1 Which Of The Following Are Risk Factors For Hepatitis C C
Image transcription text
1. Which of the following are risk factors for hepatitis C? C] Alcohol abuse and injection drug use C] Female gender and age & gt 65 years C] HIV infection and age & lt 18 years C] Male gender and incarceration
Image transcription text
2. The signs and symptoms of acute hepatitis C: include high fever, jaundice, and normal serum transaminases C] only develop if the acute infection will progress to achronic infection C] are non-specific and include fatigue and nausea C] are more common in patients & gt age 65 years
Image transcription text
3. Most patients who have acute hepatitis C: |:] do not have signs and symptoms |:] develop signs and symptoms only if co-infected withHIV C] have neurologic signs and symptoms C] will become symptomatic only if the infection isspontaneously cleared
Image transcription text
4. Spontaneous clearance of acute hepatitis C: C] provides temporary immunity against hepatitis C C] does not provide immunity against hepatitis C C] provides immunity only against the specific genotype C] provides permanent immunity against hepatitis C
Image transcription text
5. The primary injury of chronic hepatitis C infection is: renal damage liver cancer pancreatic damage liver fibrosis
Image transcription text
6. Liver damage caused by chronic hepatitis C typically: C] develops within 12-24 months C] develops only if the patient abuses alcohol C] develops decades after the initial infection C] develops 6-12weeks
Image transcription text
Pedicures Manicures And Hair Cuts
Trips to the salon or barbershop may pose a small risk of exposure to Hepatitis B and C. While there’s a small chance of transmitting hepatitis through grooming items, anytime there’s potential for exposure to blood you may be at risk for hepatitis. Reduce your risk by bringing your own nail files, cuticle clippers, razors, or other equipment.
Can You Prevent Hepatitis C Infection
Thereâs no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To avoid getting the virus:
- Use a latex condom every time you have sex.
- Don’t share personal items like razors.
- Don’t share needles, syringes, or other equipment when injecting drugs.
- Be careful if you get a tattoo, body piercing, or manicure. The equipment may have someone else’s blood on it.
Find out more on how to prevent hepatitis C.
Read Also: Hepatitis B In Blood Test
How Many People Have Hepatitis C
During 2013-2016 it was estimated that about two and half million people were chronically infected with HCV in the United States. The actual number may be as low as 2.0 million or as high as 2.8 million.Globally, hepatitis C is a common blood-borne infection with an estimated 58 million people chronically infected according to the World Health Organization.
