For Adults At High Risk Of Exposure
Adults who have not received the hepatitis B vaccine series should be immunized when they have an increased risk of exposure. Job, travel, health condition, or lifestyle all may increase a persons risk of contracting hepatitis B.
People who live or work where there is risk of exposure include:
- Health care and public safety workers who are likely to be exposed to blood or blood products.
- Clients and staff of institutions or residential settings with known or potential HBV carriers.
- People planning extended travel to China, Southeast Asia, Africa, and other areas where hepatitis B infection is high.
People who have health conditions that put them at high risk for exposure or a severe infection include:
- People who have a severe kidney disease that requires them to have their blood filtered through a machine .
- People who have chronic liver disease.
- People who have hemophilia and other conditions in which they need to have blood products on an ongoing basis.
- People who had a stem cell transplant.
People whose lifestyle puts them at high risk for exposure include:
- People who inject illegal drugs.
- Men who have sex with men.
- People who have had more than one sex partner in the past 6 months or who have a history of sexually transmitted infection.
- Household contacts and sex partners of hepatitis B carriers.
- Prison inmates.
Dont Miss: What Does Hepatitis Come From
When To Delay Or Avoid Hepb Immunization
Doctors delay giving the vaccine to babies who weigh less than 4 pounds, 7 ounces at birth whose mothers do not have the virus in their blood. The baby will get the first dose at 1 month of age or when the baby is discharged from the hospital.
The vaccine is not recommended if your child:
- is currently sick, although simple colds or other minor illnesses should not prevent immunization
- had a serious allergic reaction after an earlier dose of the vaccine or is allergic to baker’s yeast
How Long Is Hep B Vaccine Good For
How long does protection from hepatitis B vaccine last? Studies indicate that immunologic memory remains intact for at least 30 years among healthy people who initiated hepatitis B vaccination at > 6 months of age .
What is the 8-minute rule in physical therapy?
8-Minute Rule Basics Basically, a therapist must provide direct, one-on-one therapy for at least eight minutes to receive reimbursement for one unit of a time-based treatment code.
Read Also: Hepatitis C How Long Before Symptoms
Babies And Hepatitis B Vaccination
Pregnant women have a routine blood test for hepatitis B as part of their antenatal care.
Babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B need to be given a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of their birth, followed by further doses at 4, 8, 12 and 16 weeks of age, plus a final dose when they’re 1 year old.
Babies of mothers identified by the blood test as particularly infectious might also be given an injection of HBIG at birth on top of the hepatitis B vaccination to give them rapid protection against infection.
All babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B should be tested at 1 year of age to check if they have become infected with the virus.
Selected Safety Information For Recombivax Hb Selected Safety Information For Recombivax Hb
Do not administer RECOMBIVAX HB® to individuals with a history of severe allergic or hypersensitivity reactions after a previous dose of any hepatitis B-containing vaccine or to any component of RECOMBIVAX HB, including yeast.
The vial stopper and the syringe plunger stopper and tip cap contain dry natural latex rubber, which may cause allergic reactions in latex-sensitive individuals.
Apnea following intramuscular vaccination has been observed in some infants born prematurely. Decisions about when to administer an intramuscular vaccine, including RECOMBIVAX HB, to infants born prematurely should be based on consideration of the individual infants medical status and the potential benefits and possible risks of vaccination. For RECOMBIVAX HB, this assessment should include consideration of the mothers hepatitis B antigen status and high probability of maternal transmission of hepatitis B virus to infants born to mothers who are HBsAg positive if vaccination is delayed.
Hepatitis B vaccination should be delayed until 1 month of age or hospital discharge in infants weighing < 2000 g if the mother is documented to be HBsAg negative at the time of the infants birth. Infants weighing < 2000 g born to HBsAg positive or HBsAg unknown mothers should receive vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin in accordance with ACIP recommendations if HBsAg status cannot be determined.
Vaccination with RECOMBIVAX HB may not protect all individuals.
Recommended Reading: How To Prevent Hepatitis C
Don’t Miss: Difference Between Fatty Liver And Hepatitis
A Look At Each Vaccine: Hepatitis B Vaccine
View larger image The hepatitis B vaccine is given to prevent the severe liver disease that can develop when children or adults are infected with hepatitis B virus. The hepatitis B vaccine is given as a series of three shots. The first dose is given within 24 hours of birth. The second dose is given one to two months after the first dose, and the third dose is given between 6 months and 18 months of age. The vaccine is also recommended for those up to 60 years of age who have not previously received it and those 60 years and older who are at increased risk or who simply want the protection afforded by vaccination.
