Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis C
Doctors usually recommend one-time screening of all adults ages 18 to 79 for hepatitis C. Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis C. Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have hepatitis C. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis C before it causes serious health problems.
Causes Of Hepatitis C
You can become infected with hepatitis C if you come into contact with the blood of an infected person.
Other bodily fluids can also contain the virus, but blood contains the highest level of it. Just a small trace of blood can cause an infection. At room temperature, itâs thought the virus may be able survive outside the body in patches of dried blood on surfaces for up to several weeks.
The main ways you can become infected with the hepatitis C virus are described below.
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that causes liver inflammation and damage. Inflammation is swelling that occurs when tissues of the body become injured or infected. Inflammation can damage organs.
Viruses invade normal cells in your body. Many viruses cause infections that can be spread from person to person. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood.
Hepatitis C can cause an acute or chronic infection.
Although no vaccine for hepatitis C is available, you can take steps to protect yourself from hepatitis C. If you have hepatitis C, talk with your doctor about treatment. Medicines can cure most cases of hepatitis C.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Ql
Distinguishing Compensated And Decompensated Cirrhosis
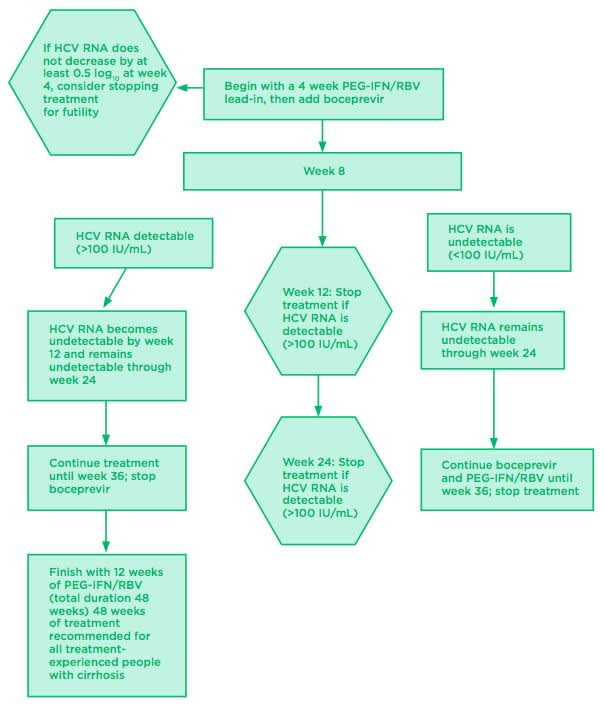
One important step in treating HCV in persons with cirrhosis is to determine whether the cirrhosis is compensated or decompensated. The Child-Turcotte-Pugh score is an important component of determining the status of the cirrhosis and predicts morbidity and mortality. The treatment approach and goals are divergent based on the classification of compensated versus decompensated cirrhosis. In particular, HCV protease inhibitor-based regimens are not recommended for use in persons with decompensated cirrhosis due to the risk of hepatotoxicity with some medications and lack of data with the others.
Sharing Toothbrushes Scissors And Razors

Thereâs a potential risk that hepatitis C may be passed on through sharing items such as toothbrushes, razors and scissors, as they can become contaminated with infected blood.
Equipment used by hairdressers, such as scissors and clippers, can pose a risk if it has been contaminated with infected blood and not been sterilised or cleaned between customers. However, most salons operate to high standards, so this risk is low.
Read Also: How Effective Is The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Disease Burden And Epidemiology
Many patients with chronic HCV infection are asymptomatic and it is estimated that 45%-85% are unaware they are even infected. Large population studies testing for positivity of anti-HCV antibody in non-institutionalized population in the United States have shown the prevalence to be approximately 1.8% in the general population. In these studies, the strongest risk factors predicting a positive HCV infection were illegal drug use, blood transfusions prior to 1992 and high risk sexual behavior with high number of lifetime sexual partners. Other risk factors associated with a positive HCV infection included poverty, having less than twelve years of education and having been divorced or separated. Surprisingly the study also showed that 15%-30% of infected patients reported no risk factors for the transmission of HCV infection. Additional studies examining the burden of HCV infection in the United States, show that by 2007, HCV had superseded human immunodeficiency virus as a cause of death in the United States. Several additional United States studies have also predicted a two-fold increase in HCV related deaths with direct medical expenditure exceeding $6.7 billion USD between 2010 and 2019 and without intervention, suggest that morbidity and mortality from HCV will peak between 2030 and 2035 forecasting for 38600 incident cases of end-stage liver disease, 3200 referrals per year for liver transplant and 36100 deaths.
