How Long Do Hep B Antibodies Last
How long does protection from hepatitis B vaccine last? Studies indicate that immunologic memory remains intact for at least 30 years among healthy people who initiated hepatitis B vaccination at > 6 months of age. The vaccine confers long-term protection against clinical illness and chronic hepatitis B virus infection.
Hbv Dna Hbv Genotype And Hbv Drug Resistance Assays
Specimen: Serum or plasma
Container: Red-top tube, yellow-top tube , gel-barrier tube, plasma preparation tube, or lavender tube
Collection method: Routine venipuncture
The specimen should be transfused to separate plasma/serum from cells within 6 hours and kept frozen when testing cannot be done promptly.
The tests use PCR amplification, DNA probe hybridization, and sequencing method.
When Should You Have The Test
Anyone who has symptoms of hepatitis B may benefit from having the test. Other people who may consider undergoing the hepatitis B panel test are those with known risk factors. These people include individuals born in places with a high incidence of HBV infection and those who use needles to inject drugs.
Recommended Reading: Where Do Hepatitis B Infections Occur
How Is Hepatitis B Spread
- Having unprotected sex.
- Sharing or using dirty needles for drug use, tattoos or piercing.
- Sharing everyday items that may contain body fluids, including razors, toothbrushes, jewelry for piercings and nail clippers.
- Being treated medically by someone who does not use sterile instruments.
- Being bitten by someone with the infection.
- Being born to a pregnant woman with the infection.
Hepatitis B is not spread by:
- Kissing on the cheek or lips.
- Coughing or sneezing.
- Hugging, shaking hands or holding hands.
- Eating food that someone with the infection has prepared.
Durability And Related Factors After Hbsag Clearance
When patients with HBeAg-positive CHB achieve a satisfactory antiviral treatment endpoint , the clinical recurrence is 2040%, and the virological recurrence can be as high as 8090% after drug withdrawal . Because the safety of drug withdrawal is uncertain, HBsAg clearance is recommended as the ideal treatment endpoint for CHB patients. The accessibility and rate of HBsAg clearance was mentioned above, but the durability of HBsAg clearance after treatment cessation remains controversial.
HBeAg status should also receive attention in the pursuit of HBsAg clearance. The clearance of HBsAg in most patients is based on HBV DNA suppression and HBeAg seroconversion, but a few patients exhibit different HBsAg response patterns, such as HBsAg clearance without HBeAg seroconversion. Only HBsAg clearance based on HBV DNA suppression and HBeAg seroconversion is safe for drug withdrawal .
Read Also: Natural Cure For Hepatitis B
New And Current Treatment Options For Hepatitis B
The search for new treatments for hepatitis B has been ongoing for decades. While effective at suppressing the virus, current treatments, which include antivirals, cannot eliminate it from the liver.
Hepatitis B is a liver infection that results from the hepatitis B virus. People acquire it through contact with the bodily fluids of someone with the virus. The liver cleanses the body of waste, and the disruption to its processes can make a person seriously ill.
This article will outline the current treatment options for HBV. It will also discuss new treatments in development that may lead to a cure for HBV.
Initial infection with HBV is an acute infection. Most healthy people with infection with this virus will not have symptoms and can shed the virus easily. If tests show that a person still has the virus 6 months after contracting it, they have a chronic, long-term infection. Doctors use blood tests to diagnose and monitor the condition.
Treatment whether a person has acute or chronic hepatitis B.
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
Don’t Miss: Royal Canin Hepatic Diet For Dogs
Reduction Of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen May Be More Significant In Pegylated Interferon
Abstract
1. Introduction
Chronic hepatitis B is a global infectious disease. There are currently about 70 million people infected with hepatitis B virus in China, with more than 20 million CHB patients. These patients are at high risks of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma , especially in developing countries , presenting an immense medical burden . Covalently closed circular DNA persistence within hepatocytes is relevant for chronic HBV infection . Hepatitis B surface antigen is a surrogate marker for cccDNA transcriptional activity . The disappearance of HBsAg, accompanied by a sustained virological response, loss of hepatitis B e-antigen , recovery of alanine aminotransferase , and improvement of liver tissue lesions, is defined as functional cure. Thus, important guidelines consider sustained HBsAg disappearance after drug withdrawal as an ideal treatment endpoint .
