Why Does Your Risk Of Hepatitis Increase If You Are Hiv Positive
As previously mentioned, people who are HIV positive are highly likely to also be diagnosed with hepatitis, primarily hype C. This is known as a co-infection. While HIV does not cause hepatitis , there is a link through the damage to the liver. HIV suppresses the immune system, making it easier to Hep-C to enter the body and damage the liver.
Another reason why co-infections of HIV and hepatitis are more common is that they are spread through the blood and other bodily fluids. If a person is engaging in high-risk behaviors, such as unprotected sex with a partner who has HIV or hepatitis or sharing needles, the risk of transmission increases.
According to the CDCs latest reports, HIV is most commonly transmitted through male-to-male sexual contact, followed by heterosexual contact and injection drug use.
Treatment Of Hepatitis C
Unlike hepatitis A and B, there is currently no vaccine available for hepatitis C. However, both acute and chronic hepatitis C infections are curable.
Current hepatitis C treatments involve taking two or more medications known as direct-acting antiviral agents . This combination of medications prevents HCV from replicating until the virus is no longer present in the body. Treatment usually takes 824 weeks but can take longer.
However, people who have both HIV and HCV need individualized treatments because the medications used to treat HCV infections can interact with HIV treatments.
A doctor will recommend a treatment plan based on different factors, such as the individuals:
- hepatitis C genotype
Should People With Hiv Get Tested For Hcv
Every person who has HIV should get tested for HCV. Usually, a person will first get an HCV antibody test. This test checks for HCV antibodies in the blood. HCV antibodies are disease-fighting proteins that the body produces in response to HCV infection.
A positive result on an HCV antibody test means that the person has been exposed to HCV at some point in their life. However, a positive antibody test does not necessarily mean the person has HCV. For this reason, a positive result on an HCV antibody test must be confirmed by a second test. This follow-up test checks to see if HCV is present in the personâs blood. A positive result on this test confirms that a person has HCV.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Low
What Are Hiv And Hepatitis
While both HIV and hepatitis are viruses, they affect the body in different ways. HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus, meaning that it primarily targets the immune system. The body naturally tries to fight off the virus, but the healthy cells can be easily overtaken by HIV. This eventually suppresses the immune system, leaving the body extremely vulnerable to more serious illnesses, such as heart disease, pneumonia, and cancer.
Hepatitis is a virus that attacks the liver, limiting its ability to filter the blood and fight off infections. There are three types of hepatitis infections and they are differentiated by the letters A, B, and C.
Hepatitis A is primarily spread through contact with stool and is often contracted due to poor hygiene. For instance, if someone does not wash their hands after using the restroom and then handles food, they could spread hep-A to another. The body can eventually fight off Hep-A and most people experience symptoms for 2 to 6 weeks.
Hepatitis B is spread through blood and can damage both the liver and immune system if it is not treated. Hep-B can be tricky to spot, as not everyone experiences symptoms after contracting the virus. When caught early enough, people can recover completely from Hep-B with the proper treatment. However, it can become a chronic condition if not treated.
Is It Safe For Children With Hiv To Receive Routine Immunizations
-
MMR, or measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine, is safe to give to children with HIV, unless they have a severely weakened immune system.
-
DTaP/Td vaccine is safe to give to infants and children with HIV.
-
Hib and Hep B vaccines are safe to give to children with HIV.
-
Hepatitis A and B vaccines are safe to give to HIV-positive children.
-
VZIG should be considered for known HIV-positive children, depending on their immune status.
-
A yearly influenza vaccine is recommended for children with HIV, as well as any individual living in the same household as a child with HIV. There are two types of influenza vaccine children and adults with HIV should receive the “shot” form of the vaccine–not the nasal spray form, as it contains a live virus. Pneumococcal vaccine can be safely administered to age-appropriate HIV-infected children.
Always consult with your child’s doctor regarding immunizations for an HIV-infected child.
You May Like: Hepatitis A Virus Ab Positive
Symptoms And Disease Progression
The majority of adults with hepatitis B have no symptoms, and infection is often only diagnosed by routine blood tests and monitoring the health of the liver. Among people living with HIV, routine liver function monitoring sometimes shows elevated liver enzymes, which can be a sign of liver inflammation due to hepatitis B.
Some people develop symptoms soon after hepatitis B infection, known as the acute phase. These can include the following:
- pain in the upper abdomen or belly
- muscle or joint aches
- feeling generally unwell
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes .
A minority of people may develop severe symptoms during acute hepatitis B infection, and in rare cases it can lead to death.
After the acute stage , many people with chronic hepatitis B have few or no symptoms. Others may experience ongoing symptoms including fatigue and feeling unwell. Even if you have no symptoms, you can still pass on hepatitis B to others.
