Hepatitis B During Pregnancy
If a woman with HBV becomes pregnant, they may transmit the virus to their baby. Women should inform the doctor who delivers their baby that they have HBV.
The infant should receive an HBV vaccine and HBIG with 1224 hours of birth. This significantly reduces the risk that they will develop HBV.
The HBV vaccine is safe to receive while pregnant.
People with a high risk of HBV include:
- the infants of mothers with HBV
- the sexual partners of people with HBV
- people who engage in sexual intercourse without contraception and those who have multiple sexual partners
- men who have sex with men
- people who inject illicit drugs
- those who share a household with a person who has a chronic HBV infection
- healthcare and public safety workers who are at risk of occupational exposure to blood or contaminated bodily fluids
- people receiving hemodialysis, which is a type of kidney treatment
- people taking medications that suppress the immune system, such as chemotherapy for cancer
People can prevent HBV infection by:
- wearing appropriate protective equipment when working in healthcare settings or dealing with medical emergencies
- not sharing needles
- following safe sexual practices
- cleaning any blood spills or dried blood with gloved hands using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 10 parts water
A vaccine against HBV has been available since 1982.
People who should receive this vaccine include:
How Many People Have Hepatitis B
In the United States, an estimated 880,000 to 1.89 million people are chronically infected with HBV. New cases of HBV infection in the United States had been decreasing until 2012. Since that time, reported cases of acute hepatitis B have been fluctuating around 3,000 cases per year. In 2020, 2,157 cases of acute hepatitis B were reported however, because of low case detection and reporting, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that there were 14,000 acute hepatitis B infections. The rate of acute cases of HBV decreased by 32% after 2019 which may be related to the disruptions of the COVID-19 pandemic. For the most recent surveillance data visit CDC Viral Hepatitis Surveillance.
Globally, HBV is the most common blood-borne infection with an estimated 296 million people infected according to the World Health Organization .
Living With Hepatitis B
If you have hepatitis, you should:
- avoid sharing needles used to inject drugs with other people
- take precautions to avoid the spread of infection such as not sharing toothbrushes or razors with other people close contacts such as family members may need to be vaccinated
- eat a generally healthy, balanced diet there’s no special diet for people with hepatitis B
- avoid drinking alcohol this can increase your risk of developing serious liver problems
- speak to your doctor if you’re thinking of having a baby
People with hepatitis B can usually have a healthy pregnancy, but it’s a good idea to discuss your plans with a doctor first as you may need extra care and your medications may need to be changed.
There’s a risk of pregnant women with hepatitis B passing the infection on to their child around the time of the birth, but this risk can be reduced by ensuring the baby is vaccinated shortly after they’re born.
You May Like: What Are Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Prevent Infection After Contact With The Virus
If you think you have been in contact with the hepatitis B virus, see your doctor right away. Doctors typically recommend a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine to prevent infection. In some cases, doctors may also recommend a medicine called hepatitis B immune globulin to help prevent infection. You must get the vaccine dose and, if needed, HBIG shortly after coming into contact with the virus, preferably within 24 hours.
Most Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis C To Watch For
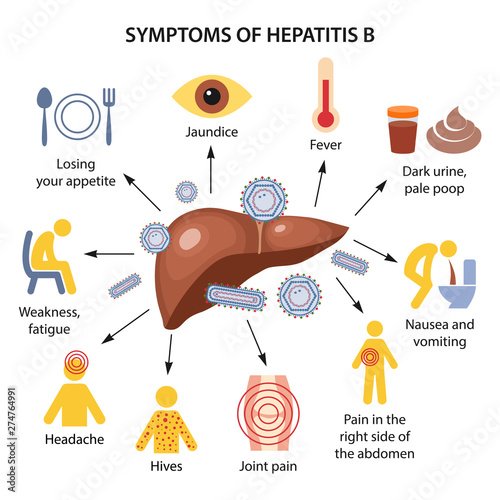
Because the symptoms can easily be mistaken for a mild stomach flu, food poisoning, dehydration, eating something you are allergic to, menstrual cramping and a number of other common occurrences, it is easy to see why so many people miss an acute Hepatitis C diagnosis.
Chronic Hepatitis C
For the majority of immune systems that are unable to mount a strong enough response to eliminate Hepatitis C from the liver, this infection becomes chronic. The longer the Hepatitis C virus resides in the body, the more inflammation and damage can be done to the liver.
Over time, soft, healthy liver tissue accumulates scars from the virus and becomes fibrotic. Known as liver fibrosis, this is a sign that liver disease is progressing.
If inflammation and liver cell damage continue, the liver can become cirrhotic. Characterized by the hardening and shrinking of liver tissue, liver cirrhosis is an advanced stage of liver disease. Once a person has severe fibrosis or cirrhosis as a consequence of Hepatitis C infection, more complex symptoms emerge.
