What Does Anti Hbs Positive Mean
Anti-HBS is a type of laboratory test that is performed on people who are thought to have hepatitis B. The test, which can be used to determine whether the person has already been immunized by exposure to Hepatitis B virus or by vaccination, can also be used to determine whether the virus has been destroyed by the body and acquired immunity for life. The anti-HBS test is also used to check whether the vaccine is retained, or in other words, whether the body produces antibodies against HBsAG, which is defined as the surface antigen of the Hepatitis B virus. Anti-RLS test is also performed to determine whether the person is immune to this virus before the hepatitis B vaccine is administered.
Counseling Practices That Educate Support And Motivate Clients Undergoing Screening
Clients might need help deciding whether to get screened, understanding the test results, and determining their next steps. Even when services offered through the substance abuse treatment program are limited, discussing testing with clients presents an opportunity for counselors to motivate clients for change by confronting substance use and by making choices that improve their overall health. However, this may also be true when services are offered on-site through substance abuse treatment programs. A study at one methadone clinic that offered hepatitis screening and vaccination revealed that although the majority of clients completed screening , only 54.7 percent of clients who lacked for hepatitis A received vaccinations and only 2.9 percent of clients who lacked immunity for received vaccinations .
The Consensus Panel makes the following general recommendations while recognizing that, in some programs, the counselors role may be limited:
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B Caused By
Question 1 What Is The Clinical Indication For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitation
Hepatitis B surface antibody quantitation is used to determine hepatitis B immune status, ie, to determine if the patient has developed immunity against the hepatitis B virus. Such immunity may develop following exposure to the hepatitis B virus or its vaccine.
Patients at higher risk of exposure to the virus include:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- Sex partners of infected persons
- People with more than 1 sex partner in the last 6 months
- People with a history of sexually transmitted infection
- Men who have sex with men
- Injection drug users
- Household contacts of an infected person
- Healthcare and safety workers who have contact with blood and body fluids
- People who have lived or traveled in an area in which hepatitis B is common
- People who live or work in a prison
Testing is not recommended routinely following vaccination. It is advised only for people whose subsequent clinical management depends on knowledge of their immune status. These people include:
- Chronic hemodialysis patients
- Immunocompromised people, including those with HIV infection, hematopoietic stem-cell transplant recipients, and people receiving chemotherapy
- Infants born to women who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Sex partners of people who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Healthcare and public safety workers who have contact with blood or body fluids
Also Check: How Long Can Hepatitis C Go Undetected
