How Common Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is fairly common in Africa and the western Pacific region. Throughout the world, there are about 292 million people who are infected with chronic hepatitis B. In the U.S., the figure exceeds 2 million people.
The number of infections had been falling in the U.S., but fewer vaccinations among adults combined with the onset of the opioid crisis and injected drug usage has resulted in the numbers rising again. Infected women can pass the infection on to their babies. Children who are infected before age 5 are more likely to have chronic infection than those infected later in life.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C An Autoimmune Disease
What Is The Role Of Liver Transplantation In Hepatitis B
Liver transplantation has been successful in patients who have irreversible, life-threatening complications of hepatitis B. This includes patients with liver failure due to end-stage cirrhosis or unusually severe hepatitis. Liver transplantation does not cure hepatitis B, and hepatitis may occur in the new liver. The incidence of recurrent hepatitis has been reduced to less than 10% through use of lamivudine and HBIG in transplant recipients. Use of these agents has also improved long-term survival, with 75% of patients alive after five years.
Causes And Risk Factors
Hepatitis B is caused by a viral infection. The virus can survive outside of the body for at least seven days. During this time, it can infect a person if it enters his or her body. It can be detected within 30 to 60 days after infection. It can persist and develop into chronic hepatitis B, especially if someone is infected at a young age.
It can be transmitted or spread in several ways, including :
Anyone can get this virus. But some people are at a greater risk of exposure to the virus. This includes people who:
- Have multiple sexual partners
- Travel to countries with a high hepatitis B rate
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis A
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis B
If you think you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
A doctor or other healthcare professional may administer the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin. This is a combination of antibodies that provide short-term protection against the virus.
Though both can be given up to a week after exposure, theyre most effective at preventing infection if administered within 48 hours.
If you receive a diagnosis of acute hepatitis B, a doctor may refer you to a specialist. They may advise you to get regular blood tests to ensure you dont develop chronic hepatitis.
Many people with acute hepatitis B dont experience serious symptoms. But if you do, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter pain mediation, like naproxen, when needed
Other lifestyle changes may also be needed to manage your infection, such as:
- eating a nutritious, balanced diet
- avoiding substances that can harm your liver, such as:
- certain herbal supplements or medications, including acetaminophen
If blood tests show you still have an active infection after 6 months, your doctor may recommend further treatment, including medications to help control the virus and prevent liver damage.
The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Getting the hepatitis B vaccine is one of the most effective ways to prevent hepatitis B. Its usually administered in two, three, or four doses. In many countries, infants receive their first dose of the vaccine at birth.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that infants receive their first dose of the vaccine at birth and finish all doses at 6 to 18 months old.
The CDC also recommends all children under the age of 19 years old be vaccinated if they havent already received the vaccination.
Adults can also get the hepatitis B vaccine. The vaccine is generally recommended if you have an increased risk of contracting the virus. Some of these risk factors include:
- traveling to or living in a region where hepatitis B is common
- being sexually active with more than one partner or with a partner who has hepatitis B
- working in a medical setting or other workplaces where youre exposed to bodily fluids
- using intravenous drugs and sharing drug equipment
- having chronic liver disease, a human immunodeficiency virus infection, a hepatitis C infection, diabetes, or kidney disease on dialysis
If youve been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and havent been vaccinated, try to see a doctor right away. They can administer the first dose of the vaccine, though youll need to follow up to receive the remaining doses over the next few months.
They may also prescribe a medication called
You May Like: How Does One Contract Hepatitis B
How Common Is It
In 2006, the Public Health Agency of Canada reported the incidence of HBV as 2.0 cases for every 100,000 or about 650 cases reported annually in Canada. In the year 2013, the incident rate was 0.5 per 100,000 . Incidence of the disease varies from region to region but has been declining due to increasing use of the vaccine and universal immunization programs.
Read Also: Hepatitis A Ab Total Reactive
Who Should Be Vaccinated For Hepatitis B
All newborns should be vaccinated. Also, people who are under 18 who were not vaccinated at birth should also get the vaccine. Other groups who should be sure to be vaccinated are those in certain high-risk categories, such as:
- People who have more than one sexual partner.