Therefore, comparing HBsAg reduction efficacy for PegIFN therapy combined with NTs or NSs in CHB patients is valuable. Thus, we conducted a retrospective study using the data of CHB patients treated with a combination of PegIFN plus different NAs.
2. Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Clinical Data
2.3. Definitions of Treatment Response
The primary endpoint was the reduction levels of HBsAg from the baseline at 48 weeks of treatment.
2.4. Laboratory Measurements
Serum HBsAg levels were determined by Elecsys HBsAg II assay .
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
Low Response Rates And Nonresponders
Low vaccination response rates have been associated with obesity, smoking, immunosuppression , and advanced age. Approximately 25-50% of persons who initially do not have a vaccine response will show a response to one additional vaccine dose, and 50-75% of individuals will have a response to a fourth higher dose of Engerix B or Recombivax HB, or a second 3-dose series.
Postvaccine antibody titers do not need to be obtained in routine vaccinations of children or adults. It is recommended that testing for anti-HBs be obtained 4-12 weeks after vaccination in the following groups :
- Immunocompromised patients, including those on hemodialysis, HIV patients, and others
- Infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers
- Healthcare professionals
- Sexual partners of HBsAg-positive patients
Nonresponders, should be revaccinated with another series of 3-dose hepatitis B vaccine. Consider delaying revaccination for several months after initiation of antiretroviral therapy in patients with CD4 counts below 200 cells/mm3 or those with symptomatic HIV disease. The delay in these individuals is an attempt to maximize the antibody response to the vaccine.
Do not defer vaccination in pregnant patients or patients who are unlikely to achieve an increased CD4 count. Individuals at increased risk of severe complications due to HBV infection include those unlikely to achieve CD4 counts of 200 cells/mm3 or above after antiretroviral therapy and HIV-infected pregnant women.
Read Also: What Causes The Hepatitis C Virus
Why Do I Need This Test
You may need this test if your healthcare provider believes you have a liver infection caused by HBV. You may need this test if you have symptoms of hepatitis B. Symptoms often start slowly. Many people have no symptoms or only feel like they have a mild case of the flu. You may not have symptoms until the infection becomes severe or chronic.
The most common symptom is extreme tiredness. Other symptoms may include:
-
Yellowed skin and eyes
-
Dark-colored urine
-
Swelling and confusion. This is in extreme cases.
You may also have this test if you have a history that puts you at risk for being in contact with the virus. Risk factors for hepatitis B infection include:
-
Having sex with someone infected with the virus
-
Living in close contact with someone who has the virus
-
Being a man who has sex with men
-
Being a child born to a mother who has the virus
-
Sharing needles for IV drug use
-
Working in a healthcare center where you are exposed to blood
-
Getting a blood transfusion or organ transplant. This is less common with active screening.
You may also have this test several times if you’ve already been diagnosed with hepatitis B to see whether your infection is getting better.
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infection of your liver. Itâs caused by a virus. There is a vaccine that protects against it. For some people, hepatitis B is mild and lasts a short time. These âacuteâ cases donât always need treatment. But it can become chronic. If that happens, it can cause scarring of the organ, liver failure, and cancer, and it even can be life-threatening.
Itâs spread when people come in contact with the blood, open sores, or body fluids of someone who has the hepatitis B virus.
It’s serious, but if you get the disease as an adult, it shouldnât last a long time. Your body fights it off within a few months, and youâre immune for the rest of your life. That means you can’t get it again. But if you get it at birth, itâs unlikely to go away.
âHepatitisâ means inflammation of the liver. There are other types of hepatitis. Those caused by viruses also include hepatitis A and hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Genotype 2 Treatment
What Is The Hbv
The viral load test, also known as hepatitis B virus DNA quantification, is a blood test that quantifies the amount of hepatitis B virus DNA in the blood of a chronically infected patient. Usually, the viral load or viremia is measured in international units per milliliter erstwhile, it was measured in copies per milliliter . The test is conducted using the Polymerase Chain Reaction technique.
The information gathered through this test must be supported by other factors such as the Hepatitis B e-antigen status, the results of the liver enzymes or serum aspartate aminotransferase or alanine aminotransferase tests, and inflammation levels. To completely understand what stage of the infection you might be experiencing, its important to check your plasma viral load frequently. The results of numerous lab tests, including viral load, are used to establish the phase of the infection.
When studied, the quantitative understanding of HBV dynamics influences drug treatment and immunotherapy timing in chronic HBV infection. It can help in developing the best treatment plans for specific patients.
