How Does Hepatitis B Affect The Liver
In acute symptomatic hepatitis B, the liver can become swollen and inflamed. However the infection is often silent, particularly in infants. If the infection becomes chronic, the virus can cause inflammation and cause the healthy, soft tissues of the liver to harden and scar. About a quarter of people with chronic hepatitis B develop serious liver diseases such as cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Patients And Study Design
A total of 82 patients with positive result for IgM anti-HBc upon clinical presentation of acute hepatitis or AE in CHB were retrospectively analyzed at Hallym University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea, from December 2004 to December 2013. All patients were divided into two groups according to their clinical diagnosis, AHB and CHB-AE.
The AHB group was defined patients with the clinical signs or symptoms suggestive of acute hepatitis without a history of HBV infection prior to this episode and with the loss of hepatitis B surface antigen within 6 mo after onset of acute hepatitis. AE was defined as serum elevation of alanine aminotransferase levels more than 10 times the upper limit of normal. Identified CHB patients with AE and positive IgM anti-HBc were recruited as the control group. Patients with other viral infections or other concomitant liver diseases or a recent history of hepatotoxic drugs including herbal medications or HCC were excluded.
The biochemical and virological profiles were compared between the AHB and CHB-AE groups. Then, the parameters with the greatest differences were selected to assess the diagnostic power for differentiating between AHB and CHB-AE. This study was approved by the Investigation and Ethics Committee for Human Research at the Hallym University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
Recommended Reading: How Do You Catch Hepatitis C
How Common Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is fairly common in Africa and the western Pacific region. Throughout the world, there are about 292 million people who are infected with chronic hepatitis B. In the U.S., the figure exceeds 2 million people.
The number of infections had been falling in the U.S., but fewer vaccinations among adults combined with the onset of the opioid crisis and injected drug usage has resulted in the numbers rising again. Infected women can pass the infection on to their babies. Children who are infected before age 5 are more likely to have chronic infection than those infected later in life.
Hepatitis B Causes And Risk Factors
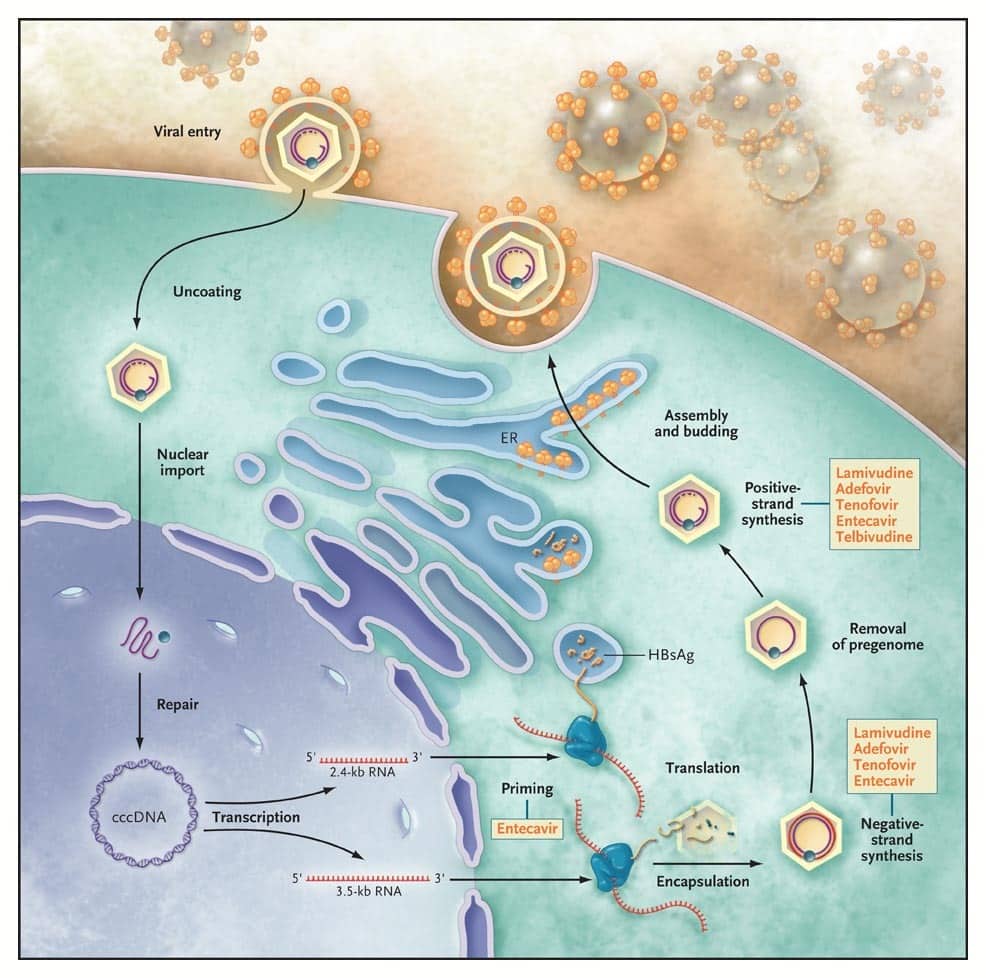
Itâs caused by the hepatitis B virus, and it can spread from person to person in certain ways. You can spread the hepatitis B virus even if you donât feel sick.
