Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if you have an active infection. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can transmit the virus to others. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B.
This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the state of a hepatitis B infection.
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis B
If you think you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
A doctor or other healthcare professional may administer the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin. This is a combination of antibodies that provide short-term protection against the virus.
Though both can be given up to a week after exposure, theyre most effective at preventing infection if administered within 48 hours.
If you receive a diagnosis of acute hepatitis B, a doctor may refer you to a specialist. They may advise you to get regular blood tests to ensure you dont develop chronic hepatitis.
Many people with acute hepatitis B dont experience serious symptoms. But if you do, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter pain mediation, like naproxen, when needed
Other lifestyle changes may also be needed to manage your infection, such as:
- eating a nutritious, balanced diet
- avoiding substances that can harm your liver, such as:
- certain herbal supplements or medications, including acetaminophen
If blood tests show you still have an active infection after 6 months, your doctor may recommend further treatment, including medications to help control the virus and prevent liver damage.
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. Its transmitted through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not transmitted through sharing utensils or kissing. Its also not transmitted through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure. Symptoms can last for several weeks.
But even without symptoms, you can still transmit the infection to others. The virus can live outside the body and remains infectious for at least
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious condition. Its associated with many serious complications, some of which can be life threatening.
But there are many treatment options available and multiple ways you can prevent infection, including getting vaccinated.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a doctor to prevent infection and determine the best course of treatment for you.
Also Check: How Do You Get Hepatitis B
How Many People Have Hepatitis B
In the United States, an estimated 880,000 to 1.89 million people are chronically infected with HBV. New cases of HBV infection in the United States had been decreasing until 2012. Since that time, reported cases of acute hepatitis B have been fluctuating around 3,000 cases per year. In 2020, 2,157 cases of acute hepatitis B were reported however, because of low case detection and reporting, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that there were 14,000 acute hepatitis B infections. The rate of acute cases of HBV decreased by 32% after 2019 which may be related to the disruptions of the COVID-19 pandemic. For the most recent surveillance data visit CDC Viral Hepatitis Surveillance.
Globally, HBV is the most common blood-borne infection with an estimated 296 million people infected according to the World Health Organization .
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Most APIs are infected at birth or early childhood, when symptoms may never develop. Thus the disease can progress undetected. If symptoms do appear, they often appear too late, when the disease has become fatal and when treatment options are limited or ineffective. Only 30% of those with acute infections develop symptoms. When symptoms of hepatitis B infection do develop, they include:
Jaundice
Read More on Hep B
Read Also: Signs Of Hepatitis C Getting Worse
Hbsag Detection By Histochemical Methods
The ovarian and placental tissue samples were processed by routine histological procedures and paraffin sections were prepared by the standard series of operations of fixation, dehydration and paraffin embedding. The slides were then stained with hematoxylin-eosin and observed using light microscopy to evaluate the histology.
Challenges To Hepatitis B Prevention In The United States
There has been a substantial reduction in the number of new HBV infections each year in the United States as a result of hepatitis B immunization. However, implementation of the comprehensive strategy to eliminate HBV transmission has been uneven, and transmission of HBV still occurs among groups for whom vaccine indications have been in place for more than a decade. The primary challenge in the prevention and control of hepatitis B in the United States is full implementation of existing immunization recommendations, particularly those related to the prevention of perinatally acquired infections and infections acquired in adulthood through sexual and needle-sharing exposures.
Don’t Miss: Cvs Minute Clinic Hepatitis B Vaccine
Whats The Prognosis For Hepatitis B
Your doctor will know youâve recovered when you no longer have symptoms and blood tests show:
- Your liver is working normally.
- You have hepatitis B surface antibody.
But some people don’t get rid of the infection. If you have it for more than 6 months, youâre whatâs called a carrier, even if you donât have symptoms. This means you can give the disease to someone else through:
- Unprotected sex
- Contact with your blood or an open sore
- Sharing needles or syringes
Doctors donât know why, but the disease does go away in a small number of carriers. For others, it becomes whatâs known as chronic. That means you have an ongoing liver infection. It can lead to cirrhosis, or hardening of the organ. It scars over and stops working. Some people also get liver cancer.