Making The Diagnosis Of Compensated Vs Decompensated Cirrhosis
- Cirrhosis can be diagnosed with clinical, laboratory, radiologic, elastographic, or biopsy findings
- The diagnosis of compensated cirrhosis is more challenging since patients may lack clinical, laboratory, and radiologic findings and may require biopsy for diagnosis
- The diagnosis of decompensated cirrhosis is easier as the patient history, physical exam, and laboratory findings are usually more evident
Child-Turcotte-Pugh score
- TheChild-Turcotte-Pugh score is used as a prognostic scoring system in cirrhosis based on 2 clinical and 3 laboratory parameters:
- Ascites: none diuretic-sensitive or mild/moderate diuretic-refractory or tense
- Encephalopathy: none episodic or overt grade 2 recurrent/chronic or grade 3-4
- Albumin in g/dL:> 3.5 3.4-2.8 < 2.8
- Bilirubin in mg/dL:< 2 2-3 > 3
- INR:< 1.7 1.7-2.3 > 2.3
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B Shot For
Read Also: Does Hepatitis B Affect The Liver
The Link Between Cirrhosis Of The Liver And Hepatitis C
The key link between Cirrhosis of the Liver Hepatitis C is that they both attack the liver. They are dangerous because they both do not sure any symptoms in the early stages. This is the reason why most people with these conditions may be oblivious to their presence. In most cases, the diagnosis comes too late to save the liver, and sometimes life.
Why Hasnt New England Made More Gains In Hepatitis C Treatment
Tracking by the Center for Health Law and Policy Innovation at Harvard Law School and National Viral Hepatitis Roundtable shows that Medicaid restrictions for hepatitis C treatment remain across much of the country today.
Seventy-three percent of states currently require prior authorization before Medicaid beneficiaries can access treatment, and 36% still put restrictions in place for those actively using drugs, despite drug users being at disproportionate risk for contracting the virus, according to the 2022 State of Hep C Report.
More:States make secret deals with drugmakers to fight hepatitis C and taxpayers pick up the tab
The federal Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services has previously told states that some of those restrictions violate federal law, and yet they persist. CMS has not released any updated guidance for states since 2015.
Dr. Arthur Kim, director of the Viral Hepatitis Clinic in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Massachusetts General Hospital, said populations that acquire and live with hepatitis C are more likely to be on Medicaid than private insurance, making Medicaid a good barometer of how the country as a whole is making progress, or not, against the virus.
Treatment roadblocks in state Medicaid programs pose extremely large barriers to eliminating hepatitis C completely, experts say, because the lionâs share of those infected have insurance through them.
All of New England has since eliminated Medicaid restrictions for substance users.
Don’t Miss: Hiv Hepatitis B And C
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people infected with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with an acute hepatitis C infection may have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include
- yellowish eyes and skin, called jaundice
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you most likely will have no symptoms until complications develop, which could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
What Are The Risk Factors For Hepatitis B And C
Hepatitis B: Although most commonly acquired early in life, adults can also contract it. Hepatitis B is largely transmitted through bodily fluids. It can be passed at birth from a hepatitis B-infected mother or through exposure in early childhood to body fluids, blood or contaminated medical instruments. Hepatitis B can also be transmitted through intranasal and injection drug use as well as infected tools used during tattooing and body piercing.
Hepatitis C: The key risk factors are also intranasal and injection drug use, tattoos and body piercings, high-risk sexual contact, blood transfusions before 1992 and organ transplantation.
Another key risk factor for hepatitis C is being born from 1945 to 1965, during the baby-boom years. Eighty percent of all people who currently have hepatitis C in the United States were born in that timeframe.
Although the reasons that baby boomers are more likely to have hepatitis C than others arent entirely understood, its believed that most were infected in the 1970s and 1980s, when rates of hepatitis C were at their peak.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend that all U.S. adults born from 1945 to 1965 undergo a one-time screening test for hepatitis C. Connecticut is one of several states that has written this recommendation into law. In Connecticut ,the law requires that primary care clinicians screen all adults born within those years.
