How Is A Person Tested For Hepatitis C
A viral-load test is used to check for hepatitis C in the bloodstream. Usually, hepatitis C virus can be found in a persons bloodstream two weeks after he or she becomes infected.
*Except in case of recent risk or in people with a weakened immune system**During the first six months after HCV infection, a person may spontaneously clear the virus if there was a recent risk, repeat viral-load testing to confirm chronic hepatitis C infection
Chronic Hepatitis B Treatment Goals
When a patient has been diagnosed with chronic hepatitis B, clinical endpoints of therapy include5,17:
- Achieving sustained suppression of HBV replication
- ALT normalization
- Reducing the risk of liver damage
- HBeAg and HBsAg loss with or without seroconversion
AASLD=American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases ALT=alanine aminotransferase CDC=Centers for Disease Control and Prevention HBeAg=hepatitis B envelope antigen HBsAg=hepatitis B surface antigen HCV=hepatitis C virus USPSTF=U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.
aHepatocellular carcinoma may occur in patients with chronic HBV without cirrhosis.4
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
BOXED WARNING: POSTTREATMENT SEVERE ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B
- Discontinuation of anti-hepatitis B therapy, including VEMLIDY, may result in severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B. Hepatic function should be monitored closely with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months in patients who discontinue anti-hepatitis B therapy, including VEMLIDY. If appropriate, resumption of anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted.
Warnings and Precautions
Adverse Reactions
Most common adverse reactions in clinical studies through week 144 were headache, upper respiratory tract infection, abdominal pain, cough, back pain, arthralgia, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, dyspepsia, and pyrexia.
Drug Interactions
Dosage and Administration
INDICATION
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists , the US Preventive Services Task Force , and the World Health Organization recommend routine prenatal screening for hepatitis B surface antigen in all pregnant womenduring every pregnancyregardless of previous test results or vaccinations. Pregnant women at risk for hepatitis B infections should be specifically targeted for vaccination. The risk of transmission of hepatitis B associated with amniocentesis is low. WHO further recommends all pregnant women undergo testing at least once for HIV and syphilis in addition to that for HBsAg and as early as possible in the pregnancy.
