention is recommended by receiving a vaccine for HBV.
Receiving an injection of the hepatitis B immune globulin within 12 hours of coming in contact with the virus may help prevent the development of the disease.
At present, there is no specific treatment for patients with acute hepatitis B. Acute infection is usually short and will often resolve on its own. Your health care provider may recommend rest, and adequate nutrition and fluids to help your body fight the infection. Hospitalization may be required for patients who suffer from severe vomiting and who are unable to maintain adequate nutritional levels. It may also be required to prevent the development of complications.
While chronic infection cannot be cured, there are two standard treatments in Canada that may control the virus and prevent further damage to the liver.
- Antiviral medications can fight the virus and slow damage to the liver.
- Interferon which may be given for short periods and if effective, results in suppression of the virus.
Also Check: How Do I Get Hepatitis B
What Is Involved In A Liver Transplant
A liver transplant is considered necessary when the liver is damaged and cannot function or in some cases of liver cancer. Your liver is very important. It is responsible for many functions related to making sure that your body stays healthy and is able to digest foods.
You may be eligible for a transplant if you have chronic hepatitis B infection or some of the diseases that may result from it, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. You will have to complete testing and be evaluated before being approved for a transplant. It is likely that you will be placed on a waiting list while an appropriate organ is found.
Donated livers come from two types of donors: living and deceased. Because the liver can regenerate, it is possible to use part of a liver for transplant. The remaining sections in both the donor and the receiver will grow into livers of adequate size.
People who get liver transplants must take anti-rejection drugs for the rest of their lives. These drugs make you more susceptible to infection. However, liver transplants have become more successful over time and continue to improve.
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis B
There are two types of hepatitis B infection: acute and chronic.
Acute
An acute infection happens at the beginning, when you first get infected with hepatitis B. Many people are able to clear it from their bodies and recover. In fact, this is true of about 4 in 5 adults who are infected.
Chronic
If you are not able to clear the infection within six months or longer, you have chronic hepatitis B. It is chronic hepatitis B that leads to inflammation and the serious, and possibly fatal, illnesses of cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer. Treatment can slow disease progress, reduce the chance of liver cancer and increase your chances of surviving.
Recommended Reading: What Organ Does Hepatitis Affect
How Can I Contract Hepatitis A
You can contract the hepatitis A virus by eating food or drinking beverages that have been contaminated by human fecal waste.
Resort activities that may put you at risk for hepatitis A include:
Eating food handled by an infected worker who did not wash his/her hands properly after using the washroom
Eating raw or undercooked seafood and shellfish that lived in sewage-polluted water
Eating salads or produce rinsed in contaminated water
Drinking contaminated water or drinks with contaminated ice
Bathing, showering, or swimming in contaminated water
How Is Hepatitis B Treated
Your healthcare provider will treat you based on what type of hepatitis B you have, acute or chronic.
Acute hepatitis B infections
If you develop an acute form of the condition, you probably wont need medical treatment. Instead, your doctor will likely suggest that you get plenty of rest, drink lots of fluids and maintain a healthy diet to support your body as it fights off the infection.
Chronic hepatitis B infections
If you have chronic hepatitis B, you might be a candidate for drug therapy. Usually, drug therapy is used only if you have active liver disease. There are seven drugs that are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat hepatitis B. Two are injectable forms of interferon, while the five other antivirals are tablets.
You will need to take these medications every day. They help by slowing the viruss ability to multiply in your system. This helps reduce swelling and liver damage. Youll need to be regularly monitored for early signs of liver damage and liver cancer. Your healthcare provider will want to see you once or twice a year.
Recommended Reading: Where To Get Hepatitis Vaccine
How To Treat Hepatitis B
This article was medically reviewed by Raj Vuppalanchi, MD. Dr. Raj Vuppalanchi is an Academic Hepatologist, a Professor of Medicine at Indiana University School of Medicine, and the Director of Clinical Hepatology at IU Health. With over ten years of experience, Dr. Vuppalanchi runs a clinical practice and provides care to patients with various liver disorders at the University Hospital in Indianapolis. He completed dual fellowships in Clinical Pharmacology and Gastroenterology-Hepatology at Indiana University School of Medicine. Dr. Raj Vuppalanchi is board certified in Internal Medicine and Gastroenterology by the American Board of Internal Medicine and is a member of the American Association for Study of Liver Diseases and the American College of Gastroenterology. His patient-oriented research is dedicated to finding new treatments for various liver disorders as well as the use of diagnostic tests for non-invasive estimation of liver fibrosis and portal hypertension .There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 83% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 116,943 times.
Chronic Hepatitis B Complications
Chronic hepatitis B can lead to
- cirrhosis, a condition in which scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue and prevents your liver from working normally. Scar tissue also partly blocks the flow of blood through the liver. As cirrhosis gets worse, the liver begins to fail.
- liver failure, in which your liver is badly damaged and stops working. Liver failure is also called end-stage liver disease. People with liver failure may require a liver transplant.
- liver cancer. Your doctor may suggest blood tests and an ultrasound or another type of imaging test to check for liver cancer. Finding cancer at an early stage improves the chance of curing the cancer.
Read Also: Natural Cure For Hepatitis B