How Do You Catch Hepatitis B Virus
Blood from a person infected with hepatitis B virus is heavily contaminated with the virus. As a result, contact with blood is the most likely way to catch hepatitis B. Even casual contact with the blood of someone who is infected can cause infection.
Healthcare workers are at high risk of catching the disease, as are intravenous drug users and newborns of mothers infected with the virus. Sexual contact can also expose people to infection. The virus is also present in low levels in saliva.
Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Adults
Hepatitis B is a vaccine-preventable viral disease that involves inflammation of the liver.
The hepatitis B virus usually leads to a short-term infection known as acute hepatitis B. If their infection is left untreated, some people develop chronic hepatitis B. Chronic hepatitis B is a serious, permanent condition that can cause organ damage, cirrhosis , liver cancer, liver failure, and even death.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , all people should be vaccinated against hepatitis B starting at birth. Adults who are at risk of developing hepatitis B should also receive the vaccine, which is highly effective in preventing infection.
Read on to learn more about the hepatitis B vaccine for adults, including who should receive it, the details of the dosage schedule, side effects, and more.
Preparations Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B vaccine is produced using recombinant DNA technology. A plasmid containing the gene for hepatitis B surface antigen is inserted into common bakers yeast, which then produces HBsAg. The HBsAg is harvested and purified. This vaccine cannot cause hepatitis B virus infection because no potentially infectious viral DNA or complete viral particles are produced during this process.
Single-antigen and a combination formulation that combines hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines are available. Two single-antigen vaccines, Engerix-B® and Recombivax HB®, are conjugated with aluminum. A newer formulation, HepB-CpG , uses the immune-stimulating adjuvant, cytidine-phosphate-guanosine oligodeoxynucleotide .
Also Check: How Dangerous Is Hepatitis C
The Hepatitis B Vaccine And Immunosuppressants
If you are taking or about to start taking a medication that suppresses your immune response, let your healthcare provider know. Immunosuppressants may make certain vaccines less effective. Your healthcare provider may recommend that you get the hepatitis B vaccine at a particular time during your course of medication.
For Adults And Children
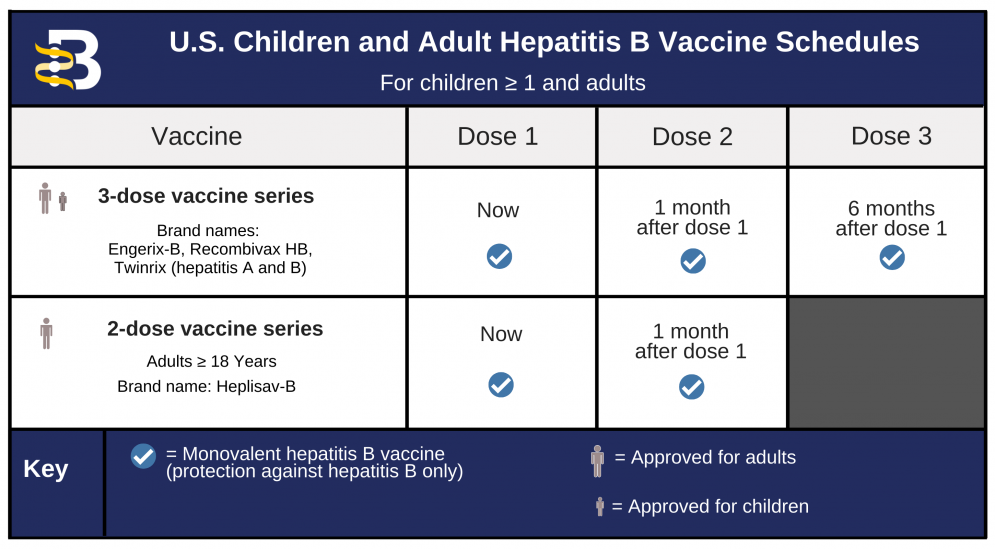
This vaccine schedule involves three doses within 2 months, followed by a booster dose at 1 year.
The initial accelerated doses provide immediate protection from HBV, and the booster dose helps provide long-term protection.