Question 2 What Is The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
The hepatitis B surface antibody is the antibody that is produced in response to hepatitis B surface antigen , a protein present on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. Anti-HBs appears after convalescence from acute infection and lasts for many years. It can also be produced in response to hepatitis B vaccination.
Other hepatitis B antibodies are not produced in response to vaccination. This is because these antigens are not in the vaccine.
What Do The Results Mean
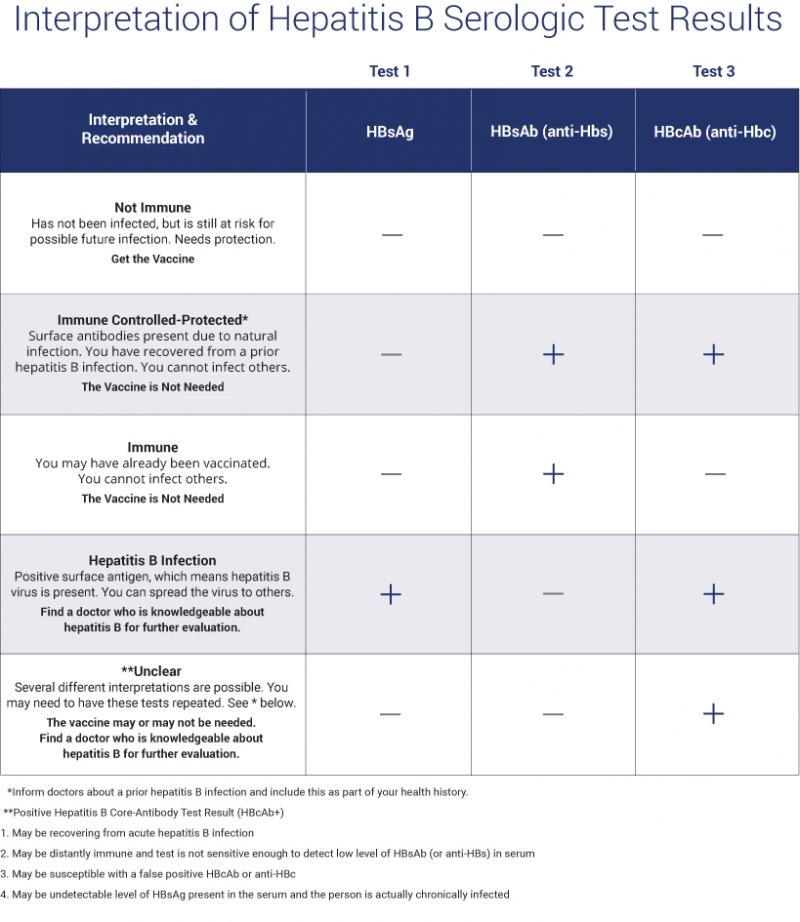
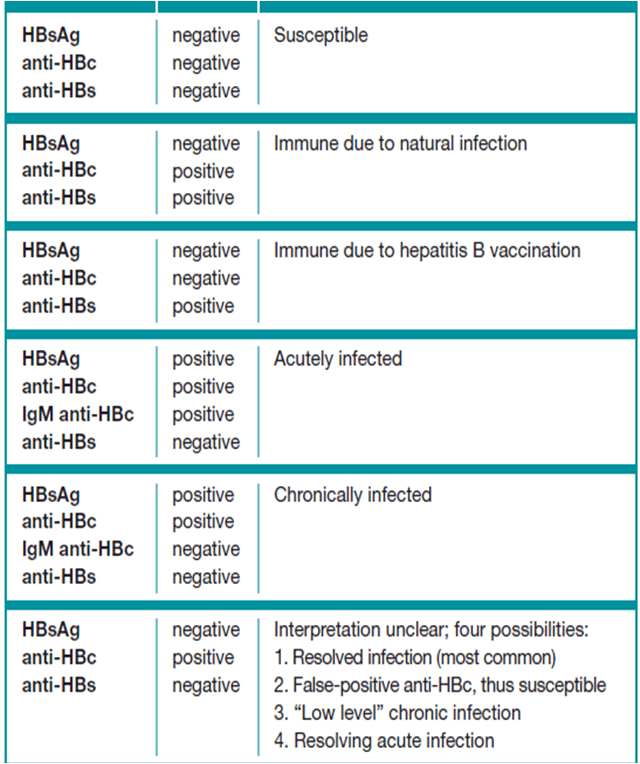
A hepatitis B blood panel consists of three tests that can be done with just one blood sample:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen . A positive test indicates that youre infected with hepatitis B and that you can spread it to other people. Further tests are needed to see if you have an acute or chronic infection.
- Hepatitis B core antibody . A positive result can indicate a past or current hepatitis B infection, but doesnt mean youre immune. A positive result needs to be interpreted by a doctor by examining the results of the other two tests.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody . A positive test indicates that youre protected from hepatitis B either through previous infection or vaccination .
The combination of these tests can indicate your hepatitis B status and whether you need to be vaccinated. Your test will give a negative or positive result for each category depending on whether your results are above or below the cutoff value.
Most peoples test results fall into the following categories. But its possible to have a result that doesnt fall into one of these groups. If youre reading your results yourself, be careful not to confuse HBsAb with HBcAb.
| HBsAG |
is associated with hepatitis B immunity after vaccination. But research has found that anti-HBs decline over time.
A found that more than 95 percent of people had anti-HBs levels greater than 10IU/L two years after vaccination. But this rate decreased to 70 percent after eight years.
Recommended Reading: Ok Google How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Is Hepatitis Related To The Liver
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the blood, and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis.
Why It Is Done
You may need testing if:
- You have symptoms of hepatitis.
- You may have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus. You are more likely to have been exposed to the virus if you inject drugs, have many sex partners, or are likely to be exposed to body fluids .
- You’ve had other tests that show you have liver problems.
- You are pregnant.
- You or your doctor wants to know if you are protected from getting the disease.
The tests also are done to help your doctor decide about your treatment and see how well it’s working.
Don’t Miss: Incubation Period Of Hepatitis D
The Fourth Or Reactivation Phase
The previous phase of HBeAg-negative/anti-HBe-positive inactive HBsAg carrier state is not synonymous with permanent termination of HBV replication and of HBV-induced chronic liver damage. Although the majority of patients may remain for life in an inactive HBsAg carrier state, and a number of them may also lose HBsAg and enjoy a complete recovery, others retain or redevelop over time significant HBV replication and progressive liver damage .