If youâre a carrier or are infected with hepatitis B, donât donate blood, plasma, body organs, tissue, or sperm. Tell anyone you could infect — whether itâs a sex partner, your doctor, or your dentist — that you have it.
Show Sources
CDC: âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for Health Professionals,â âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Mayo Clinic: âHepatitis B.â
UpToDate: âHepatitis B virus: Screening and diagnosis.â
CDC.
HealthyPeople.gov: âHepatitis B in Pregnant Women: Screening.â
Annals of Internal Medicine: âScreening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.â
Other Body Fluids And Tissues
Synovial fluid , amniotic fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, and peritoneal fluid can contain the hepatitis B virus, but the risk of transmission to workers is not known.
Feces, nasal secretions, sputum, sweat, tears, urine, and vomit have not been implicated in the spread of hepatitis B. Unless they are visibly contaminated with blood, the risk of contracting hepatitis B from these fluids in the workplace is very low.
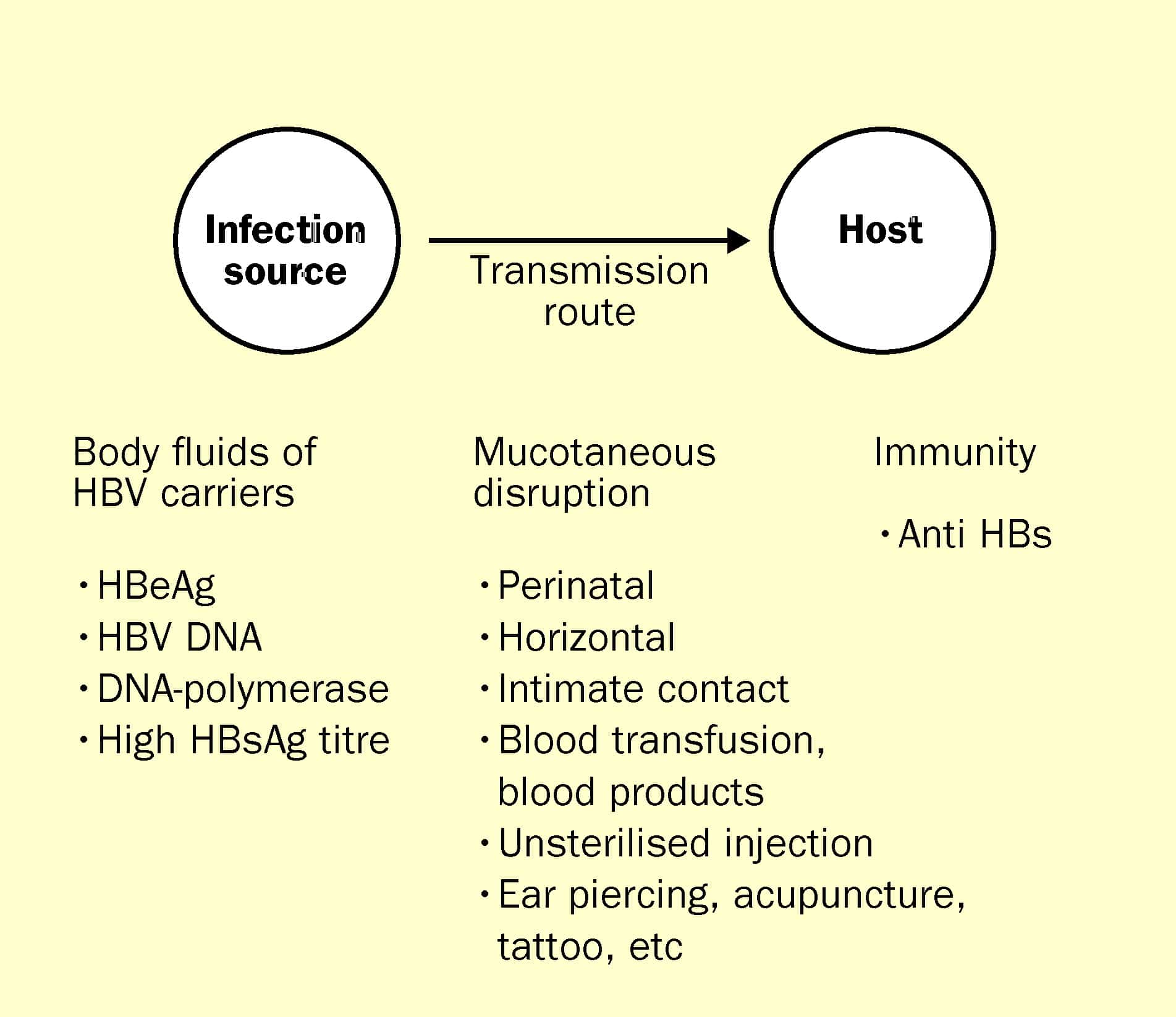
Hepatitis B is not transmitted by casual contact. For example, hospital employees who have no contact with blood, blood products, or blood-contaminated fluids are at no greater risk than the general public. However, the virus can spread through intimate contact with carriers in a household setting, possibly because of frequent physical contact with small cuts or skin rashes. The virus can also spread through biting and possibly by the sharing of toothbrushes or razors. It is not spread through sneezing, coughing, hand holding, hugging, kissing, breastfeeding, sharing eating utensils, water or food.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine Series For Adults
Hepatitis B Transmission And Risks
Transmission
- Sex with an infected partner
- Acquired at birth from an infected mother
- Sharing injection drug equipment
- Contact with blood or open sores of an infected person
- Needle stick or other skin puncture
- Sharing items such as glucose monitors, razors or toothbrushes with an infected person.
Hepatitis B may also be spread through non-injection drugs as a result of exposure to blood. An unsterilized instrument may transmit HBV during acupuncture, tattooing and body piercing. A human bite may spread hepatitis B.
Hep B is not spread through food or water, sharing eating utensils, breast feeding, hugging, kissing, hand holding, coughing or sneezing.
HBV may live outside the body for at least seven days and still be potentially infectious.