Below is the accelerated vaccination schedule approved for both adults and children:
| Vaccine series | |
|---|---|
| 2 months after the first dose | 1 year after the first dose |
Don’t Miss: Latest Medicine For Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
Most people only experience mild, short-term side effects from the hepatitis B vaccine. Common side effects include:
- Headache
- Fever
- Pain, redness, or swelling at the site of injection
Severe allergic reactions to the hepatitis B vaccine are very rare. If you have symptoms of an allergic reaction shortly after getting the HepB vaccinesuch as difficulty breathing, facial swelling, or hivesseek medical help immediately.
The hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective for most people. However, there are certain people who should not get the HepB vaccine, including:
- People who are moderately or severely ill at the time of vaccination
- People who have had a severe allergic reaction to yeast
- People who have had a severe allergic reaction to a hepatitis B vaccine in the past
International Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
The hepatitis B vaccine is an injection that is generally given in the arm and as a three-dose series. The World Health Organization recommends a 0, 1, and 6-month vaccine schedule, though schedules may vary based on a countrys national immunization program. Completing the hepatitis B vaccine series, preferably beginning at birth, will ensure protection against hepatitis B, hepatitis delta and lower the lifetime risk of liver cancer. Greater than 90% of babies and up to 50% of young children who are not vaccinated and are infected with hepatitis B will have lifelong infection, which makes the birth dose essential to their protection. Please note that the vaccine brand name, manufacturer and associated schedules for adults, children and infants may be unique to different countries, though there is a list of WHO prequalified vaccines.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
The World Health Organization recommends all infants receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth and to complete the vaccine series with additional shots at 1 month and 6 months of age. Beginning the hepatitis B vaccine at birth will ensure protection against hepatitis B for life.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
4-Dose Combination Vaccine Series for Infants
Additional Resource Links:
Recommended Reading: How Do You Contract Hepatitis C Virus
Hepatitis B Vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide
For health professionals
Last partial content update : May 2022
The footnotes in and the accompanying text description for the figure have been revised to align with the corresponding figure in Protocole d’immunisation du Québec, 5e édition from which it was adapted.
Last complete chapter revision :
Who Should Get The Hepatitis A Vaccine
The CDC recommends that all children between ages 12 months and 23 months get this vaccine as well as for any infant aged 6 to 11 months who is traveling internationally.
The following people are also at risk for the disease and should be vaccinated:
- Children and teens through age 18 who live in states or communities that have made this vaccination routine because of a high rate of disease
- Men who have sex with men
- Anyone who uses illegal drugs
- People with chronic liver disease
- Anyone treated with blood clotting drugs, such as people with hemophilia
- People who work with HAV-infected primates or in HAV research laboratories.
- Travelers to countries where hepatitis A is common. A good source to check is the CDCâs travelersâ health website, which you can search by the country youâre going to.
- People adopting or close to a child adopted from a country where hepatitis A is common
You should not get the vaccine if you’re allergic to any ingredients in it or if you had a severe allergic reaction to an earlier dose of it. Tell your doctor or pharmacist about any allergies you have.
If you’re pregnant, let your doctor know. The safety of this vaccine for pregnant women is unknown, although the risk is considered to be very low.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Non Reactive Test Result
Transmission Symptoms And Treatment
How is HBV transmitted?
HBV is transmitted through activities that involve percutaneous or mucosal contact with infectious blood or body fluids , including
- sex with a partner who has HBV infection
- injection drug use that involves sharing needles, syringes, or drug-preparation equipment
- birth to a person who has HBV infection
- contact with blood from or open sores on a person who has HBV infection
- exposures to needle sticks or sharp instruments and
- sharing certain items with a person who has HBV infection that can break the skin or mucous membranes , potentially resulting in exposure to blood.
How long does HBV survive outside the body?
HBV can survive outside the body and remains infectious for at least 7 days .
What should be used to clean environmental surfaces potentially contaminated with HBV?
Any blood spills should be disinfected using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 9 parts water. Gloves should be worn when cleaning up any blood spills.
Who is at risk for HBV infection?
