How Much Does The Test Cost
The cost of hepatitis B testing depends on the tests that are performed, where the test is conducted, and a patientâs health insurance coverage. When testing is ordered by a doctor, patients with health insurance may find it helpful to discuss the cost of testing with their health insurance company as they may be responsible for testing costs as well as other out-of-pocket costs such as copays and deductibles.
For patients without health insurance or for whom insurance doesnât cover the cost of testing, it may be helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis B testing with a doctor or hospital administrator.
The cost of at-home hepatitis B testing starts around $45. At-home test kits may also test for additional types of viral hepatitis in the same sample. The cost of test panels that look for more than one type of viral hepatitis start around $80.
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to HBV, your body mounts an immune defense to specifically target and neutralize the invader. Unlike innate immunity which mounts a generalized defense against all invaders, this type of immunity is disease-specific.
This immune response occurs whether you are exposed to HBV through blood or sexual contact, or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The virus has proteins on its surface, called antigens, that serve as unique identification tags. When HBV enters the body, the immune system “encodes” antibodies specific to these antigens so that it can recognize and attack the virus should it appear again.
There are two types of antibodies produced in response to the virus:
- Immunoglobulin M is the antibody that mounts the initial attack but eventually fades away.
- Immunoglobulin G is the antibody that provides long-lasting immune protection against HBV. The immunity can last for many years, but it gradually wanes over time.
Question 3 How Is The Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test Performed
An immunometric technique is used. The anti-HBs binds to HBsAg ad and ay subtypes, which are coated on the test wells. Binding of a horseradish peroxidase-labeled HBsAg conjugate to the anti-HBs completes the sandwich formation. Unbound materials are then washed away. In the next step, the horseradish peroxidase catalyzes oxidation of a luminogenic substrate, producing light. Light signals are detected and quantified. Intensity of the light is proportional to the amount of anti-HBs present in the patient sample. The result is standardized to an international unit system and reported as milliinternational units per milliliter .
You May Like: Is There A Cure For Hepatitis C Virus
Module 3 Interpretation Of Hbv Diagnostic Test Results
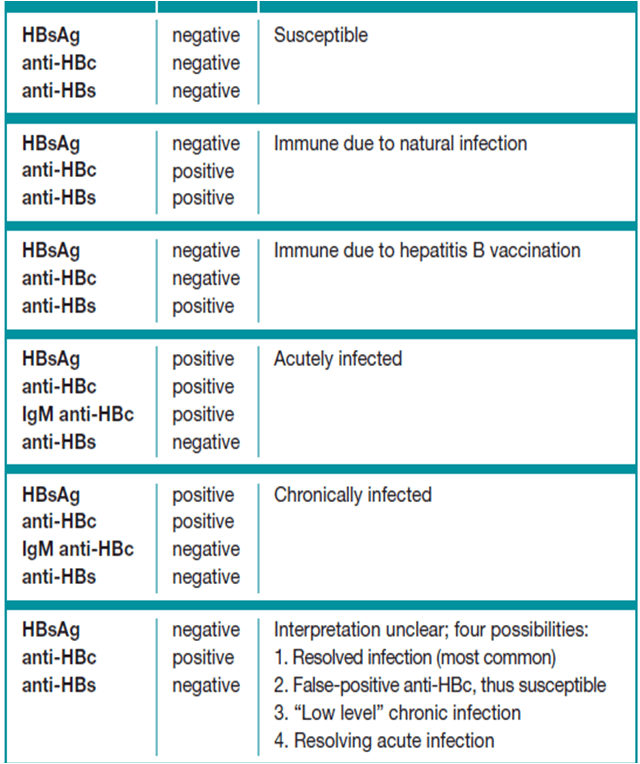
This table describes 6 possible interpretations of diagnostic test results and subsequent recommended actions for clinicians.
In the first scenario of this table, a patient should be considered to be susceptible to hepatitis B when: hepatitis B surface antigen results are negative hepatitis B surface antibody results are negative total hepatitis B core antibody results are negative and the IgM marker of the hepatitis B core antibody is not available/or not done.