Also Vaccination Possible For Hepatitis A + B
Men who have sex with men are also at risk of getting hepatitis A. Hepatitis A is a different form of hepatitis and can be caught by anilingus. Almost everyone recovers from hepatitis A, but the disease can make you quite ill for a few months. There is a special vaccine for both hepatitis A and B . This combined vaccine is given in a series of three vaccination shots. Men who have sex with men get the hepatitis B for free but pay 25,- per shot for the combined hepatitis A-B vaccine.
Read Also: How Can Hepatitis C Be Treated
If I Already Have Hepatitis B Can The Vaccine Treat It
No. The hepatitis vaccine prevents hepatitis, but doesnt cure it if you already have it. If you have hepatitis B, there are other treatment options.
However, if you recently got exposed to the hepatitis B virus and you havent had the vaccine yet, tell your doctor right away. The vaccine and possibly other treatment can reduce your chances of getting hepatitis B if you get it within 2 weeks after you came into contact with the virus. The sooner you seek care after being exposed to hepatitis B, the better, so try to get there right away.
Why Is The Hepb Vaccine Recommended
People who dont know they’re infected can spread the hepatitis B virus. So it cant be avoided just by being careful. That’s why health experts recommend that all babies get the vaccine right from birth.
The HepB injection usually creates long-term immunity. Most infants who get the HepB series are protected from hepatitis B infection beyond childhood, into their adult years.
Eliminating the risk of infection also decreases risk for cirrhosis of the liver, chronic liver disease, and liver cancer.
Read Also: Blood Test For Hepatitis C Screening
How Are Cvs Pharmacy And Minuteclinic Different
At CVS Pharmacy, vaccinations for adolescents through seniors are administered by a certified immunizing pharmacist. Age and state restrictions apply.* No appointment necessary.
At MinuteClinic, vaccinations for children through seniors are administered by a medical provider. View wait times and schedule a visit online, or walk in anytime.
CVS Pharmacy and MinuteClinic are also at Target
Persons New To Canada
Health care providers who see persons newly arrived in Canada should review the immunization status and update immunization for these individuals, as necessary. In many countries outside of Canada, HB vaccine is in limited use.
All persons from a country that is endemic for HB should be assessed and vaccinated against HB if not immune and not infected. Individuals born in developing countries are more likely to be carriers of HB, necessitating vaccination of their sexual and household contacts based on review of their serologic test results. HB vaccine is recommended for all household contacts whose families have immigrated to Canada from areas in which there is a high prevalence of HB and who may be exposed to HB carriers through their extended families or when visiting their country of origin.
Children adopted from countries in which there is a high prevalence of HB infection should be screened for HBsAg and, if positive, household or close contacts in the adopting family should be immunized before adoption or as soon as possible thereafter. Adults going to pick-up children from these countries should be vaccinated before departure. Refer to Immunization of Persons New to Canada in Part 3 for additional information.