The most common ways to get hepatitis B include:
- Sex. You can get it if you have unprotected sex with someone who has it and your partnerâs blood, saliva, , or vaginal secretions enter your body.
- Sharing needles. The virus spreads easily via needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood.
- Accidental needle sticks.Health care workers and anyone else who comes in contact with human blood can get it this way.
- Mother to child.Pregnant women with hepatitis B can pass it to their babies during childbirth. But thereâs a vaccine to prevent newborns from becoming infected.
Hepatitis B doesnât spread through kissing, food or water, shared utensils, coughing or sneezing, or through touch.
Don’t Miss: Can Chronic Hepatitis C Be Cured
What Happens After A Hepatitis B Infection
Some people carry the virus in their bodies and are contagious for the rest of their lives. They should not drink alcohol, and should check with their doctor before taking any medicines to make sure these won’t cause more liver damage.
Anyone who has ever tested positive for hepatitis B cannot be a blood donor.
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus . HBV is one of five types of viral hepatitis. The others are hepatitis A, C, D, and E. Each is a different type of virus. Types B and C are most likely to become chronic, or long lasting.
According to the , around 296 million people around the world are living with hepatitis B. Around 1.5 million people newly contracted chronic hepatitis B in 2019.
HBV infection can be acute or chronic.
Acute hepatitis B causes symptoms to appear quickly in adults. Infants who contract it at birth rarely develop only acute hepatitis B. Nearly all hepatitis B infections in infants go on to become chronic.
Chronic hepatitis B develops slowly. Symptoms may not be noticeable unless complications develop.
Symptoms of acute hepatitis B may not be apparent for months. But common symptoms include:
- yellowing of the whites of the eyes and skin
Any symptoms of hepatitis B need urgent evaluation. Symptoms of acute hepatitis B are worse in people over age 60.
Let your doctor know immediately if youve been exposed to hepatitis B. You may be able to prevent infection.
Some of the ways hepatitis B can be transmitted include:
Although the virus may be found in the saliva, hepatitis B is not transmitted through:
To screen for hepatitis B, your doctor will perform a series of blood tests.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C 0.1 Results
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen And Antibodies
Acute HBV infection is characterized by high titers of HBsAg, which appear within 34 weeks postexposure, peaks at ~12 weeks, and becomes undetectable after 46 months. Detection of HBsAg often requires confirmation, especially when the signal-to-cutoff threshold is low, to prevent the reporting of false-positive results. Algorithms for samples requiring reflex to confirmatory testing is usually established by manufacturers and performed per package insert instructions. Confirmation is done via a neutralization assay, in which the positive patient serum sample is pretreated with or without high titers of anti-HBsAg. The resulting antigenantibody complex effectively neutralizes the HBsAg, if present. A decrease of at least 50% in the intensity of the signal between the neutralized and nonneutralized samples is considered confirmation of HBsAg presence. False-negative HBsAg results may occur due to genetic variants that result in structural changes in the a determinant, the major antigenic determinant of HBV, which is recognized by most of the commercial monoclonal antibodies. These HBsAg variants are designated escape mutants and may cause occult HBV infection, in which HBV DNA is detected in the liver with or without detectable HBV DNA in the serum in an HBsAg negative patient.