Awareness Of Hcv Infection Status
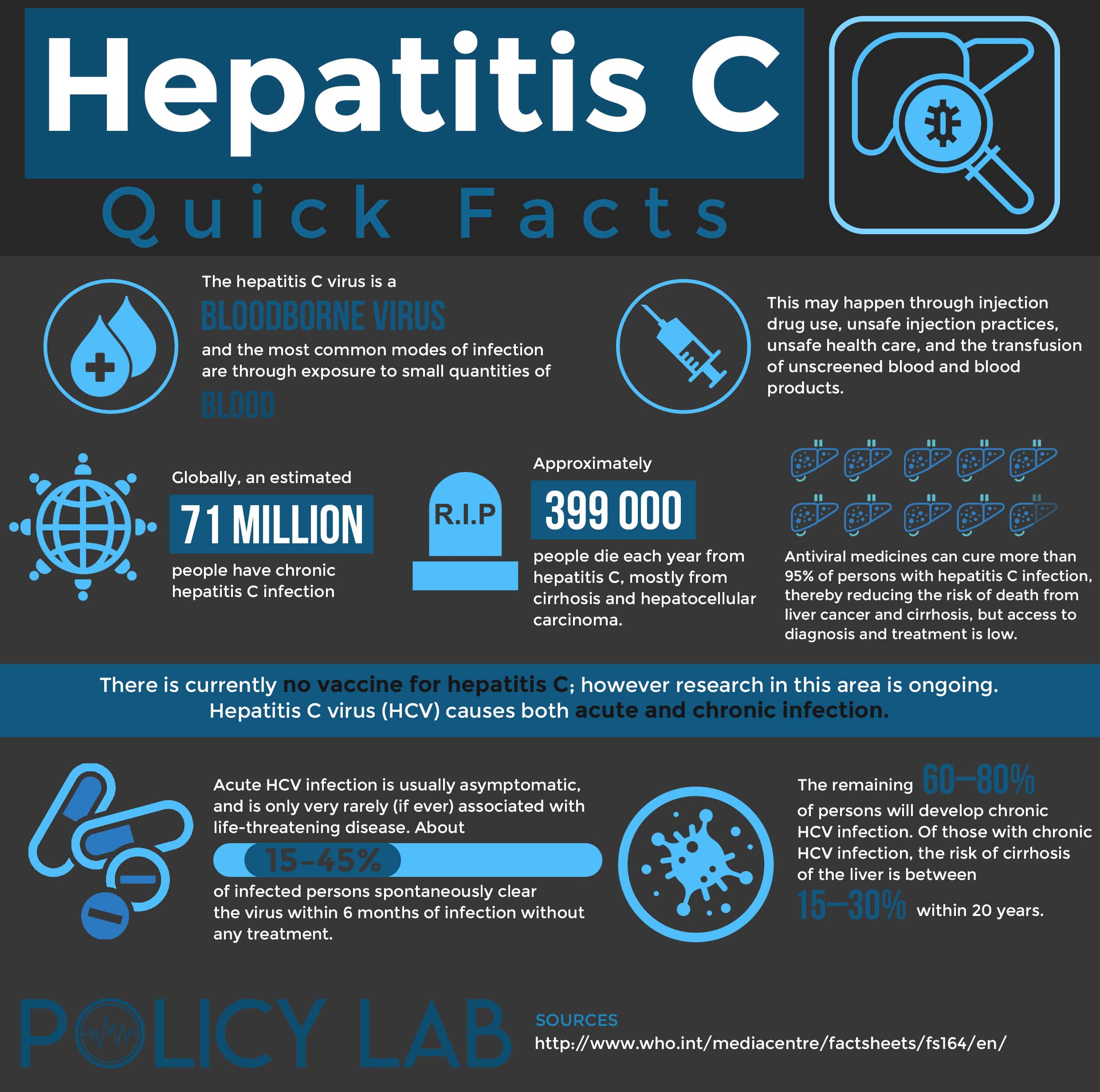
Using the most recent NHANES data, investigators estimated only 55.6% of persons infected with HCV in the United States were aware of their HCV infection status. Awareness of infection status was lower in persons who were foreign-born and in persons with income below the poverty level. These most recent NHANES data do not show a major improvement from a prior analysis of NHANES data that reported 50% of persons infected with HCV were aware of their HCV infection status. Awareness of HCV status may be higher among persons engaged in the private health care sectora study involving persons with access to medical care in four private health care organizations during the years 2006 to 2008 showed an estimated 57% were aware of their HCV infection.
Recommended Reading: How Much Are Hepatitis B Shots
Overview Of Risk Factors For Hcv Acquisition
Investigators and public health officials have identified multiple risk factors for acquiring HCV in the United States: injection drug use, history of receiving a blood product transfusion prior to July 1992, receipt of a solid organ transplantation, hemophilia with receipt of factor concentrates made before 1987, male-to-male sex, body tattoos, and intranasal cocaine use. Among these, injection drug use is the most common and important risk factor for acquiring HCV in the United States. Several studies have indicated that approximately 45% of persons with HCV infection do not report an exposure. Many of these patients, after undergoing careful questioning, eventually identified injection drug use as a risk factor. In the 1970s and 1980s, receipt of HCV-infected blood products or organs accounted for nearly 50% of new cases of HCV, but after the discovery of HCV as the cause of non-A, non-B hepatitis in 1989 and introduction of blood screening tests in the early 1990s, the proportion of new HCV cases caused by contaminated blood or organs dramatically declined. Persons in different ethnic groups may have relatively different routes of acquiring HCV.
Stages Of Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus affects people in different ways and has several stages:
- Incubation period. This is the time between first exposure to the start of the disease. It can last anywhere from 14 to 80 days, but the average is 45
- Acute hepatitis C. This is a short-term illness that lasts for the first 6 months after the virus enters your body. After that, some people who have it will get rid of, or clear, the virus on their own.