The five stages of Hepatitis B infection are
- Immune tolerance,
- HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B, and
- Hepatitis B surface antigen -negative
Chronic hepatitis B is when hepatitis B surface antigen persists for six months or more. Most infected persons are unaware of their HBV infection and present advanced disease.
Whats The Prognosis For Hepatitis B

Your doctor will know youâve recovered when you no longer have symptoms and blood tests show:
- Your liver is working normally.
- You have hepatitis B surface antibody.
But some people don’t get rid of the infection. If you have it for more than 6 months, youâre whatâs called a carrier, even if you donât have symptoms. This means you can give the disease to someone else through:
- Unprotected sex
- Contact with your blood or an open sore
- Sharing needles or syringes
Doctors donât know why, but the disease does go away in a small number of carriers. For others, it becomes whatâs known as chronic. That means you have an ongoing liver infection. It can lead to cirrhosis, or hardening of the organ. It scars over and stops working. Some people also get liver cancer.
If youâre a carrier or are infected with hepatitis B, donât donate blood, plasma, body organs, tissue, or sperm. Tell anyone you could infect — whether itâs a sex partner, your doctor, or your dentist — that you have it.
Show Sources
CDC: âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for Health Professionals,â âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Mayo Clinic: âHepatitis B.â
UpToDate: âHepatitis B virus: Screening and diagnosis.â
CDC.
HealthyPeople.gov: âHepatitis B in Pregnant Women: Screening.â
Annals of Internal Medicine: âScreening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.â
Read Also: How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis C Untreated
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
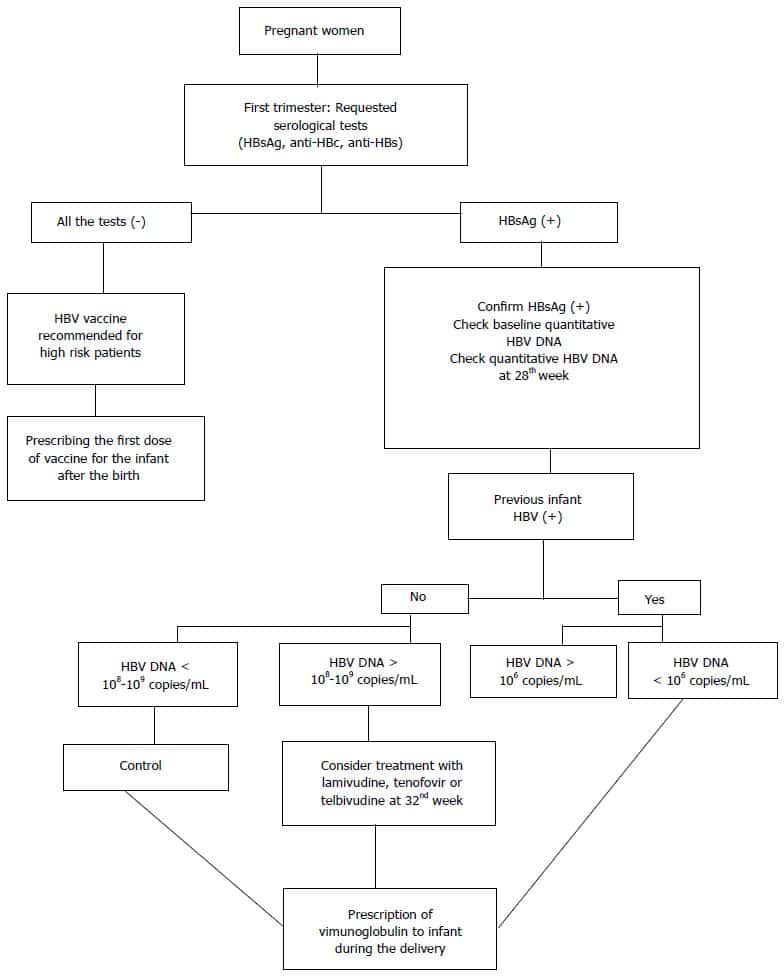
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists , the US Preventive Services Task Force , and the World Health Organization recommend routine prenatal screening for hepatitis B surface antigen in all pregnant womenduring every pregnancyregardless of previous test results or vaccinations. Pregnant women at risk for hepatitis B infections should be specifically targeted for vaccination. The risk of transmission of hepatitis B associated with amniocentesis is low. WHO further recommends all pregnant women undergo testing at least once for HIV and syphilis in addition to that for HBsAg and as early as possible in the pregnancy.