Itâs noted that approximately 5 percent to 10 percent of people will not respond to vaccine or else do not produce protective levels of antibody post-vaccination .
The recommended action when a patient is considered to be susceptible to hepatitis B is to vaccinate.
In the second scenario of this table, a patient should be considered to be immune to hepatitis B due to vaccination when: hepatitis B surface antigen results are negative hepatitis B surface antibody results are positive total hepatitis B core antibody results are negative and the IgM marker of the hepatitis B core antibody is not available/or not done. Regarding the hepatitis B surface antibody, clinicians are reminded that about 5 percent to 10 percent of people will not respond to the vaccine or else do not produce a protective level of antibody post-vaccination . Note that in immune individuals, levels of hepatitis B surface antibody may decline over time and become undetectable.
How Much Does A Hepatitis B Titer Test Cost
The cost of a hepatitis B test varies based on where you get the test. Prices range from roughly $24 to $110.
Your insurance may cover some or all of the cost. Under the Affordable Care Act, all new health plans must cover preventative services including hepatitis B vaccination and testing without a deductible or copay.
Recommended Reading: New Treatment For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Can I Take The Test At Home
Samples for hepatitis B testing can be collected at home. At-home hepatitis B testing requires a patient to collect a blood sample, typically from a fingerstick using a very small needle provided in the test kit. Once a blood sample is collected, it is prepared according to the instructions contained in the test kit and mailed to a laboratory for testing.
Because there are numerous types of tests for HBV, it is important to look closely at the specific components of any at-home test kit. Many at-home test kits only look for hepatitis B surface antigen .
Data Analysis And Statistics
All analyses were done using nonparametric statistical software with penalized maximum likelihood to remove first-order bias. A p-value < 0.05 for two-sided tests was considered statistically significant. Continuous variables were expressed as means plus/minus standard deviation or mean , categorical variables as numbers . Conditional logistic regression analysis was used to estimate risk ratios and 95% confidence intervals for loss of anti-HBs putative associated factors included age, sex, type of rheumatic disease, conventional DMARDs, biologic DMARDs , comorbidity, and baseline anti-HBs titer.
Also Check: Why Do You Need Hepatitis B Vaccine
What Are My Next Steps Once I Get My Results
It can be difficult to understand what the results of your test mean. A healthcare provider can help you interpret your results and decide whether you need to take further action:
- If your results suggest that youre already immune to hepatitis B and arent contagious, you likely wont need to do anything.
- If your results suggest that youre not immune, a doctor may recommend vaccination, especially if youre somebody whos at a high risk of infection.
You may also need additional testing if more information is needed to interpret your results.
About The Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus is a small DNA virus that belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family. Related viruses in this family are also found in woodchucks, ground squirrels, tree squirrels, Peking ducks, and herons.
Structure of the Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus contains an outer envelope and an inner core.
- The outer envelope of the virus is composed of a surface protein called the hepatitis B surface antigen or HBsAg. The HBsAg can be detected by a simple blood test and a positive test result indicates a person is infected with the hepatitis B virus.
- The inner core of the virus is a protein shell referred to as the hepatitis B core antigen or HBcAg, which contains the hepatitis B virus DNA and enzymes used in viral replication.
Life Cycle of the Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus has a complex life cycle. The virus enters the host liver cell and is transported into the nucleus of the liver cell. Once inside the nucleus, the viral DNA is transformed into a covalently closed circular DNA , which serves as a template for viral replication . New HBV virus is packaged and leaves the liver cell, with the stable viral cccDNA remaining in the nucleus where it can integrate into the DNA of the host liver cell, as well as continue to create new hepatitis B virus. Although the life cycle is not completely understood, parts of this replicative process are error prone, which accounts for different genotypes or genetic codes of the hepatitis B virus.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Home Test Kit
Hbv Dna Hbv Genotype And Hbv Drug Resistance Assays
Specimen: Serum or plasma
Container: Red-top tube, yellow-top tube , gel-barrier tube, plasma preparation tube, or lavender tube
Collection method: Routine venipuncture
The specimen should be transfused to separate plasma/serum from cells within 6 hours and kept frozen when testing cannot be done promptly.
