Hepatitis B Core Antibody Total Test
This test looks for the presence of Hepatitis B Core Antibodies. Hep B is a viral liver infection that is spread through exposure to infected blood or bodily fluids. It is the most common cause of acute viral Hepatitis. Core antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to the inner core of the hepatitis B virus. There are 2 types of core antibodies. IgM antibodies develop shortly after infection and fade away after a short period of time. As IgM antibody levels go down, IgG antibodies begin to develop and usually persist indefinitely. The core antibody test looks for both IgM and IgG antibodies but does not differentiate between them. Results of this test are qualitative and provide a positive or negative result.
The presence of core HBc antibodies typically indicates that a person either had Hepatitis B in the past or has a current infection. The results of this test cannot distinguish between an active or past infection. A core antibody test is most useful when taken along with other tests such as a Hep B Surface Antigen and Hepatitis B Surface Antibody. A positive core antibody along with a positive surface antigen typically indicates a recent or current infection. A positive core antibody along with a positive surface antibody typically indicates that a person has had Hep B in the past, recovered, and now has immunity from future infection. Request A Test offers a Hepatitis B Panel which includes all 3 tests at a discounted price.
Requirements:
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patients vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
You May Like: What Are The First Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Demographic Characteristics And Clinical Status
The analytic samples drawn from 294 patients with HBsAg/anti-HBs+serostatus at baseline, comprised 23 cases and 311 matched controls Table shows their demographic and clinical characteristics. Mean age and rheumatic disease types were similar between case and control groups. No patients with HBsAg/anti-HBs+serostatus had detectable HBV DNA at enrolment. Compared with controls, cases had lower baseline serum anti-HBs titers, more prevalent comorbidities , and relatively higher accumulated doses of sulfasalazine, leflunomide, and prednisolone. Most people in both groups used anti-TNF agents . No study subjects were kidney transplant recipients.
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of cases and controls treated with biologic DMARDs
No cases had clinical HBV reactivation during follow-up , and no cases developed alanine transaminase elevation, or received any anti-viral treatment during median follow-up of 30months after anti-HBs loss. Only one of the 16/23 cases whose serum HBV DNA was monitored after anti-HBs loss ever had a detectable viral load , which was observed only once, with no recurrence as of August 2020.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take To Cure Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B And Your Liver
The liver is such an important organ that we can survive only one or two days if it completely shuts down â if the liver fails, your body will fail, too. Fortunately, the liver can function even when up to 80% of it is diseased or removed. This is because it has the amazing ability to regenerate â or create â itself from healthy liver cells that still exist.
If your body were an automobile, your liver would be considered the engine. It does hundreds of vital things to make sure everything runs smoothly:
- Stores vitamins, sugar and iron to help give your body energy
- Controls the production and removal of cholesterol
- Clears your blood of waste products, drugs and other poisonous substances
- Makes clotting factors to stop excessive bleeding after cuts or injuries
- Produces immune factors and removes bacteria from the bloodstream to combat infection
- Releases a substance called âbileâ to help digest food and absorb important nutrients
The word hepatitis actually means inflammation of the liver. Thus, hepatitis B refers to inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus. With early detection and appropriate follow-up medical care, people living with a chronic hepatitis B infection can expect to enjoy a long and healthy life.