Read Also: Hepatitis A Is Caused By
Recommended Reading: How Does Hepatitis Spread From Person To Person
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
As hepatitis B infection is highly transmissible via accidental needlesticks, healthcare providers involved in taking care of a patient with HBV should exercise caution and practice proper preventative measures such as vaccination. Patient education should also include counseling about HBV transmission. The interprofessional teamâs role is crucial in ensuring the best patient outcomes.
The vaccination rate is low in many developing countries, and the majority of patients are undiagnosed. Educational programs and improved awareness among the general public and healthcare providers are necessary to improve the identification of the patients, reduce transmission of the disease, and reduce the complications of hepatitis B infection.
How To Reduce Your Risk
Dont share needles or other drug-use equipment. If you use intravenous drugs, take part in a needle exchange program.
Dont share personal care articles, such as razors, scissors, nail clippers or toothbrushes, with an infected person.
If you get a tattoo, body piercing or acupuncture, make sure all equipment is clean and sterile. Needles should always be new, not used, and never homemade.
Wear latex gloves whenever you might come into contact with someone elses blood or body fluids.
Also Check: Hepatitis A Is A Virus
Complications Of Hepatitis B
Most people do not have any lasting problems after having a hepatitis B infection.
If left untreated, chronic hepatitis B can cause liver damage and increase your risk of getting liver cancer.
It is important to take any medicine you have been prescribed and go for regular check-ups to make sure your liver is working properly.
Page last reviewed: 01 July 2022 Next review due: 01 July 2025
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Hbv Infection
HBV can cause a wide range of symptoms, from a mild illness and general feeling of being unwell to more serious chronic liver disease that can lead to liver cancer.
Someone with hepatitis B may have symptoms similar to those caused by other viral infections, like the flu. The person might:
- have a mild fever
HBV also can cause darker than usual pee, jaundice , and belly pain.
People exposed to hepatitis B may start to have symptoms from 1 to 6 months later. Symptoms can last for weeks to months.
In some people, hepatitis B causes few or no symptoms. But even someone who doesnât have any symptoms can still spread the disease to others.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Be Contracted Sexually
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Spread Through Sweat
What Is Chronic Hepatitis B
Doctors refer to hepatitis B infections as either acute or chronic:
- An acute HBV infection is a short-term illness that clears within 6 months of when a person is exposed to the virus.
- A person who still has HBV after 6 months is said to have a chronic hepatitis B infection. This is a long-term illness, meaning the virus stays in the body and causes lifelong illness. An estimated 850,000 to more than 2 million people in the U.S. have chronic HBV.
The younger someone is when infected, the greater the chances for chronic hepatitis B.
The Symptoms Are Variable
Though doctors can list common symptoms of hepatitis, not everyone will have these symptoms. Some people may have only one or two common symptoms. Others may have all of the symptoms. People experience viral hepatitis in different ways. These symptoms are known to exist in people with viral hepatitis. Your situation might be different.
