Whats The Prognosis For Hepatitis B
Your doctor will know youâve recovered when you no longer have symptoms and blood tests show:
- Your liver is working normally.
- You have hepatitis B surface antibody.
But some people dont get rid of the infection. If you have it for more than 6 months, youâre whatâs called a carrier, even if you donât have symptoms. This means you can give the disease to someone else through:
- Unprotected sex
- Contact with your blood or an open sore
- Sharing needles or syringes
Doctors donât know why, but the disease does go away in a small number of carriers. For others, it becomes whatâs known as chronic. That means you have an ongoing liver infection. It can lead to cirrhosis, or hardening of the organ. It scars over and stops working. Some people also get liver cancer.
If youâre a carrier or are infected with hepatitis B, donât donate blood, plasma, body organs, tissue, or sperm. Tell anyone you could infect whether itâs a sex partner, your doctor, or your dentist that you have it.
Show Sources
CDC: âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for Health Professionals,â âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Mayo Clinic: âHepatitis B.â
UpToDate: âHepatitis B virus: Screening and diagnosis.â
CDC.
HealthyPeople.gov: âHepatitis B in Pregnant Women: Screening.â
Annals of Internal Medicine: âScreening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.â
How Much Does A Hepatitis B Titer Test Cost
The cost of a hepatitis B test varies based on where you get the test. Prices range from roughly $24 to $110.
Your insurance may cover some or all of the cost. Under the Affordable Care Act, all new health plans must cover preventative services including hepatitis B vaccination and testing without a deductible or copay.
The Level Of Serum Anti
To evaluate the correlation between anti-HBc and the severity of liver inflammation in a longitudinal cohort, of the aforementioned 655 patients, 45 CHB patients undergoing second liver biopsies after 78 weeks of antiviral-treatment were further analyzed. The levels of serum anti-HBc decreased in accordance with the alleviated histological inflammation, and the levels were significantly different between the baseline and 78th week time point . However, in this study, the fibrosis score remained stable after 78 weeks antiviral therapy .
Figure 2
The level of serum anti-HBc decreased along with alleviated histological inflammation in CHB patients receiving antivirus treatment. Dynamic changes of histological activity index score in HBeAg and HBeAg CHB patients receiving antiviral treatment after a second liver biopsy. Dynamic changes of serum anti-HBc levels in HBeAg and HBeAg CHB patients receiving antiviral treatment after a second liver biopsy. The correlation between serum anti-HBc levels and HAI score in the baseline and 78th week time point .
As shown in Fig. , there was a significant correlation of between the anti-HBc level and HAI score both in the first liver biopsy and the second liver biopsy , suggested that serum anti-HBc levels were positively correlated with severity of hepatic inflammation in the longitudinal cohort study.
Also Check: How Long Hepatitis C Virus Survive Outside Body
Understanding Of Lab Tests Results
Please visit the page about Hepatitis B Testing on the site associated with The American Association for Clinical Chemistry for better understanding of tests. There you will find the most detailed and full information regarding lab tests. In common questions tab you will find answers on the most common questions.
In addition, you can use a special form to ask the question. It is useful, if there is no answer on your question on the web site. A laboratory scientist will answer your question. It is a part of voluntary service provided by the American Society for Clinical Laboratory Science.