What Does Hepatitis B Core Antibody Being Positive Mean
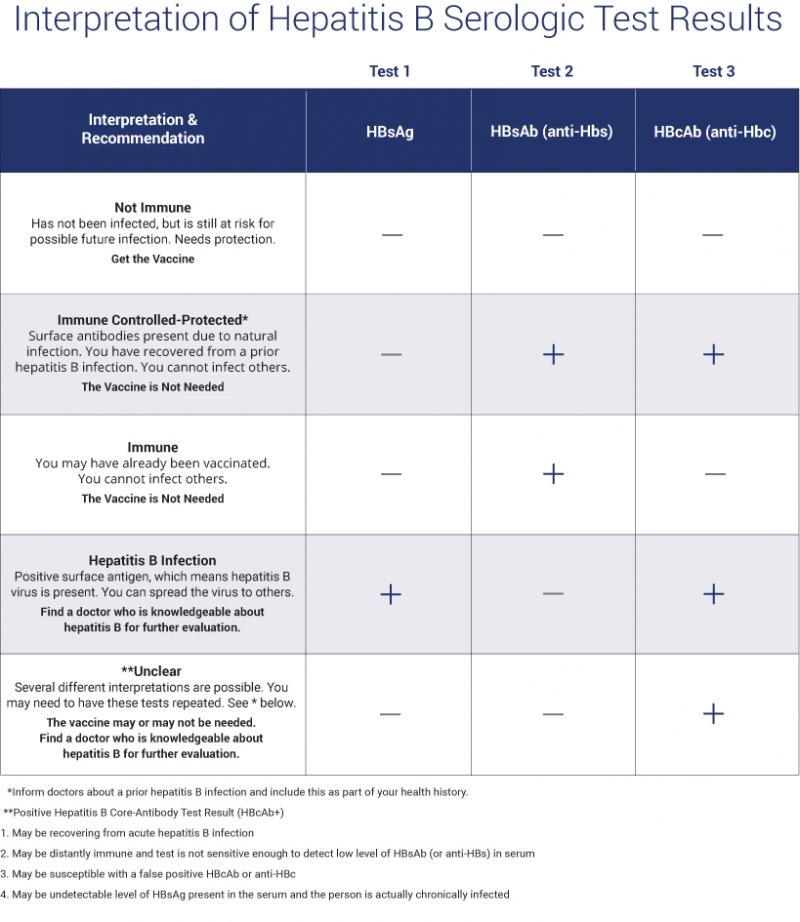
Q:What Does Hepatitis B Core Antibody Being Positive Mean?
A:Hepatitis B Core Antibody is one of the blood tests available to diagnose hepatitis B. It is produced by the body in response to a part of the hepatitis B virus.
The meaning of this test often relies on the results of two other tests: Hepatitis B Surface Antigen and Hepatitis B Surface Antibody .
A positive test has two possible meanings:
- A person is infected with hepatitis B virus, or
- A person was infected in the past but the infection has been cleared.
Keywords: Hepatitis B Core Antibody anti-HBc Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Antibody Negative Means
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitative
The hepatitis B surface antibody is the antibody that is produced in response to hepatitis B surface antigen , a protein present on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. Anti-HBs appears after convalescence from acute infection and lasts for many years. It can also be produced in response to hepatitis B vaccination.
Hepatitis B Core Ab Total Reactive
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â its anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â its anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Dont Miss: What Does Hepatitis B Come From
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis B Be Cured Totally
What Are Some Of The Proven Ways To Prevent Hepatitis B
Healthcare providers stand by vaccination as a reliable prevention measure known to be effective to all age groups- adults, infants, and children. Therefore, close family members and sexual partners of infected persons must get tested and avail HBV vaccination to protect themselves. Medications have also been in use to prevent chronic HBV infection. Additionally, the power of vaccination of sexual partners and close family people cannot be overemphasized in aiding protection against the disease. Apart from vaccination, a few pointers to prevent hepatitis B Infection: Always make sure needles used for acupuncture, body piercing, tattoos, and ear piercing are sterile. Sanitary napkins and tampons need to be disposed of in a hygienic manner. Adopt effective hygiene upon exposure to contaminated blood like washing your hands well using soap. Avoid exposure of wounds to contamination. Avoid direct contact with blood and bodily fluids.
Understanding Of Lab Tests Results
Please visit the page about Hepatitis B Testing on the site associated with The American Association for Clinical Chemistry for better understanding of tests. There you will find the most detailed and full information regarding lab tests. In common questions tab you will find answers on the most common questions.
In addition, you can use a special form to ask the question. It is useful, if there is no answer on your question on the web site. A laboratory scientist will answer your question. It is a part of voluntary service provided by the American Society for Clinical Laboratory Science.