BARBARA HABER, in, 2008
Treatment Of Acute Hepatitis B
-
General measures
Liver transplantation Liver Transplantation Liver transplantation is the surgical removal of a healthy liver or sometimes a part of a liver from a living person and then its transfer into a person whose liver no longer functions. (See… read more is the most effective treatment for fulminant hepatitis B and is the best hope of survival, particularly for adults.
You May Like: How Often Should I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Can Hepatitis B Be Prevented
The hepatitis B vaccine is one of the best ways to control the disease. It is safe, effective and widely available. More than one billion doses of the vaccine have been administered globally since 1982. The World Health Organization says the vaccine is 98-100% effective in guarding against the virus. Newborns should be vaccinated.
The disease has also been more widely prevented thanks to:
- Widespread global adoption of safe blood-handling practices. WHO says 97% of the blood donated around the world is now screened for HBV and other diseases.
- Safer blood injection practices, using clean needles.
- Safe-sex practices.
You can help prevent hepatitis B infections by:
- Practicing safe sex .
- Never sharing personal care items like toothbrushes or razors.
- Getting tattoos or piercings only at shops that employ safe hygiene practices.
- Not sharing needles to use drugs.
- Asking your healthcare provider for blood tests to determine if you have HBV or if you are immune.
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis B
If you think you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
A doctor or other healthcare professional may administer the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin. This is a combination of antibodies that provide short-term protection against the virus.
Though both can be given up to a week after exposure, theyre most effective at preventing infection if administered within 48 hours.
If you receive a diagnosis of acute hepatitis B, a doctor may refer you to a specialist. They may advise you to get regular blood tests to ensure you dont develop chronic hepatitis.
Many people with acute hepatitis B dont experience serious symptoms. But if you do, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter pain mediation, like naproxen, when needed
Other lifestyle changes may also be needed to manage your infection, such as:
- eating a nutritious, balanced diet
- avoiding substances that can harm your liver, such as:
- certain herbal supplements or medications, including acetaminophen
If blood tests show you still have an active infection after 6 months, your doctor may recommend further treatment, including medications to help control the virus and prevent liver damage.
Also Check: Cvs Minute Clinic Hepatitis B Vaccine
What Are The Complications Of Hepatitis B
The course of hepatitis B infection depends mostly on the age at which a person is infected.
People infected as infants are likely to develop long term infection and can get complications such as scarring of the liver or liver cancer. Infants have a 9 in 10 chance and children have a 3 in 10 chance of developing a chronic, lifelong infection.
People infected as teenagers or adults are likely to become unwell with symptoms , but have a smaller chance of developing a chronic infection. Others develop a silent infection, without any symptoms.
Most people infected as adults clear the virus from the body within 6 months. They develop immunity to future hepatitis B infections and do not develop long-term liver damage.
However, approximately 1 in 20 adults cannot clear the virus and develop chronic hepatitis B. They are at risk of developing complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer in the longer term.
Clinical Differentiation Between Acute Viral Hepatitis B And Chronic Hepatitis B With Acute Exacerbation
A detailed history of chronic hepatitis B infection or previous blood transfusions in the distant past are likely to suggest CHB-AE while recent possible exposure like recent blood transfusion, needle stick exposure are suggestive of AVH-B. Family history of chronic HBV is helpful in differentiating between AVH-B and CHB-AE.71 The presence of a family history is more likely to be seen in CHB-AE in developing nations where majority of infections are vertical or acquired by horizontal transmission in childhood.
While some patients with CHB-AE can have symptoms similar to AVH-B, many are asymptomatic. Symptomatic cases are more likely in AVH-B.71 Clinical stigmata of chronic liver disease, splenomegaly and ascites may suggest underlying chronic liver disease in patients with CHB-AE. Jaundice is more common in AVH-B and splenomegaly more common in CHB-AE.71 However clinical examination may not differentiate between AVH-B and CHB-AE.
Recommended Reading: Can You Die From Hepatitis C
Is Hepatitis B Curable
Theres currently no known cure for hepatitis B, but there are many ways you can prevent infection and avoid transmitting the virus to others.
The most effective and safe way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated. You can also use barrier methods, like condoms, when having sex and avoid sharing needles.
What Is Involved In A Liver Transplant
A liver transplant is considered necessary when the liver is damaged and cannot function or in some cases of liver cancer. Your liver is very important. It is responsible for many functions related to making sure that your body stays healthy and is able to digest foods.