Donât Miss: Can Patients With Impaired Hepatic Function Be Treated With Buprenorphine
Hepatitis B Serologic Markers And Definition Of The Isolated Anti
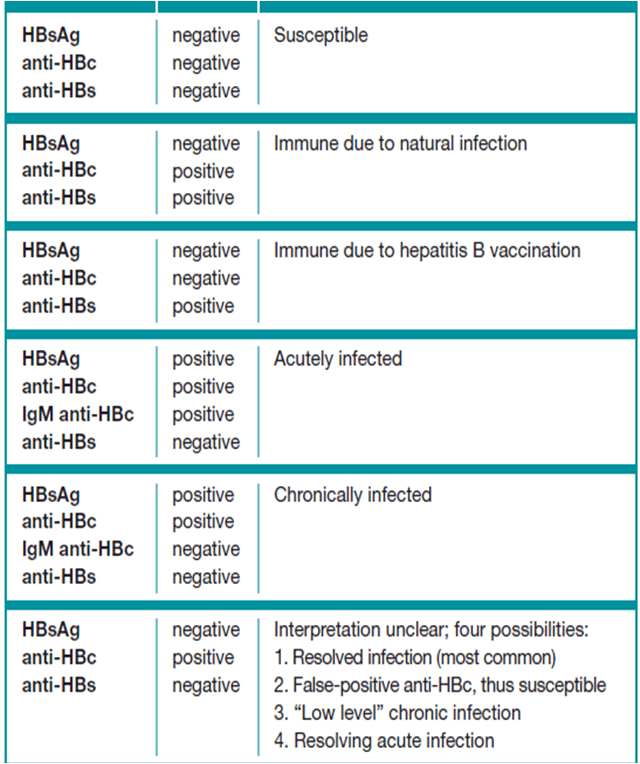
As hepatitis B infection progresses or resolves, clinical states of infection are reflected in HBV serologies. The presence of hepatitis B surface antigen marks active acute or chronic HBV infection. Suboptimal immune responses due to host factors such as age at time of exposure, or advanced immunosuppression, increase the risk for chronic HBV and subsequent complications. Due to mechanisms of immune control, and the presence of covalently closed circular DNA that persists lifelong after HBV exposure, HBV reactivation is always possible even following immunologic recovery and clearance of HBsAg. During chronic infection, markers for HBeAg and anti-HBe may be helpful in delineating phases of chronic HBV infection. Hepatitis B core antibody may be seen in acute or chronic infection, and also may persist for life after immunity is developed . As infection resolves hepatitis B surface antibody develops . Anti-HBs, in the absence of HBsAg or anti-HBc, denotes immunity from hepatitis B vaccination. The isolated anti-HBc profile is defined as the presence of anti-HBc in the absence of HBsAg and anti-HBs. Interpretations of hepatitis B serologies are listed below .
Read Also: Liver Cancer From Hepatitis C
What Is The Most Challenging Aspect Of Hepatitis B Infection
Hepatitis B can very easily escape diagnosis, as most victims do not know they are suffering can spread the disease. This is because symptoms are almost negligible during the onset of hepatitis B infection. Although the infection is treatable and largely preventable, yet early diagnosis can go a long way in the better prognosis of the condition. Further, even though there are good treatment options for hepatitis B, close to a million people with the infection do not make it.Asian countries portray a high prevalence of hepatitis B. This infection is very common among high-risk groups such as people with multiple sex partners, homosexuals, injection drug users or people staying lose to victims of Hepatitis B.
What Is Hep Be Ag
The hepatitis e antigen, or HBeAg, is a marker of an actively replicating HBV virus infection. Those with a positive HBeAg have active replication in their liver cells, more of the virus circulating in their blood, and as a result, they are more infectious, with a higher likelihood of transmitting HBV to others.
Donât Miss: Can You Get Hepatitis From Sex
Don’t Miss: Which Hepatitis Is Not Curable
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. It spreads through contact with infected blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not spread through sharing utensils or kissing. It also doesnt spread through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding. Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure and can last for 212 weeks. However, you are still contagious, even
To screen for hepatitis B, your doctor will perform a series of blood tests.
Hepatitis B And Your Liver
The liver is such an important organ that we can survive only one or two days if it completely shuts down â if the liver fails, your body will fail, too. Fortunately, the liver can function even when up to 80% of it is diseased or removed. This is because it has the amazing ability to regenerate â or create â itself from healthy liver cells that still exist.
If your body were an automobile, your liver would be considered the engine. It does hundreds of vital things to make sure everything runs smoothly:
- Stores vitamins, sugar and iron to help give your body energy
- Controls the production and removal of cholesterol
- Clears your blood of waste products, drugs and other poisonous substances
- Makes clotting factors to stop excessive bleeding after cuts or injuries
- Produces immune factors and removes bacteria from the bloodstream to combat infection
- Releases a substance called âbileâ to help digest food and absorb important nutrients
The word hepatitis actually means inflammation of the liver. Thus, hepatitis B refers to inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus. With early detection and appropriate follow-up medical care, people living with a chronic hepatitis B infection can expect to enjoy a long and healthy life.