This state of HBV-induced liver damage has been first referred to as HBeAg-negative/anti-HBe-positive CHB, and similarly to HBeAg-positive CHB, it also represents an immune active phase in the natural course of chronic HBV infection. It is generally viewed as a fourth phase in the natural history of chronic HBV infection usually developing because of reactivation of HBV replication, though in some patients, it may immediately follow the second phase of HBeAg-positive CHB despite clearance and even seroconversion of HBeAg .
Stephen N.J. Korsman MMed FCPath, … Wolfgang Preiser MRCPath, in, 2012
Provides Information To Assist In Interpretation Of The Test Results
A positive result indicates recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection or acquired immunity from HBV vaccination. This assay does not differentiate between a vaccine-induced immune response and an immune response induced by infection with HBV. A positive total antihepatitis B core result would indicate that the hepatitis B surface antibody response is due to past HBV infection.
Per assay manufacturers instructions for use, positive results, defined as anti-HBs levels of 12.0 mIU/mL or greater, indicate adequate immunity to hepatitis B from past hepatitis B or HBV vaccination. However, per current CDC guidance, individuals with anti-HBs levels greater than 10 mIU/mL after completing an HBV vaccination series are considered protected from hepatitis B.
Negative results, defined as anti-HBs levels of less than 5.0 mIU/mL, indicate a lack of recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B or inadequate immune response to HBV vaccination. The US Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices does not recommend more than 2 HBV vaccine series in nonresponders.
Indeterminate results, defined as anti-HBs levels in the range from 5 to 11.9 mIU/mL, indicate inability to determine if anti-HBs is present at levels consistent with recovery or immunity. Repeat testing is recommended in 1 to 3 months.
Dont Miss: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
Don’t Miss: What Medicine Do You Take For Hepatitis C
What Are My Next Steps Once I Get My Results
It can be difficult to understand what the results of your test mean. A healthcare provider can help you interpret your results and decide whether you need to take further action:
- If your results suggest that youre already immune to hepatitis B and arent contagious, you likely wont need to do anything.
- If your results suggest that youre not immune, a doctor may recommend vaccination, especially if youre somebody whos at a high risk of infection.
You may also need additional testing if more information is needed to interpret your results.
Status Of General Information And Serum Test Results Of The Survey Respondents
A total of 506 neonates were included in this study, and 48 were lost to follow-up. Among them, 3 patients died, 9 patients had incomplete case data, and 36 patients had incomplete information. Of the 458 neonates who were finally included, 125 were not tested for serology, and 333 were tested for hepatitis B antibodies. Among the newborns tested for serum antibodies, 269 were antibody positive and 64 were antibody negative.
Read Also: Hepatitis B How To Treat
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
Health Streets Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test checks for a current infection of the hepatitis B virus. If the test is positive, then the person can be contagious to others.
Online registration is simple. You choose the lab location based on ZIP code during registration. An authorization barcode is instantly emailed to you and texted directly to the phone of the person being tested. A map of the clinic location will accompany the barcode. The registrant can then walk into the testing facility and show the barcode along with photo ID. Results are fast and stored securely online. Individuals and employers can register online or call to order tests.
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
Also Check: Cost For Hepatitis B Test
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
Donât Miss: What Does Diffuse Hepatic Steatosis Mean
Question 5 What Is The Natural History Of Hepatitis B Surface Antibody During Acute Hepatitis B Infection And Convalescence
HBsAg can be detected in the blood 4 to 10 weeks after exposure. This corresponds to onset of symptoms and viremia detectable by nucleic acid amplification methods. Most hepatitis B infections are self-limited and are associated with disappearance of HBsAg within 4 weeks of onset of symptoms. The anti-HBs then appears and increases to a plateau level that persists indefinitely.2
You May Like: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Virus
Analysis Of The Positive Results And Influencing Factors Of Hepatitis B Antibody In Hospitalized Neonates With Aghbs Positive Mothers
- Department of Neonatology, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children’s Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China
Purpose: To investigate the results of positive antibody to hepatitis surface antigenin hospitalized neonates whose mothers were hepatitis B surface antigen positive and to explore the influencing factors.
Method: The study subjects were hospitalized neonates whose mothers were positive for AgHBs. According to the serological test results of five immune markers of hepatitis B virus , they were divided into positive for anti-HBs and negative for anti-HBs. Retrospective analysis of relevant factors affecting results of anti-HBs.
Result: 269 cases were positive for anti-HBs and 64 cases were negative for anti-HBs. Univariate analysis results: the number of hepatitis B immunoglobulin injections after birth, whether HBIG was injected within 6h, whether Hepatitis B vaccine was injected within 6h, whether combined immunization within 12h, whether Hep B was vaccinated on time after discharge, whether preterm birth, and whether low birth weight infants were statistically significant . The results of binary logistic regression analysis: HBIG injection time 6h , combined immunization time 12h were protective factors premature infants , ALB/GLO and failure to complete three vaccinations on time were risk factors .