With or without symptoms, chronic hepatitis B infection can lead to serious liver disease over years or decades, including fibrosis, cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Preventing Hepatitis C Infection
Here’s how you can protect yourself against hepatitis C:
- Do not share needles, syringes or any other equipment to inject drugs.
- Use latex gloves for fisting, with a new glove with each partner.
- Do not share pots of lubricant.
- Do not share sex toys, or put a new condom on the sex toy each time you use it.
- Properly used condoms provide excellent protection against the transmission of HIV, hepatitis C and other sexually transmitted infections.
- A caesarean delivery can reduce the risk of mother-to-child transmission of the virus.
Theres no vaccine for hepatitis C. Unlike hepatitis A and B, having hepatitis C once doesnt mean youre then immune from getting it again. Its possible to be reinfected with the hepatitis C virus.
You May Like: Does Hepatitis C Cause Itching
Hiv Treatment And Prevention
Simple, effective treatments for HIV are widely available in Australia. In addition to protecting the health and wellbeing of people living with HIV, these treatments significantly reduce the risk of HIV transmission. Almost all people on HIV treatments have very low levels of virus in their body. This is called having an undetectable viral load. There is no risk of HIV transmission from a person with an undetectable viral load. This is sometimes referred to as undetectable equals untransmissible, or U=U.
For people who do not have HIV, but may be at higher risk of it, affordable medication is available that is more than 99 per cent effective at preventing HIV. Known as PrEP , this medication is available through the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme from your regular GP.
Hiv And Hcv Treatment
Your doctor will consider your HIV and HCV treatment together if you have both viruses. Your doctor will choose an antiretroviral therapy that does not interfere with HCV treatment.
There are a few ways you can get tested for HIV and HCV:
- talk with a doctor
- visit a local clinic in your community that offers testing
- find a testing location online, like from the CDC
The CDC hopes to diagnose all HCV infections by recommending that the following people get tested:
- people with HIV
- adults ages 18 and over
- pregnant people
- people who use injectable drugs
You will need to work with a doctor if your test results are positive for HIV or HCV. This may include a primary care doctor or a specialist. You may add other professionals to your healthcare team as you navigate the treatment process for HIV and HCV.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Antibody Test Non Reactive
Protecting Against Hiv And Hepatitis Off The Field
It is important to practise safer sex when off the field by using condoms and water or silicone-based lubricant to protect yourself from HIV, hepatitis B and other sexually transmissible infections.
People who inject steroids or other performance enhancing drugs are at risk of HIV, and both hepatitis B and C, if they share needles, syringes or any injecting equipment such as swabs or tourniquets. Injecting equipment should be used once only and never shared.
How Can I Prevent Getting Hepatitis C
There are no vaccines available for hepatitis C. However, to reduce the risk of contracting hepatitis C, its a good idea to:
- Always change condoms between different partners
- Avoid sharing sex toys and use condoms over toys
- Sterilise sex toys completely with disinfectant and rinse in boiling water between sessions
- Wash your hands and sex toys during sex and between partners
- Always use new injecting equipment and avoid sharing injecting equipment
- Always wash your hands before and after injecting
- Avoid sharing personal items such as toothbrushes, razors and nail scissors & clippers
- Make sure body artists use new and sterile equipment for tattooing, body piercing and other body art, and ensure they work at premises registered by the local council
For more information contact NSW Sexual Health Infolink on 1800 451 624 www.shil.nsw.gov.au or visit your local sexual health clinic or doctor.
Read Also: Liver Cancer And Hepatitis B
What Laboratory Studies Should You Order And What Should You Expect To Find
Results consistent with the diagnosis
Liver enzymes
An initial step in detecting liver damage is to determine the presence of liver enzymes in the blood. Under normal circumstances, these enzymes reside within the cells of the liver. But when the liver is injured, they spill into the blood stream. Among the most sensitive and widely used of these liver enzymes are the aminotransferases. They include aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase . The ACTG grading of liver enzyme elevations is listed in Table I.
The prevailing pattern of lab abnormalities allows to further differentiate different causes of liver disease. Acute cytolytic damage is characterized by high ALT or ALT/Alkaline phosphatase greater than 5, whereas acute cholestatic damage shows high AP or ALT/AP less than 2. A mixed pattern shows high ALT and AP or ALT/AP between 2 and 5.
Bilirubin
Bilirubin is measured to diagnose and/or monitor liver diseases such as cirrhosis, hepatitis, or cholestasis due to gallstones. Bilirubin which is bound to glucuronide to form conjugated bilirubin is called direct bilirubin. Unbound bilirubin is also referred to as indirect bilirubin. Jaundice may be noticeable in the sclera of the eyes at levels of about 2 to 3 mg/dL and in the skin at higher levels. Increased total or unconjugated bilirubin may be a result of hemolytic anemias.