Risk Factors
Hepatitis B vaccination has dramatically reduced the risk of HBV in the United States. To further reduce risk of transmitting hepatitis B, all health care workers and pregnant women are screened and or immunized. Contact your health care provider for a blood test if you havent been immunized and have any of the following hep B risk factors:
When To Call The Doctor
- The child has not felt hungry or wanted to eat in the past 24 hours.
- Your childs fever is over 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit for more than 2 days.
- Your child has a stomachache.
- Your child vomits more than 2 times in an hour.
- Your childs skin or the white part of the eyes turns yellow.
- Your child is overly tired for more than 2 days.
You May Like: Difference Between Hepatitis B And Hiv
Genetics Of Infection With Hepatitis B
Several genes, many having to do with the host immune response, have been implicated in the susceptibility to chronic hepatitis B infection. The TNFSF9 gene encodes the CD137L protein, and its expression was found to be significantly higher in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection than in healthy controls. Its expression was also found to be higher in patients who had chronic hepatitis B with cirrhosis, in contrast to those without cirrhosis.
Research done in West Africa, where 90% of the population is infected with hepatitis B, shows that certain human leukocyte antigen class II haplotypes influence the likelihood of chronic infection. For reasons that are not completely clear, patients in the study who were heterozygous for the HLA-DRA and HLA-DQA1 genes were found to be less likely to develop a chronic infection.
IFNGR1 gene
Several additional genes are associated with susceptibility to hepatitis B infection. The IFNGR1 gene is located at 6q23.3 and encodes the interferon gamma receptor 1, which has an important role in cell-to-cell communications and can be activated in response to infection, but it is not specific to hepatitis B. Patients with significant dysfunction in this gene have a particular immune deficiency that leaves them extremely susceptible to mycobacterial infections.
IFNAR2 gene
IL1OR2 gene
Variations in vaccine response
How Is It Treated
Hepatitis A is treated using supportive methods. These can include things like rest, fluids, and healthy foods. Medications can also help to ease some symptoms like fever, aches, and pains.
Theres a vaccine available to protect against infection with HAV. This is typically recommended for children as well as for people at an increased risk for contracting the virus.
