What Is The Purpose Of A Hepatitis B Test
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B blood tests involve the measurement of several HBV-specific antigens and antibodies. In addition, HBV blood tests also include liver enzymes and liver function tests to assess and monitor the condition of the liver and provide appropriate treatment.
The HBV specific tests include the following:
- HBsAg: HBsAg is an antigen found on the surface of hepatitis B virus. HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks.
- Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the bodys immune system to fight HBsAg. Anti-HBs from a prior infection or vaccination provides immunity against further infection.
- Hepatitis B core antigen : HBcAg is an antigen found in the core layer which covers the hepatitis B viral DNA.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : Anti-HBc is the antibody that fights HBcAg. Anti-HBc is the first detectable antibody after HBV infection. There are two kinds of Anti-HBc:
- Immunoglobulin M hepatitis B core antibody : IgM anti-HBc indicates acute or reactivated recent infection within the previous 6 months.
- Immunoglobulin G hepatitis B core antibody : IgG anti-HBc may indicate previous or chronic infection. Once present, IgG anti-HBc persists for a lifetime.
What Does Hepatitis B Core Antibody Positive Mean
Hepatitis B is an inflammation of the liver caused by a virus. Signs of hepatitis include tiredness or fatigue, fevers, loss of appetite, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, headache, itchy skin, muscle soreness , jaundice , dark urine, and light stools.Here are some hepatitis B facts:
1. HBV infections will occur in one out of every 20 people at some time in the United States
2. Your risk of HBV is greater if you have sex with someone who has HBV.
3. Your risk is greater if you have a job that places you in contact with human blood.
4. Your risk is greater if you travel to areas where HBV is common.
Some people who donate blood get a letter from the blood bank saying that they are hepatitis B core antibody positive. Dont panic. This does not mean that you have hepatitis B, but you should get a more thorough screening. There are three blood tests that are used to diagnose hepatitis B: hepatitis B surface antigen, hepatitis B surface antibody, and hepatitis B core antibody positive. If your blood tests show that you are hepatitis B core body positive, it means that you either have a present infection or that you were infected in the past. There is a possibility of having a false hepatitis B core antibody positive. Blood banks only screen for hepatitis B core antibody positive and not for surface antigens or antibodies.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Spread Through Saliva
Risk Of Transfusion Transmission
In the US, with testing for HBsAg and anti-HBc, the estimated residual risk of HBV transmission before DNA testing was 1:280,000â1:357,000, significantly higher than that for HIV or HCV. Voluntary minipool testing for HBV DNA has been widely implemented in the US, and is now required by the FDA. Current residual risk estimates are 1:750,000 or less in an era of universal immunization. Minipool HBV DNA assays have similar sensitivity to current HBsAg tests, accounting for the clinically marginal decrease of the window period .
Gregory L. Armstrong, Susan T. Goldstein, in, 2007
Recommended Reading: Where Do I Get A Hepatitis A Vaccine
Question 2 What Is The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
The hepatitis B surface antibody is the antibody that is produced in response to hepatitis B surface antigen , a protein present on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. Anti-HBs appears after convalescence from acute infection and lasts for many years. It can also be produced in response to hepatitis B vaccination.
Other hepatitis B antibodies are not produced in response to vaccination. This is because these antigens are not in the vaccine.
Susceptibility To Hbv Infection
In HIV infection, the presence of the isolated anti-HBc pattern does not necessarily indicate immunity to HBV infection. Indeed, varying anamnestic responses to a single dose of HBV vaccine have been reported, ranging from as low as 7% to 32% , with higher levels of response to multiple doses of HBV vaccine administered. A prospective study conducted by Piroth and colleagues demonstrated that in 54 HIV-infected patients with the isolated anti-HBc profile, a single dose of 20 μg HBV vaccine resulted in a 46% response rate, defined as anti-HBs > 10 mIU/ml in those who did not respond to a single dose, a 3-dose series of double-dose 40 μg HBV vaccine resulted in 89% of remaining patients developing anti-HBs titers of > 10 mIU/mL at 28 weeks following vaccination . Based on the results of this study, the current DHHS guidelines recommend that HIV infected patients with the isolated anti-HBc profile receive one standard dose of HBV vaccine followed by anti-HBs assessment 1-2 months post dose. If anti-HBs is < 100 IU/mL then the individual should receive the full series of either single or double-dose HBV vaccine, with subsequent anti-HBs testing 1-2 months after completion of the vaccine series .