The following populations are at increased risk for becoming infected with HBV:
- Infants born to people with HBV infection
- Sex partners of people with HBV infection
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household contacts or sexual partners of known people with chronic HBV infection
- Health care and public safety workers at risk for occupational exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Patients on hemodialysis
Who should be screened for HBV?
Interchangeability And Dosing Schedule
- 2-dose HepB vaccine series only applies when both doses consist of HepB-CpG, administered at least 4 weeks apart.
- Series consisting of a combination of 1 dose of HepB-CpG and a vaccine from a different manufacturer should do the following:
- Adhere to the 3-dose schedule minimum intervals of 4 weeks between dose 1 and 2, 8 weeks between dose 2 and 3, and 16 weeks between dose 1 and 3. However, if HepB-CpG is substituted for dose 2 of HepB-alum, a provider has the option of administering the next dose of HepB-CpG a minimum of 4 weeks from the previous dose for a complete series.
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis B And C Transmitted
Why Should I Vaccinate My Newborn Child If I Know That I Am Not Infected With Hepatitis B Virus
Before the hepatitis B vaccine, every year in the United States about 18,000 children were infected with hepatitis B virus by the time they were 10 years old. This statistic is especially important because people are much more likely to develop liver cancer or cirrhosis if they are infected early in life, rather than later in life .
About 9,000 of the 18,000 children infected in the first 10 years of life caught the virus from their mother during birth. However, many young children didn’t catch the disease from their mother. They caught it from either another family member or someone else who came in contact with the child. Because hepatitis B can be transmitted by relatively casual contact with items contaminated with the blood of an infected person, and because many people who are infected with hepatitis B virus don’t know that they have it, it is virtually impossible to be “careful enough” to avoid this infection.
For these reasons, all young children are recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccine. The best time to receive the first dose is right after birth. This will ensure that the child will be protected as early as possible from catching hepatitis B from people who dont know that they are infected with the virus.
Listen to Dr. Offit explain why newborns get the hepatitis B vaccine by watching this short video, part of the series Talking About Vaccines with Dr. Paul Offit.
Which Adults Should Be Vaccinated Against Hepatitis B

According to CDC recommendations, adults in the following groups are recommended to receive hepatitis B vaccine:
General
- All people age 18 years and younger.
- Anyone 19 years and older who wants to be protected from hepatitis B.
People at risk for infection by sexual exposure
- Sex partners of people who are hepatitis B surface antigen -positive.
- Sexually active people who are not in long-term, mutually monogamous relationships.
- People seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually transmitted disease.
- Men who have sex with men.
People at risk for infection by percutaneous or permucosal exposure to blood or body fluids
- Current or recent illegal injection drug users.
- Household contacts of people who are HBsAg-positive.
- Residents and staff of facilities for developmentally challenged people.
- Healthcare and public safety workers with reasonably anticipated risk for exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids.
- People with end-stage renal disease, including predialysis, hemo-, peritoneal- and home-dialysis patients.
Others
- International travelers to regions with intermediate or high levels of endemic HBV infection.
- People with chronic liver disease.
- People with HIV infection.
- People with diabetes who are age 19 through 59 years. For those age 60 and older, clinicians should make a determination of need for
- vaccination based on their patients’ situation.
In a future issue, we will review the various hepatitis B serologic tests, who needs testing, and when they need it .
Don’t Miss: Purina Pro Plan Hepatic Cat
Advisory Committee On Immunization Practices Recommendations
In February 2018, ACIP approved recommendations for Heplisav-B vaccine as an option for previously unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated persons, including:
- Adults 18 years of age and older who have a specific risk, or lack a risk factor but want protection. See ACIP Recommended Immunization Schedule for Adults for risk factors.