It is recommended that all infants receive their first dose of hepatitis B vaccine as soon as possible after birth , followed by two or three doses to complete the primary series.
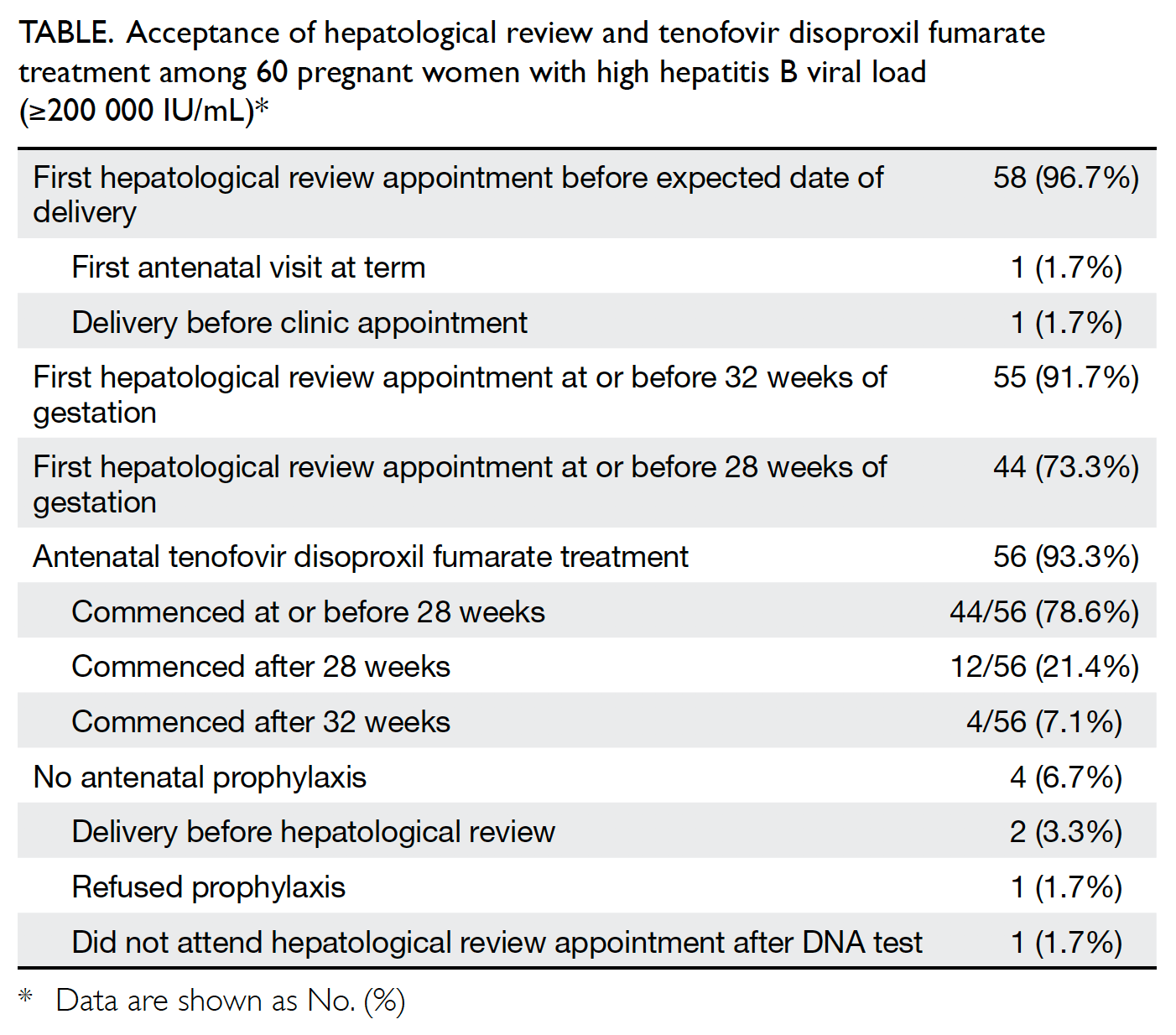
To prevent maternal-fetal HBV transmission, a conditional WHO recommendation is that HBsAg-positive gravida who have an HBV DNA 5.3 log10 IU/mL receive tenofovir prophylaxis beginning the 28th week of pregnancy until at least birth. This is in addition to the three-dose hepatitis B vaccination in all infants, including a timely birth dose. When antenatal HBV DNA testing is not available, HBeAg testing can be used as an alternative study to determine eligibility for tenofovir prophylaxis to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HBV.
Also Check: Does Hepatitis Cause Itchy Skin
Testing And Treatment During Pregnancy
A hepatitis B virus infection should not cause any problems for you or your unborn baby during your pregnancy if you take the correct precautions. It is important for your doctor to be aware of your hepatitis B infection so that he or she can run appropriate tests and evaluate and monitor the health of your liver, and so your baby can be protected from infection with hepatitis B when it is born. The U.S. CDC and WHO recommend that ALL pregnant people are tested for hepatitis B. Please ask your doctor to test you for hepatitis B early in your pregnancy!
The birth dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin can sometimes fail to prevent transmission to newborns. This typically occurs in pregnant people who are HBeAg positive and have a very high viral load, allowing for the transmission of hepatitis B to your baby. Fortunately, there is a way to prevent transmission even if you are a person with a high viral load.
All people who are diagnosed with hepatitis B in pregnancy should be referred for follow up care with a physician skilled at managing hepatitis B infection. Your physician should perform additional laboratory testing, including HBV DNA level , and should be checked to see if there is evidence of cirrhosis . (.
All babies born to people with hepatitis B should receive a birth dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of delivery whether they receive treatment with an antiviral or not.