The tests use PCR amplification, DNA probe hybridization, and sequencing method.
Potent Human Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies To Hepatitis B Virus From Natural Controllers
Disclosures: V. Hehle reported a patent to anti-HBV antibodies and methods of use, pending. M. Beretta reported a patent to anti-HBV antibodies and methods of use, pending. M. Bourgine reported a patent to anti-HBV antibodies and methods of use, pending. M. Ait-Goughoulte reported a patent planned on the antibodies pending, Roche. S. Pol reported personal fees from Gilead, Abbvie, BMS, Janssen, and Roche outside the submitted work. H. Strick-Marchand reported a patent to human neutralizing HBV antibodies and their use thereof, pending. N. Pelletier reported personal fees from Hoffmann-La Roche outside the submitted work in addition, N. Pelletier had a patent planned to be submitted, pending Roche Innovation Center Basel. H. Mouquet reported grants from Institut Roche during the conduct of the study in addition, H. Mouquet had a patent to anti-HBV antibodies and methods of use, pending. No other disclosures were reported.
V. Hehle and M. Beretta contributed equally to this paper.
H. Strick-Marchand and N. Pelletier contributed equally to this paper.
J Exp Med
Also Check: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Normal Range
When Should I Get Hepatitis B Testing
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups that are at an increased risk of infection. Groups that may benefit from hepatitis B screening include:
- Pregnant people
- People born in parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- People who didnât receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- HIV-positive people
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may be used before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that a patient has previously been infected with HBV or has already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people who are at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
For Patients With Chronic Hbv
Reducing the risk of liver damage
- Have liver enzymes monitored every 6-12 months.
- Reduce or eliminate alcohol.
- Stop smoking, as it increases the risk of liver cancer.
- You may drink coffee 3 or more cups per day may reduce the risk of liver cancer.Endnote 21
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A if you are not already immune â talk to your HCP or contact your local public health department.
- Stick to your medication schedule and your regular lab testing and follow-up visits.
- Tell your HCP before starting any immunosuppressive therapy.
About medications for patients with cirrhosis
- Avoid aminoglycosides , benzodiazepines, and narcotics including codeine .
- Whenever possible, avoid ASA or NSAIDs. Acetaminophen, oral contraceptive pills, and statins are safe to use.
- Do not drink alcohol.
- If you require surgery, discuss it with your specialist first.
- If you have black stools, call your specialist immediately or go to the ER.
- Tell your HCP about any complementary/alternative therapies or over the counter supplements including herbal remedies that you are taking.
- Follow your HCPâs advice on how frequently you require abdominal ultrasounds.
Living well with HBV
You May Like: Glomerulonephritis Due To Infectious Hepatitis
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days . Common symptoms include malaise, fever, gastroenteritis, and jaundice . After acute infection, HBV infection becomes chronic in 30% to 90% of infected children younger than 5 years of age and in 5% to 10% of infected individuals age 5 or older. Some of these chronic carriers are asymptomatic, while others progress to chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatitis B surface antigen is the first serologic marker, appearing in the serum 6 to 16 weeks following HBV infection. In acute cases, HBsAg usually disappears 1 to 2 months after the onset of symptoms with the appearance of hepatitis B surface antibody . Anti-HBs also appears as the immune response following hepatitis B vaccination.
Also Check: How Common Is Hepatitis B
Don’t Miss: How Much Are Hepatitis B Shots
Discusses Conditions That May Cause Diagnostic Confusion Including Improper Specimen Collection And Handling Inappropriate Test Selection And Interfering Substances
Individuals who have received blood component therapies , plasma, or intravenous immunoglobulin infusion) in the previous 3 to 6 months may have false-positive hepatitis B surface antibody results due to passive transfer of anti-HBs present in these products.