Alkaline phosphatase
International normalized ratio
Albumin
Results that confirm the diagnosis
Viral hepatitis testing
Hepatitis A
Hiv And Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Coinfection
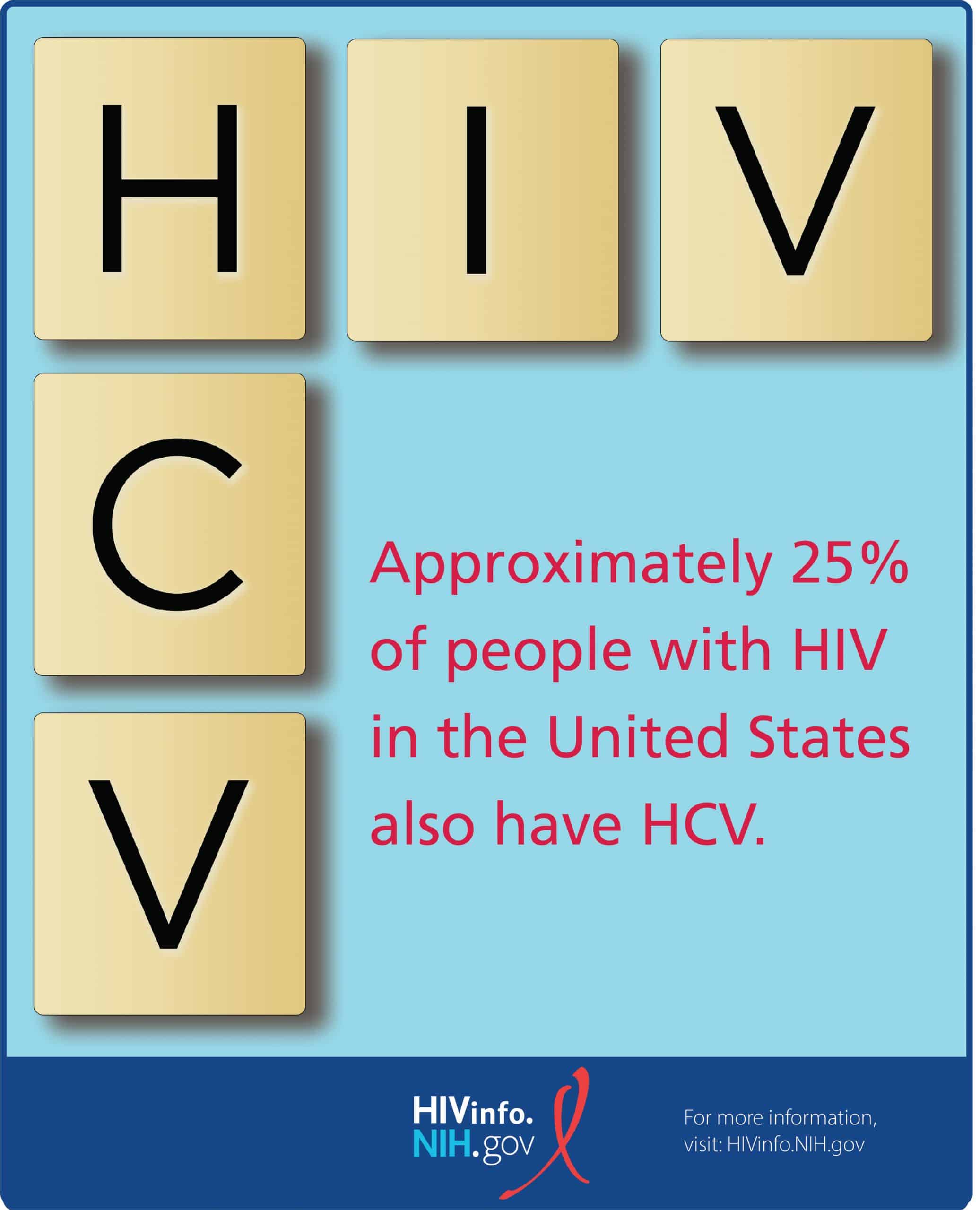
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are liver infections caused by a virus. Because these infections can be spread in the same ways as HIV, people with HIV in the United States are often also affected by chronic viral hepatitis.
Viral hepatitis progresses faster and causes more liver-related health problems among people with HIV than among those who do not have HIV. Liver disease, much of which is related to HBV or HCV, is a major cause of non-AIDS-related deaths among people with HIV.
Given the risks of hepatitis B or hepatitis C coinfection to the health of people living with HIV, it is important to understand these risks, take steps to prevent infection, know your status, and, if necessary, get medical care from someone who is experienced in treating people who are coinfected with HIV and HBV, or HIV and HCV.