- Men who have sex with men.
- Adults with diabetes.
- Sexual partners of infected people and people who share households with infected individuals.
- People who are exposed to blood and other bodily fluids, including healthcare and public safety professionals, and people who work in jails and other places taking care of people who cant take care of themselves.
Don’t Miss: What Does The Hepatitis B Vaccine Prevent
What Are The Symptoms Of Hbv
Hepatitis B virus can cause an acute illness with symptoms that last several weeks, including yellowing of the skin and eyes , dark urine, extreme fatigue, nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain. Most of the time HBV infection is ASYMPTOMATIC.
Joint pains, muscle aches, rash, and jaundice may occur in some people. People can take several months to a year to recover from the symptoms. These people may not know that they are infected, and may therefore not go and see a doctor. People with chronic hepatitis B infection may later develop serious problems like liver cancer and liver failure. These people may not know that they are infected, and may therefore not go and see a doctor. People with chronic hepatitis B infection may later develop serious problems like liver cancer and liver failure.
Prevention And Control Of Hepatitis B
- The hepatitis B vaccine is the mainstay of hepatitis B prevention.
- WHO recommends that all infants receive the hepatitis B vaccine as soon as possible after birth, preferably within 24 hours.
- Simple environmental procedures can limit the risk of infection to health care workers, laboratory personnel, and others. Examples of specific precautions include the following:
- Gloves should be used when handling all potentially infectious materials
- protective garments should be worn and removed before leaving the work area
- masks and eye protection should be worn whenever splashes or droplets from infectious material pose a risk
- only disposable needles should be used
- needles should be discarded directly into special containers without re-sheathing
- work surfaces should be decontaminated using a bleach solution and laboratory personnel should refrain from mouth pipetting, eating, drinking, and smoking in the work area.
- Metal objects and instruments can be disinfected by autoclaving or by exposure to ethylene oxide gas.
You May Like: What’s The Signs Of Hepatitis C
Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis B
Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis B. Many people who have hepatitis B dont have symptoms and dont know they are infected with hepatitis B. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis B, which can lower your chances of developing serious health problems.
Your doctor may recommend screening for hepatitis B if you9,14
- were born in an area of the world where 2 percent or more of the population has hepatitis B infection, which includes Africa, Asia, and parts of the Middle East, Eastern Europe, and South America
- didnt receive the hepatitis B vaccine as an infant and have parents who were born in an area where 8 percent or more of the population had hepatitis B infection, which includes sub-Saharan Africa and parts of Asia
- are HIV-positive
- are a man who has sex with men
- have lived with or had sex with a person who has hepatitis B
- have an increased chance of infection due to other factors
Immunisation For Hepatitis B
Immunisation is the best protection against hepatitis B infection. A course of vaccination is recommended for all babies and people in high-risk groups.
Immunisation can be with a vaccine against hepatitis B alone or with a combination vaccine. To be immunised, contact your doctor or local council.
Protection against hepatitis B is available free of charge under the National Immunisation Program Schedule. In Victoria, immunisation against hepatitis B is free for:
- Babies at birth immunisation against hepatitis B alone as soon as possible after birth.
- Babies at 2, 4 and 6 months combination immunisation in the form of a diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, hepatitis B, polio and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine .
- Premature babies at 12 months premature babies born under 32 weeks gestation or under 2,000g birth weight receive a single booster dose.
- Children up to and including 9 years of age.
- People aged less than 20 years having a catch-up immunisation.
- Refugees and humanitarian entrants aged 20 years and above.