Read Also: Can Hepatitis Cause Low Platelets
Hbc Antibody Positive/hbs Antigen Negative/hbs Antibody Positive
There are reports of HBV reactivation in HBc-ab negative/HBs-ag positive/HBs-ab positive cases, and reactivation occurred in 6.9% of them. HBV reactivation in HBc antibody negative/HBs antigen negative/HBs antibody positive cases has also been reported , and reactivation was reported in 3.4% of them.
Particular attention must be paid to patients with < 300 mIU/mL of HBs antibody during maintenance treatment with rituximab since the HBs antibody status might become negative .
Since HBV reactivation was reported even in patients with a high HBs antibody titer, HBs antibody follow-up is not sufficient for detecting the occurrence of reactivation. Monthly follow-up for the presence of HBV-DNA is necessary during treatment.
Hepatitis B Core Ab Total Reactive
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â its anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â its anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Donât Miss: Can Hepatitis B Be Cured Totally
Don’t Miss: What Are The Symptoms Of Having Hepatitis C
Administration Of Nucleoside Analogs Upon Hbv Reactivation
We must evaluate whether to discontinue nucleoside analog administration in patients receiving those drugs that promote HBV reactivation. Since HBs antibody might become negative during rituximab treatment, discontinuation should be considered after the treatments completion. An additional problem exists with regard to determining the duration of the discontinuation period. Cases of HBV reactivation even after long periods of discontinuation have been documented. For example, even after HBs antibody became temporarily positive, it disappeared later and HBV reactivation was induced. If nucleoside analog treatment is given to HBs antibody negative patients who later become antibody positive, such treatment can be discontinued. On the other hand, HBV vaccination is unable to suppress HBV reactivation. If rituximab is administered continuously, HBs antibody may not be induced even after HBV vaccination. It is necessary to evaluate not only the induction of HBs antibody after HBV vaccination but also diseases that are appropriate for the discontinuation of nucleoside analog treatment. Based on the above discussion, Figure shows the modified guidelines from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare.
The review is summarized as schematics. The treatment direction described here is based on the assumption that all patients are screened in advance. HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
Hbcab Or The Hepatitis B Core Antibody Test
The hepatitis B core antibody is produced by your immune system after infection by the hepatitis B virus, and it can persist for life. It is a sign that you either have an new, active hepatitis B infection or that you acquired hepatitis B in the past.
HBcAb is an immune system response to a protein in the core of the virus, and it is only present if you have been infected, rather than immunized against the virus. It is part of a routine screening panel of tests for hepatitis B. If your rest results turn out to be positive, your healthcare provider will order further tests to determine the stage of the infection: acute or chronic .
Also Known As: anti-HBc, HBcAb
You May Like: How Is Hepatitis Transmitted From Person To Person
Hepatitis B Core Antibody Total Test
This test looks for the presence of Hepatitis B Core Antibodies. Hep B is a viral liver infection that is spread through exposure to infected blood or bodily fluids. It is the most common cause of acute viral Hepatitis. Core antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to the inner core of the hepatitis B virus. There are 2 types of core antibodies. IgM antibodies develop shortly after infection and fade away after a short period of time. As IgM antibody levels go down, IgG antibodies begin to develop and usually persist indefinitely. The core antibody test looks for both IgM and IgG antibodies but does not differentiate between them. Results of this test are qualitative and provide a positive or negative result.
The presence of core HBc antibodies typically indicates that a person either had Hepatitis B in the past or has a current infection. The results of this test cannot distinguish between an active or past infection. A core antibody test is most useful when taken along with other tests such as a Hep B Surface Antigen and Hepatitis B Surface Antibody. A positive core antibody along with a positive surface antigen typically indicates a recent or current infection. A positive core antibody along with a positive surface antibody typically indicates that a person has had Hep B in the past, recovered, and now has immunity from future infection. Request A Test offers a Hepatitis B Panel which includes all 3 tests at a discounted price.