Combined Immunization Within 12h Is A Protective Factor For Anti
The results of this study showed that the time interval between the injection of Hep B and HBIG 12h was a protective factor for the production of anti-HBs. This is consistent with the research results of China’s 20162017 National Project on Prevention of Mother-to-Child Hepatitis B Transmission. Children who received combined immunization within 12h to 24h after birth were 2.9 times more likely to be infected with HBV than newborns vaccinated within 12h . The blocking effect of combined immunization is better than that of Hep B alone, and the protection rate of combined immunization within 1h of birth can reach 97% , A prospective, multi-center observational study of neonates born to AgHBs positive mothers found that the mother-to-child transmission rate was 0.9% when the neonates were injected with HBIG and Hep B within an average of 0.17h after birth . The guidelines recommend that neonates must inject HBIG intramuscularly within 12h after birth, and at the same time inject the first dose of Hep B intramuscularly in different parts . At present, most neonates can be vaccinated with Hep B within 24h after birth, and few can be vaccinated within 1h. It is recommended to optimize the workflow of combined immunization to ensure that newborns are vaccinated within 1h after birth.
Also Check: Most Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Question 7 Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Antibody Always Acquired After A Completed Vaccination Protocol
No. After 3 intramuscular doses of vaccine, > 90% of healthy adults and > 95% of those < 19 years of age develop immunity .1 However, there is an age-specific decline in development of immunity. After age 40 years, about 90% of people become immune, but by age 60 years, only 75% of people become immune.1 Larger vaccine doses or an increased number of doses are required to induce immunity in many hemodialysis patients and in other immunocompromised people.1
References
This FAQ is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. A clinicians test selection and interpretation, diagnosis, and patient management decisions should be based on his/her education, clinical expertise, and assessment of the patient.Document FAQS.105 Revision: 0
Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
The aim of treating chronic HBV infection is primarily to prevent complications since cure is often not achievable.
Evaluation to decide if therapy is indicated includes HBeAg and anti-HBe serology, HBV load, transaminases and liver biopsy. Patients with evidence of significant viraemia and chronic inflammation without cirrhosis will benefit the most from therapy. Since HBV has a reverse transcriptase enzyme it is susceptible to a range of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: lamivudine, emtricitabin, telbivudine, tenofovir entecavir and adefovir dipivoxil show response rates of between 20% and 40%. These drugs are well-tolerated, but resistance develops, especially to lamivudine and emtricitabine.
The other alternative for chronic HBV therapy is pegylated interferon therapy. Interferon has the advantage of a higher rate of permanent response but has more side effects and adverse effects than the nucleoside analogues .
Janice Main, Howard C. Thomas, in, 2010
Recommended Reading: Is There A Cure For Hepatitis B
Purpose Of The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test
The HBsAb test determines the presence and quantity of HBV antibodies in your blood in order to establish how immune you are to the virus. These antibodies are “encoded” by your immune system when it encounters the HBV virus through blood or sexual contact, or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine. Your body uses the antibodies to attack the virus if it appears again.
There are two types of antibodies produced in response to the hepatitis B virus:
- Immunoglobulin M is the antibody that mounts the initial attack but eventually fades away.
- Immunoglobulin G is the antibody that provides long-lasting immune protection against HBV. The immunity can last for many years, but it gradually wanes over time.
The HBsAb test may be used to look for prior exposure to HBV . By comparing levels of IgM and IgG, a healthcare practitioner can also use the test to monitor your recovery from an acute HBV infection.
Additionally, the HBsAb test can reveal whether you are successfully vaccinated, not successfully vaccinated, or indeterminately vaccinated. A booster vaccine may be needed if the HBsAb level drops below protective levels.
The HBsAb test should not be confused with either the hepatitis B surface antigen test or the hepatitis B core antibody test, both of which are used to determine if you have been infected with HBV.
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. Its transmitted through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not transmitted through sharing utensils or kissing. Its also not transmitted through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure. Symptoms can last for several weeks.
But even without symptoms, you can still transmit the infection to others. The virus can live outside the body and remains infectious for at least
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious condition. Its associated with many serious complications, some of which can be life threatening.
But there are many treatment options available and multiple ways you can prevent infection, including getting vaccinated.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a doctor to prevent infection and determine the best course of treatment for you.
Don’t Miss: How Bad Is Hepatitis B