Also Check: Reactive Hepatitis B Core Antibody
Who Should Get Tested
You should consider getting tested for hepatitis C if you’re worried you could have been infected or you fall into one of the groups at an increased risk of being infected.
- Hepatitis C often has no symptoms, so you may still be infected if you feel healthy.
- The following groups of people are at an increased risk of hepatitis C:
- ex-drug users and current drug users, particularly users of injected drugs
- people who received blood transfusions before September 1991
- recipients of organ or tissue transplants before 1992
- people who have lived or had medical treatment in an area where hepatitis C is common high risk areas include North Africa, the Middle East and Central and East Asia
- babies and children whose mothers have hepatitis C
- anyone accidentally exposed to the virus, such as health workers
- people who have received a tattoo or piercing where equipment may not have been properly sterilised
- sexual partners of people with hepatitis C
If you continue to engage in high-risk activities, such as injecting drugs frequently, regular testing may be recommended. Your doctor will be able to advise you about this.
How Can I Best Prepare For Treatment
There are a number of things you can do to improve your health and increase your chances of being able to take your medications as prescribed:
- Avoid alcohol and drugs. If you cannot quit, seek help.
- Talk to your doctor about getting the Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B vaccines.
- Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep every night and rest when tired.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Eat healthy meals: Strive for a diet low in fat and high in fiber. Include fruit, vegetables, and whole grains. Avoid trans fatty acids and saturated fats.
- Avoid dietary supplements that may harm the liver, such as iron or vitamin A, kava, and valerian. Take only the medications recommended by your doctor.
- Drink 6-8 glasses of water per day.
- Exercise: Be as physically active as possible on a regular basis, balancing rest and activity.
- Avoid or reduce stress. Some people find meditation, prayer, or simply a quiet walk to be helpful.
- Engage in activities that give you pleasure and make you laugh.
- Discuss your feelings with family and close friends.
- Join a Hepatitis C support group.
In addition, its important to become an effective healthcare consumer and advocate for yourself. You can do this by:
- Learning all you can about your disease and its treatment. Seek information from Hepatitis C related organizations.
- Getting all your medical and insurance information organized in one place. This should include:
- Recent test results
- Emergency contact numbers
Read Also: How To Spread Hepatitis B
Importance Of Adhering To Your Treatment Plan
Once you begin treatment for your Hepatitis C infection, youll want to do everything you can to make it a success. Adherence to your Hepatitis C medication regimen is an important predictor of successful treatment. When it comes to medications, this means that you want to adhere to taking them as prescribed meaning taking the right dose, the right way, at the right time, for as long as prescribed.
The goal of using medications to treat Hepatitis C is to:
- Clear the Hepatitis C virus from your body
- Prevent or slow down scarring of your liver
- Reduce your chance of developing cirrhosis and liver cancer
Proper adherence to Hepatitis C therapy will increase your chance of being cured and decrease the long-term complications of Hepatitis C.
Adhering to other aspects of your treatment plan is also important. Keeping your medical appointments and getting the necessary lab tests will help to maximize your chance of treatment success and minimize potential problems.
Paritaprevir/ritonavir + Ombitasvir Ribavirin
Dasabuvir has no significant antiviral activity in genotype 4 therefore, treatment with paritaprevir/ritonavir and ombitasvir is sufficient. In a recently published study, paritaprevir/ritonavir + ombitasvir + ribavirin was compared for 12 and 16 weeks in patients with cirrhosis. In both groups high SVR rates were achieved . The combination is approved for a 24-week treatment with ribavirin in patients with cirrhosis.
Read Also: How Does A Person Contract Hepatitis
When Should I Call 911 Or Go To The Emergency Room
If you have cirrhosis and experience the following, call 911:
- Your poop are black and tarry or contain blood .
- You are vomiting blood.
- You have muscle tremors or shakiness.
- You are confused, irritable, disoriented, sleepy, forgetful or foggy.
- You have a change in your level of consciousness or alertness you pass out.