Also Check: How Do You Know If You Have Alcoholic Hepatitis
Don’t Miss: Can Patients With Impaired Hepatic Function Be Treated With Buprenorphine
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
Is Hepatitis B Core Antibody Curable
Theres no cure for hepatitis B. The good news is it usually goes away by itself in 4 to 8 weeks. More than 9 out of 10 adults who get hepatitis B totally recover. However, about 1 in 20 people who get hepatitis B as adults become carriers, which means they have a chronic hepatitis B infection.
What does reactive mean on a hepatitis B test?
HBsAg : when this is positive or reactive, it means the person is currently infected with hepatitis B and is able to pass the infection on to others. Questions Frequently Asked About Hepatitis B.
Don’t Miss: Xifaxan Dosage For Hepatic Encephalopathy
How Long Do Hep B Antibodies Last
How long does protection from hepatitis B vaccine last? Studies indicate that immunologic memory remains intact for at least 30 years among healthy people who initiated hepatitis B vaccination at > 6 months of age. The vaccine confers long-term protection against clinical illness and chronic hepatitis B virus infection.
Results Of The Hbcab Test
There are two variations of antibodies. The IgM antibody is the largest antibody and the first produced in an infection. It shows that you may have a current, active infection. Sometimes it persists for years, but it usually drops to undetectable levels.
The HBcAb IgG variant is produced later in the course of the infection, and it’s likely that you will have a positive HBcAb IgG test the rest of your life.
The screening panel usually has a test that is for total HBcAb, which includes both IgM and IgG. The IgM test may be ordered to help determine if you have an acute infection.
A positive HBcAb test must be interpreted along with the results of the other tests. You may have an active or chronic infection, or you may be immune to hepatitis B due to past infection. Discuss the results with your healthcare provider. In any case, a positive HBcAb test means your blood or organs cannot be donated to a recipient.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If You Have Hepatitis B
Risk Of Transfusion Transmission
In the US, with testing for HBsAg and anti-HBc, the estimated residual risk of HBV transmission before DNA testing was 1:280,000â1:357,000, significantly higher than that for HIV or HCV. Voluntary minipool testing for HBV DNA has been widely implemented in the US, and is now required by the FDA. Current residual risk estimates are 1:750,000 or less in an era of universal immunization. Minipool HBV DNA assays have similar sensitivity to current HBsAg tests, accounting for the clinically marginal decrease of the window period .
Gregory L. Armstrong, Susan T. Goldstein, in, 2007
What Is Hep Be Ag
The hepatitis e antigen, or HBeAg, is a marker of an actively replicating HBV virus infection. Those with a positive HBeAg have active replication in their liver cells, more of the virus circulating in their blood, and as a result, they are more infectious, with a higher likelihood of transmitting HBV to others.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Hepatitis From Sex
Administration Of Nucleoside Analogs Upon Hbv Reactivation
We must evaluate whether to discontinue nucleoside analog administration in patients receiving those drugs that promote HBV reactivation. Since HBs antibody might become negative during rituximab treatment, discontinuation should be considered after the treatments completion. An additional problem exists with regard to determining the duration of the discontinuation period. Cases of HBV reactivation even after long periods of discontinuation have been documented. For example, even after HBs antibody became temporarily positive, it disappeared later and HBV reactivation was induced. If nucleoside analog treatment is given to HBs antibody negative patients who later become antibody positive, such treatment can be discontinued. On the other hand, HBV vaccination is unable to suppress HBV reactivation. If rituximab is administered continuously, HBs antibody may not be induced even after HBV vaccination. It is necessary to evaluate not only the induction of HBs antibody after HBV vaccination but also diseases that are appropriate for the discontinuation of nucleoside analog treatment. Based on the above discussion, Figure shows the modified guidelines from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare.