How Can We Help
Hepatitis C test only require basic blood sample, which can also be collected from help to get the test done and to help you do so is our highly reliable and well established at home healthcare services, wherein you can not only get Hepatitis C home test but, can also get doctors consultation at home. So, you neednt have to worry of getting tested, collecting the hepatitis test reports and then running to a doctors. As we have designed our at home healthcare services keeping the comfort of patients at mind. So, if you need Hepatitis C home test done or hepatitis C treatment at home or any other healthcare services at home just give us a call and we will be there at your service.
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis From Saliva
Recommended Reading: Can You Give Yourself Hepatitis B
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
There are three main ways to diagnose HBV infection. They include:
- Blood tests: Tests of the blood serum shows how your bodys immune system is responding to the virus. A blood test can also tell you if you are immune to HBV.
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to show the size and shape of your liver and how well the blood flows through it.
- Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis.
The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit. Often, people whove become infected first learn they have hepatitis B when they go to donate blood. Blood donations are routinely scanned for the infection.
The virus can be detected within 30 to 60 days of infection. About 70% of adults with hepatitis B develop symptoms, which tend to appear an average of 90 days after initial exposure to the virus.
Screening The Pregnant Patient
The American Congress of Obstetrics and Gynecology recommend that every pregnant patient undergo HBV screening. Levels of HBsAg and surface antibody should be measured at the earliest prenatal visit.28 If the testing shows negativity for both, then an HBV vaccination series should be administered to the high-risk individuals. If the HBsAg testing shows positivity, then the clinician should confirm infection with quantitative measurement of HBV DNA at baseline and at week 28, along with HBeAg status and ALT levels. Individuals who are sexual contacts and household members of the HBsAg-positive pregnant woman should also be screened. The ACOG recommends referral to a specialist immediately if viral load is > 20,000 IU/mL, ALT is > 19 IU/mL or HBeAg is positive.28,29 If these criteria are not met the referral can be post-partum. If the patients viral load > 1 million copies , then consideration of antiviral therapy at week 32 is recommended. If the viral load is < 200,000 IU/mL, antiviral therapy is not recommended unless the pregnant female has active liver disease. All infants require the HBV vaccination series and HBIG within 12 hours of birth. Delays in obtaining passive-active immunoprophylaxis can also lead to viral transmission to the fetus. Fig. 1 summarizes these recommendations.
Suggested management of HBV in pregnant patients.
Adapted from AASLD5, ACOG28 and Pan et al25.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis D And E
Treatment For Antiviral Resistance In Children
The 2015 APASL guidelines recommend that tenofovir or IFN should be used for the treatment of children who develop lamivudine resistance. When adefovir resistance develops, the guidelines recommend that entecavir or tenofovir should be used if the child has no history of NA treatment before receiving adefovir .
How Is Hepatitis B Prevented
Testing & Vaccination
- The hepatitis B vaccine offers excellent protection against HBV. The vaccine is safe and highly effective. Vaccination consists of 3 doses of vaccine over the course of 6 months. Protection lasts for 20 years to life.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all children should receive hepatitis B vaccine starting at birth. .
- The CDC recommends hepatitis B vaccine for persons traveling to countries where HBV is common .
- If you have one or more risk factors for hepatitis B infection, you should get a simple HBV blood test. The blood test will determine whether you are:
- immune to hepatitis B or
- susceptible to hepatitis B and need vaccination or
- infected with hepatitis B and need further evaluation by a physician
Perinatal Hepatitis
- California law requires testing of all pregnant women for hepatitis B infection
- If the mother is HBV-infected, she will pass the infection to the baby during the birth process, unless the baby gets immunized within hours of birth
- Giving the infant HBIG and HBV vaccine right away will reliably prevent infection of the infant
- Other family members should best tested for hepatitis B too, and given vaccine if they are not already infected or immune
Healthy Habits
After Exposure to Hepatitis B
You May Like: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Spit
Baseline Characteristics And Hcc Risk
In casecohort analysis, the risk of HCC was increased starting at the fourth quintile of HBV viral load , as compared with the lowest quintile of viral load. HBeAg positivity, genotype C HBV infection and elevated ALT activity were also associated with increased risk for HCC .