In Victoria, free hepatitis B vaccine is provided for people who are at increased risk of infection, including:
Immunisation is also recommended, but not necessarily free, for people who are at increased risk of infection, including:
Read Also: How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis C Without Treatment
What Is Delta Hepatitis
Delta hepatitis is caused by a virus that only infects people who already have hepatitis B. The delta hepatitis virus is an RNA virus, meaning that its genetic material is made up of ribonucleic acid. It is spread through exposure to contaminated blood, especially with illicit, intravenous drug use, and by sexual contact. Delta hepatitis can be acquired at the same time as acute hepatitis B. When this happens, infected people are quite sick but most are eventually able to eliminate the viruses from their bodies. People who already have chronic hepatitis B can acquire delta hepatitis as well. This often causes severe inflammation of the liver, and the viruses are less likely to be cleared.
Delta hepatitis makes chronic hepatitis B much worse. It increases the risk of complications, especially cirrhosis, which occurs in up to two-thirds of patients.
There is no vaccine against delta hepatitis. Interferon treatment may cause improvement in the hepatitis, but relapse is common after therapy is stopped. Prevention includes avoiding contaminated needles and practicing safer sex . Universal vaccination of newborns with hepatitis B vaccine effectively prevents delta hepatitis because the delta hepatitis virus only causes disease in the presence of hepatitis B virus.
Treatment For Acute Hepatitis B
If youre diagnosed with hepatitis B, your GP will usually refer you to a specialist, such as a hepatologist .
Many people dont have any troublesome symptoms, but if you do feel unwell, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter painkillers, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen, for abdominal pain
- maintain a cool, well-ventilated environment, wear loose clothing, and avoid hot baths or showers if itching is a problem
- take medication such as metoclopramide to stop you feeling sick and chlorphenamine to reduce itching your doctor can give you a prescription for these if necessary
Most people recover completely in a couple of months, but youll be advised to have regular blood tests to check that youre free of the virus and havent developed chronic hepatitis B.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B What Causes It
What Happens After A Hepatitis B Infection
Some people carry the virus in their bodies and are contagious for the rest of their lives. They should not drink alcohol, and should check with their doctor before taking any medicines to make sure these won’t cause more liver damage.
Anyone who has ever tested positive for hepatitis B cannot be a blood donor.
What Are The Treatment Options For Chronic Hep B
For people with acute hep B infection experiencing mild symptoms, doctors often recommend rest, a healthy diet, and fluids to speed up recovery. Severe symptoms may need to be treated in a hospital.
According to the Hepatitis B Foundation, there are currently seven drugs approved by the FDA to treat chronic hep B in the United States. Not everybody needs to take medication, but some people will need to take medication for the rest of their lives.
These drugs fall into one of two categories:
- Antiviral drugs. These drugs help reduce inflammation and liver damage. Theyre usually taken daily in pill form for at least a year.
- Immune modulator drugs. These drugs boost your immune system to help your body fight off the virus. Theyre administered as an injection over 6 to 12 months.
Theres no cure for hep B, acute or chronic, at the moment. However, clinical trials continue to investigate new treatment options.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Antibody Screen Result
Important Things To Know About Hepatitis B Core Antibody
Someone who has markers of past infection, particularly hepatitis B core antibody, can be at risk for hepatitis B reactivation. Reactivation can be triggered by immunosuppressive therapies and cause significant life-threatening challenges. If you test HBcAb+, please talk to your doctor about what that means, and make sure you notify all future health care providers.