The review is summarized as schematics. The treatment direction described here is based on the assumption that all patients are screened in advance. HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
What Do My Test Results Mean
Your age, gender, and medical history will also be factors that will come into play for the results of the test. Your healthcare provider is the best person who can help you with decoding your test results. If the result is Non-reactive or Negative, it indicates the absence of Hepatitis B core IgM antibodies in the blood. It means there is no recent or earlier HBV infection in the blood. If your test result is positive, it shows the presence of acute hepatitis B infection. The IgM anti-HBcshows up in the blood at about the same time symptoms manifest. The time taken to completely recover from this infection is about 06 months this also means that you will develop immunity from the HBV virus. Therefore, you will not contribute to the spread of the infection. Doctors recommend a followup of blood tests for hepatitis after 6 months. In case, you do not recover in 6months, then it is a far greater problem as the virus stays in the blood. It can damage the liver as well as spread the infection to others.
Read Also: How Do You Find Out If You Have Hepatitis C
What Is The Hepatitis B Virus And What Causes Its Transmission
The Hepatitis B virus consists of five types names as A, B, C, D and E. These viruses target the liver. The spread of hepatitis B infection takes place through contact with contaminated bodily fluids such as blood, seminal fluid and vaginal secretions. While the virus cannot spread through mere touch, sneezing or coughing, HBV can spread to others through the use of contaminated needles, illegal drugs, and unprotected sex. An infected mother can pass on the infection to her unborn baby during pregnancy or childbirth. Most patients complain of symptoms of Hepatitis only several weeks after the infection.
Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
Doctors must closely monitor pregnant people who have HBV.
There is a risk that the virus can pass from parent to child during delivery without the correct treatment. Therefore, all people should receive hepatitis B testing during pregnancy. A person with chronic hepatitis B should talk with a doctor about the risks and benefits of antiviral treatment while pregnant.
According to the Hepatitis B Foundation, if someone has HBV, their newborn must immediately receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin within 12 hours of birth. The infant should then receive the second and third doses of the vaccine according to the standard childhood immunization schedule.
Pregnant people unsure of their vaccination status can receive the hepatitis B vaccine during pregnancy and breastfeeding or chestfeeding.
However, there is currently not enough safety information about Heplisav-B and PreHevbrio, so pregnant people
Also Check: How Do You Get Hepatitis C Virus
Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B core antibodies appear shortly after the onset of symptoms of hepatitis B infection and soon after the appearance of hepatitis B surface antigen . Initially, anti-HBc Ab consist almost entirely of the IgM class, followed by appearance of anti-HBc IgG, for which there is no commercial diagnostic assay.
The anti-HBc total antibodies test, which detects both IgM and IgG antibodies, and the test for anti-HBc IgM antibodies may be the only markers of a recent hepatitis B infection detectable in the window period. The window period begins with the clearance of HBsAg and ends with the appearance of antibodies to hepatitis B surface antigen . Anti-HBc total Ab may be the only serologic marker remaining years after exposure to hepatitis B.
This assay is FDA-approved for in vitro diagnostic use and not for screening cell, tissue, and blood donors.