You May Like: How Can You Get Hepatitis C
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis A
People more likely to get hepatitis A are those who
- travel to developing countries
- have sex with an infected person
- are men who have sex with men
- use illegal drugs, including drugs that are not injected
- experience unstable housing or homelessness
- live with or care for someone who has hepatitis A
- live with or care for a child recently adopted from a country where hepatitis A is common
How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
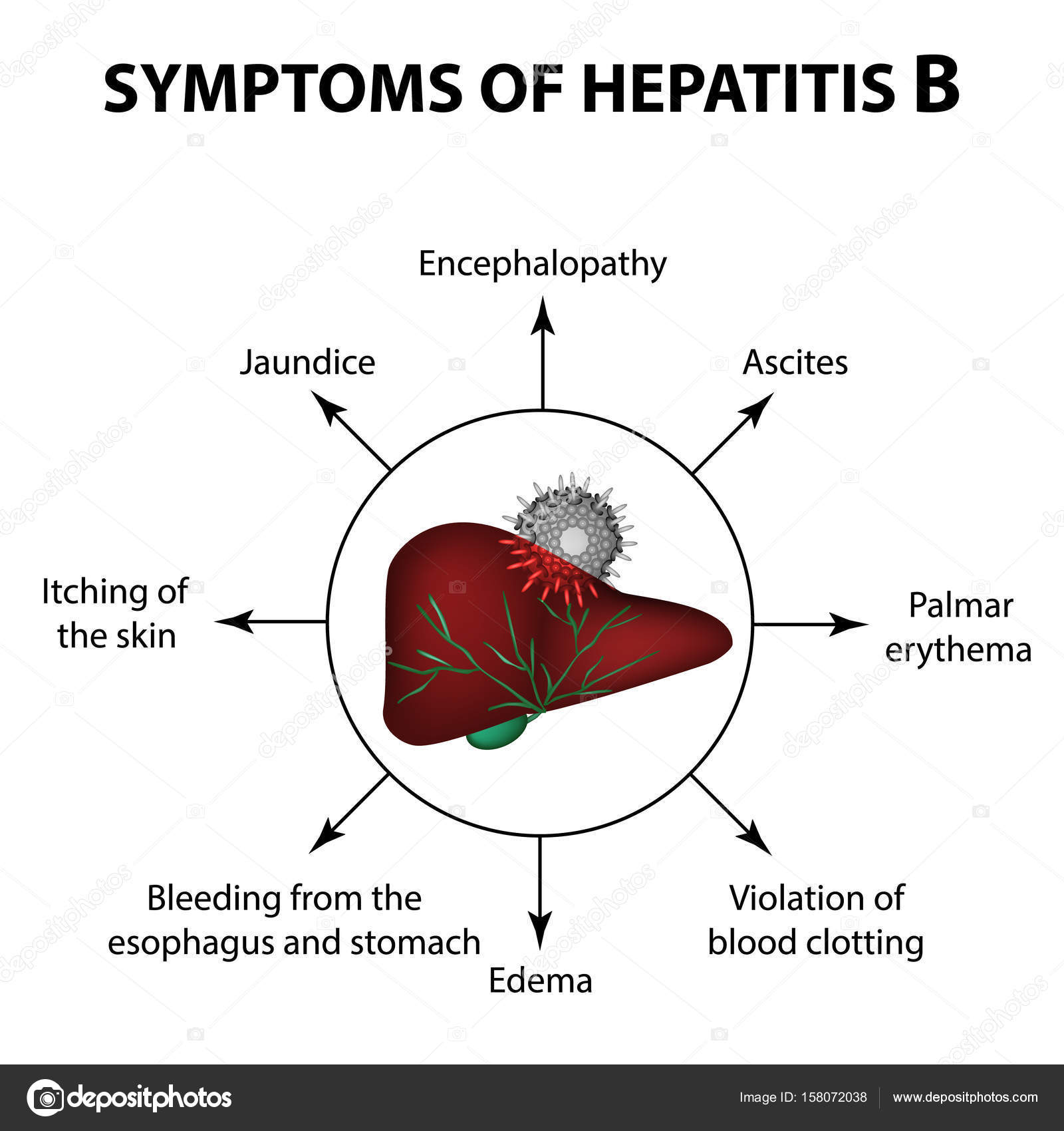
Most people who contract hepatitis B during adulthood fully recover within 1 to 3 months.
People with chronic hepatitis B may have a higher risk of developing long-term liver problems, like cirrhosis or liver cancer, which require treatment and may be life threatening.
Keep in mind that the risk of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for babies and children, especially if they have not been vaccinated against the virus.
Don’t Miss: Is There Treatment For Hepatitis B
What Is Acute Fulminant Hepatitis
Rarely, individuals with acute infections with HAV and HBV develop severe inflammation, and the liver fails . These patients are extremely ill with the symptoms of acute hepatitis already described and the additional problems of confusion or coma , as well as bruising or bleeding . In fact, up to 80% of people with acute fulminant hepatitis can die within days to weeks therefore, it is fortunate that acute fulminant hepatitis is rare. For example, less than 0.5% of adults with acute infection with HBV will develop acute fulminant hepatitis. This is even less common with HCV alone, although it becomes more frequent when both HBV and HCV are present together.
Hiv And Hbv Coinfection
About 2% of people with HIV in the United States are coinfected with HBV both infections have similar routes of transmission. People with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HBV infection. All people with HIV are recommended to be tested for HBV, and if susceptible, are further recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccination or, if chronically infected, evaluated for treatment to prevent liver disease and liver cancer. For more information about HIV and HBV coinfection, visit HIV.govâs pages about hepatitis B and HIV coinfection.
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis C Twice
What Happens With Hepatitis C
Is hepatitis C a virus? Yes. With acute hepatitis C, the virus is eliminated in 25% of people. The rest of the people become chronically infected and later may develop serious complications such as liver failure and liver cancer. There is treatment, however, for hepatitis C that usually can prevent the complications.
Also Check: What Does Non Reactive Mean For Hepatitis C
How Is Hepatitis C Infection Prevented
Unfortunately, there is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To reduce your risk of getting hepatitis C:
- Injection drug use is the most common way people get hepatitis C. Avoid injecting drugs to reduce your risk. If you do inject drugs, use sterile injection equipment. Avoid reusing or sharing.
- Avoid sharing personal care items that might have blood on them
- If you are a health care or public safety worker, follow universal blood/body fluid precautions and safely handle needles and other sharps
- Consider the risks if you are thinking about tattooing, body piercing, or acupuncture are the instruments properly sterilized?