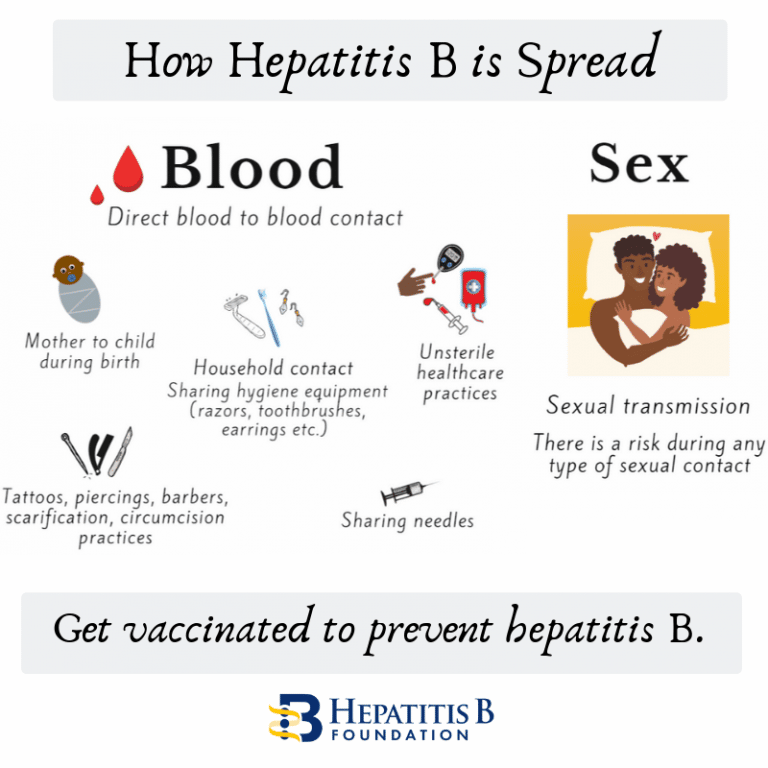
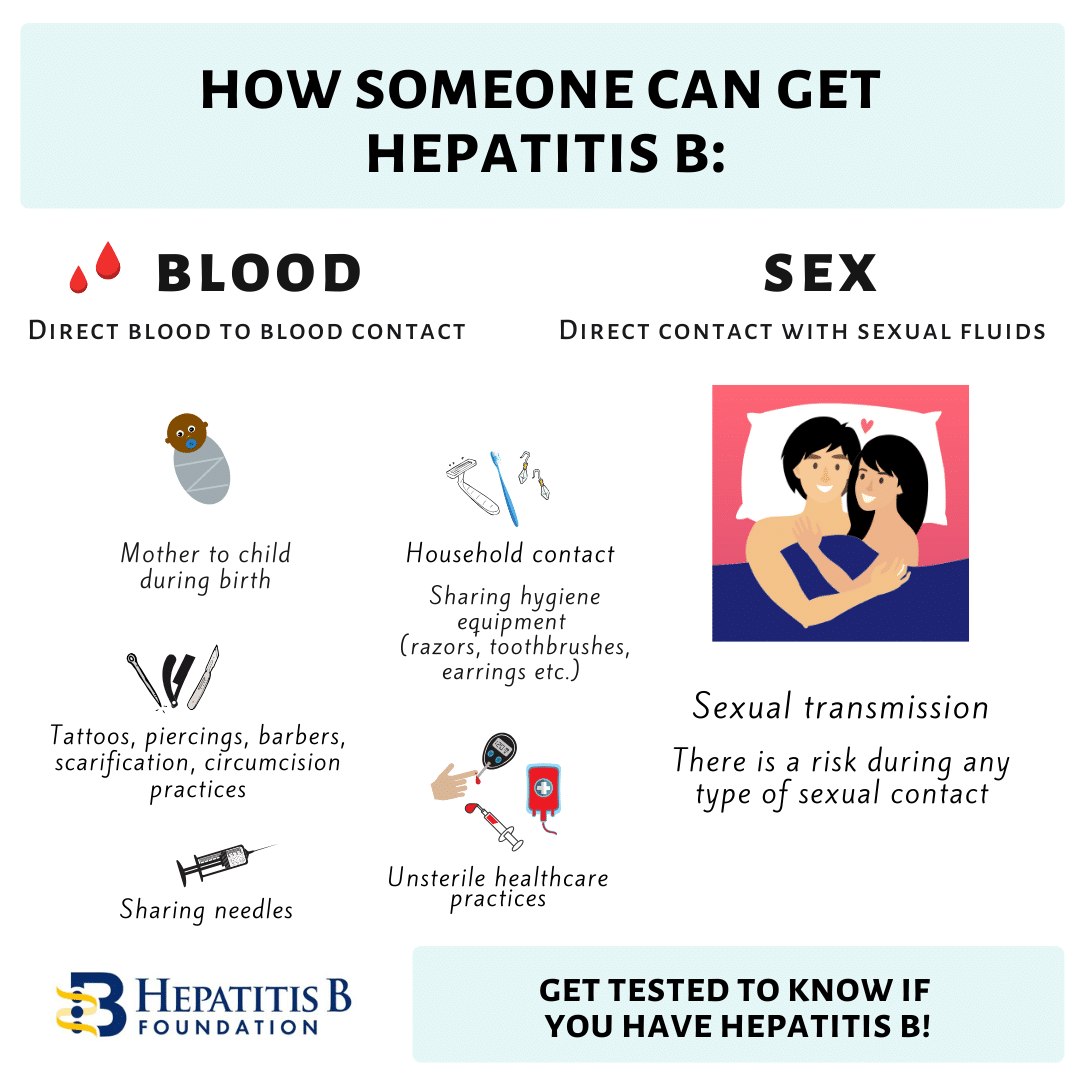
How Can I Catch Hbv
Hepatitis B virus is transmitted between people by contact with the blood or other body fluids of an infected person. In Africa the virus is mainly transmitted early in life, from mother-to-child or between children. HBV is spread through a break in the skin , or through sexual intercourse. HBV is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV. Unlike HIV, HBV can survive outside the body for at least 7 days. During that time, the virus can still cause infection if it enters the body of a person who is not infected.
Unless vaccinated at the time of birth, these babies can become chronic carriers, which means they are infected with the virus for life. Of children who become infected with the virus between one and five years of age, 30-50 percent become carriers.
In many developed countries , patterns of transmission are different than those mentioned above. Today, the majority of infections in these countries are transmitted during young adulthood by sexual activity and injecting drug use. HBV is a major infectious occupational hazard of health workers.
HBV is not spread by contaminated food or water, and cannot be spread casually in the workplace.
The virus incubation period is 90 days on average, but can vary from about 30 to 180 days. HBV may be detected 30 to 60 days after infection and persist for widely variable periods of time.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Screening Guidelines Cdc
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis B
There are two types of hepatitis B infection: acute and chronic.
Acute
An acute infection happens at the beginning, when you first get infected with hepatitis B. Many people are able to clear it from their bodies and recover. In fact, this is true of about 4 in 5 adults who are infected.
Chronic