Mutant Viruses And Chronic Infection
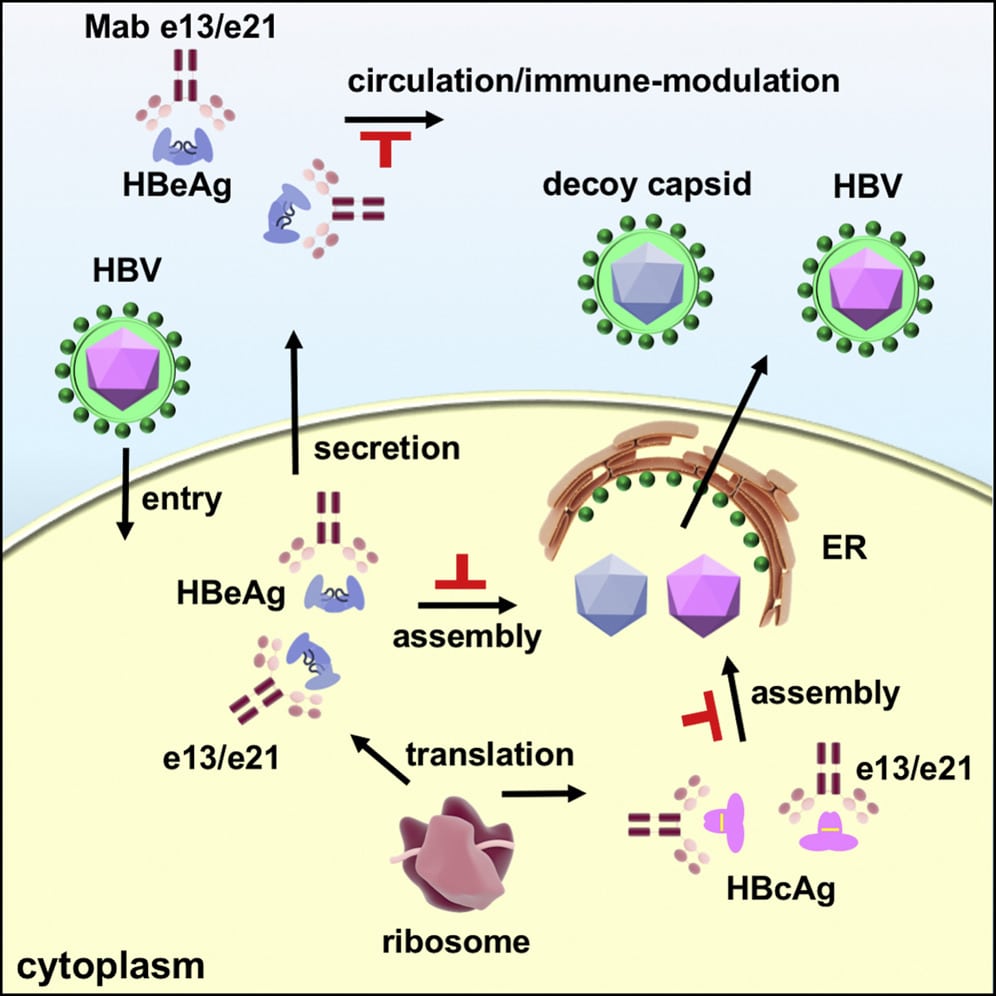
Anti-HBe-positive patients in the reactivated phase of the disease are also referred to as the HBeAg-negative viremic group. Genomic analyses has revealed that such patients carry natural mutants of the virus that have either reduced levels or complete abrogation of HBeAg production. These variants are selected at the time of, or soon after, seroconversion, and become dominant during the reactivation phase. The most common precore mutation is the G1896A substitution, which creates a premature stop codon in the precursor protein from which HBeAg is elaborated. This mutation affects the stem of the encapsidation signal, but leads to stronger base pairing with the A1896 change in genotypes with a T at position 1858 of the precore region, such as B, C, D, and E. The double mutation affecting the core promoter region is thought to result in decreased transcription of the precore mRNA, with a knockon effect on HBeAg production, while pgRNA production remains the same or is even upregulated. It is now apparent that additional mutations in this region may contribute to this phenotype.
Geoffrey M. Dusheiko, in, 2003
You May Like: How Much Does Hepatitis B Vaccine Cost
The Treatment Programs Role In The Screening Process
Medical staff members at substance abuse treatment programs might assume the primary role for screening individuals for and explaining the screening process and test results. Opioid treatment programs with medical staff members should screen for and C at intake and periodically as indicated. In programs without onsite medical staff, clients may be referred elsewhere for screening with minimal involvement of the substance abuse treatment program.
Regardless of the type of program, counselors should have a basic understanding of the importance of screening, the screening process, and the meaning of the results. Counselors can encourage clients referred for screening to follow through and complete the screening and evaluation process . Clients might feel anxious about being diagnosed with hepatitis, and they might delay or avoid getting screened.