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis Cause Low Platelets
Can Hiv/aids Be Prevented
You can reduce the risk of spreading HIV by:
- Getting tested for HIV.
- Choosing less risky sexual behaviors. This includes limiting the number of sexual partners you have and using latex condoms every time you have sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
- Getting tested and treated for sexually transmitted diseases .
- Not injecting drugs.
- Talking to your health care provider about medicines to prevent HIV:
- PrEP is for people who don’t already have HIV but are at very high risk of getting it. PrEP is daily medicine that can reduce this risk.
- PEP is for people who have possibly been exposed to HIV. It is only for emergency situations. PEP must be started within 72 hours after a possible exposure to HIV.
NIH: National Institutes of Health
Know When To Call Your Provider
There isn’t a need to panic every time you have a headache or feel tired. But if a symptom is concerning you or is not going away even if it doesn’t feel like a big deal, it is always best to have your provider check it out. The earlier you see a provider when you have unusual symptoms, the better off you are likely to be. While you are being treated for hepatitis C, call your provider if you experience the following:
- Extreme dizziness or shortness of breath
- Chest discomfort
- Swelling in your legs, feet, or ankles
- Diarrhea for more than 48 hours, or blood in the stool
- Fever or other sign of infection that lasts more than 48 hours
- Extreme fatigue
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule Booster
Is Hepatitis Testing Recommended For People With Hiv
Yes. Everyone living with HIV should be tested for HBV and HCV when they are first diagnosed with HIV and begin treatment. People living with HIV who have ongoing risk factors for getting hepatitis B or hepatitis C should be tested annually.
In addition, new HCV screening recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention call for:
- One-time screening for all adults 18 years and older
- Screening of all pregnant women during every pregnancy
- Testing for all persons with risk factors, with testing continued periodic testing those with ongoing risk.
What Is Chronic Infection With Hepatitis B
Early in the infection, most people will clear the virus without treatment and develop protective immunity. However, in 5-10% of adults hepatitis B continues to reproduce in the body long after infection. These people become chronically infected with hepatitis B, meaning that they continue to be infectious although they may not experience any symptoms at all, or not for many years.
People living with HIV, especially if they have a low CD4 cell count, are less likely to clear the virus naturally than people without HIV.
Without treatment, some people with chronic hepatitis B eventually develop cirrhosis of the liver. About one in 20 people with cirrhosis will go on to develop cancer of the liver.
Recommended Reading: How Long Can A Person Live With Hepatitis C
How Can Infection With Hepatitis B Be Prevented
Hepatitis B can be avoided by:
- using a condom or dental dam during oral sex
- not sharing sex toys
- not sharing drug-taking and injecting equipment.
If you’re living with HIV, do not have hepatitis B, and a test shows that youre not naturally immune against hepatitis B, you should be vaccinated.
People living with HIV can lose their immunity to hepatitis B if their immune system weakens, and should have their level of immunity checked regularly to see whether they need a booster dose of the vaccination.
There is a combined vaccination for hepatitis A and hepatitis B, though it might be less effective than the separate vaccinations for people with a low CD4 count or a detectable viral load. Ask your doctor which would be most suitable for you.
Treating Hepatitis C Together With Hiv
If youre HIV positive and have hepatitis C infection, then you must receive care from a doctor skilled in the treatment of both HIV and hepatitis.
Due to the new direct-acting antiviral drugs, people living with HIV and hepatitis C co-infection can be treated with most of the same hepatitis C drug regimens as HIV-negative people. Research has shown that cure rates are the same.
Unlike treatment for HIV, hepatitis C treatment is not for life. New drugs to treat hepatitis C only need to be taken for up to 3 months.
You May Like: Natural Remedies For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Looking After Your Liver When You Have Hepatitis B
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Stick to a healthy diet.
- If your skin is itchy keep cool, avoid hot showers and baths and wear loose clothes.
- Avoid alcohol and recreational drugs.
- Attend all your medical appointments and check-ups.
Ibuprofen or paracetamol can help with stomach pain in the acute phase. Check with a clinician if you’re unsure whether you should take them.
Stage : Acute Hiv Infection

Within 2 to 4 weeks after infection with HIV, about two-thirds of people will have a flu-like illness. This is the bodys natural response to HIV infection.
Flu-like symptoms can include:
- Swollen lymph nodes
These symptoms can last anywhere from a few days to several weeks. But some people do not have any symptoms at all during this early stage of HIV.
Dont assume you have HIV just because you have any of these symptomsthey can be similar to those caused by other illnesses. But if you think you may have been exposed to HIV, get an HIV test.
Heres what to do:
Also Check: Is There Immunization For Hepatitis C