Is It Okay To Get An Extra Dose Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Yes. Although extra doses of vaccine are not recommended, you can think of the extra dose as another chance for the immune system to see the hepatitis B virus. A vaccine is not the only time the immune system will see the virus or bacteria contained in it. People may be exposed to the virus or bacteria at school or the store or when visiting family or friends. An extra dose of vaccine is like one more exposure, except the difference is that the virus or bacteria in any vaccine has been made safe, so it wont make you ill.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Hepatitis C Virus
Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule: Standard Accelerated And Combination
Getting poked with a needle is never fun, but its an extremely important part of protecting yourself and others from infectious diseases! The hepatitis B vaccine is known to be one of the most effective vaccines in the world and very safe too! As a blood-borne disease that typically has no symptoms, hepatitis B can easily be spread by accident simply because people are unaware that they have it! Modes of transmission include mother-to-child during birth, unprotected sex, injection drug use, unsafe medical procedures, and the sharing of personal items that may contain blood remnants, such as body jewelry, razors, and toothbrushes. Although certain precautions can be taken to prevent transmission, the only way to completely protect yourself is to get vaccinated. Once you have been vaccinated, you are protected for life!
There are a few options for receiving the hepatitis B vaccination. In most countries, the vaccine is available through a doctors office or a health clinic. The most common option is the standard three-dose vaccine. This consists of three separate doses of the vaccine given through intramuscular injections. In order for the vaccine to be effective, there must be a minimum amount of time between doses. If the minimum amount of time is not followed, the vaccine will not provide full, long term protection from the infection.
3 Dose Schedule:
2-Dose Schedule :
- 1st shot At any given time
- 2nd shot At least 28 days after the first shot.
Many People With Hbv Dont Know They Have It
HBV infections are becoming less common in the United States. But HBV is still widespread in other parts of the world. Around 257 million people living around the world currently have HBV, and many of them dont know it. Chronic HBV is often asymptomatic, and even when it isnt, it can take months for symptoms to show up.
HBV can be transmitted through sexual contact and the use of IV drugs , and other risk factors. Although rare, there
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Treatment And Prevention
What Is Hepatitis B Virus
Hepatitis B virus attacks the liver. Hepatitis B virus infections are known as the “silent epidemic” because many infected people don’t experience symptoms until decades later when they develop hepatitis , cirrhosis , or cancer of the liver . Every year in the United States about 22,000 new hepatitis B infections occur and about 2,000 people die from their infections.
How Common Is Hepatitis B
About 257 million people around the world have hepatitis B. In the U.S., estimates suggest that around 21,600 people have acute hepatitis B, while about 862,000 are living with chronic hepatitis B.
However, research indicates that only about one-third of people in the U.S. with chronic hepatitis are aware that they have the condition.
Hepatitis B spreads through direct contact with bodily fluids, such as semen or blood. Examples include:
- Sharing needles or other sharp instruments, such as tattooing or piercing instruments
- Unprotected sex
- Sharing medical equipment, such as a glucose monitor
- Sharing personal items, such as razors or nail clippers
- Contact with the open sores or blood of someone who has hepatitis B
- Birth
While anyone can get hepatitis B, certain people are more at risk. Risk factors for HBV include:
- Having a sexual partner with hepatitis B
- Living with someone who has hepatitis B
- Having more than one sexual partner within the last six months
- A history of sexually transmitted infections
- Being born in, living in, or traveling to regions where hepatitis B is common
- If male, having sex with other men
- Injection drug use
- Working in a health care setting
- Working in a prison
- Working in a care facility for people with dementia or developmental disabilities
You May Like: Hepatitis B Or C Which Is Worse
Recommended Adult Dosing Volume Of Monovalent Hepatitis B Vaccine
- Age 19 years and younger: Use 0.5 mL per dose .
- Age 20 years and older: 1.0 mL per dose .
For a one-page sheet reviewing the hepatitis B dosing schedule for children and adults, consult IACs Hepatitis A and B Vaccines: Be Sure Your Patients Get the Correct Dose. For complete dosing information, consult the ACIP hepatitis B vaccine recommendations for adults.
Emergency Hepatitis B Vaccination
If you have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and have not been vaccinated before, you should get immediate medical advice, as you may benefit from having the hepatitis B vaccine.
In some situations, you may also need to have an injection of antibodies, called specific hepatitis B immunoglobulin , along with the hepatitis B vaccine.
HBIG should ideally be given within 48 hours, but you can still have it up to a week after exposure.
Also Check: Pro Plan Hepatic Dog Food