- If youre having sex with more than one partner, use latex condoms correctly and every time to prevent the spread of sexually transmitted diseases, including hepatitis C.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B Core Antibody
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Antibody Blood Test
How Are Hepatitis B And C Diagnosed
Hepatitis B is diagnosed by a series of blood tests. The test may show an ongoing infection or antibodies that indicate that the patient is protected against hepatitis B. In patients who have a positive screening test that suggests the possibility of ongoing infection, further testing is done to determine the levels of the virus in the bloodstream.
Hepatitis C is diagnosed via a blood test called a Hepatitis C Antibody Test. A positive result means that hepatitis C antibodies are present in the blood. But a positive antibody test doesnt necessarily mean a person has hepatitis C. A further blood test is needed to confirm the diagnosis. This second blood test quantifies the amount of the virus or the viral load in the liver and the bloodstream.
Transmission Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is less easily transmitted than hepatitis A. Transmission commonly occurs when needles are reused without being first sterilizedas when people share needles to inject drugs or when needles are reused to apply tattoos.
Transmission through blood transfusions is possible but is now rare in the United States because blood is screened.
Transmission may occur between sex partners, both heterosexual and homosexual. Also at increased risk are people living in close quarters because contact with another person’s body fluid is more likely.
Anyone with hepatitis B, even people who do not have symptoms, can transmit the virus.
Whether insect bites can transmit this virus is not clear.
Many cases of hepatitis B have no known source.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis A Vaccine
When To See A Healthcare Provider
If you develop any of the symptoms of chronic hepatitis, liver damage, or liver cancer, see your healthcare provider. It takes only a blood test to detect the presence of a hepatitis virus in your body .
A blood test also can determine which hepatitis virus you’re infected with, which will determine what your treatment should be .
Is Hepatitis Treatable
For most people with viral hepatitis, effective treatments do exist. The earlier you see Dr. Rivas for an evaluation, the sooner you can receive an accurate diagnosis and begin treatment. The type of treatment Dr. Rivas recommends depends on the type of hepatitis you have.
Some forms of hepatitis respond well to rest, hydration, a healthy diet, and time. In other cases, you may need to take antiviral medications for months or years and maintain regular check-ups with Dr. Rivas. In severe cases or if you develop cirrhosis as the result of your hepatitis, you may require a liver transplant.
Dont wait to contact the Rivas Digestive Center in Hollywood, Florida, if you have any signs of hepatitis. You can call our office at 954-228-5882 or book an online consultation now.
Recommended Reading: The Vaccine For Hepatitis B
Causes Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infection caused by the hepatitis B virus. The virus is found in the blood and bodily fluids of an infected person.
Many people with hepatitis B have few symptoms and may not know they’re infected. They may spread the infection without realising it.
Hepatitis B is most often caught in parts of the world where the infection is more common, although certain groups of people are at risk of picking up the infection in the UK.
Is There A Vaccine For Hepatitis
There are vaccines for hepatitis A and hepatitis B that are available in the U.S. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. Since you can only get hepatitis D if you have hepatitis B, getting the vaccine against B should protect you against hepatitis D. There is no FDA approved vaccine against hepatitis E, but vaccines against hepatitis E exist overseas .
Recommended Reading: How Is Hepatitis C And B Transmitted
Also Check: How Often Should I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis B
Currently, there is no complete cure for hepatitis B. But when managed properly, those living with the virus can expect to live a normal life. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding beverages that contain alochol and tobacco products are crucial components in managing the disease.
You should also visit a doctor familiar with hepatitis B at least annually though twice a year might be best to monitor your liver through blood tests and medical imaging. As with most diseases, detecting it early leads to a better outcome. If youre exposed to the virus, you should get an antibody injection within 12 hours of exposure.
Eating Diet And Nutrition For Hepatitis B
If you have hepatitis B, you should eat a balanced, healthy diet. Obesity can increase the chance of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease , and NAFLD can increase liver damage in people who have hepatitis B. Talk with your doctor about healthy eating and maintaining a healthy weight.
You should also avoid alcohol because it can cause more liver damage.
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis C Spread
Hiv And Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Coinfection
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are liver infections caused by a virus. Because these infections can be spread in the same ways as HIV, people with HIV in the United States are often also affected by chronic viral hepatitis.
Viral hepatitis progresses faster and causes more liver-related health problems among people with HIV than among those who do not have HIV. Liver disease, much of which is related to HBV or HCV, is a major cause of non-AIDS-related deaths among people with HIV.
Given the risks of hepatitis B or hepatitis C coinfection to the health of people with HIV, it is important to understand these risks, take steps to prevent infection, know your status, and, if necessary, get medical care from a health care provider who is experienced in treating people who are coinfected with HIV and HBV, or HIV and HCV.