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Chronic Hepatitis C
Also Check: Is Hepatitis C Contagious After Being Cured
Mechanisms Of The Isolated Anti
Hepatitis B virus persists as cccDNA following exposure. Persistent HBV infection with low or undetectable levels of HBV viremia in the setting of an isolated anti-HBc potentially involves methylation of HBV cccDNA within the hepatocyte, thereby downregulating DNA and subsequent mRNA expression, with subsequent quiescence of HBsAg production . Other epigenetic factors such as downregulation of acetylation may also play important roles towards transcriptional suppression of cccDNA in hepatocytes to explain serological patterns noted in patients with the isolated anti-HBc profile.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitative
The Frequency And Significance Of Isolated Hepatitis B Core Antibody And The Suggested Management Of Patients
Hepatitis B core antibody is the first antibody to appear following acute hepatitis B infection and will persist in high levels following resolution of infection and in chronically infected patients. Resolved infection is generally recognized by the presence of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen in the serum, whereas in chronic infection hepatitis B surface antigen itself is typically present.
Isolated HBcAb, which is defined as positive HBcAb with undetectable HBsAg and HBsAb, may occur in any of several clinical situations. It may be the only serum marker of acute hepatitis B infection during the so-called window phase between disappearance of HBsAg and appearance of HBsAb. It may also represent a remote resolved infection with the decline of HBsAb to undetectable levels or ongoing chronic infection with HBsAg that is escaping detection, either because of low levels of HBsAg or because of mutations in the protein that render it undetectable using certain diagnostic assays. It rarely represents a false-positive test. Acute hepatitis B virus infection is often recognized by its clinical presentation, and repeat testing after several weeks will generally detect the appearance of HBsAb. The other clinical possibilities are not easily distinguished on routine serological testing but may have important consequences, particularly in situations of chronic infection with no detection of HBsAg.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Hepatitis A Vaccine Last
You May Like: How Is Hepatitis C Contracted
Resolution Of Acute Infection
During resolution of acute infection, IgM anti-HBc is replaced by antibody of the IgG subclass , and anti-HBs develops . Anti-HBs is a protective, neutralizing antibody, and its presence indicates recovery from acute infection and immunity to reinfection. The period when all HBsAg has been neutralized by anti-HBs, and neither HBsAg nor anti-HBs is detectable, is referred to as the window period. During the window period, the only serologic marker of infection is IgM anti-HBc. During resolution, anti-HBe replaces HBeAg. In people with past HBV infection, IgG anti-HBc usually remains detectable for life, but anti-HBs might become undetectable in remote infection.3,109
Howard C. Thomas, Jennifer A. Waters, in, 1998
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patients vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
You May Like: What Are The First Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
You May Like: Hepatitis B Home Test Kit
Hbcab Or The Hepatitis B Core Antibody Test
The hepatitis B core antibody is produced by your immune system after infection by the hepatitis B virus, and it can persist for life. It is a sign that you either have an new, active hepatitis B infection or that you acquired hepatitis B in the past.
HBcAb is an immune system response to a protein in the core of the virus, and it is only present if you have been infected, rather than immunized against the virus. It is part of a routine screening panel of tests for hepatitis B. If your rest results turn out to be positive, your healthcare provider will order further tests to determine the stage of the infection: acute or chronic .