Also, receiving a single dose of the hepatitis A vaccine may prevent you from becoming ill if youve been exposed to HAV. For it to be effective, the vaccine needs to be given of exposure.
Dont Miss: How Do You Get Rid Of Hepatitis B
You May Like: Facts About Hepatitis C Virus
Where Is Hbv Most Common
Hepatitis B is endemic in China and other parts of Asia. Most people in the region become infected with HBV during childhood.
In these regions, 8% to 10% of the adult population are chronically infected. Liver cancer caused by HBV is among the first three causes of death from cancer in men, and a major cause of cancer in women. High rates of chronic infections are also found in the Amazon and the southern parts of eastern and central Europe. In the Middle East and Indian sub-continent, an estimated 2% to 5% of the general population is chronically infected. Less than 1% of the population in western Europe and North American is chronically infected.
What Is Hepatitis B Virus
Hepatitis B is a potentially life-threatening liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus. It is a major global health problem and the most serious type of viral hepatitis. It can cause chronic liver disease and puts people at high risk of death from cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer.
Worldwide, an estimated two billion people have been infected with the HBV and about 250 million have chronic liver infections.A vaccine to prevent catching HBV has been available since 1982. Hepatitis B vaccine is 95% effective in preventing HBV infection and its chronic consequences, and is the first vaccine against a major human cancer.
You May Like: Royal Canin Feline Hepatic Diet
Recommended Reading: How Do I Get Hepatitis C
Who Publishes New Guidelines On Hiv Hepatitis And Stis For Key Populations
Today, WHO published new Consolidated guidelines on HIV, viral hepatitis and STI prevention, diagnosis, treatment and care for key populations. The guidelines are officially launched at the AIDS 2022 Conference in Montreal, Canada, in a satellite session entitled: Launching new WHO guidelines for key populations: Focus for impact.
The guidelines outline a public health response to HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections for 5 key populations .
WHO promotes an evidence and rights based approach to addressing these health issues which puts key populations at the centre of the response. Key populations must be prioritized, in every setting and this means as outlined in these new guidelines, planning to reach them first with prevention, testing and treatment as well as prioritizing key populations in funding programmes, said Erika Castellanos, Director of programmes at GATE , who was the co-chair of the WHO Guidelines Development Group.
Particularly for key populations, social, legal, structural and other contextual factors both increase vulnerability to HIV, viral hepatitis and STIs and obstruct access to health and other essential services. These guidelines highlight the critical importance of addressing structural barriers in all settings as a priority.
A summary of the guidelines is provided in the policy brief.
How Do I Know If I Have Hbv
A rapid point-of-care test after a finger prick or a simple blood test can tell if you are infected with the hepatitis B virus.
These tests can also help your doctor determine whether you are currently ill with hepatitis B, or if you are a chronic carrier. Although there is no treatment for the disease, bed rest and a good diet are important. Alcohol and medications should be restricted. Follow-up blood tests are necessary to tell if the disease has gone.
You May Like: Common Treatment For Hepatitis C
Symptoms And Causative Agent
Hepatitis is a general term for inflammation of the liver, which may result from infectious or non-infectious causes. Viruses responsible for many cases of infectious hepatitis include hepatitis A, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, hepatitis D, and hepatitis E. Hepatitis A and B are the only hepatitis viruses for which vaccines are currently available in the United States .
The hepatitis B virus is a partly double-stranded DNA virus in the hepadnavirus family. The hepatitis A virus is a single-stranded RNA virus in the Picornavirus family. Both viruses, though structurally unrelated, infect and replicate primarily in liver cells.
The symptoms of acute hepatitis A infection are identical to those of hepatitis B infection. Early symptoms are headache, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever, rash, body aches and pains, and dark colored urine. Following this phase, jaundice , light stools, and liver pain may appear.
What Is Hbv Treatment
Not everyone infected with HBV will need treatment. Doctors usually only recommend treatment if the virus is damaging your liver.