If you are not able to clear the infection within six months or longer, you have chronic hepatitis B. It is chronic hepatitis B that leads to inflammation and the serious, and possibly fatal, illnesses of cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer. Treatment can slow disease progress, reduce the chance of liver cancer and increase your chances of surviving.
What Are Clinical Trials For Hepatitis B
Clinical trialsand other types of clinical studiesare part of medical research and involve people like you. When you volunteer to take part in a clinical study, you help doctors and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future.
Researchers are studying many aspects of hepatitis B, such as
- progression of hepatitis B and long-term outcomes
- new treatments for hepatitis B
- prevention of reactivated or worsening hepatitis B in people receiving cancer treatment
Don’t Miss: Genotype Test For Hepatitis C
Who’s Most At Risk Of Hepatitis B
People at highest risk of hepatitis B include:
- people born or brought up in a country where the infection is common
- babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B
- people who have ever injected drugs
- close contacts, such as family members, of someone with long-term hepatitis B infection
The risk of getting hepatitis B for travellers going to places where the infection is common is generally considered to be low if the activities mentioned above are avoided.
Your GP can arrange for you to have a blood test to check for hepatitis B and have the hepatitis B vaccination if you’re at a high risk.
How Do I Know If I Have Hbv
A rapid point-of-care test after a finger prick or a simple blood test can tell if you are infected with the hepatitis B virus.
These tests can also help your doctor determine whether you are currently ill with hepatitis B, or if you are a chronic carrier. Although there is no treatment for the disease, bed rest and a good diet are important. Alcohol and medications should be restricted. Follow-up blood tests are necessary to tell if the disease has gone.
Also Check: Hepatitis Vaccine Schedule For Adults