- Chronic hepatitis C. For most people who get hepatitis C — up to 85% — the illness moves into a long-lasting stage . This is called a chronic hepatitis C infection and can lead to serious health problems like liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis. This disease leads to inflammation that, over time, replaces your healthy liver cells with scar tissue. It usually takes about 20 to 30 years for this to happen, though it can be faster if you drink alcohol or have HIV.
- Liver cancer. Cirrhosis makes liver cancer more likely. Your doctor will make sure you get regular tests because there are usually no symptoms in the early stages.
Learn more about the stages and progression of hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: Can You Spread Hepatitis C
Acute Hepatitis C2020 Case Definition
The CDC 2020 Case Definition for Acute Hepatitis C infection includes clinical and laboratory criteria , along with a case classification as probable or confirmed. Of note, a patient can have a confirmed case of acute hepatitis C based on laboratory data alone . Symptomatic cases often go unreported and for multiple reasons, including many persons with symptomatic acute HCV do not seek medical care, the diagnosis may be missed, and medical providers may fail to report diagnosed cases. It is important not to report cases that have already been reported. A more detailed discussion of the Acute Hepatitis C 2020 Case Definition is included in the lesson Diagnosis of Acute HCV Infection.
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
You May Like: Hepatitis B Anti Surface Antibody
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis C virus . Hepatitis C is a blood-borne virus. Today, most people become infected with HCV by sharing needles or other equipment to inject drugs. For some people, HCV infection is a short-term or acute illness but for more than half of people who become infected with HCV, it becomes a long-term, chronic infection. Chronic HCV infection is a serious disease that can result in long-term health problems, even death. The majority of infected people might not be aware of their infection because they do not have any symptoms. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. The best way to prevent HCV infection is by avoiding behaviors that can spread the disease, especially injecting drugs.
Whos Most At Risk Of Developing Hepatitis C
Injection drug use is still the most common risk factor in both the United States and the United Kingdom.
People who used injection drugs and shared equipment long ago may still develop symptoms of chronic hepatitis C later in life, especially if the virus was never detected and treated.
Others at risk for hepatitis C infection include:
- healthcare workers who experience accidental needle pricks while caring for people with hepatitis C
- infants birthed by a parent with hepatitis C
- people who received transfusions, organ transplants, or other blood products before proper screening was introduced in June 1992
Hepatitis C is transmitted by:
- yellowing of the skin or eyes
It can take anywhere from 2 weeks to 6 months for a hepatitis C infection to develop after exposure to the virus.
In some cases, the body can clear the infection on its own before diagnosis or treatment occurs.
Hepatitis C is diagnosed using an antibody test and a PCR test. Both blood tests offer slightly different insights into the state of infection.
You May Like: Natural Remedies For Hepatitis C
Receipt Of Clotting Factor Concentrates
Two types of clotting factor concentrates are used in clinical practice: plasma factor concentrate and recombinant factor concentrate. Most often, these involve use of factor VIII or factor IX concentrates. In the late 1970s through the mid-1980s, most persons with hemophilia acquired HCV infection via the receipt of contaminated plasma clotting factor concentrates. In 1985, several companies introduced virus inactivation procedures for hemophilia blood products and by 1987 these procedures were uniformly used, virtually eliminating the risk of transmission of HCV via clotting factor concentrates. Use of recombinant factor concentrate also provides an option for providing factor concentrate with no risk of viral contamination.