Also Check: Cvs Pharmacy Hepatitis B Vaccine
Read Also: Which Hepatitis Affects The Liver
Why Is The Hepatitis B Vaccine Important
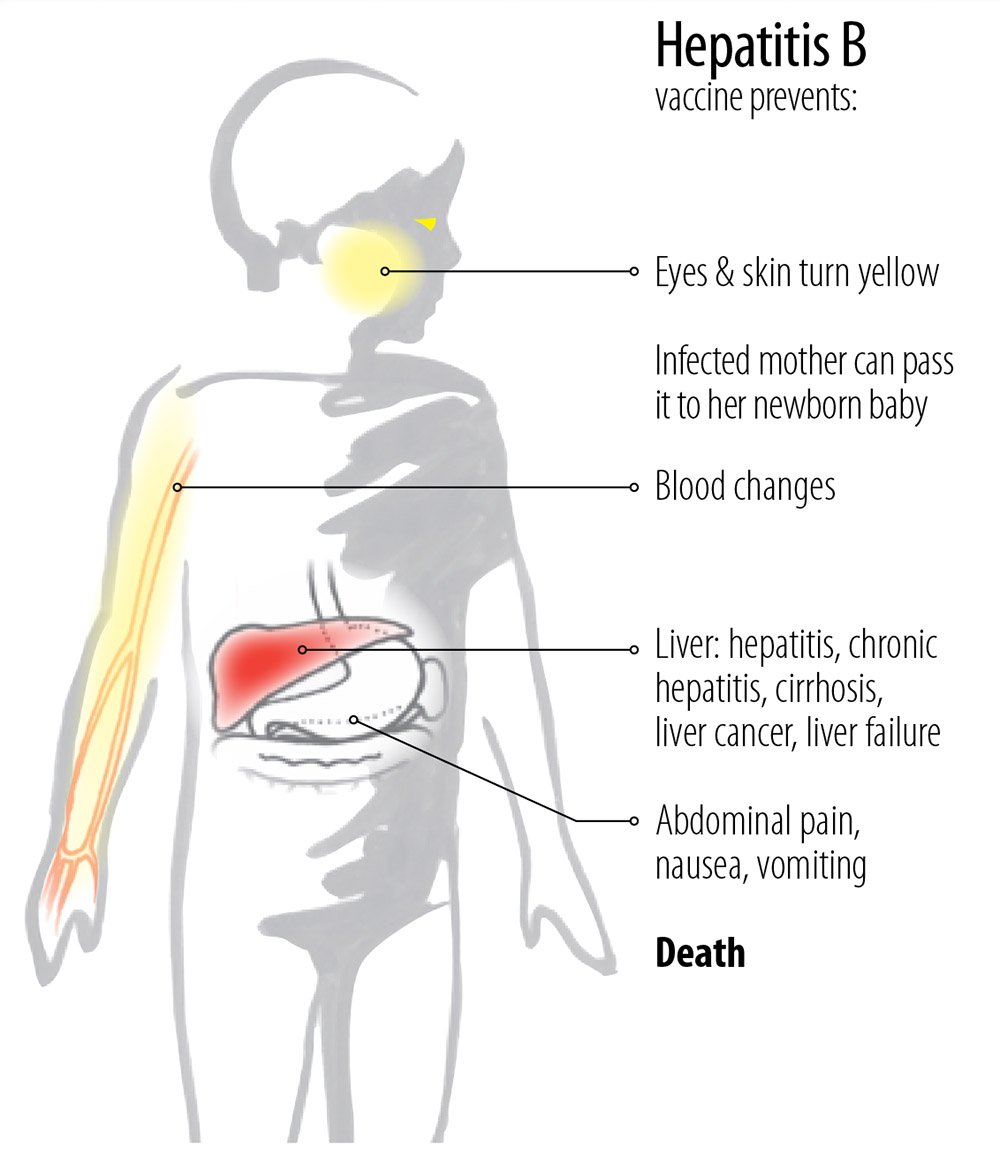
Because of the vaccine, cases of acute hepatitis B have decreased by a lot in the United States. But chronic hepatitis B is still common up to 2.2 million people in the United States have it. Chronic hepatitis B can lead to serious liver problems and even death.
Getting vaccinated is the best way to prevent hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B is a liver disease caused by a virus. There are 2 types of hepatitis B:
- Acute hepatitis B
- Chronic hepatitis B
Many children who get acute hepatitis B dont have any symptoms, but most adults do. Symptoms may include:
- Dark pee or clay-colored poop
- Pain in the muscles, joints, and stomach
Acute hepatitis B symptoms usually last a few weeks but they can last as long as 6 months.
If the acute hepatitis B infection does not go away after 6 months, its considered a chronic hepatitis B infection. Most people who have chronic hepatitis B dont have symptoms at first. But chronic hepatitis B is a lifelong illness that can lead to serious and possibly deadly liver problems, like:
- Has sex with a person who has hepatitis B
- Touches the blood or open sores of a person who has hepatitis B
All children and most adults need to get the hepatitis B vaccine.
Infants and children
All children need to get the hepatitis B vaccine as part of their routine vaccine schedule.
Children need 3 doses of the vaccine at the following ages:
- Birth for the first dose
- 1 through 2 months for the second dose
- 6 through 18 months for the third dose
Adults
Is It Okay To Get An Extra Dose Of Hepatitis B Vaccine

Yes. Although extra doses of vaccine are not recommended, you can think of the extra dose as another chance for the immune system to see the hepatitis B virus. A vaccine is not the only time the immune system will see the virus or bacteria contained in it. People may be exposed to the virus or bacteria at school or the store or when visiting family or friends. An extra dose of vaccine is like one more exposure, except the difference is that the virus or bacteria in any vaccine has been made safe, so it wont make you ill.
Don’t Miss: What Is Drug Induced Hepatitis
How Do You Catch Hepatitis B Virus
Blood from a person infected with hepatitis B virus is heavily contaminated with the virus. As a result, contact with blood is the most likely way to catch hepatitis B. Even casual contact with the blood of someone who is infected can cause infection.
Healthcare workers are at high risk of catching the disease, as are intravenous drug users and newborns of mothers infected with the virus. Sexual contact can also expose people to infection. The virus is also present in low levels in saliva.
How Does Hepatitis B Spread
Hepatitis B is transmitted when bodily fluids from an infected person enter the body of a noninfected person. The most common body fluids that transmit HBV are:
HBV can also spread by sharing toothbrushes or razors, or by chewing a baby’s food for them. Transmission most often occurs when someone has bleeding gums, nicks themselves shaving, or has a sore in their mouth. It’s also important to note that HBV can live on objects for seven days or more.