Also Known As: anti-HBc, HBcAb
Question 7 Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Antibody Always Acquired After A Completed Vaccination Protocol
No. After 3 intramuscular doses of vaccine, > 90% of healthy adults and > 95% of those < 19 years of age develop immunity .1 However, there is an age-specific decline in development of immunity. After age 40 years, about 90% of people become immune, but by age 60 years, only 75% of people become immune.1 Larger vaccine doses or an increased number of doses are required to induce immunity in many hemodialysis patients and in other immunocompromised people.1
References
This FAQ is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. A clinicians test selection and interpretation, diagnosis, and patient management decisions should be based on his/her education, clinical expertise, and assessment of the patient.Document FAQS.105 Revision: 0
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Dosage Newborn
Understanding Your Test Results
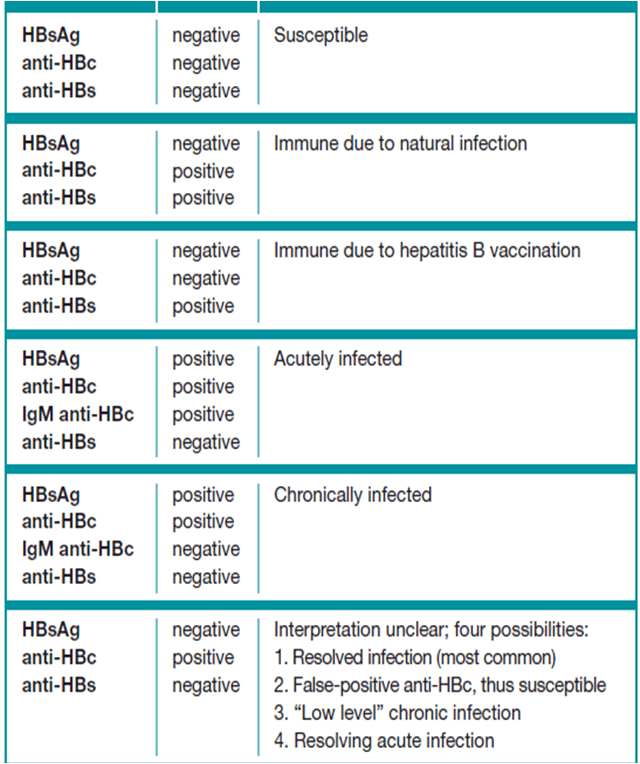
Understanding your hepatitis B blood tests can be confusing. It is important to talk to your health care provider so you understand your test results and your hepatitis B status. Are you infected? Protected? Or at risk? The Hepatitis B Panel of blood tests includes 3 tests and all three results must be known in order to confirm your status.
Below is a chart with the most common explanation of the test results, but unusual test results can occur. Please note that this chart is not intended as medical advice, so be sure to talk to your health care provider for a full explanation and obtain a printed copy of your test results. In some cases, a person could be referred to a liver specialist for further evaluation.
More Detailed Information About Hepatitis B Blood Tests
An acute hepatitis B infection follows a relatively long incubation period – from 60 to 150 days with an average of 90 days. It can take up to six months, however, for a person to get rid of the hepatitis B virus. And it can take up to six months for a hepatitis B blood test to show whether as person has recovered from an acute infection or has become chronically infected .
The following graphic from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention represents the typical course of an acute hepatitis B infection from first exposure to recovery.
According to the CDC, a hepatitis B blood test result varies depending on whether the infection is a new acute infection or a chronic infection.
Hepatitis B Virus Life
Hepatitis B virus establishes itself in chronic infection by way of dynamic processes involving viral and host immunity defenses. Attachment entry of the HBV virus requires interaction between HBsAg and hepatocyte surface proteins. HBV relaxed circular DNA is converted to covalently closed circular DNA , which serves as a transcriptional template for subsequent viral mRNA production and pregenomic RNA . This matures into nucleocapsid with viral polymerase, for viral propagation in the forms of virions outside the hepatocyte, or return to the nucleus as cccDNA . The persistence of cccDNA despite effective inhibition of HBV viral polymerase through nucleoside analogues is the key reason why cure of HBV remains elusive , as it provides a transcriptional reservoir for continued replication of virus . The presence of cccDNA also leads to production of the core antigen to which antibody is formed in the form of anti-HBc. This explains why anti-HBc is present in acute, chronic, and resolved infection.
Hepatitis B Virus Life Cycle
Figure 1 depicts the HBV lifecycle. Yellow arrows highlight cccDNA and the production of the core protein, demonstrating that the production of core protein occurs independent of HBV viral replication and as a direct result of the presence of the transcriptionally active reservoir of cccDNA
Dont Miss: New Drug To Cure Hepatitis C
Also Check: Hepatitis Panel Acute With Reflex To Confirmation
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Qualitative
Presence of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen is used to determine immune status to HBV or disease progression in individuals infected with HBV. Anti-HBs levels can be measured to determine if vaccination is needed, or following a vaccination regimen, to determine if protective immunity has been achieved.