Frequency Of Risk Factors
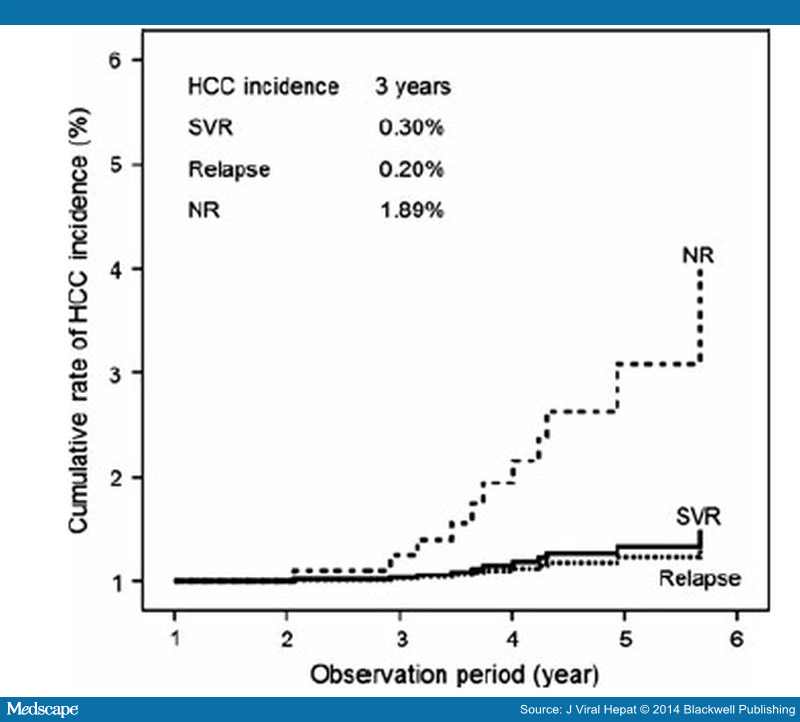
Most patients reported more than one potential exposure to HCV . Only 7 individuals reported no risk factor . Injection drug use was strongly associated with cocaine use and therefore they were combined in the analysis. Among those who did not report concomitant cocaine and injection drug use, the majority reported only using injection drugs and as a result of these small numbers, an analysis of cocaine as a sole risk factor was precluded. Of the 23 persons with one risk factor, 10 had received a transfusion, 7 used intravenous drugs or cocaine 3 underwent body/ear piercing, 2 shared razors and toothbrushes, and 1 had occupational exposure . In no case was sexual activity reported as an independent risk factor.
Table 1B B. Number and % of the 148 patients exposed to successively higher numbers of different risk factors simultaneously .
Also Check: What Are Warning Signs Of Hepatitis C
Importance Of Hcv Incidence Data
The United States HCV incidence data provide important information for monitoring trends in transmission patterns, developing hepatitis C prevention strategies, monitoring the effectiveness of any implemented plans, and identifying focal outbreaks or regional patterns of infection. In addition, valuable information emerges when data is categorized by age group, gender, race/ethnicity, and risk factor for acquiring hepatitis C virus these data may inform major prevention strategies.
Who Should Get Tested
The CDC recommends that you get tested at least once no matter what. Pay particular attention if any of these things apply to you:
- Had a blood transfusion before 1992
- Received blood products for clotting problems before 1987
- Have high-risk sex
- Live with or care for someone who has HCV
- Were born between 1945 and 1965
- Ever shared tools to snort cocaine
- Were born to a mother with hepatitis C
Learn more on why you should get tested for hepatitis C.
Also Check: Can I Donate Plasma If I Had Hepatitis B
Receipt Of Immune Globulin
Scattered cases and outbreaks of HCV transmission via gamma globulin have occurred in the United States and in Europe. In 1993 and 1994, a major outbreak of HCV transmission in the United States occurred following patient receipt of HCV-contaminated lots of intravenous immune globulin, with a total of 23 persons acquiring HCV. Advances in virus inactivation procedures have nearly eliminated any risk of HCV transmission with immune globulin, and the manufacturers of intravenous immune globulin use vigorous viral inactivation and removal procedures. No cases of HCV transmission have been documented with administration of intramuscular immune globulin. All immune globulin products undergo solvent detergent.
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C spreads when blood or body fluids contaminated with the hepatitis C virus get into your bloodstream through contact with an infected person.
You can be exposed to the virus from:
- Sharing injection drugs and needles
- Having sex, especially if you have HIV, another STD, several partners, or have rough sex
- Being stuck by infected needles
- Birth — a mother can pass it to a child
- Sharing personal care items like toothbrushes, razor blades, and nail clippers
- Getting a tattoo or piercing with unclean equipment
You canât catch hepatitis C through:
- Have been on long-term kidney dialysis
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Were born to a mother with hepatitis C
Since July 1992, all blood and organ donations in the U.S. are tested for the hepatitis C virus. The CDC says it is now rare that someone getting blood products or an organ would get hepatitis C. That said, The CDC recommends that anyone over the age of 18 get tested for Hepatitis C. If you haven’t been screened, you should consider having it done.