It is recommended that all infants receive their first dose of hepatitis B vaccine as soon as possible after birth , followed by two or three doses to complete the primary series.
To prevent maternal-fetal HBV transmission, a conditional WHO recommendation is that HBsAg-positive gravida who have an HBV DNA 5.3 log10 IU/mL receive tenofovir prophylaxis beginning the 28th week of pregnancy until at least birth. TDF should be used rather than TAF due to lack of safety data in pregnancy. This is in addition to the 3-dose hepatitis B vaccination in all infants, including a timely dose at birth. When antenatal HBV DNA testing is not available, HBeAg testing can be used as an alternative study to determine eligibility for tenofovir prophylaxis to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HBV.
Is Hepatitis B Curable
Theres currently no known cure for hepatitis B, but there are many ways you can prevent infection and avoid transmitting the virus to others.
The most effective and safe way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated. You can also use barrier methods, like condoms, when having sex and avoid sharing needles.
You May Like: How Long Can A Person Live With Hepatitis C
What Is The Outlook For People With Hepatitis B
The outlook for people with HBV is better now than ever before. You are certainly able to live a full life and help yourself stay healthy. You should make sure to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider who is qualified to treat hepatitis B, possibly a liver doctor.
Make sure you are vaccinated against hepatitis A. Check with your healthcare provider or pharmacist before taking other medications or over-the-counter products, including supplements and natural products. These could interfere with your medication or damage your liver. For instance, taking acetaminophen in large doses may harm your liver.
Follow the usual guidelines for living a healthy life:
- Eat nutritious foods, choosing from a variety of vegetables, fruits and healthy proteins. It is said that cruciferous vegetables are especially good at protecting the liver.
- Exercise regularly.
- Dont smoke and dont drink. Both tobacco and alcohol are bad for your liver.
- Do things that help you cope with stress, like journaling, talking with others, meditating and doing yoga.
- Avoid inhaling toxic fumes.
What Other Tests Might I Have Along With This Test
Your healthcare provider may order other blood tests to look for HBV. These tests can look for antigens on the surface, envelope, and core of the virus, as well as the antibodies to these antigens. The symptoms of all 5 hepatitis infections are much the same. So this blood test is often done along with other hepatitis blood tests to tell your provider which type of virus and what stage of infection you may have.
Your healthcare provider may also order a series of blood tests called a hepatitis B monitoring panel to see if your infection is getting better.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Vaccine Declination Form
Characterization Of Binding Kinetics Of Molecule 5 With Hbsag
To experimentally analyze the binding kinetics of computationally predicted molecule 5 with HBsAg, we performed surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy. The equilibrium constant is the ratio of the dissociation rate to the association rate . The KD value obtained from the SPR analysis is 6.53×108 M with the association rate constant of 6.21×105 M1 s1 and dissociation rate constant of 0.04057 s1. The smaller the KD value, the greater the binding affinity of the ligand for its target and vice-versa. The binding affinities of varying concentrations of molecule 5 to HBsAg are shown in Fig. . For the negative control, we performed the binding kinetics study of ciclopirox with HBsAg. Ciclopirox is a synthetic antifungal drug which binds to the HBV core protein and not the HBV surface antigen. In the control SPR experiment, no binding or negative binding affinity was observed . The statistical parameters Chi2 and U-value indicate the quality of fit. The parameters for goodness of fit and kinetic constants are reported in Table . A low U-value less than 15 indicates greater confidence in the results,. Therefore, the KD value obtained for ciclopirox is erroneous and indicates no binding with HBsAg.
Figure 2
How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Most people who contract hepatitis B during adulthood fully recover within 1 to 3 months.
People with chronic hepatitis B may have a higher risk of developing long-term liver problems, like cirrhosis or liver cancer, which require treatment and may be life threatening.
Keep in mind that the risk of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for babies and children, especially if they have not been vaccinated against the virus.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Hiv And Hepatitis
Transfection Of Hbv Constructs Into Huh7 Cells
Huh7 cells were seeded overnight at a density of 5×104 cells per well in a 48-well plate and transfected with HBV construct using Lipofectamine 2000. Six hours post-transfection, media containing molecules dissolved in DMSO was added culture supernatant and cells were harvested at 48 h. Transfections were performed in triplicates.
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccination How Long Does It Last