According to the CDC, the risk of transmitting HBV to a baby through breast milk is not a concern. This changes, however, if a mother has cracked or bleeding nipples. In this case, the mother should wait to resume breastfeeding until the nipples are no longer bleeding.
While transmission through kissing is not likely, this is controversial in the scientific and medical communities. This is because “deep kissing” with the exchange of a lot of saliva in someone with a cut or sore in their mouth could theoretically transmit HBV.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Treatment For Chronic Hepatitis B
Managing Fever After Immunisation
Common side effects following immunisation are usually mild and temporary . Specific treatment is not usually required.
There are a number of treatment options that can reduce the side effects of the vaccine such as giving extra fluids to drink and not overdressing if there is a fever.
Although routine use of paracetamol after vaccination is not recommended, if fever is present, paracetamol can be given check the label for the correct dose or speak with your pharmacist, especially when giving paracetamol to children.
What Hepatitis B Immunisation Involves
Full protection involves having 3 injections of the hepatitis B vaccine at the recommended intervals.
Babies born to mothers with hepatitis B infection will be given 6 doses of hepatitis B-containing vaccine to ensure long-lasting protection.
If you’re a healthcare worker or you have kidney failure, you’ll have a follow-up appointment to see if you have responded to the vaccine.
If you have been vaccinated by your employer’s occupational health service, you can request a blood test to see if you have responded to the vaccine.
You May Like: Why Do You Need 3 Hepatitis B Shots
Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis B
Over half of those infected with HBV dont have symptoms. The best way to know if you have HBV is to get a blood test. These tests can detect HBV years before symptoms develop. Having this information is important because early treatment can prevent liver damage.
HBV testing is recommended for the following populations:
- People who have household or sexual contact with those infected with HBV
- People who inject drugs
- Those with elevated alanine aminotransferase levels
- People born in countries with a greater than 2% rate of HBV
What Is In The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Vaccines are given by a course of three injections, usually as part of the 6-in-1 vaccine scheme.
Although there are different types of vaccines, they usually contain one of the proteins from the surface of the hepatitis B virus thats then inserted in to the genetic code into yeast cells which stops the risk of viral DNA getting into the final product.
They also contain small amounts of sodium chloride and aluminium, and can contain yeast and formaldehyde.
Dont Miss: What Is Hepatitis A B C
Also Check: Can A Hepatitis B Carrier Get Vaccinated
What Should I Tell My Health Care Provider Before Receiving A Hepatitis B Vaccine
Before receiving a hepatitis B vaccine, tell your health care provider:
Ask your health care provider about possible side effects from getting a hepatitis B vaccine. Your health care provider will tell you what to do if you have side effects.
Who Should Receive The Hepatitis B Vaccine
For most people, the hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective. About 90% of people who receive three vaccine doses are protected against hepatitis B for over 30 years.
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends the hepatitis B vaccine for the following groups:
- All babies, starting just after birth
- Children and adolescents under 19 years old
- Adults ages 1959 who have not previously completed vaccination
- Adults ages 60 and over with a high risk of contracting HBV
Adults ages 60 and over who do not have any hepatitis B risk factors can receive the hepatitis B vaccine, but it is optional.
Hepatitis B spreads when the bodily fluids of an infected person enter another person’s body. Sexual contact is one way it can be spread. A person with HBV can spread it to their baby during childbirth. Other ways in which HBV may be transmitted include:
- Sharing medical equipment, whether at home or in a hospital setting, with a person who has an HBV infection
- Sharing syringes with a person who has hepatitis B, such as during injection drug use or at-home piercing or tattooing
- Sharing personal items, such as razors or toothbrushes, with someone who has hepatitis B
- Coming into contact with the sores or blood of a person who has hepatitis B
Read Also: Can You Donate Blood If You Have Hepatitis B
Are Hepatitis B Virus Infections Easily Avoided
Large quantities of hepatitis B virus are present in the blood of people with hepatitis B in fact, as many as one billion infectious viruses can be found in a milliliter of blood from an infected individual. Therefore, hepatitis B virus is transmitted in the blood of infected individuals during activities that could result in exposure to blood, such as intravenous drug use, tattooing, or sex with people who are infected. However, it is also possible to catch hepatitis B virus through more casual contact, such as sharing washcloths, toothbrushes or razors. In each of these cases, unseen amounts of blood can contain enough viral particles to cause infection. In addition, because many people who are infected don’t know that they are infected, it is very hard to avoid the chance of getting infected with hepatitis B virus.