You may be eligible for a transplant if you have chronic hepatitis B infection or some of the diseases that may result from it, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. You will have to complete testing and be evaluated before being approved for a transplant. It is likely that you will be placed on a waiting list while an appropriate organ is found.
Donated livers come from two types of donors: living and deceased. Because the liver can regenerate, it is possible to use part of a liver for transplant. The remaining sections in both the donor and the receiver will grow into livers of adequate size.
People who get liver transplants must take anti-rejection drugs for the rest of their lives. These drugs make you more susceptible to infection. However, liver transplants have become more successful over time and continue to improve.
Also Check: Which Of The Following Are Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
What Is The Long
Children with chronic hepatitis B can lead completely normal lives, attend school, and play sports without any special arrangements, just like any other child.
A child with chronic HBV infection could be infected for life. Over the decades, the virus can cause progressive damage to the liver and lead to such complications as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
When they become older, children with hepatitis B should avoid drinking alcohol, as it can make the disease progress more quickly. Once they become sexually active, they should practice safe sex to protect their partners from infection.
Hepatitis B Vs Hepatitis C
Hepatitis has many different types. HBV and the hepatitis C virus have both acute and chronic forms.
The main difference between HBV and HCV is how they spread from person to person. Although HCV is transmissible via sexual activity, this is rare. HCV usually spreads when blood that carries the virus comes into contact with blood that does not.
Don’t Miss: Fast Track Hepatitis B Vaccine In Houston Tx
Treatment For Chronic Hbv Infection
For chronic HBV infection, antiviral medications are available.
This is not a cure for chronic HBV. However, it can stop the virus from replicating and prevent its progression into advanced liver disease.
A person with a chronic HBV infection can develop cirrhosis or liver cancer rapidly and without warning. If a person does not have access to adequate treatment or facilities, liver cancer can be fatal within months of diagnosis.
People with a chronic HBV infection require ongoing medical evaluation and an ultrasound of the liver
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
Don’t Miss: What Does Hepatitis C Do To Your Body
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis B
There are two types of hepatitis B infection: acute and chronic.
Acute
An acute infection happens at the beginning, when you first get infected with hepatitis B. Many people are able to clear it from their bodies and recover. In fact, this is true of about 4 in 5 adults who are infected.
Chronic
If you are not able to clear the infection within six months or longer, you have chronic hepatitis B. It is chronic hepatitis B that leads to inflammation and the serious, and possibly fatal, illnesses of cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer. Treatment can slow disease progress, reduce the chance of liver cancer and increase your chances of surviving.
Interpreting Hepatitis B Laboratory Results
Many jurisdictions have regulations requiring laboratories to report all positive HBsAg, HBV DNA, and anti-HBc IgM laboratory results to the HD while a subset might also routinely receive positive total anti-HBc and anti-HBs results.
Additionally, some HDs might receive negative hepatitis B laboratory results, which are useful for determining false-positive results and monitoring patients through their infection and recovery. Table 3-1 shows how to interpret the combinations of laboratory results frequently available in hepatitis B test panels, following the biomarker changes over the course of disease as shown in Figure 3-1.
Table 3-1. Interpretation of hepatitis B laboratory results
| HBsAg |
|---|
- Concurrent ALT and total bilirubin result
- Other hepatitis serological results
- Negative HBsAg and/or negative/undetectable HBV DNA results
Total anti-HBc is detectable, on average, approximately 5 weeks post-HBV exposure, remains detectable indefinitely following exposure, and indicates past or current infection. In the presence of total anti-HBc, a positive HBsAg, HBeAg, or anti-HBc IgM result is a more reliable indication of recent or current infection. Jurisdictions that receive total anti-HBc laboratory results can use these results to clarify a persons HBV infection status.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Core Antibody Igg And Igm
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
As hepatitis B infection is highly transmissible via accidental needlesticks, healthcare providers involved in taking care of a patient with HBV should exercise caution and practice proper preventative measures such as vaccination. Patient education should also include counseling about HBV transmission. The interprofessional team’s role is crucial in ensuring the best patient outcomes.
The vaccination rate is low in many developing countries, and the majority of patients are undiagnosed. Educational programs and improved awareness among the general public and healthcare providers are necessary to improve the identification of the patients, reduce transmission of the disease, and reduce the complications of hepatitis B infection.