Requirements:
Resolution Of Acute Infection
During resolution of acute infection, IgM anti-HBc is replaced by antibody of the IgG subclass , and anti-HBs develops . Anti-HBs is a protective, neutralizing antibody, and its presence indicates recovery from acute infection and immunity to reinfection. The period when all HBsAg has been neutralized by anti-HBs, and neither HBsAg nor anti-HBs is detectable, is referred to as the window period. During the window period, the only serologic marker of infection is IgM anti-HBc. During resolution, anti-HBe replaces HBeAg. In people with past HBV infection, IgG anti-HBc usually remains detectable for life, but anti-HBs might become undetectable in remote infection.3,109
Howard C. Thomas, Jennifer A. Waters, in, 1998
Read Also: Symptoms Of Acute Alcoholic Hepatitis
Timing And Differential Diagnosis With Hbv
The hepatitis flare is first detected as an increase in ALT levels, typically within 3 to 12 weeks after starting antiretroviral therapy. The differential diagnosis includes direct drug or alcohol hepatotoxicity, a new viral hepatitis infection , or an opportunistic infection. To help distinguish between these conditions, a review of the medication history, prior hepatitis A immunization, and history of recent HCV exposure would be indicated, as well as measurement of serum HBV DNA, HIV RNA, and CD4 cell count.
What Does It Mean If Your Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Is Negative
Your test results may not mean you have a problem. Ask your healthcare provider what your test results mean for you. Normal results are negative or nonreactive, meaning that no hepatitis B surface antigen was found. If your test is positive or reactive, it may mean you are actively infected with HBV.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis B Cause Meningitis
You May Like: What Is True About Hepatitis B
Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
Doctors must closely monitor pregnant people who have HBV.
There is a risk that the virus can pass from parent to child during delivery without the correct treatment. Therefore, all people should receive hepatitis B testing during pregnancy. A person with chronic hepatitis B should talk with a doctor about the risks and benefits of antiviral treatment while pregnant.
According to the Hepatitis B Foundation, if someone has HBV, their newborn must immediately receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin within 12 hours of birth. The infant should then receive the second and third doses of the vaccine according to the standard childhood immunization schedule.
Pregnant people unsure of their vaccination status can receive the hepatitis B vaccine during pregnancy and breastfeeding or chestfeeding.
However, there is currently not enough safety information about Heplisav-B and PreHevbrio, so pregnant people
Also Check: How Do You Get Hepatitis C Virus
Understanding Changes In Biomarkers During Disease Progression
Understanding the changes in HBV biomarkers over the course of a persons infection and recovery is key to interpreting the test results. Figure 3-1 and Figure 3-2 depict the typical biomarker changes over the course of hepatitis B disease.
Figure 3-1. Typical serologic course of acute hepatitis B to recovery
Acute, resolved, and chronic hepatitis BApproximately 90% of people > 5 years of age with acute hepatitis B will spontaneously clear their infection . People with resolved hepatitis B will remain positive for total anti-HBc and develop anti-HBs that protect against future HBV infection . Chronic hepatitis B is defined as an HBV infection lasting > 6 months. During the typical course of chronic infection, the total anti-HBc and HBsAg markers will always be present, whereas anti-HBc IgM will disappear . Hepatitis B e antigen and hepatitis B e antibody are variably present. HBV DNA levels vary during the course of chronic infection. Any detectable HBV DNA level is considered positive for surveillance purposes.
HBV-infected people with mutations in HBsAg that cannot be detected by current serologic assays may present with a negative HBsAg result despite high blood levels of HBV DNA. Some laboratories have the capacity to detect HBsAg mutants. Any HD interested in determining which laboratories can detect HBsAg mutants should follow-up with the major laboratories that perform HBsAg testing in their jurisdiction.
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis C Be Sexually Transmitted
Demographic Characteristics And Clinical Status
The analytic samples drawn from 294 patients with HBsAg/anti-HBs+serostatus at baseline, comprised 23 cases and 311 matched controls Table shows their demographic and clinical characteristics. Mean age and rheumatic disease types were similar between case and control groups. No patients with HBsAg/anti-HBs+serostatus had detectable HBV DNA at enrolment. Compared with controls, cases had lower baseline serum anti-HBs titers, more prevalent comorbidities , and relatively higher accumulated doses of sulfasalazine, leflunomide, and prednisolone. Most people in both groups used anti-TNF agents . No study subjects were kidney transplant recipients.
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of cases and controls treated with biologic DMARDs
No cases had clinical HBV reactivation during follow-up , and no cases developed alanine transaminase elevation, or received any anti-viral treatment during median follow-up of 30months after anti-HBs loss. Only one of the 16/23 cases whose serum HBV DNA was monitored after anti-HBs loss ever had a detectable viral load , which was observed only once, with no recurrence as of August 2020.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take To Cure Hepatitis C