In subcohort analysis, men infected with HBV genotype C had a higher cumulative incidence of HCC than men with B or B plus C mixed genotype infection . The cumulative incidence of HCC within 10 years was 14.49% for genotype C subjects and 2.14% for other genotype subjects. The difference in the cumulative HCC incidences between the two groups was greater if baseline viral load was 4.39 log copies/ml and lesser if baseline viral load was < 4.39 log copies/ml .
KaplanMeier estimates of the cumulative incidences of HCC by HBV genotype. The analysis was based on the subcohort randomly selected from the entire cohort.
Stability Testing Of Viral Load On Dbs
Three patients were selected for storage studies of DBS. All 3 had low to moderate viral load, near the recommended threshold for treatment eligibility. Several DBS cards were prepared from each patient and stored at room temperature over time. At time points 0, 2, 6 and 12 weeks, DNA was extracted from the DBS , as well as a sample control stored at -70°C. The extracts were stored at -70°C for 12 weeks, when all samples were analyzed with an in-house real-time PCR. The PCR was run twice on all samples.
Recommended Reading: Difference Between Hepatitis B And C
What Viral Load Can Tell You About Your Hepatitis B Infection
Hepatitis B is one of the most serious liver infections in the world. Untreated hepatitis B can cause fibrosis, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and end-stage liver disease. Doctors run several blood tests to see if the infection is harming your liver and to identify what stage of infection you are in. Heres why one of those blood tests the HBV DNA matters and what it can tell you about your hepatitis B infection.
Probbability Of Response To Treatment And Appearance Of Resistance
Treatment is indicated if there is a high risk of liver-related mortality and morbility and a high likehood of manteined viral supression after a defined course of therapy. This risk is variable during the course of HBV infection.
There are several treatment strategies for CHB: IFN and PEG-IFN, lamivudine, adefovir dipivoxil, telbivudine and entecavir. None of theses achieves complete HBV eradication and they have limited long-term efficacy. In the majority of patients, particularly those with HBeAg-negative disease, HBV is suppressed but not eradicated by treatment, and relapses occur when drug treatment is interrupted.
For HBeAg-negative patients, the sustained response is low: 15% show normalization of serum ALT and suppression of serum HBV DNA. For HBeAg-positive patients, the likelihood of response to nucleoside64/nucleotide analogs/PEG-IFN depends greatly upon degree of serum aminotransferase elevation. In general, treatment with any of these drugs does not result in higher rates of HBeAg seroconversion compared to non- treatment in those who have a serum ALT < 2 × ULN. After a year of treatment, HBeAg seroconversion occurs in < 10% of these patients treated with IFN, lamivudine or adefovir. ASSLD guidelines do not recommend treatment in normal ALT patients, because it is unlikely to achieve HbeAg seroconversion.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis B Antibody
How Common Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is fairly common in Africa and the western Pacific region. Throughout the world, there are about 292 million people who are infected with chronic hepatitis B. In the U.S., the figure exceeds 2 million people.
The number of infections had been falling in the U.S., but fewer vaccinations among adults combined with the onset of the opioid crisis and injected drug usage has resulted in the numbers rising again. Infected women can pass the infection on to their babies. Children who are infected before age 5 are more likely to have chronic infection than those infected later in life.
Read Also: Is There A Cure For Hepatitis B Virus
Measuring Viral Activity Tells Us How Effectively A Treatment Is Working
A viral load is simply the measurement of the amount of virus in your blood. Viral load measurements are commonly used to monitor chronic viral diseases such as HIV, hepatitis B , and hepatitis C .