Antivirals: These are oral medications that make it hard for HBV to reproduce, but they usually work for only as long as you take them. They are able to lower the amount of HBV in your body and stop liver damage in about 70% to 90% of patients. Unfortunately, these treatments cannot cure hepatitis B to date.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Affects What Organs
How Can You Prevent Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B: Vaccination is the best way to prevent all the ways that hepatitis B is transmitted. People with HIV who do not have active HBV infection should be vaccinated against it. The hepatitis B vaccine is now recommended for all infants, children and adults ages 19-59, as well as adults ages 60+ at high risk for infection. There is a 3-dose series of hepatitis B vaccine given over 6 months, and a 2-dose series given over 1 month. Additionally, there is a 2-dose combination vaccine that protects against both hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C: No vaccine exists for HCV and no effective pre- or post-exposure prophylaxis is available. Injection drug use is one of the risk factors for hepatitis C. For people who inject drugs, the best way to prevent hepatitis C infection is to always use new, sterile needles or syringes, and never reuse or share needles or syringes, water, or other drug preparation equipment. Community-based prevention programs, such as medication-assisted treatment and syringe services programs provide support and services aimed at preventing and reducing the transmission of HCV. Although the risk of sexual transmission of HCV is considered to be low, avoiding unprotected sexual exposure by using condoms has been shown to reduce the chance of sexually transmitted infections.
Groups At High Risk Of Hep B Transmission
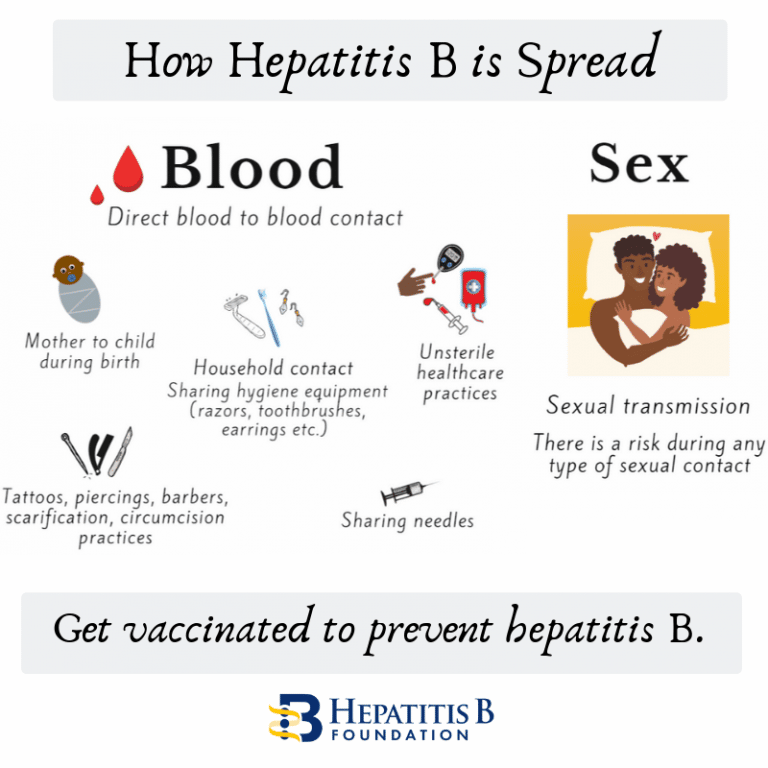
Hep B can only be passed on through blood-to-blood contact, unprotected sex or during birth so you might be at risk of having hep B if you:
- have moved to Australia from a country where hep B is widespread
- were born to a mother who was hep B positive during her pregnancy
- live or have lived with someone with hep B
- have or have had a sexual partner who has hep B
- have ever injected drugs or steroids
- are in prison or have ever been in prison
- have had blood transfusions, blood products or organ transplant in Australia before February 1990
- are of Aboriginal ancestry
- have had unsterile cosmetic or medical procedures.
- have had unsterile tattooing or piercing
- have ever taken part in unsterile traditional practices such as traditional tattooing, circumcision, initiation rituals involving blood, and scarification
- do not meet the above profiles but have abnormal liver function tests or experience hep B symptoms
Read Also: How Does Someone Contract Hepatitis C