You May Like: Hepatitis B And C Test
Recommended For All Patients With Hcv Infection Who Have Decompensated Cirrhosis
RECOMMENDED RATING Patients with HCV infection who have decompensated cirrhosismoderate or severe hepatic impairment, ie, Child-Turcotte-Pugh class B or class Cshould be referred to a medical practitioner with expertise in that condition, ideally in a liver transplant center. I, C
Clinical trial data demonstrate that in the population of persons with decompensated cirrhosis, most patients receiving direct-acting antiviral therapy experience improvement in clinical and biochemical indicators of liver disease between baseline and posttreatment week 12, including patients with CTP class C cirrhosis . Improvements, however, may be insufficient to avoid liver-related death or the need for liver transplantation , highlighting that not everyone benefits from DAA therapy . Most deaths among those receiving DAA therapy relate to the severity of the underlying liver disease. Predictors of improvement or decline have not been clearly identified, although patients with a Model for End-Stage Liver Disease score > 20 or severe portal hypertension complications may be less likely to improve and might be better served by transplantation than antiviral treatment .
Also Check: What Should I Do If I Have Hepatitis B
How We Care For Hepatitis C
The Center for Childhood Liver Disease at Boston Childrenâs Hospital is one of the leading centers in the world for the care of children with hepatitis C. The centerâs director, Maureen Jonas, MD is a national leader in the care, diagnosis and treatment for children with viral hepatitis. Dr. Jonas, along with her team, wrote the clinical guidelines that shape the way pediatric GI specialists and pediatricians around the country treat hepatitis C.
In addition to the standard treatments, our team of certified pediatric hepatologists is also at the forefront of treatment research, treating adolescents with newly approved treatments for adults and conducting clinical trials to help make them available to children as young as 3 years of age.
Disadvantages To Treatment In Hcv Cirrhosis Patients
The treatment of patients with HCV cirrhosis has shown to have lower SVR rates than in patients who are non-cirrhotic. Studies show that treatment with peg IFN plus ribavirin in patients with advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis leads to a significantly lower SVR when compared with patients with mild to moderate fibrosis. Additionally, previous studies evaluating the use of triple therapy in patients with cirrhosis showed not only a lower SVR but also a high incidence of significant adverse events including worsening of liver disease, severe infection and difficult to manage anemia. Hence due to the risk of adverse effects, treatment of these patients requires significant oversight and should be considered only at experienced centers with transplantation capabilities leading to increasing cost and accessibility issues. Unfortunately, the treatment in some transplant centers is also controversial. There may be a tendency in some liver transplant centers to wait until transplantation and pursue treatment post-transplant. Additionally, having positive HCV infection in a cirrhotic liver may also provide access to HCV positive liver transplant options in such patients given the paucity of available organs.
You May Like: Chronic Hep C Without Hepatic Coma Icd 10
How Do Doctors Treat Cirrhosis
Doctors do not have specific treatments that can cure cirrhosis. However, they can treat many of the diseases that cause cirrhosis. Some of the diseases that cause cirrhosis can be cured. Treating the underlying causes of cirrhosis may keep your cirrhosis from getting worse and help prevent liver failure. Successful treatment may slowly improve some of your liver scarring.
How Hepatitis C Damages The Liver
Hepatitis C causes damage to the liver mainly in the form of inflammation, which then leads to scarring or fibrosis.
Hepatitis C results in the death of liver cells. It is uncertain whether the virus kills the cells or if it is the immune systems response to invasion by the virus. At present it is thought that it is probably a combination of the two, but that the immune systems response is what causes the most damage. The death of liver cells triggers the dispatching of inflammatory cells to the affected area. Inflammation leads to the enlargement of the liver in over 60% of people infected with hepatitis C and can cause the fibroelastic sheath surrounding the liver to stretch, which may be the cause of pain in the liver area.
Inflammation begins the processes that lead to fibrosis. Fibrosis is not a disease but is a condition caused by the bodys response to liver damage. Inflammation triggers a reaction by a group of cells in the liver called stellate or fat cells. When the liver is functioning normally stellate cells store fat and vitamin A in the liver. They also help regulate the flow of blood through the liver. But when the liver is inflamed by the presence of hepatitis C, a reaction occurs amongst different liver cells. This leads stellate cells to dispense with vitamin A, altering their function.
Free Radicals and Fibrosis
Free radicals are of concern for people with hepatitis C for a number of reasons:
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C Serious Disease