Individuals possessing IgM anti-rubella virus may have falsely high results with the VITROS Anti-HBs quantitative test.
Anti-HBs levels from past hepatitis B or hepatitis B virus vaccination may fall below detectable levels over time.
A positive anti-HBs result does not exclude infection by another hepatitis virus.
Performance characteristics have not been established for the following specimen characteristics:
-Grossly icteric
Also Check: How To Check For Hepatitis
In Vivo Hbv Suppression By Potent Broadly Neutralizing Antibody Bc1187
To determine whether potent HBV neutralizers from natural controllers can stably suppress HBV viremia in vivo, HBV-carrier mice were treated for 17 d with Bc1.187 antibody . Viremic mice experienced a decrease in circulating HBsAg levels upon treatment with Bc1.187 but not with the isotype control . However, the development of murine anti-human IgG antibodies rapidly altered therapy effectiveness . To overcome or limit ADA production, we generated a chimeric version of Bc1.187 by combining the antibodys variable domains with the murine Ig2a and IgK constant regions. The chimeric Bc1.187 antibody had a serum half-life of 3.9 d in nontransduced wild-type mice , and led to reproducible viremia drops when administrated weekly in HBV-carrier mice . 16 d of treatment with 0.5 mg i.v. injections of c-Bc1.187 every 2 d but not control antibody led to a loss of circulating HBsAg in all mice from day 4 with an average 2.5 log10 fold decrease compared with the set-point . During c-Bc1.187 therapy, serum HBV DNA content was also drastically diminished by an average 2.5 log10 fold and reached the detection limit by day 21 in all but one mouse . HBsAg and HBV viremia were still suppressed for 2 wk after the last antibody injection before rising back to baseline levels . As expected in this model, serum levels of HBe antigen, a surrogate marker for viral replication, remained unchanged during therapy .
Also Check: How Can You Cure Hepatitis B
Whats The Procedure For A Hepatitis B Titer Test
A hepatitis titer test requires a healthcare professional to draw a small amount of blood for testing.
No special preparation is needed beforehand. If needles or the sight of blood make you anxious, you may want to arrange a drive ahead of time in case you feel faint.
Heres what will typically happen during this test:
Home tests that require a fingerpick are also available. The results of your tests are generally available within 3 days.
High Titers Of Hepatitis B Surface Antibodies Indicating Low Risk Of Hepatitis B Virus
Sung-Nan Pei, Ming-Chung Wang, Ming-Chung Ma, Ching-Yuan Kuo, Chien-Hung Chen, Po-Nan Wang High Titers of Hepatitis B Surface Antibodies Indicating Low Risk of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatitis in Lymphoma Patients Treated with Rituximab-Based Chemotherapy. Blood 2015 126 : 3869. doi:
Also Check: Hepatitis B Virus Dna Quantitative
Also Check: Dose For Hepatitis B Vaccine
Question 2 What Is The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
The hepatitis B surface antibody is the antibody that is produced in response to hepatitis B surface antigen , a protein present on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. Anti-HBs appears after convalescence from acute infection and lasts for many years. It can also be produced in response to hepatitis B vaccination.
Other hepatitis B antibodies are not produced in response to vaccination. This is because these antigens are not in the vaccine.
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Blood Test Qualitative
The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Blood Test, Qualitative is useful in the detection of previous exposure to HBV.
Also Known As: Anti-HBs, Antibody to Hepatitis B Surface Antigen, HBsAB, Hepatitis Bs Antibody.
Methodology: Immunochemiluminometric assay
Preparation: No special preparation required.
Test Results: 2-3 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
Also Known As: Anti-HBs, Antibody to Hepatitis B Surface Antigen, HBsAB, Hepatitis Bs Antibody.
Methodology: Immunoassay
Preparation: No special preparation required.
Test Results: 2-3 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
Read Also: Foods To Avoid With Hepatitis