Learn more about the risk factors for hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Spread Through Sweat
Perinatal Infection Hepatitis C Infection2018 Case Definition
The CDC 2018 Case Definition for Hepatitis C, Perinatal Infection includes clinical criteria, laboratory criteria for diagnosis, criteria to distinguish a new case from an existing case, and a case definition. A confirmed case definition requires the following:
- Infant who has a positive test for HCV RNA nucleic acid amplification test , HCV antigen, or detectable HCV genotype at 2 months and 36 months of age and is not known to have been exposed to HCV via a mechanism other than perinatal.
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
You are more likely to get hepatitis C if you:
- Have injected drugs
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you probably will not have symptoms until it causes complications. This can happen decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis C And What Causes It
Of Estimating Hcv Incidence
Most individuals with acute HCV infection do not have a clinically-evident illness and most do not seek medical care. In addition, many cases of diagnosed acute hepatitis C are not reported. Thus, determining the true incidence of new HCV infections per year based on the number of reported cases requires highly complex epidemiology modeling techniques. For each new acute HCV case that is reported in the United States, the CDC estimates there are approximately 13.9 actual new acute HCV cases that have occurred. This high ratio is primarily a result of the large proportion of persons with acute HCV who have asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic infection and do not seek medical care, or have undiagnosed infection the passive HCV reporting system likely also contributes to the low number of reported acute HCV cases. The CDC provides several numbers related to the incidence of hepatitis C in the United States, including number of reported acute cases, estimated number of acute clinical cases, estimated number of new infections, and rates per 100,000 persons at the state and national level.
Sharing Toothbrushes Scissors And Razors
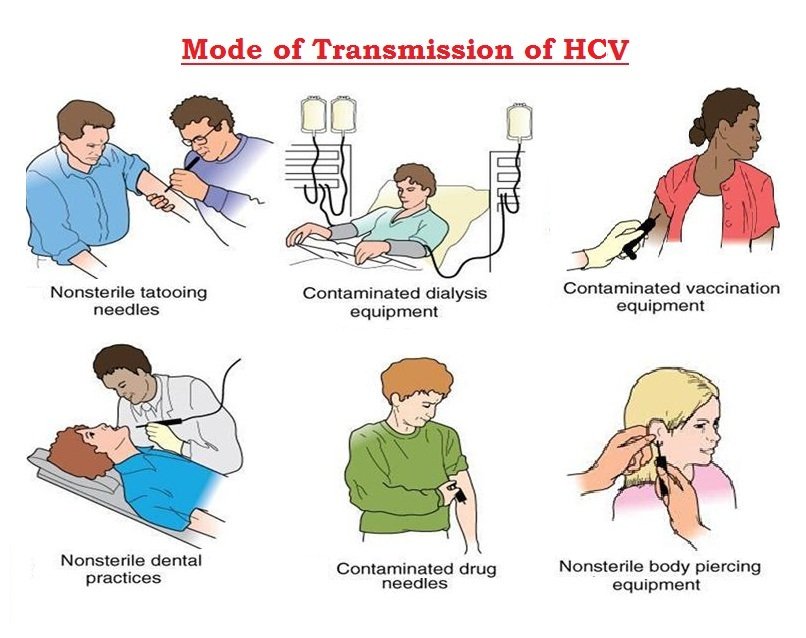
There’s a potential risk that hepatitis C may be passed on through sharing items such as toothbrushes, razors and scissors, as they can become contaminated with infected blood.
Equipment used by hairdressers, such as scissors and clippers, can pose a risk if it has been contaminated with infected blood and not sterilised or cleaned between customers. However, most salons operate to high standards, so this risk is low.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Symptoms In Women
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
How To Lower Your Odds Of Infection
Thereâs no vaccine against HCV. Take some precautions in high-risk situations. If youâre a health care worker, be careful with blood. If you have sex with more than one partner, use condoms. And if you use drugs, donât share needles, syringes, or anything that goes up your nose.
Spouses, partners and others in close contact with people who have hep C should not share toothbrushes and razors. If you have the disease, cover your wounds and throw out blood-soaked bandages, tampons, or pads. Donât let anyone else in the house touch them.
Show Sources
Also Check: How Do You Get Hepatitis C Antibodies