Anti-HBs usually can be detected several weeks to several months after HBsAg is no longer found, and it may persist for many years or for life after acute infection has been resolved.
It may disappear in some patients, with only antibody to core remaining.
People with this antibody are not overtly infectious.
Presence of the antibody without the presence of the antigen is evidence for immunity from reinfection, with virus of the same subtype.
What is the Hepatitis B virus?
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days .
What are common symptoms?
Prevalence And Predictors Of The Anti
Wide variation exists on the prevalence of isolated anti-HBc findings. In HIV+ cohorts, 17% to 40% of patients have been reported to have the isolated anti-HBc, owing to similar routes of transmission for HIV and HBV. Predictors of the isolated anti-HBc pattern include HIV infection, HCV infection, and specifically HCV viremia, older age, IDU, multiple sexual partners, and elevated HIV RNA levels . The isolated anti-HBc pattern is particularly common in HIV/HCV coinfection, likely due to shared routes of transmission and viral interplay . Estimates of prevalence of isolated anti-HBc may be limited due to differences in geography, as well as sensitivities of different immunoassays used in each study. This is in contrast to HIV negative cohorts, where the prevalence of the isolated anti-HBc ranges from 5.3-31.6% .
Don’t Miss: Foods To Avoid Hepatitis B
Whats The Prognosis For Hepatitis B
Your doctor will know youâve recovered when you no longer have symptoms and blood tests show:
- Your liver is working normally.
- You have hepatitis B surface antibody.
But some people dont get rid of the infection. If you have it for more than 6 months, youâre whatâs called a carrier, even if you donât have symptoms. This means you can give the disease to someone else through:
- Unprotected sex
- Contact with your blood or an open sore
- Sharing needles or syringes
Doctors donât know why, but the disease does go away in a small number of carriers. For others, it becomes whatâs known as chronic. That means you have an ongoing liver infection. It can lead to cirrhosis, or hardening of the organ. It scars over and stops working. Some people also get liver cancer.
If youâre a carrier or are infected with hepatitis B, donât donate blood, plasma, body organs, tissue, or sperm. Tell anyone you could infect whether itâs a sex partner, your doctor, or your dentist that you have it.
Show Sources
CDC: âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for Health Professionals,â âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Mayo Clinic: âHepatitis B.â
UpToDate: âHepatitis B virus: Screening and diagnosis.â
CDC.
HealthyPeople.gov: âHepatitis B in Pregnant Women: Screening.â
Annals of Internal Medicine: âScreening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.â
How Do I Get Hepatitis B Treatment
Usually for adults, hepatitis B goes away on its own and you wont need treatment. Your doctor might tell you to rest, eat well, and get plenty of fluids. You may also get medicines to help with any symptoms you might have but be sure to talk with your doctor or nurse before taking anything.
If you have chronic hepatitis, there are medicines you can take to treat it. Your doctor will tell you about your options and help you get whatever treatment you need.
Read Also: Is Hepatitis A Sexually Transmitted Disease
For Patients With Chronic Hbv
Reducing the risk of liver damage
- Have liver enzymes monitored every 6-12 months.
- Reduce or eliminate alcohol.
- Stop smoking, as it increases the risk of liver cancer.
- You may drink coffee 3 or more cups per day may reduce the risk of liver cancer.Endnote 21
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A if you are not already immune â talk to your HCP or contact your local public health department.
- Stick to your medication schedule and your regular lab testing and follow-up visits.
- Tell your HCP before starting any immunosuppressive therapy.
About medications for patients with cirrhosis
- Avoid aminoglycosides , benzodiazepines, and narcotics including codeine .
- Whenever possible, avoid ASA or NSAIDs. Acetaminophen, oral contraceptive pills, and statins are safe to use.
- Do not drink alcohol.
- If you require surgery, discuss it with your specialist first.
- If you have black stools, call your specialist immediately or go to the ER.
- Tell your HCP about any complementary/alternative therapies or over the counter supplements including herbal remedies that you are taking.
- Follow your HCPâs advice on how frequently you require abdominal ultrasounds.
Living well with HBV
Read Also: How Soon Can You Test For Hepatitis C