In the case of HCV, a test called a quantitative HCV RNA assay is used to measure the viruss genetic material detected in a milliliter of blood. Other technologies can be also used to monitor viral activity, most of which do so by detecting either viral DNA or RNA.
Also Check: The Difference Between Hepatitis B And C
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine 3rd Dose
Low Response Rates And Nonresponders
Low vaccination response rates have been associated with obesity, smoking, immunosuppression, and advanced age. Approximately 25-50% of persons who initially do not have a vaccine response will show a response to 1 additional vaccine dose, and 50-75% of individuals will have a response to a second 3-dose series.
It is recommended that testing for anti-HBs be obtained 4-12 weeks following vaccination. Revaccinate nonresponders, with another series of 3-dose hepatitis B vaccine. Consider delaying revaccination for several months after initiation of antiretroviral therapy in patients with CD4 counts below 200 cells/mm3 or those with symptomatic HIV disease. The delay in these individuals is an attempt to maximize the antibody response to the vaccine.
Do not defer vaccination in pregnant patients or patients who are unlikely to achieve an increased CD4 count. Individuals at increased risk of severe complications due to HBV infection include those unlikely to achieve CD4 counts of 200 cells/mm3 or above after antiretroviral therapy and HIV-infected pregnant women.
A combined hepatitis A virus /HBV vaccine is licensed in many countries and offers the advantage of protection against both of these viruses at the same time. The vaccine seems to be safe, although some questions exist regarding neurologic complications.
Hbv Primary Care Workgroup
The HBV Primary Care Workgroup includes members in the United States from hepatology, infectious diseases, pharmacy, primary care, and public health. The 2020 HBV Primary Care Workgroup Guidance was first released in early 2020 and is accessible on this web site , with the aim to have regular updated versions posted online. The goal of this document is to provide simplified, up-to-date, and readily accessible HBV management guidance for primary care medical providers. Note, this guidance does not incorporate HBeAg status in the initial decision-making process, but persons positive for HBeAg are recommended to undergo monitoring of HBeAg for evidence of HBeAg seroconversion. The 2020 HBV Primary Care Workgroup Guidance recommends initiating HBV treatment in the following situations.
- : Treatment is recommended but persons should be promptly referred to a hepatologist.
- Cirrhosis: Treatment is recommended for all persons with cirrhosis, regardless of HBV DNA level, ALT level, or HBeAg status.
- Without Cirrhosis: For persons without cirrhosis, treatment is recommended if the HBV DNA level is greater than 2,000 IU/mL and the ALT level is elevated, regardless of HBeAg status. For this purpose, elevated ALT is defined as greater than 25 U/L in females and greater than 35 U/L in males that is persistent for at least 3 to 6 months.
Also Check: What Happens To Your Body When You Have Hepatitis C
With Over 5 Years Of Experience7
FDA-approved in 2016, VEMLIDY is the latest treatment from Gilead with 5 years of experience treating adult chronic HBV patients with compensated liver disease.1,6,7
aNon-Gilead product
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
BOXED WARNING: POSTTREATMENT SEVERE ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B
- Discontinuation of anti-hepatitis B therapy, including VEMLIDY, may result in severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B. Hepatic function should be monitored closely with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months in patients who discontinue anti-hepatitis B therapy, including VEMLIDY. If appropriate, resumption of anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted.
Warnings and Precautions
Adverse Reactions
Most common adverse reactions in clinical studies through week 144 were headache, upper respiratory tract infection, abdominal pain, cough, back pain, arthralgia, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, dyspepsia, and pyrexia.
Drug Interactions
Consult the full prescribing information for VEMLIDY for more information on potentially significant drug interactions, including clinical comments.
Dosage and Administration
INDICATION
VEMLIDY is indicated for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection in adults with compensated liver disease.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
BOXED WARNING: POSTTREATMENT SEVERE ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B
©2022 Gilead Sciences, Inc. All rights reserved. US-VEMP-0084 09/22